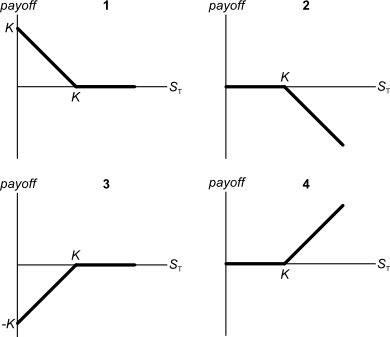
Below are 4 option graphs. Note that the y-axis is payoff at maturity (T). What options do they depict? List them in the order that they are numbered.
Question 246 foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate, cross currency interest rate parity
Suppose the Australian cash rate is expected to be 8.15% pa and the US federal funds rate is expected to be 3.00% pa over the next 2 years, both given as nominal effective annual rates. The current exchange rate is at parity, so 1 USD = 1 AUD.
What is the implied 2 year forward foreign exchange rate?
A 2 year corporate bond yields 3% pa with a coupon rate of 5% pa, paid semi-annually.
Find the effective monthly rate, effective six month rate, and effective annual rate.
##r_\text{eff monthly}##, ##r_\text{eff 6 month}##, ##r_\text{eff annual}##.
When someone says that they're "buying American dollars" (USD), what type of asset are they probably buying? They're probably buying:
One method for calculating a firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to ignore interest expense. That is, pretend that interest expense ##(IntExp)## is zero:
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - 0)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC - 0\\ \end{aligned}###
One of the reasons why firms may not begin projects with relatively small positive net present values (NPV's) is because they wish to maximise the value of their:
The accounting identity states that the book value of a company's assets (A) equals its liabilities (L) plus owners equity (OE), so A = L + OE.
The finance version states that the market value of a company's assets (V) equals the market value of its debt (D) plus equity (E), so V = D + E.
Therefore a business's assets can be seen as a portfolio of the debt and equity that fund the assets.
Let ##\sigma_\text{V total}^2## be the total variance of returns on assets, ##\sigma_\text{V syst}^2## be the systematic variance of returns on assets, and ##\sigma_\text{V idio}^2## be the idiosyncratic variance of returns on assets, and ##\rho_\text{D idio, E idio}## be the correlation between the idiosyncratic returns on debt and equity.
Which of the following equations is NOT correct?
A company conducts a 4 for 3 stock split. What is the percentage change in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order.
An effective monthly return of 1% ##(r_\text{eff monthly})## is equivalent to an effective annual return ##(r_\text{eff annual})## of:
You bought a house, primarily funded using a home loan from a bank. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?