A wholesale shop offers credit to its customers. The customers are given 21 days to pay for their goods. But if they pay straight away (now) they get a 1% discount.
What is the effective interest rate given to customers who pay in 21 days? All rates given below are effective annual rates. Assume 365 days in a year.
An old company's Firm Free Cash Flow (FFCF, same as CFFA) is forecast in the graph below.
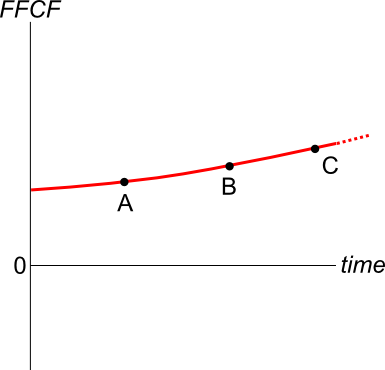
To value the firm's assets, the terminal value needs to be calculated using the perpetuity with growth formula:
###V_{\text{terminal, }t-1} = \dfrac{FFCF_{\text{terminal, }t}}{r-g}###
Which point corresponds to the best time to calculate the terminal value?
Two years ago Fred bought a house for $300,000.
Now it's worth $500,000, based on recent similar sales in the area.
Fred's residential property has an expected total return of 8% pa.
He rents his house out for $2,000 per month, paid in advance. Every 12 months he plans to increase the rental payments.
The present value of 12 months of rental payments is $23,173.86.
The future value of 12 months of rental payments one year ahead is $25,027.77.
What is the expected annual growth rate of the rental payments? In other words, by what percentage increase will Fred have to raise the monthly rent by each year to sustain the expected annual total return of 8%?
A fairly valued share's current price is $4 and it has a total required return of 30%. Dividends are paid annually and next year's dividend is expected to be $1. After that, dividends are expected to grow by 5% pa in perpetuity. All rates are effective annual returns.
What is the expected dividend income paid at the end of the second year (t=2) and what is the expected capital gain from just after the first dividend (t=1) to just after the second dividend (t=2)? The answers are given in the same order, the dividend and then the capital gain.
A man has taken a day off from his casual painting job to relax.
It's the end of the day and he's thinking about the hours that he could have spent working (in the past) which are now:
The standard deviation of monthly changes in the spot price of corn is 50 cents per bushel. The standard deviation of monthly changes in the futures price of corn is 40 cents per bushel. The correlation between the spot price of corn and the futures price of corn is 0.9.
It is now March. A corn chip manufacturer is committed to buying 250,000 bushels of corn in May. The spot price of corn is 381 cents per bushel and the June futures price is 399 cents per bushel.
The corn chip manufacturer wants to use the June corn futures contracts to hedge his risk. Each futures contract is for the delivery of 5,000 bushels of corn. One bushel is about 127 metric tons.
How many corn futures should the corn chip manufacturer buy to hedge his risk? Round your answer to the nearest whole number of contracts. Remember to tail the hedge.
A stock, a call, a put and a bond are available to trade. The call and put options' underlying asset is the stock they and have the same strike prices, ##K_T##.
Being long the call and short the stock is equivalent to being:
Question 880 gold standard, no explanation
Under the Gold Standard (1876 to 1913), currencies were priced relative to:
A Brazilian lady wishes to convert 1 million Brazilian Real (BRL) into Chinese Renminbi (RMB, also called the Yuan or CNY). The exchange rate is 3.42 BRL per USD and 6.27 RMB per USD. How much is the BRL 1 million worth in RMB?
The market's expected total return is 10% pa and the risk free rate is 5% pa, both given as effective annual rates.
A stock has a beta of 0.7.
In the last 5 minutes, bad economic news was released showing a higher chance of recession. Over this time the share market fell by 2%. The risk free rate was unchanged. What do you think was the stock's historical return over the last 5 minutes, given as an effective 5 minute rate?