A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 8 | 8 | 8 | 20 | 8 | ... |
After year 4, the dividend will grow in perpetuity at 4% pa. The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates. Note that the $8 dividend at time zero is about to be paid tonight.
What is the current price of the stock?
Why is Capital Expenditure (CapEx) subtracted in the Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) formula?
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume half as much now (t=0) as in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end.
How much can you consume at time zero and one? The answer choices are given in the same order.
What is the covariance of a variable X with itself?
The cov(X, X) or ##\sigma_{X,X}## equals:
Which of the following statements about option contracts is NOT correct? For every:
The standard deviation of monthly changes in the spot price of corn is 50 cents per bushel. The standard deviation of monthly changes in the futures price of corn is 40 cents per bushel. The correlation between the spot price of corn and the futures price of corn is 0.9.
It is now March. A corn chip manufacturer is committed to buying 250,000 bushels of corn in May. The spot price of corn is 381 cents per bushel and the June futures price is 399 cents per bushel.
The corn chip manufacturer wants to use the June corn futures contracts to hedge his risk. Each futures contract is for the delivery of 5,000 bushels of corn. One bushel is about 127 metric tons.
How many corn futures should the corn chip manufacturer buy to hedge his risk? Round your answer to the nearest whole number of contracts. Remember to tail the hedge.
Question 794 option, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing, option delta, no explanation
Which of the following quantities from the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing formula gives the Delta of a European call option?
Where:
###d_1=\dfrac{\ln[S_0/K]+(r+\sigma^2/2).T)}{\sigma.\sqrt{T}}### ###d_2=d_1-\sigma.\sqrt{T}=\dfrac{\ln[S_0/K]+(r-\sigma^2/2).T)}{\sigma.\sqrt{T}}###A stock, a call, a put and a bond are available to trade. The call and put options' underlying asset is the stock they and have the same strike prices, ##K_T##.
Being long the call and short the stock is equivalent to being:
Question 892 foreign exchange reserve, foreign exchange rate, no explanation
The Chinese central bank has the largest amount of foreign currency reserves.
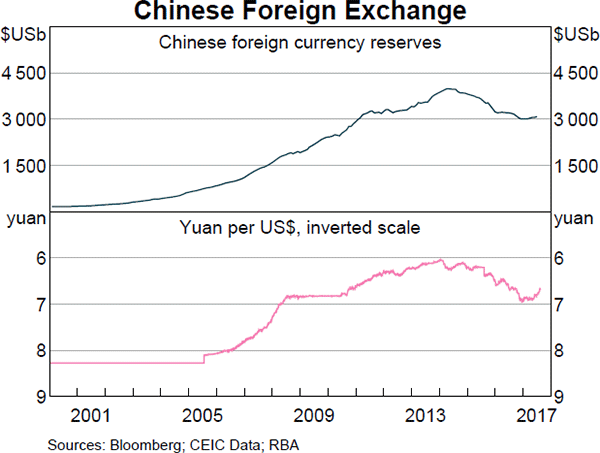
What could the large amounts of foreign exchange reserves held by the Chinese government be used for in a currency crisis? China's currency is called the Renminbi (RMB) or Yuan (CNY). In a Chinese currency crisis the Chinese government is likely to use its FX reserves to:
You work for XYZ company and you’ve been asked to evaluate a new project which has double the systematic risk of the company’s other projects.
You use the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) formula and input the treasury yield ##(r_f )##, market risk premium ##(r_m-r_f )## and the company’s asset beta risk factor ##(\beta_{XYZ} )## into the CAPM formula which outputs a return.
This return that you’ve just found is: