A project has the following cash flows. Normally cash flows are assumed to happen at the given time. But here, assume that the cash flows are received smoothly over the year. So the $250 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 200 |
| 2 | 250 |
What is the payback period of the project in years?
An industrial chicken farmer grows chickens for their meat. Chickens:
- Cost $0.50 each to buy as chicks. They are bought on the day they’re born, at t=0.
- Grow at a rate of $0.70 worth of meat per chicken per week for the first 6 weeks (t=0 to t=6).
- Grow at a rate of $0.40 worth of meat per chicken per week for the next 4 weeks (t=6 to t=10) since they’re older and grow more slowly.
- Feed costs are $0.30 per chicken per week for their whole life. Chicken feed is bought and fed to the chickens once per week at the beginning of the week. So the first amount of feed bought for a chicken at t=0 costs $0.30, and so on.
- Can be slaughtered (killed for their meat) and sold at no cost at the end of the week. The price received for the chicken is their total value of meat (note that the chicken grows fast then slow, see above).
The required return of the chicken farm is 0.5% given as an effective weekly rate.
Ignore taxes and the fixed costs of the factory. Ignore the chicken’s welfare and other environmental and ethical concerns.
Find the equivalent weekly cash flow of slaughtering a chicken at 6 weeks and at 10 weeks so the farmer can figure out the best time to slaughter his chickens. The choices below are given in the same order, 6 and 10 weeks.
Question 213 income and capital returns, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds
The coupon rate of a fixed annual-coupon bond is constant (always the same).
What can you say about the income return (##r_\text{income}##) of a fixed annual coupon bond? Remember that:
###r_\text{total} = r_\text{income} + r_\text{capital}###
###r_\text{total, 0 to 1} = \frac{c_1}{p_0} + \frac{p_1-p_0}{p_0}###
Assume that there is no change in the bond's total annual yield to maturity from when it is issued to when it matures.
Select the most correct statement.
From its date of issue until maturity, the income return of a fixed annual coupon:
Which of the following investable assets is the LEAST suitable for valuation using PE multiples techniques?
Question 444 investment decision, corporate financial decision theory
The investment decision primarily affects which part of a business?
"Buy low, sell high" is a phrase commonly heard in financial markets. It states that traders should try to buy assets at low prices and sell at high prices.
Traders in the fixed-coupon bond markets often quote promised bond yields rather than prices. Fixed-coupon bond traders should try to:
Below is the Australian federal government’s budget balance as a percent of GDP. Note that the columns to the right of the vertical black line were a forecast at the time. The x-axis shows financial years, so for example the 06/07 financial year represents the time period from 1 July 2006 to 30 June 2007.
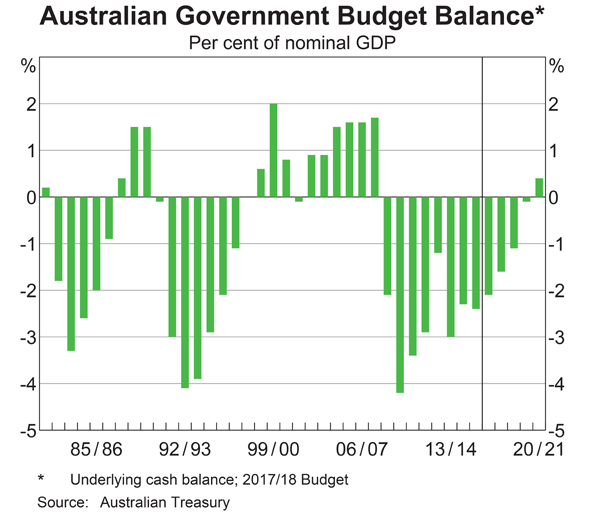
Comparing the 2008/09 financial year to the previous one, the Australian federal government implemented:
Which form of production is included in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) reported by the government statistics agency?
Which one of the following businesses is likely to be a public company in Australia, judging by its name?
Question 968 foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate, cross currency interest rate parity, no explanation
Below is a graph showing the spread or difference between government bond yields in different countries compared to the US. Assume that all governments have zero credit risk.
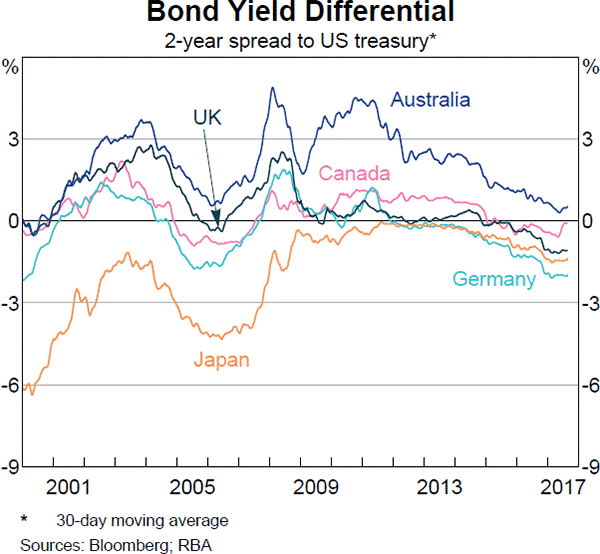
According to the principle of cross-currency interest rate parity, which country is likely to have the greatest expected currency appreciation against the USD over the next 2 years?