Find Trademark Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Trademark Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 100 | |
| COGS | 25 | |
| Operating expense | 5 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Interest expense | 20 | |
| Income before tax | 30 | |
| Tax at 30% | 9 | |
| Net income | 21 | |
| Trademark Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets | 120 | 80 |
| PPE | ||
| Cost | 150 | 140 |
| Accumul. depr. | 60 | 40 |
| Carrying amount | 90 | 100 |
| Total assets | 210 | 180 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | 75 | 65 |
| Non-current liabilities | 75 | 55 |
| Owners' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | 10 | 10 |
| Contributed equity | 50 | 50 |
| Total L and OE | 210 | 180 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
What is the net present value (NPV) of undertaking a full-time Australian undergraduate business degree as an Australian citizen? Only include the cash flows over the duration of the degree, ignore any benefits or costs of the degree after it's completed.
Assume the following:
- The degree takes 3 years to complete and all students pass all subjects.
- There are 2 semesters per year and 4 subjects per semester.
- University fees per subject per semester are $1,277, paid at the start of each semester. Fees are expected to remain constant in real terms for the next 3 years.
- There are 52 weeks per year.
- The first semester is just about to start (t=0). The first semester lasts for 19 weeks (t=0 to 19).
- The second semester starts immediately afterwards (t=19) and lasts for another 19 weeks (t=19 to 38).
- The summer holidays begin after the second semester ends and last for 14 weeks (t=38 to 52). Then the first semester begins the next year, and so on.
- Working full time at the grocery store instead of studying full-time pays $20/hr and you can work 35 hours per week. Wages are paid at the end of each week and are expected to remain constant in real terms.
- Full-time students can work full-time during the summer holiday at the grocery store for the same rate of $20/hr for 35 hours per week.
- The discount rate is 9.8% pa. All rates and cash flows are real. Inflation is expected to be 3% pa. All rates are effective annual.
The NPV of costs from undertaking the university degree is:
Question 452 limited liability, expected and historical returns
What is the lowest and highest expected share price and expected return from owning shares in a company over a finite period of time?
Let the current share price be ##p_0##, the expected future share price be ##p_1##, the expected future dividend be ##d_1## and the expected return be ##r##. Define the expected return as:
##r=\dfrac{p_1-p_0+d_1}{p_0} ##
The answer choices are stated using inequalities. As an example, the first answer choice "(a) ##0≤p<∞## and ##0≤r< 1##", states that the share price must be larger than or equal to zero and less than positive infinity, and that the return must be larger than or equal to zero and less than one.
The standard deviation and variance of a stock's annual returns are calculated over a number of years. The units of the returns are percent per annum ##(\% pa)##.
What are the units of the standard deviation ##(\sigma)## and variance ##(\sigma^2)## of returns respectively?
Hint: Visit Wikipedia to understand the difference between percentage points ##(\text{pp})## and percent ##(\%)##.
An economy has only two investable assets: stocks and cash.
Stocks had a historical nominal average total return of negative two percent per annum (-2% pa) over the last 20 years. Stocks are liquid and actively traded. Stock returns are variable, they have risk.
Cash is riskless and has a nominal constant return of zero percent per annum (0% pa), which it had in the past and will have in the future. Cash can be kept safely at zero cost. Cash can be converted into shares and vice versa at zero cost.
The nominal total return of the shares over the next year is expected to be:
Question 638 option, option payoff at maturity, no explanation
Which of the below formulas gives the payoff ##(f)## at maturity ##(T)## from being long a put option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T## and the exercise price be ##X_T##.
Which one of the following businesses is likely to be a public company in Australia, judging by its name?
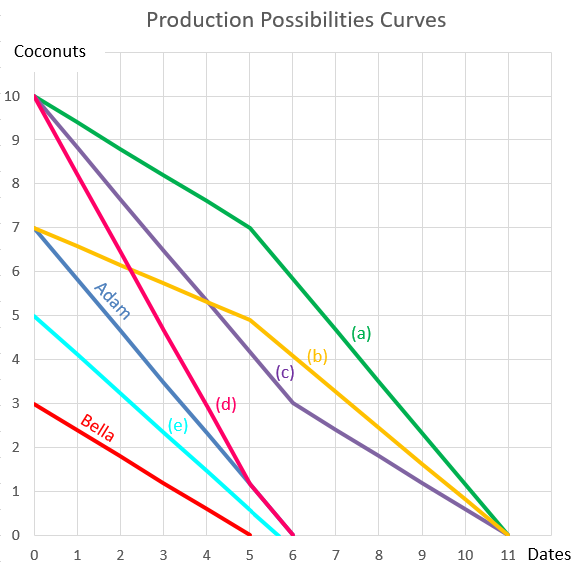
Question 898 comparative advantage in trade, production possibilities curve, no explanation
Adam and Bella are the only people on a remote island. Their production possibility curves are shown in the graph.
Assuming that Adam and Bella cooperate according to the principles of comparative advantage, what will be their combined production possibilities curve?