Katya offers to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years (t=1,2,3,4,5) if you pay her $50 now (t=0). You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. Ignore credit risk.
You want to buy an apartment priced at $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
Question 452 limited liability, expected and historical returns
What is the lowest and highest expected share price and expected return from owning shares in a company over a finite period of time?
Let the current share price be ##p_0##, the expected future share price be ##p_1##, the expected future dividend be ##d_1## and the expected return be ##r##. Define the expected return as:
##r=\dfrac{p_1-p_0+d_1}{p_0} ##
The answer choices are stated using inequalities. As an example, the first answer choice "(a) ##0≤p<∞## and ##0≤r< 1##", states that the share price must be larger than or equal to zero and less than positive infinity, and that the return must be larger than or equal to zero and less than one.
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume half as much now (t=0) as in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end.
How much can you consume at time zero and one? The answer choices are given in the same order.
Which of the below formulas gives the profit ##(\pi)## from being long a call option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T##, the exercise price be ##X_T## and the option price be ##f_{LC,0}##. Note that ##S_T##, ##X_T## and ##f_{LC,0}## are all positive numbers.
The standard deviation of monthly changes in the spot price of corn is 50 cents per bushel. The standard deviation of monthly changes in the futures price of corn is 40 cents per bushel. The correlation between the spot price of corn and the futures price of corn is 0.9.
It is now March. A corn chip manufacturer is committed to buying 250,000 bushels of corn in May. The spot price of corn is 381 cents per bushel and the June futures price is 399 cents per bushel.
The corn chip manufacturer wants to use the June corn futures contracts to hedge his risk. Each futures contract is for the delivery of 5,000 bushels of corn. One bushel is about 127 metric tons.
How many corn futures should the corn chip manufacturer buy to hedge his risk? Round your answer to the nearest whole number of contracts. Remember to tail the hedge.
A one year European-style put option has a strike price of $4. The option's underlying stock pays no dividends and currently trades at $5. The risk-free interest rate is 10% pa continuously compounded. Use a single step binomial tree to calculate the option price, assuming that the price could rise to $8 ##(u = 1.6)## or fall to $3.125 ##(d = 1/1.6)## in one year. The put option price now is:
Question 905 market capitalisation of equity, PE ratio, payout ratio
The below graph shows the computer software company Microsoft's stock price (MSFT) at the market close on the NASDAQ on Friday 1 June 2018.
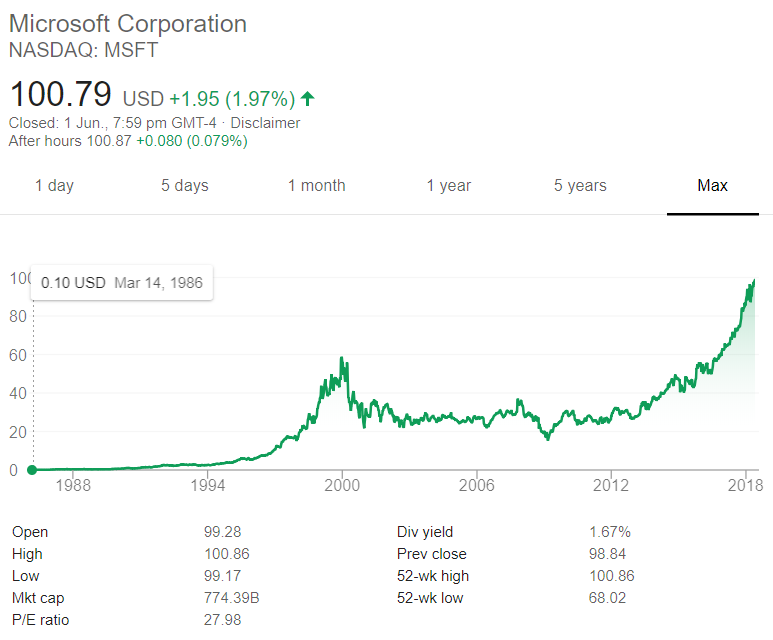
Based on the screenshot above, which of the following statements about MSFT is NOT correct? MSFT's:
Question 923 omitted variable bias, CAPM, single factor model, single index model, no explanation
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and the Single Index Model (SIM) are single factor models whose only risk factor is the market portfolio’s return. Say a Taxi company and an Umbrella company are influenced by two factors, the market portfolio return and rainfall. When it rains, both the Taxi and Umbrella companies’ stock prices do well. When there’s no rain, both do poorly. Assume that rainfall risk is a systematic risk that cannot be diversified and that rainfall has zero correlation with the market portfolio’s returns.
Which of the following statements about these two stocks is NOT correct?
The CAPM and SIM:
Question 980 balance of payments, current account, no explanation
Observe the below graph of the US current account surplus as a proportion of GDP.
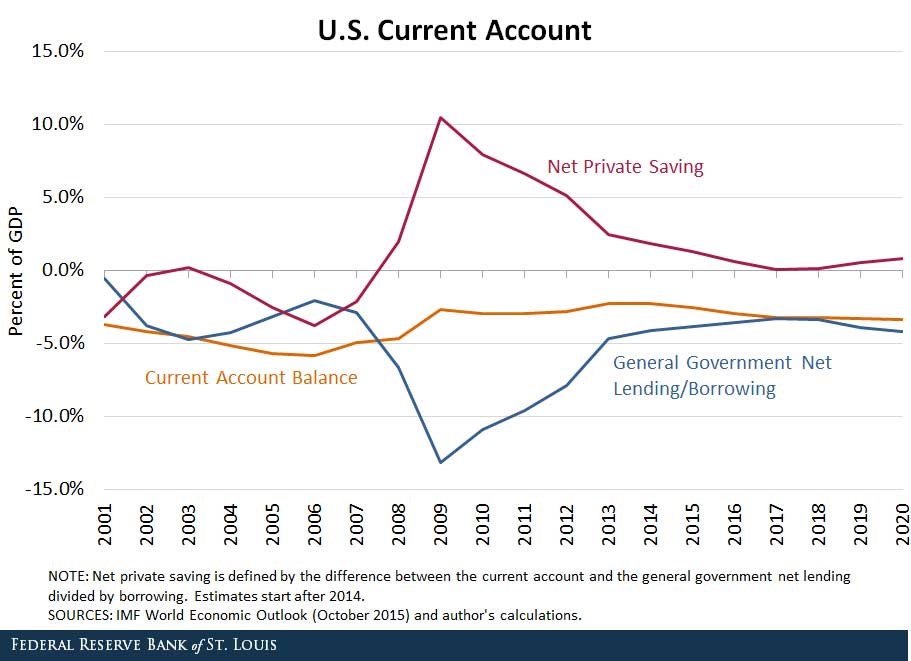
Define lending as buying (or saving or investing in) debt and equity assets.
The sum of US ‘net private saving’ plus ‘net general government lending’ equals the US: