Question 215 equivalent annual cash flow, effective rate conversion
You're about to buy a car. These are the cash flows of the two different cars that you can buy:
- You can buy an old car for $5,000 now, for which you will have to buy $90 of fuel at the end of each week from the date of purchase. The old car will last for 3 years, at which point you will sell the old car for $500.
- Or you can buy a new car for $14,000 now for which you will have to buy $50 of fuel at the end of each week from the date of purchase. The new car will last for 4 years, at which point you will sell the new car for $1,000.
Bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that there are exactly 52 weeks in a year. Ignore taxes and environmental and pollution factors.
Should you buy the or the ?
Question 321 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
The market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to increase the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 50 basis points due to high future GDP and inflation forecasts.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar will:
There are many ways to calculate a firm's free cash flow (FFCF), also called cash flow from assets (CFFA). Some include the annual interest tax shield in the cash flow and some do not.
Which of the below FFCF formulas include the interest tax shield in the cash flow?
###(1) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp### ###(2) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp.(1-t_c)### ###(3) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c )+ Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(4) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c) + Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(5) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(6) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(7) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(8) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c### ###(9) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(10) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c###The formulas for net income (NI also called earnings), EBIT and EBITDA are given below. Assume that depreciation and amortisation are both represented by 'Depr' and that 'FC' represents fixed costs such as rent.
###NI=(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###EBIT=Rev - COGS - FC-Depr### ###EBITDA=Rev - COGS - FC### ###Tax =(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).t_c= \dfrac{NI.t_c}{1-t_c}###Private equity firms are known to buy medium sized private companies operating in the same industry, merge them together into a larger company, and then sell it off in a public float (initial public offering, IPO).
If medium-sized private companies trade at PE ratios of 5 and larger listed companies trade at PE ratios of 15, what return can be achieved from this strategy?
Assume that:
- The medium-sized companies can be bought, merged and sold in an IPO instantaneously.
- There are no costs of finding, valuing, merging and restructuring the medium sized companies. Also, there is no competition to buy the medium-sized companies from other private equity firms.
- The large merged firm's earnings are the sum of the medium firms' earnings.
- The only reason for the difference in medium and large firm's PE ratios is due to the illiquidity of the medium firms' shares.
- Return is defined as: ##r_{0→1} = (p_1-p_0+c_1)/p_0## , where time zero is just before the merger and time one is just after.
An investor owns an empty block of land that has local government approval to be developed into a petrol station, car wash or car park. The council will only allow a single development so the projects are mutually exclusive.
All of the development projects have the same risk and the required return of each is 10% pa. Each project has an immediate cost and once construction is finished in one year the land and development will be sold. The table below shows the estimated costs payable now, expected sale prices in one year and the internal rates of returns (IRR's).
| Mutually Exclusive Projects | |||
| Project | Cost now ($) |
Sale price in one year ($) |
IRR (% pa) |
| Petrol station | 9,000,000 | 11,000,000 | 22.22 |
| Car wash | 800,000 | 1,100,000 | 37.50 |
| Car park | 70,000 | 110,000 | 57.14 |
Which project should the investor accept?
Question 554 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
On his 20th birthday, a man makes a resolution. He will put $30 cash under his bed at the end of every month starting from today. His birthday today is the first day of the month. So the first addition to his cash stash will be in one month. He will write in his will that when he dies the cash under the bed should be given to charity.
If the man lives for another 60 years, how much money will be under his bed if he dies just after making his last (720th) addition?
Also, what will be the real value of that cash in today's prices if inflation is expected to 2.5% pa? Assume that the inflation rate is an effective annual rate and is not expected to change.
The answers are given in the same order, the amount of money under his bed in 60 years, and the real value of that money in today's prices.
Which of the following statements about futures contracts on shares is NOT correct, assuming that markets are efficient?
When an equity future is first negotiated (at t=0):
The price of gold is currently $700 per ounce. The forward price for delivery in 1 year is $800. An arbitrageur can borrow money at 10% per annum given as an effective discrete annual rate. Assume that gold is fairly priced and the cost of storing gold is zero.
What is the best way to conduct an arbitrage in this situation? The best arbitrage strategy requires zero capital, has zero risk and makes money straight away. An arbitrageur should sell 1 forward on gold and:
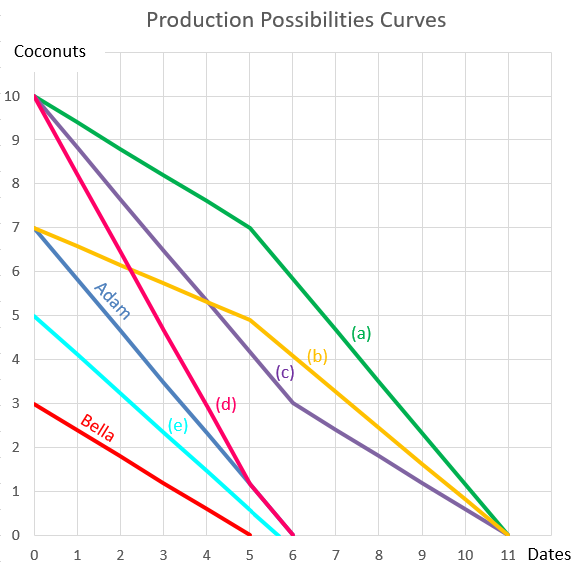
Question 898 comparative advantage in trade, production possibilities curve, no explanation
Adam and Bella are the only people on a remote island. Their production possibility curves are shown in the graph.
Assuming that Adam and Bella cooperate according to the principles of comparative advantage, what will be their combined production possibilities curve?
A bank bill was bought for $99,000 and sold for $100,000 thirty (30) days later. There are 365 days in the year. Which of the following formulas gives the simple interest rate per annum over those 30 days?
Note: To help you identify which is the correct answer without doing any calculations yourself, the formulas used to calculate the numbers are given.