A project has the following cash flows. Normally cash flows are assumed to happen at the given time. But here, assume that the cash flows are received smoothly over the year. So the $105 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -90 |
| 1 | 30 |
| 2 | 105 |
What is the payback period of the project in years?
In the 1997 Asian financial crisis many countries' exchange rates depreciated rapidly against the US dollar (USD). The Thai, Indonesian, Malaysian, Korean and Filipino currencies were severely affected. The below graph shows these Asian countries' currencies in USD per one unit of their currency, indexed to 100 in June 1997.
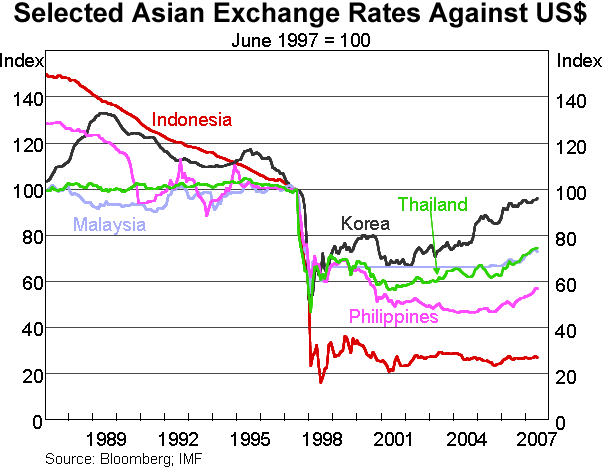
Of the statements below, which is NOT correct? The Asian countries':
Question 419 capital budgeting, NPV, interest tax shield, WACC, CFFA, CAPM, no explanation
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $6m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $6m | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | 0 | |
| Unit sales per year | 9m | |
| Sale price per unit | $8 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $6 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $1m | |
| Interest expense in first year (at t=1) | $0.53m | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Government treasury bond yield | 5% | |
| Bank loan debt yield | 6% | |
| Market portfolio return | 10% | |
| Covariance of levered equity returns with market | 0.08 | |
| Variance of market portfolio returns | 0.16 | |
| Firm's and project's debt-to-assets ratio | 50% | |
Notes
- Due to the project, current assets will increase by $5m now (t=0) and fall by $5m at the end (t=1). Current liabilities will not be affected.
Assumptions
- The debt-to-assets ratio will be kept constant throughout the life of the project. The amount of interest expense at the end of each period has been correctly calculated to maintain this constant debt-to-equity ratio.
- Millions are represented by 'm'.
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 2% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The 50% capital gains tax discount is not available since the project is undertaken by a firm, not an individual.
What is the net present value (NPV) of the project?
Question 432 option, option intrinsic value, no explanation
An American style call option with a strike price of ##K## dollars will mature in ##T## years. The underlying asset has a price of ##S## dollars.
What is an expression for the current intrinsic value in dollars from owning (being long) the American style call option? Note that the intrinsic value of an option does not subtract the premium paid to buy the option.
Which of the following decisions relates to the current assets and current liabilities of the firm?
To value a business's assets, the free cash flow of the firm (FCFF, also called CFFA) needs to be calculated. This requires figures from the firm's income statement and balance sheet. For what figures is the balance sheet needed? Note that the balance sheet is sometimes also called the statement of financial position.
A company advertises an investment costing $1,000 which they say is underpriced. They say that it has an expected total return of 15% pa, but a required return of only 10% pa. Of the 15% pa total expected return, the dividend yield is expected to always be 7% pa and rest is the capital yield.
Assuming that the company's statements are correct, what is the NPV of buying the investment if the 15% total return lasts for the next 100 years (t=0 to 100), then reverts to 10% after that time? Also, what is the NPV of the investment if the 15% return lasts forever?
In both cases, assume that the required return of 10% remains constant, the dividends can only be re-invested at 10% pa and all returns are given as effective annual rates.
The answer choices below are given in the same order (15% for 100 years, and 15% forever):
One year ago you bought a $1,000,000 house partly funded using a mortgage loan. The loan size was $800,000 and the other $200,000 was your wealth or 'equity' in the house asset.
The interest rate on the home loan was 4% pa.
Over the year, the house produced a net rental yield of 2% pa and a capital gain of 2.5% pa.
Assuming that all cash flows (interest payments and net rental payments) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates are given as effective annual rates, what was the total return on your wealth over the past year?
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
A Brazilian lady wishes to convert 1 million Brazilian Real (BRL) into Chinese Renminbi (RMB, also called the Yuan or CNY). The exchange rate is 3.42 BRL per USD and 6.27 RMB per USD. How much is the BRL 1 million worth in RMB?
Question 908 effective rate, return types, gross discrete return, return distribution, price gains and returns over time
For an asset's price to double from say $1 to $2 in one year, what must its gross discrete return (GDR) be? If the price now is ##P_0## and the price in one year is ##P_1## then the gross discrete return over the next year is:
###\text{GDR}_\text{annual} = \dfrac{P_1}{P_0}###