A share was bought for $20 (at t=0) and paid its annual dividend of $3 one year later (at t=1). Just after the dividend was paid, the share price was $16 (at t=1). What was the total return, capital return and income return? Calculate your answers as effective annual rates.
The choices are given in the same order: ## r_\text{total},r_\text{capital},r_\text{income} ##.
The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of the project?
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 11 |
| 2 | 121 |
Which business structure or structures have the advantage of limited liability for equity investors?
The below screenshot of Microsoft's (MSFT) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 28 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.
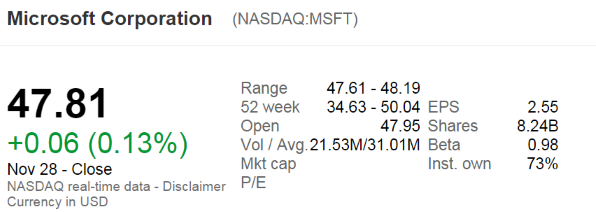
What was MSFT's market capitalisation of equity?
Question 494 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system
A firm pays a fully franked cash dividend of $100 to one of its Australian shareholders who has a personal marginal tax rate of 15%. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What will be the shareholder's personal tax payable due to the dividend payment?
Question 559 variance, standard deviation, covariance, correlation
Which of the following statements about standard statistical mathematics notation is NOT correct?
On 22-Mar-2013 the Australian Government issued series TB139 treasury bonds with a combined face value $23.4m, listed on the ASX with ticker code GSBG25.
The bonds mature on 21-Apr-2025, the fixed coupon rate is 3.25% pa and coupons are paid semi-annually on the 21st of April and October of each year. Each bond's face value is $1,000.
At market close on Friday 11-Sep-2015 the bonds' yield was 2.736% pa.
At market close on Monday 14-Sep-2015 the bonds' yield was 2.701% pa. Both yields are given as annualised percentage rates (APR's) compounding every 6 months. For convenience, assume 183 days in 6 months and 366 days in a year.
What was the historical total return over those 3 calendar days between Friday 11-Sep-2015 and Monday 14-Sep-2015?
There are 183 calendar days from market close on the last coupon 21-Apr-2015 to the market close of the next coupon date on 21-Oct-2015.
Between the market close times from 21-Apr-2015 to 11-Sep-2015 there are 143 calendar days. From 21-Apr-2015 to 14-Sep-2015 there are 146 calendar days.
From 14-Sep-2015 there were 20 coupons remaining to be paid including the next one on 21-Oct-2015.
All of the below answers are given as effective 3 day rates.
An effective semi-annual return of 5% ##(r_\text{eff 6mth})## is equivalent to an effective annual return ##(r_\text{eff annual})## of:
The symbol ##\text{GDR}_{0\rightarrow 1}## represents a stock's gross discrete return per annum over the first year. ##\text{GDR}_{0\rightarrow 1} = P_1/P_0##. The subscript indicates the time period that the return is mentioned over. So for example, ##\text{AAGDR}_{1 \rightarrow 3}## is the arithmetic average GDR measured over the two year period from years 1 to 3, but it is expressed as a per annum rate.
Which of the below statements about the arithmetic and geometric average GDR is NOT correct?
Question 860 idiom, hedging, speculation, arbitrage, market making, insider trading, no explanation
Which class of derivatives market trader is NOT principally focused on ‘buying low and selling high’?