Let the standard deviation of returns for a share per month be ##\sigma_\text{monthly}##.
What is the formula for the standard deviation of the share's returns per year ##(\sigma_\text{yearly})##?
Assume that returns are independently and identically distributed (iid) so they have zero auto correlation, meaning that if the return was higher than average today, it does not indicate that the return tomorrow will be higher or lower than average.
Over the next year, the management of an unlevered company plans to:
- Achieve firm free cash flow (FFCF or CFFA) of $1m.
- Pay dividends of $1.8m
- Complete a $1.3m share buy-back.
- Spend $0.8m on new buildings without buying or selling any other fixed assets. This capital expenditure is included in the CFFA figure quoted above.
Assume that:
- All amounts are received and paid at the end of the year so you can ignore the time value of money.
- The firm has sufficient retained profits to pay the dividend and complete the buy back.
- The firm plans to run a very tight ship, with no excess cash above operating requirements currently or over the next year.
How much new equity financing will the company need? In other words, what is the value of new shares that will need to be issued?
Question 449 personal tax on dividends, classical tax system
A small private company has a single shareholder. This year the firm earned a $100 profit before tax. All of the firm's after tax profits will be paid out as dividends to the owner.
The corporate tax rate is 30% and the sole shareholder's personal marginal tax rate is 45%.
The United States' classical tax system applies because the company generates all of its income in the US and pays corporate tax to the Internal Revenue Service. The shareholder is also an American for tax purposes.
What will be the personal tax payable by the shareholder and the corporate tax payable by the company?
Below are some statements about loans and bonds. The first descriptive sentence is correct. But one of the second sentences about the loans' or bonds' prices is not correct. Which statement is NOT correct? Assume that interest rates are positive.
Note that coupons or interest payments are the periodic payments made throughout a bond or loan's life. The face or par value of a bond or loan is the amount paid at the end when the debt matures.
A low-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $1,000 and will last for 1 year before it will be scrapped for nothing.
A high-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $4,900 and it will last for 5 years before it will be scrapped for nothing.
What is the equivalent annual cost of each car? Assume a discount rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
The answer choices are given as the equivalent annual cost of the low-quality car and then the high quality car.
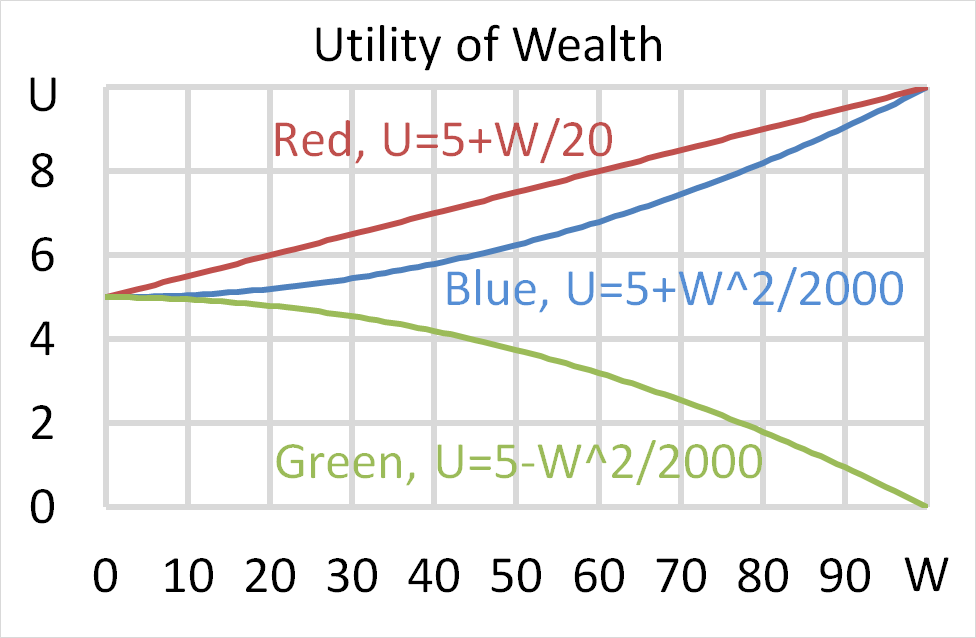
Question 701 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 771 debt terminology, interest expense, interest tax shield, credit risk, no explanation
You deposit money into a bank account. Which of the following statements about this deposit is NOT correct?
Question 786 fixed for floating interest rate swap, intermediated swap
The below table summarises the borrowing costs confronting two companies A and B.
| Bond Market Yields | ||||
| Fixed Yield to Maturity (%pa) | Floating Yield (%pa) | |||
| Firm A | 3 | L - 0.4 | ||
| Firm B | 5 | L + 1 | ||
Firm A wishes to borrow at a floating rate and Firm B wishes to borrow at a fixed rate. Design an intermediated swap (which means there will actually be two swaps) that nets a bank 0.1% and shares the remaining swap benefits between Firms A and B equally. Which of the following statements about the swap is NOT correct?
Question 948 VaR, expected shortfall
Below is a historical sample of returns on the S&P500 capital index.
| S&P500 Capital Index Daily Returns Ranked from Best to Worst |
||
| 10,000 trading days from 4th August 1977 to 24 March 2017 based on closing prices. |
||
| Rank | Date (DD-MM-YY) |
Continuously compounded daily return (% per day) |
| 1 | 21-10-87 | 9.23 |
| 2 | 08-03-83 | 8.97 |
| 3 | 13-11-08 | 8.3 |
| 4 | 30-09-08 | 8.09 |
| 5 | 28-10-08 | 8.01 |
| 6 | 29-10-87 | 7.28 |
| … | … | … |
| 9980 | 11-12-08 | -5.51 |
| 9981 | 22-10-08 | -5.51 |
| 9982 | 08-08-11 | -5.54 |
| 9983 | 22-09-08 | -5.64 |
| 9984 | 11-09-86 | -5.69 |
| 9985 | 30-11-87 | -5.88 |
| 9986 | 14-04-00 | -5.99 |
| 9987 | 07-10-98 | -6.06 |
| 9988 | 08-01-88 | -6.51 |
| 9989 | 27-10-97 | -6.55 |
| 9990 | 13-10-89 | -6.62 |
| 9991 | 15-10-08 | -6.71 |
| 9992 | 29-09-08 | -6.85 |
| 9993 | 07-10-08 | -6.91 |
| 9994 | 14-11-08 | -7.64 |
| 9995 | 01-12-08 | -7.79 |
| 9996 | 29-10-08 | -8.05 |
| 9997 | 26-10-87 | -8.4 |
| 9998 | 31-08-98 | -8.45 |
| 9999 | 09-10-08 | -12.9 |
| 10000 | 19-10-87 | -23.36 |
| Mean of all 10,000: | 0.0354 | |
| Sample standard deviation of all 10,000: | 1.2062 | |
| Sources: Bloomberg and S&P. | ||
Assume that the one-tail Z-statistic corresponding to a probability of 99.9% is exactly 3.09. Which of the following statements is NOT correct? Based on the historical data, the 99.9% daily: