A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 1.15 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at 5% pa, so;
- the dividend at t=5 will be $1.15(1+0.05),
- the dividend at t=6 will be $1.15(1+0.05)^2, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates. What is the current price of the stock?
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 1.15 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at 5% pa, so;
- the dividend at t=5 will be $1.15(1+0.05),
- the dividend at t=6 will be $1.15(1+0.05)^2, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates.
What will be the price of the stock in three and a half years (t = 3.5)?
Your friend just bought a house for $400,000. He financed it using a $320,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $80,000.
In the context of residential housing and mortgages, the 'equity' tied up in the value of a person's house is the value of the house less the value of the mortgage. So the initial equity your friend has in his house is $80,000. Let this amount be E, let the value of the mortgage be D and the value of the house be V. So ##V=D+E##.
If house prices suddenly fall by 10%, what would be your friend's percentage change in equity (E)? Assume that the value of the mortgage is unchanged and that no income (rent) was received from the house during the short time over which house prices fell.
Remember:
### r_{0\rightarrow1}=\frac{p_1-p_0+c_1}{p_0} ###
where ##r_{0-1}## is the return (percentage change) of an asset with price ##p_0## initially, ##p_1## one period later, and paying a cash flow of ##c_1## at time ##t=1##.
A person is thinking about borrowing $100 from the bank at 7% pa and investing it in shares with an expected return of 10% pa. One year later the person intends to sell the shares and pay back the loan in full. Both the loan and the shares are fairly priced.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of this one year investment? Note that you are asked to find the present value (##V_0##), not the value in one year (##V_1##).
You just signed up for a 30 year interest-only mortgage with monthly payments of $3,000 per month. The interest rate is 6% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 15 years, just after the 180th payment at that time, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 6% and is not expected to change. Remember that the mortgage is interest-only and that mortgage payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
Question 50 DDM, stock pricing, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Most listed Australian companies pay dividends twice per year, the 'interim' and 'final' dividends, which are roughly 6 months apart.
You are an equities analyst trying to value the company BHP. You decide to use the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) as a starting point, so you study BHP's dividend history and you find that BHP tends to pay the same interim and final dividend each year, and that both grow by the same rate.
You expect BHP will pay a $0.55 interim dividend in six months and a $0.55 final dividend in one year. You expect each to grow by 4% next year and forever, so the interim and final dividends next year will be $0.572 each, and so on in perpetuity.
Assume BHP's cost of equity is 8% pa. All rates are quoted as nominal effective rates. The dividends are nominal cash flows and the inflation rate is 2.5% pa.
What is the current price of a BHP share?
A stock pays semi-annual dividends. It just paid a dividend of $10. The growth rate in the dividend is 1% every 6 months, given as an effective 6 month rate. You estimate that the stock's required return is 21% pa, as an effective annual rate.
Using the dividend discount model, what will be the share price?
For a price of $6, Carlos will sell you a share which will pay a dividend of $1 in one year and every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
Your friend wants to borrow $1,000 and offers to pay you back $100 in 6 months, with more $100 payments at the end of every month for another 11 months. So there will be twelve $100 payments in total. She says that 12 payments of $100 equals $1,200 so she's being generous.
If interest rates are 12% pa, given as an APR compounding monthly, what is the Net Present Value (NPV) of your friend's deal?
A wholesale horticulture nursery offers credit to its customers.
Customers are given 60 days to pay for their goods, but if they pay immediately they will get a 3% discount.
What is the effective interest rate implicit in the discount being offered? Assume 365 days in a year and that all customers pay either immediately or on the 60th day. All rates given below are effective annual rates.
For a price of $13, Carla will sell you a share paying a dividend of $1 in one year and every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same US company. Both bonds yield 10% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X and Y's coupon rates are 8 and 12% pa respectively. Which of the following statements is true?
Question 35 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
A European company just issued two bonds, a
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the company's forward rate over the second year (from t=1 to t=2)? Give your answer as an effective annual rate, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
A company has:
- 100 million ordinary shares outstanding which are trading at a price of $5 each. Market analysts estimated that the company's ordinary stock has a beta of 1.5. The risk-free rate is 5% and the market return is 10%.
- 1 million preferred shares which have a face (or par) value of $100 and pay a constant annual dividend of 9% of par. The next dividend will be paid in one year. Assume that all preference dividends will be paid when promised. They currently trade at a price of $90 each.
- Debentures that have a total face value of $200 million and a yield to maturity of 6% per annum. They are publicly traded and their market price is equal to 110% of their face value.
The corporate tax rate is 30%. All returns and yields are given as effective annual rates.
What is the company's after-tax Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)? Assume a classical tax system.
For a price of $1040, Camille will sell you a share which just paid a dividend of $100, and is expected to pay dividends every year forever, growing at a rate of 5% pa.
So the next dividend will be ##100(1+0.05)^1=$105.00##, and the year after it will be ##100(1+0.05)^2=110.25## and so on.
The required return of the stock is 15% pa.
When using the dividend discount model to price a stock:
### p_{0} = \frac{d_1}{r - g} ###
The growth rate of dividends (g):
Question 64 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, APR, effective rate
In Germany, nominal yields on semi-annual coupon paying Government Bonds with 2 years until maturity are currently 0.04% pa.
The inflation rate is currently 1.4% pa, given as an APR compounding per quarter. The inflation rate is not expected to change over the next 2 years.
What is the real yield on these bonds, given as an APR compounding every 6 months?
For a price of $129, Joanne will sell you a share which is expected to pay a $30 dividend in one year, and a $10 dividend every year after that forever. So the stock's dividends will be $30 at t=1, $10 at t=2, $10 at t=3, and $10 forever onwards.
The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
You want to buy an apartment priced at $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
The following cash flows are expected:
- 10 yearly payments of $60, with the first payment in 3 years from now (first payment at t=3 and last at t=12).
- 1 payment of $400 in 5 years and 6 months (t=5.5) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
A 2 year government bond yields 5% pa with a coupon rate of 6% pa, paid semi-annually.
Find the effective six month rate, effective annual rate and the effective daily rate. Assume that each month has 30 days and that there are 360 days in a year.
All answers are given in the same order:
##r_\text{eff semi-annual}##, ##r_\text{eff yrly}##, ##r_\text{eff daily}##.
You're trying to save enough money to buy your first car which costs $2,500. You can save $100 at the end of each month starting from now. You currently have no money at all. You just opened a bank account with an interest rate of 6% pa payable monthly.
How many months will it take to save enough money to buy the car? Assume that the price of the car will stay the same over time.
You're advising your superstar client 40-cent who is weighing up buying a private jet or a luxury yacht. 40-cent is just as happy with either, but he wants to go with the more cost-effective option. These are the cash flows of the two options:
- The private jet can be bought for $6m now, which will cost $12,000 per month in fuel, piloting and airport costs, payable at the end of each month. The jet will last for 12 years.
- Or the luxury yacht can be bought for $4m now, which will cost $20,000 per month in fuel, crew and berthing costs, payable at the end of each month. The yacht will last for 20 years.
What's unusual about 40-cent is that he is so famous that he will actually be able to sell his jet or yacht for the same price as it was bought since the next generation of superstar musicians will buy it from him as a status symbol.
Bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. You can assume that 40-cent will live for another 60 years and that when the jet or yacht's life is at an end, he will buy a new one with the same details as above.
Would you advise 40-cent to buy the or the ?
Note that the effective monthly rate is ##r_\text{eff monthly}=(1+0.1)^{1/12}-1=0.00797414##
A 90-day Bank Accepted Bill (BAB) has a face value of $1,000,000. The simple interest rate is 10% pa and there are 365 days in the year. What is its price now?
A four year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 6% and a fixed coupon rate of 12%, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at par?
A firm wishes to raise $20 million now. They will issue 8% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 5 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 6% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
A share just paid its semi-annual dividend of $10. The dividend is expected to grow at 2% every 6 months forever. This 2% growth rate is an effective 6 month rate. Therefore the next dividend will be $10.20 in six months. The required return of the stock is 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the price of the share now?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### p_0 = \frac{d_1}{r - g} ###
Which expression is NOT equal to the expected dividend yield?
Harvey Norman the large retailer often runs sales advertising 2 years interest free when you purchase its products. This offer can be seen as a free personal loan from Harvey Norman to its customers.
Assume that banks charge an interest rate on personal loans of 12% pa given as an APR compounding per month. This is the interest rate that Harvey Norman deserves on the 2 year loan it extends to its customers. Therefore Harvey Norman must implicitly include the cost of this loan in the advertised sale price of its goods.
If you were a customer buying from Harvey Norman, and you were paying immediately, not in 2 years, what is the minimum percentage discount to the advertised sale price that you would insist on? (Hint: if it makes it easier, assume that you’re buying a product with an advertised price of $100).
Question 58 NPV, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, Annuity
A project to build a toll bridge will take two years to complete, costing three payments of $100 million at the start of each year for the next three years, that is at t=0, 1 and 2.
After completion, the toll bridge will yield a constant $50 million at the end of each year for the next 10 years. So the first payment will be at t=3 and the last at t=12. After the last payment at t=12, the bridge will be given to the government.
The required return of the project is 21% pa given as an effective annual nominal rate.
All cash flows are real and the expected inflation rate is 10% pa given as an effective annual rate. Ignore taxes.
The Net Present Value is:
Question 218 NPV, IRR, profitability index, average accounting return
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A project has an internal rate of return (IRR) which is greater than its required return. Select the most correct statement.
A project's Profitability Index (PI) is less than 1. Select the most correct statement:
A project's NPV is positive. Select the most correct statement:
A very low-risk stock just paid its semi-annual dividend of $0.14, as it has for the last 5 years. You conservatively estimate that from now on the dividend will fall at a rate of 1% every 6 months.
If the stock currently sells for $3 per share, what must be its required total return as an effective annual rate?
If risk free government bonds are trading at a yield of 4% pa, given as an effective annual rate, would you consider buying or selling the stock?
The stock's required total return is:
A wholesale store offers credit to its customers. Customers are given 60 days to pay for their goods, but if they pay immediately they will get a 1.5% discount.
What is the effective interest rate implicit in the discount being offered? Assume 365 days in a year and that all customers pay either immediately or the 60th day. All of the below answer choices are given as effective annual interest rates.
A furniture distributor offers credit to its customers. Customers are given 25 days to pay for their goods, but if they pay immediately they will get a 1% discount.
What is the effective interest rate implicit in the discount being offered? Assume 365 days in a year and that all customers pay either immediately or on the 25th day. All rates given below are effective annual rates.
Question 180 equivalent annual cash flow, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Details of two different types of light bulbs are given below:
- Low-energy light bulbs cost $3.50, have a life of nine years, and use about $1.60 of electricity a year, paid at the end of each year.
- Conventional light bulbs cost only $0.50, but last only about a year and use about $6.60 of energy a year, paid at the end of each year.
The real discount rate is 5%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that all cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% given as an effective annual rate.
Find the Equivalent Annual Cost (EAC) of the low-energy and conventional light bulbs. The below choices are listed in that order.
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
###P_0=\frac{d_1}{r-g}###
A stock pays dividends annually. It just paid a dividend, but the next dividend (##d_1##) will be paid in one year.
According to the DDM, what is the correct formula for the expected price of the stock in 2.5 years?
Question 271 CAPM, option, risk, systematic risk, systematic and idiosyncratic risk
All things remaining equal, according to the capital asset pricing model, if the systematic variance of an asset increases, its required return will increase and its price will decrease.
If the idiosyncratic variance of an asset increases, its price will be unchanged.
What is the relationship between the price of a call or put option and the total, systematic and idiosyncratic variance of the underlying asset that the option is based on? Select the most correct answer.
Call and put option prices increase when the:
A 2 year corporate bond yields 3% pa with a coupon rate of 5% pa, paid semi-annually.
Find the effective monthly rate, effective six month rate, and effective annual rate.
##r_\text{eff monthly}##, ##r_\text{eff 6 month}##, ##r_\text{eff annual}##.
A 60-day Bank Accepted Bill has a face value of $1,000,000. The interest rate is 8% pa and there are 365 days in the year. What is its price now?
You want to buy a house priced at $400,000. You have saved a deposit of $40,000. The bank has agreed to lend you $360,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 8% pa payable monthly and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments?
A share just paid its semi-annual dividend of $5. The dividend is expected to grow at 1% every 6 months forever. This 1% growth rate is an effective 6 month rate.
Therefore the next dividend will be $5.05 in six months. The required return of the stock 8% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the price of the share now?
A company's shares just paid their annual dividend of $2 each.
The stock price is now $40 (just after the dividend payment). The annual dividend is expected to grow by 3% every year forever. The assumptions of the dividend discount model are valid for this company.
What do you expect the effective annual dividend yield to be in 3 years (dividend yield from t=3 to t=4)?
A student won $1m in a lottery. Currently the money is in a bank account which pays interest at 6% pa, given as an APR compounding per month.
She plans to spend $20,000 at the beginning of every month from now on (so the first withdrawal will be at t=0). After each withdrawal, she will check how much money is left in the account. When there is less than $500,000 left, she will donate that remaining amount to charity.
In how many months will she make her last withdrawal and donate the remainder to charity?
Your main expense is fuel for your car which costs $100 per month. You just refueled, so you won't need any more fuel for another month (first payment at t=1 month).
You have $2,500 in a bank account which pays interest at a rate of 6% pa, payable monthly. Interest rates are not expected to change.
Assuming that you have no income, in how many months time will you not have enough money to fully refuel your car?
Value the following business project to manufacture a new product.
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 2 yrs | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $6m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $3m | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | $0.6m | |
| Unit sales per year | 4m | |
| Sale price per unit | $8 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $5 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $1m | |
| Interest expense per year | 0 | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Weighted average cost of capital after tax per annum | 10% | |
Notes
- The firm's current assets and current liabilities are $3m and $2m respectively right now. This net working capital will not be used in this project, it will be used in other unrelated projects.
Due to the project, current assets (mostly inventory) will grow by $2m initially (at t = 0), and then by $0.2m at the end of the first year (t=1).
Current liabilities (mostly trade creditors) will increase by $0.1m at the end of the first year (t=1).
At the end of the project, the net working capital accumulated due to the project can be sold for the same price that it was bought. - The project cost $0.5m to research which was incurred one year ago.
Assumptions
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The business considering the project is run as a 'sole tradership' (run by an individual without a company) and is therefore eligible for a 50% capital gains tax discount when the equipment is sold, as permitted by the Australian Tax Office.
What is the expected net present value (NPV) of the project?
You own a nice suit which you wear once per week on nights out. You bought it one year ago for $600. In your experience, suits used once per week last for 6 years. So you expect yours to last for another 5 years.
Your younger brother said that retro is back in style so he wants to wants to borrow your suit once a week when he goes out. With the increased use, your suit will only last for another 4 years rather than 5.
What is the present value of the cost of letting your brother use your current suit for the next 4 years?
Assume: that bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate; you will buy a new suit when your current one wears out and your brother will not use the new one; your brother will only use your current suit so he will only use it for the next four years; and the price of a new suit never changes.
The following table shows a sample of historical total returns of shares in two different companies A and B.
| Stock Returns | ||
| Total effective annual returns | ||
| Year | ##r_A## | ##r_B## |
| 2007 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| 2008 | 0.04 | -0.2 |
| 2009 | -0.1 | -0.3 |
| 2010 | 0.18 | 0.5 |
What is the historical sample covariance (##\hat{\sigma}_{A,B}##) and correlation (##\rho_{A,B}##) of stock A and B's total effective annual returns?
Question 239 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, interest only loan
A bank grants a borrower an interest-only residential mortgage loan with a very large 50% deposit and a nominal interest rate of 6% that is not expected to change. Assume that inflation is expected to be a constant 2% pa over the life of the loan. Ignore credit risk.
From the bank's point of view, what is the long term expected nominal capital return of the loan asset?
Stock A has a beta of 0.5 and stock B has a beta of 1. Which statement is NOT correct?
Carlos and Edwin are brothers and they both love Holden Commodore cars.
Carlos likes to buy the latest Holden Commodore car for $40,000 every 4 years as soon as the new model is released. As soon as he buys the new car, he sells the old one on the second hand car market for $20,000. Carlos never has to bother with paying for repairs since his cars are brand new.
Edwin also likes Commodores, but prefers to buy 4-year old cars for $20,000 and keep them for 11 years until the end of their life (new ones last for 15 years in total but the 4-year old ones only last for another 11 years). Then he sells the old car for $2,000 and buys another 4-year old second hand car, and so on.
Every time Edwin buys a second hand 4 year old car he immediately has to spend $1,000 on repairs, and then $1,000 every year after that for the next 10 years. So there are 11 payments in total from when the second hand car is bought at t=0 to the last payment at t=10. One year later (t=11) the old car is at the end of its total 15 year life and can be scrapped for $2,000.
Assuming that Carlos and Edwin maintain their love of Commodores and keep up their habits of buying new ones and second hand ones respectively, how much larger is Carlos' equivalent annual cost of car ownership compared with Edwin's?
The real discount rate is 10% pa. All cash flows are real and are expected to remain constant. Inflation is forecast to be 3% pa. All rates are effective annual. Ignore capital gains tax and tax savings from depreciation since cars are tax-exempt for individuals.
Question 308 risk, standard deviation, variance, no explanation
A stock's standard deviation of returns is expected to be:
- 0.09 per month for the first 5 months;
- 0.14 per month for the next 7 months.
What is the expected standard deviation of the stock per year ##(\sigma_\text{annual})##?
Assume that returns are independently and identically distributed (iid) and therefore have zero auto-correlation.
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume an equal amount now (t=0), in one year (t=1) and in two years (t=2), and still have $50,000 in the bank after that (t=2).
How much can you consume at each time?
Question 245 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, foreign exchange rate direct quote, no explanation
Investors expect Australia's central bank, the RBA, to leave the policy rate unchanged at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the policy rate is reduced due to fears that Australia's GDP growth is slowing.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate? Direct and indirect quotes are given from the perspective of an Australian.
The Australian dollar will:
Find Ching-A-Lings Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Ching-A-Lings Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 100 | |
| COGS | 20 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Rent expense | 11 | |
| Interest expense | 19 | |
| Taxable Income | 30 | |
| Taxes at 30% | 9 | |
| Net income | 21 | |
| Ching-A-Lings Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Inventory | 49 | 38 |
| Trade debtors | 14 | 2 |
| Rent paid in advance | 5 | 5 |
| PPE | 400 | 400 |
| Total assets | 468 | 445 |
| Trade creditors | 4 | 10 |
| Bond liabilities | 200 | 190 |
| Contributed equity | 145 | 145 |
| Retained profits | 119 | 100 |
| Total L and OE | 468 | 445 |
Note: All figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
The cash flow from assets was:
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Correlation | Dollars invested |
||
| A | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 60 | ||
| B | 0.2 | 0.6 | 140 | |||
What is the expected return of the above portfolio?
Which firms tend to have low forward-looking price-earnings (PE) ratios?
Only consider firms with positive earnings, disregard firms with negative earnings and therefore negative PE ratios.
The Chinese government attempts to fix its exchange rate against the US dollar and at the same time use monetary policy to fix its interest rate at a set level.
To be able to fix its exchange rate and interest rate in this way, what does the Chinese government actually do?
- Adopts capital controls to prevent financial arbitrage by private firms and individuals.
- Adopts the same interest rate (monetary policy) as the United States.
- Fixes inflation so that the domestic real interest rate is equal to the United States' real interest rate.
Which of the above statements is or are true?
One formula for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to use earnings before interest and tax (EBIT).
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (EBIT)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ \end{aligned} \\###
One method for calculating a firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to ignore interest expense. That is, pretend that interest expense ##(IntExp)## is zero:
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - 0)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC - 0\\ \end{aligned}###
Question 345 capital budgeting, break even, NPV
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 10 yrs | |
| Initial investment in factory | $10m | |
| Depreciation of factory per year | $1m | |
| Expected scrap value of factory at end of project | $0 | |
| Sale price per unit | $10 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $6 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $2m | |
| Interest expense per year | 0 | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Cost of capital per annum | 10% | |
Notes
- The firm's current liabilities are forecast to stay at $0.5m. The firm's current assets (mostly inventory) is currently $1m, but is forecast to grow by $0.1m at the end of each year due to the project.
At the end of the project, the current assets accumulated due to the project can be sold for the same price that they were bought. - A marketing survey was used to forecast sales. It cost $1.4m which was just paid. The cost has been capitalised by the accountants and is tax-deductible over the life of the project, regardless of whether the project goes ahead or not. This amortisation expense is not included in the depreciation expense listed in the table above.
Assumptions
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
Find the break even unit production (Q) per year to achieve a zero Net Income (NI) and Net Present Value (NPV), respectively. The answers below are listed in the same order.
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume an equal amount now (t=0) and in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end (t=1).
How much can you consume at each time?
Acquirer firm plans to launch a takeover of Target firm. The deal is expected to create a present value of synergies totaling $105 million. A 40% scrip and 60% cash offer will be made that pays the fair price for the target's shares plus 75% of the total synergy value. The cash will be paid out of the firm's cash holdings, no new debt or equity will be raised.
| Firms Involved in the Takeover | ||
| Acquirer | Target | |
| Assets ($m) | 6,000 | 700 |
| Debt ($m) | 4,800 | 400 |
| Share price ($) | 40 | 20 |
| Number of shares (m) | 30 | 15 |
Ignore transaction costs and fees. Assume that the firms' debt and equity are fairly priced, and that each firms' debts' risk, yield and values remain constant. The acquisition is planned to occur immediately, so ignore the time value of money.
Calculate the merged firm's share price and total number of shares after the takeover has been completed.
Question 418 capital budgeting, NPV, interest tax shield, WACC, CFFA, CAPM
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $8m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $8m | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | 0 | |
| Unit sales per year | 4m | |
| Sale price per unit | $10 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $5 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $2m | |
| Interest expense in first year (at t=1) | $0.562m | |
| Corporate tax rate | 30% | |
| Government treasury bond yield | 5% | |
| Bank loan debt yield | 9% | |
| Market portfolio return | 10% | |
| Covariance of levered equity returns with market | 0.32 | |
| Variance of market portfolio returns | 0.16 | |
| Firm's and project's debt-to-equity ratio | 50% | |
Notes
- Due to the project, current assets will increase by $6m now (t=0) and fall by $6m at the end (t=1). Current liabilities will not be affected.
Assumptions
- The debt-to-equity ratio will be kept constant throughout the life of the project. The amount of interest expense at the end of each period has been correctly calculated to maintain this constant debt-to-equity ratio.
- Millions are represented by 'm'.
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The project is undertaken by a firm, not an individual.
What is the net present value (NPV) of the project?
A managed fund charges fees based on the amount of money that you keep with them. The fee is 2% of the end-of-year amount, paid at the end of every year.
This fee is charged regardless of whether the fund makes gains or losses on your money.
The fund offers to invest your money in shares which have an expected return of 10% pa before fees.
You are thinking of investing $100,000 in the fund and keeping it there for 40 years when you plan to retire.
How much money do you expect to have in the fund in 40 years? Also, what is the future value of the fees that the fund expects to earn from you? Give both amounts as future values in 40 years. Assume that:
- The fund has no private information.
- Markets are weak and semi-strong form efficient.
- The fund's transaction costs are negligible.
- The cost and trouble of investing your money in shares by yourself, without the managed fund, is negligible.
- The fund invests its fees in the same companies as it invests your funds in, but with no fees.
The below answer choices list your expected wealth in 40 years and then the fund's expected wealth in 40 years.
Question 363 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 8% pa and nominal capital return of 3% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns? The answer choices below are given in the same order.
A European call option will mature in ##T## years with a strike price of ##K## dollars. The underlying asset has a price of ##S## dollars.
What is an expression for the payoff at maturity ##(f_T)## in dollars from having written (being short) the call option?
You want to buy an apartment worth $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as a fully amortising mortgage loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments?
In the 'Austin Powers' series of movies, the character Dr. Evil threatens to destroy the world unless the United Nations pays him a ransom (video 1, video 2). Dr. Evil makes the threat on two separate occasions:
- In 1969 he demands a ransom of $1 million (=10^6), and again;
- In 1997 he demands a ransom of $100 billion (=10^11).
If Dr. Evil's demands are equivalent in real terms, in other words $1 million will buy the same basket of goods in 1969 as $100 billion would in 1997, what was the implied inflation rate over the 28 years from 1969 to 1997?
The answer choices below are given as effective annual rates:
Question 96 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds paying semi-annual coupons:
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
A stock just paid its annual dividend of $9. The share price is $60. The required return of the stock is 10% pa as an effective annual rate.
What is the implied growth rate of the dividend per year?
A stock is expected to pay a dividend of $15 in one year (t=1), then $25 for 9 years after that (payments at t=2 ,3,...10), and on the 11th year (t=11) the dividend will be 2% less than at t=10, and will continue to shrink at the same rate every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10%. All rates are effective annual rates.
What is the price of the stock now?
When using the dividend discount model, care must be taken to avoid using a nominal dividend growth rate that exceeds the country's nominal GDP growth rate. Otherwise the firm is forecast to take over the country since it grows faster than the average business forever.
Suppose a firm's nominal dividend grows at 10% pa forever, and nominal GDP growth is 5% pa forever. The firm's total dividends are currently $1 billion (t=0). The country's GDP is currently $1,000 billion (t=0).
In approximately how many years will the company's total dividends be as large as the country's GDP?
Question 472 quick ratio, accounting ratio
A firm has current assets totaling $1.5b of which cash is $0.25b and inventories is $0.5b. Current liabilities total $2b of which accounts payable is $1b.
What is the firm's quick ratio, also known as the acid test ratio?
A share just paid its semi-annual dividend of $10. The dividend is expected to grow at 2% every 6 months forever. This 2% growth rate is an effective 6 month rate. Therefore the next dividend will be $10.20 in six months. The required return of the stock 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the price of the share now?
A project has the following cash flows:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 200 |
| 2 | 250 |
What is the Profitability Index (PI) of the project? Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time. The required return is 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
A low-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $1,000 and will last for 1 year before it will be scrapped for nothing.
A high-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $4,900 and it will last for 5 years before it will be scrapped for nothing.
What is the equivalent annual cost of each car? Assume a discount rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
The answer choices are given as the equivalent annual cost of the low-quality car and then the high quality car.
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.15 | 1.10 | 1.05 | 1.00 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at -5% pa. Note that this is a negative growth rate, so the dividend will actually shrink. So,
- the dividend at t=5 will be ##$1(1-0.05) = $0.95##,
- the dividend at t=6 will be ##$1(1-0.05)^2 = $0.9025##, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates.
What will be the price of the stock in four and a half years (t = 4.5)?
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 8 | 8 | 8 | 20 | 8 | ... |
After year 4, the dividend will grow in perpetuity at 4% pa. The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates. Note that the $8 dividend at time zero is about to be paid tonight.
What is the current price of the stock?
Question 513 stock split, reverse stock split, stock dividend, bonus issue, rights issue
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| One Year Mining Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in building mine and equipment | $9m | |
| Depreciation of mine and equipment over the year | $8m | |
| Kilograms of gold mined at end of year | 1,000 | |
| Sale price per kilogram | $0.05m | |
| Variable cost per kilogram | $0.03m | |
| Before-tax cost of closing mine at end of year | $4m | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
Note 1: Due to the project, the firm also anticipates finding some rare diamonds which will give before-tax revenues of $1m at the end of the year.
Note 2: The land that will be mined actually has thermal springs and a family of koalas that could be sold to an eco-tourist resort for an after-tax amount of $3m right now. However, if the mine goes ahead then this natural beauty will be destroyed.
Note 3: The mining equipment will have a book value of $1m at the end of the year for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $2.5m when it is sold.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero and one. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m), with the first cash flow at time zero, and the second at time one.
You really want to go on a back packing trip to Europe when you finish university. Currently you have $1,500 in the bank. Bank interest rates are 8% pa, given as an APR compounding per month. If the holiday will cost $2,000, how long will it take for your bank account to reach that amount?
An investor bought a 10 year 2.5% pa fixed coupon government bond priced at par. The face value is $100. Coupons are paid semi-annually and the next one is in 6 months.
Six months later, just after the coupon at that time was paid, yields suddenly and unexpectedly fell to 2% pa. Note that all yields above are given as APR's compounding semi-annually.
What was the bond investors' historical total return over that first 6 month period, given as an effective semi-annual rate?
Question 335 foreign exchange rate, American and European terms
Investors expect Australia's central bank, the RBA, to reduce the policy rate at their next meeting due to fears that the economy is slowing. Then unexpectedly, the policy rate is actually kept unchanged.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate?
What is the correlation of a variable X with itself?
The corr(X, X) or ##\rho_{X,X}## equals:
You want to buy an apartment priced at $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $30,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $270,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 12% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments? Remember that mortgage loan payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
A European bond paying annual coupons of 6% offers a yield of 10% pa.
Convert the yield into an effective monthly rate, an effective annual rate and an effective daily rate. Assume that there are 365 days in a year.
All answers are given in the same order:
### r_\text{eff, monthly} , r_\text{eff, yearly} , r_\text{eff, daily} ###
Question 241 Miller and Modigliani, leverage, payout policy, diversification, NPV
One of Miller and Modigliani's (M&M's) important insights is that a firm's managers should not try to achieve a particular level of leverage in a world with zero taxes and perfect information since investors can make their own leverage. Therefore corporate capital structure policy is irrelevant since investors can achieve their own desired leverage at the personal level by borrowing or lending on their own.
This principal of 'home-made' or 'do-it-yourself' leverage can also be applied to other topics. Read the following statements to decide which are true:
(I) Payout policy: a firm's managers should not try to achieve a particular pattern of equity payout.
(II) Agency costs: a firm's managers should not try to minimise agency costs.
(III) Diversification: a firm's managers should not try to diversify across industries.
(IV) Shareholder wealth: a firm's managers should not try to maximise shareholders' wealth.
Which of the above statement(s) are true?
An American wishes to convert USD 1 million to Australian dollars (AUD). The exchange rate is 0.8 USD per AUD. How much is the USD 1 million worth in AUD?
The equations for Net Income (NI, also known as Earnings or Net Profit After Tax) and Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA, also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm) per year are:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c)###
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+IntExp###
For a firm with debt, what is the formula for the present value of interest tax shields if the tax shields occur in perpetuity?
You may assume:
- the value of debt (D) is constant through time,
- The cost of debt and the yield on debt are equal and given by ##r_D##.
- the appropriate rate to discount interest tax shields is ##r_D##.
- ##\text{IntExp}=D.r_D##
Question 554 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
On his 20th birthday, a man makes a resolution. He will put $30 cash under his bed at the end of every month starting from today. His birthday today is the first day of the month. So the first addition to his cash stash will be in one month. He will write in his will that when he dies the cash under the bed should be given to charity.
If the man lives for another 60 years, how much money will be under his bed if he dies just after making his last (720th) addition?
Also, what will be the real value of that cash in today's prices if inflation is expected to 2.5% pa? Assume that the inflation rate is an effective annual rate and is not expected to change.
The answers are given in the same order, the amount of money under his bed in 60 years, and the real value of that money in today's prices.
An investor owns a whole level of an old office building which is currently worth $1 million. There are three mutually exclusive projects that can be started by the investor. The office building level can be:
- Rented out to a tenant for one year at $0.1m paid immediately, and then sold for $0.99m in one year.
- Refurbished into more modern commercial office rooms at a cost of $1m now, and then sold for $2.4m when the refurbishment is finished in one year.
- Converted into residential apartments at a cost of $2m now, and then sold for $3.4m when the conversion is finished in one year.
All of the development projects have the same risk so the required return of each is 10% pa. The table below shows the estimated cash flows and internal rates of returns (IRR's).
| Mutually Exclusive Projects | |||
| Project | Cash flow now ($) |
Cash flow in one year ($) |
IRR (% pa) |
| Rent then sell as is | -900,000 | 990,000 | 10 |
| Refurbishment into modern offices | -2,000,000 | 2,400,000 | 20 |
| Conversion into residential apartments | -3,000,000 | 3,400,000 | 13.33 |
Which project should the investor accept?
Question 568 rights issue, capital raising, capital structure
A company conducts a 1 for 5 rights issue at a subscription price of $7 when the pre-announcement stock price was $10. What is the percentage change in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order. Ignore all taxes, transaction costs and signalling effects.
Question 624 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system, no explanation
Which of the following statements about Australian franking credits is NOT correct? Franking credits:
You own some nice shoes which you use once per week on date nights. You bought them 2 years ago for $500. In your experience, shoes used once per week last for 6 years. So you expect yours to last for another 4 years.
Your younger sister said that she wants to borrow your shoes once per week. With the increased use, your shoes will only last for another 2 years rather than 4.
What is the present value of the cost of letting your sister use your current shoes for the next 2 years?
Assume: that bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate; you will buy a new pair of shoes when your current pair wears out and your sister will not use the new ones; your sister will only use your current shoes so she will only use it for the next 2 years; and the price of new shoes never changes.
Your poor friend asks to borrow some money from you. He would like $1,000 now (t=0) and every year for the next 5 years, so there will be 6 payments of $1,000 from t=0 to t=5 inclusive. In return he will pay you $10,000 in seven years from now (t=7).
What is the net present value (NPV) of lending to your friend?
Assume that your friend will definitely pay you back so the loan is risk-free, and that the yield on risk-free government debt is 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
An equity index stands at 100 points and the one year equity futures price is 102.
The equity index is expected to have a dividend yield of 4% pa. Assume that investors are risk-neutral so their total required return on the shares is the same as the risk free Treasury bond yield which is 10% pa. Both are given as discrete effective annual rates.
Assuming that the equity index is fairly priced, an arbitrageur would recognise that the equity futures are:
Question 700 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
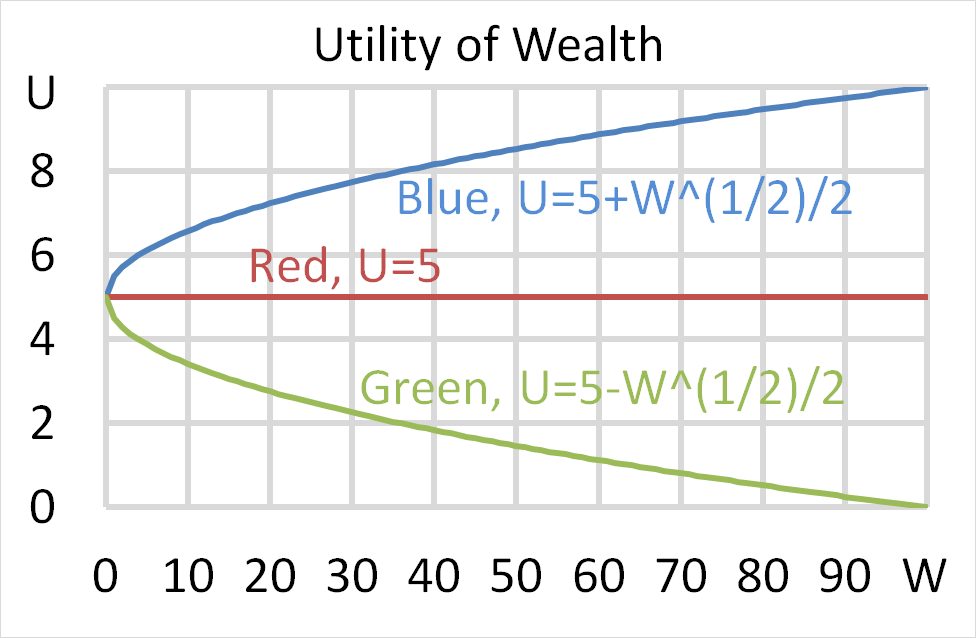
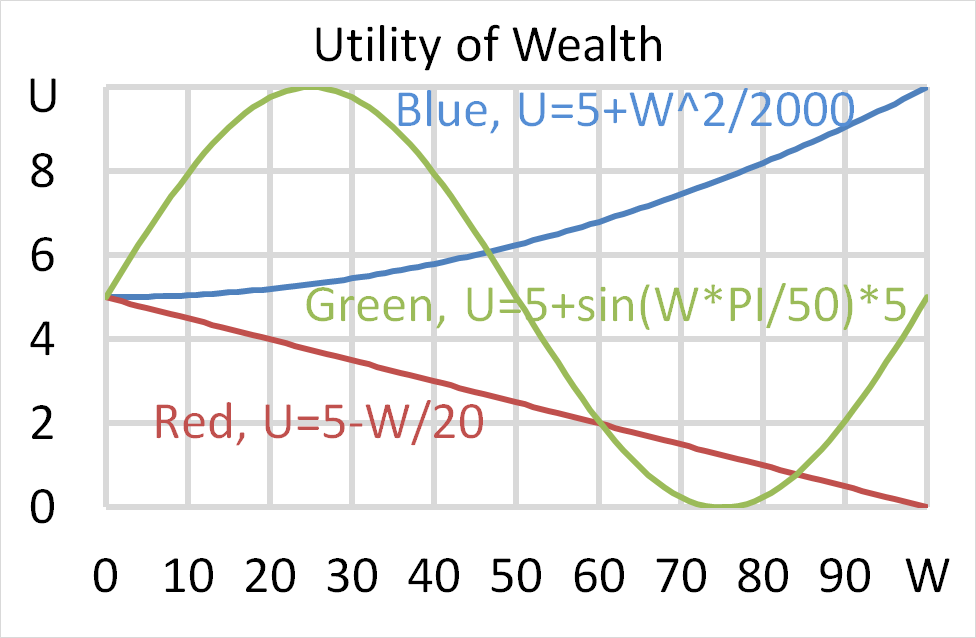
Question 703 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $500 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $500. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $500. If they flip tails then they will lose $500. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
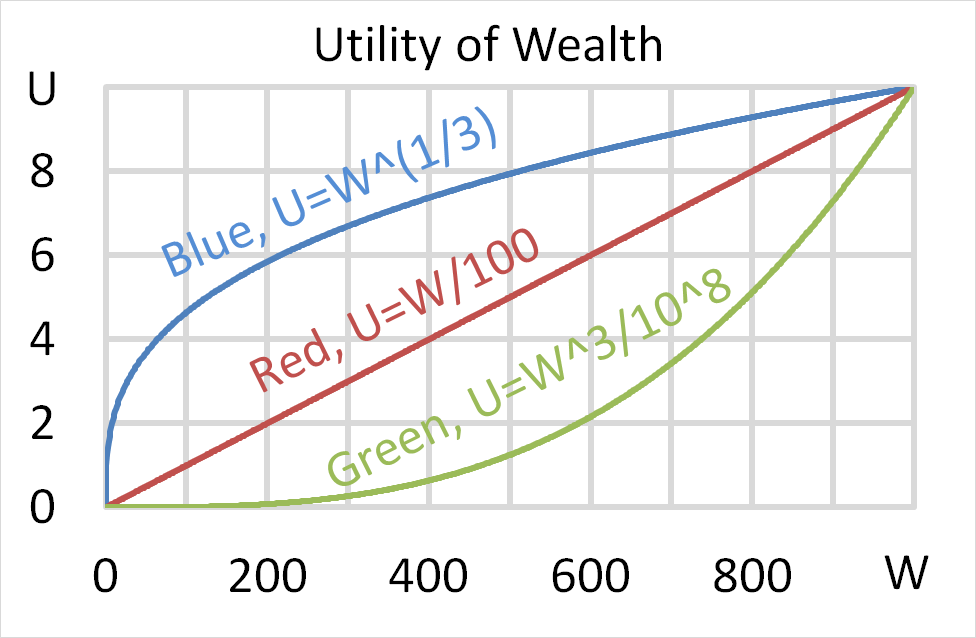
Question 702 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 691 continuously compounding rate, effective rate, continuously compounding rate conversion, no explanation
A bank quotes an interest rate of 6% pa with quarterly compounding. Note that another way of stating this rate is that it is an annual percentage rate (APR) compounding discretely every 3 months.
Which of the following statements about this rate is NOT correct? All percentages are given to 6 decimal places. The equivalent:
Question 728 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, income and capital returns, no explanation
Which of the following statements about gold is NOT correct? Assume that the gold price increases by inflation. Gold has a:
Stocks in the United States usually pay quarterly dividends. For example, the software giant Microsoft paid a $0.23 dividend every quarter over the 2013 financial year and plans to pay a $0.28 dividend every quarter over the 2014 financial year.
Using the dividend discount model and net present value techniques, calculate the stock price of Microsoft assuming that:
- The time now is the beginning of July 2014. The next dividend of $0.28 will be received in 3 months (end of September 2014), with another 3 quarterly payments of $0.28 after this (end of December 2014, March 2015 and June 2015).
- The quarterly dividend will increase by 2.5% every year, but each quarterly dividend over the year will be equal. So each quarterly dividend paid in the financial year beginning in September 2015 will be $ 0.287 ##(=0.28×(1+0.025)^1)##, with the last at the end of June 2016. In the next financial year beginning in September 2016 each quarterly dividend will be $0.294175 ##(=0.28×(1+0.025)^2)##, with the last at the end of June 2017, and so on forever.
- The total required return on equity is 6% pa.
- The required return and growth rate are given as effective annual rates.
- Dividend payment dates and ex-dividend dates are at the same time.
- Remember that there are 4 quarters in a year and 3 months in a quarter.
What is the current stock price?
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume twice as much now (t=0) as in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end.
How much can you consume at time zero and one? The answer choices are given in the same order.
A highly levered risky firm is trying to raise more debt. The types of debt being considered, in no particular order, are senior bonds, junior bonds, bank accepted bills, promissory notes and bank loans.
Which of these forms of debt is the safest from the perspective of the debt investors who are thinking of investing in the firm's new debt?
A company conducts a 2 for 3 rights issue at a subscription price of $8 when the pre-announcement stock price was $9. Assume that all investors use their rights to buy those extra shares.
What is the percentage increase in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order.
You just entered into a fully amortising home loan with a principal of $600,000, a variable interest rate of 4.25% pa and a term of 25 years.
Immediately after settling the loan, the variable interest rate suddenly falls to 4% pa! You can't believe your luck. Despite this, you plan to continue paying the same home loan payments as you did before. How long will it now take to pay off your home loan?
Assume that the lower interest rate was granted immediately and that rates were and are now again expected to remain constant. Round your answer up to the nearest whole month.
You just agreed to a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $2,500. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 10 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change. The below choices are given in the same order.
A company has:
- 140 million shares outstanding.
- The market price of one share is currently $2.
- The company's debentures are publicly traded and their market price is equal to 93% of the face value.
- The debentures have a total face value of $50,000,000 and the current yield to maturity of corporate debentures is 12% per annum.
- The risk-free rate is 8.50% and the market return is 13.7%.
- Market analysts estimated that the company's stock has a beta of 0.90.
- The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What is the company's after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC) in a classical tax system?
In mid 2009 the listed mining company Rio Tinto announced a 21-for-40 renounceable rights issue. Below is the chronology of events:
- 04/06/2009. Share price opens at $69.00 and closes at $66.90.
- 05/06/2009. 21-for-40 rights issue announced at a subscription price of $28.29.
- 16/06/2009. Last day that shares trade cum-rights. Share price opens at $76.40 and closes at $75.50.
- 17/06/2009. Shares trade ex-rights. Rights trading commences.
All things remaining equal, what would you expect Rio Tinto's stock price to open at on the first day that it trades ex-rights (17/6/2009)? Ignore the time value of money since time is negligibly short. Also ignore taxes.
One year ago you bought a $1,000,000 house partly funded using a mortgage loan. The loan size was $800,000 and the other $200,000 was your wealth or 'equity' in the house asset.
The interest rate on the home loan was 4% pa.
Over the year, the house produced a net rental yield of 2% pa and a capital gain of 2.5% pa.
Assuming that all cash flows (interest payments and net rental payments) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates are given as effective annual rates, what was the total return on your wealth over the past year?
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
A project has the following cash flows. Normally cash flows are assumed to happen at the given time. But here, assume that the cash flows are received smoothly over the year. So the $105 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -90 |
| 1 | 30 |
| 2 | 105 |
What is the payback period of the project in years?
In Australia, domestic university students are allowed to buy concession tickets for the bus, train and ferry which sell at a discount of 50% to full-price tickets.
The Australian Government do not allow international university students to buy concession tickets, they have to pay the full price.
Some international students see this as unfair and they are willing to pay for fake university identification cards which have the concession sticker.
What is the most that an international student would be willing to pay for a fake identification card?
Assume that international students:
- consider buying their fake card on the morning of the first day of university from their neighbour, just before they leave to take the train into university.
- buy their weekly train tickets on the morning of the first day of each week.
- ride the train to university and back home again every day seven days per week until summer holidays 40 weeks from now. The concession card only lasts for those 40 weeks. Assume that there are 52 weeks in the year for the purpose of interest rate conversion.
- a single full-priced one-way train ride costs $5.
- have a discount rate of 11% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Approach this question from a purely financial view point, ignoring the illegality, embarrassment and the morality of committing fraud.
Question 791 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate, log-normal distribution, VaR, confidence interval
A risk manager has identified that their pension fund’s continuously compounded portfolio returns are normally distributed with a mean of 5% pa and a standard deviation of 20% pa. The fund’s portfolio is currently valued at $1 million. Assume that there is no estimation error in the above figures. To simplify your calculations, all answers below use 2.33 as an approximation for the normal inverse cumulative density function at 99%. All answers are rounded to the nearest dollar. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A pig farmer in the US is worried about the price of hogs falling and wants to lock in a price now. In one year the pig farmer intends to sell 1,000,000 pounds of hogs. Luckily, one year CME lean hog futures expire on the exact day that he wishes to sell his pigs. The futures have a notional principal of 40,000 pounds (about 18 metric tons) and currently trade at a price of 63.85 cents per pound. The underlying lean hogs spot price is 77.15 cents per pound. The correlation between the futures price and the underlying hogs price is one and the standard deviations are both 4 cents per pound. The initial margin is USD1,500 and the maintenance margin is USD1,200 per futures contract.
Which of the below statements is NOT correct?