The saying "buy low, sell high" suggests that investors should make a:
An asset's total expected return over the next year is given by:
###r_\text{total} = \dfrac{c_1+p_1-p_0}{p_0} ###
Where ##p_0## is the current price, ##c_1## is the expected income in one year and ##p_1## is the expected price in one year. The total return can be split into the income return and the capital return.
Which of the following is the expected capital return?
One and a half years ago Frank bought a house for $600,000. Now it's worth only $500,000, based on recent similar sales in the area.
The expected total return on Frank's residential property is 7% pa.
He rents his house out for $1,600 per month, paid in advance. Every 12 months he plans to increase the rental payments.
The present value of 12 months of rental payments is $18,617.27.
The future value of 12 months of rental payments one year in the future is $19,920.48.
What is the expected annual rental yield of the property? Ignore the costs of renting such as maintenance, real estate agent fees and so on.
Question 407 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
A stock has a real expected total return of 7% pa and a real expected capital return of 2% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What is the nominal expected total return, capital return and dividend yield? The answers below are given in the same order.
You're considering making an investment in a particular company. They have preference shares, ordinary shares, senior debt and junior debt.
Which is the safest investment? Which has the highest expected returns?
Question 531 bankruptcy or insolvency, capital structure, risk, limited liability
Who is most in danger of being personally bankrupt? Assume that all of their businesses' assets are highly liquid and can therefore be sold immediately.
A project has the following cash flows:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 500 |
What is the payback period of the project in years?
Normally cash flows are assumed to happen at the given time. But here, assume that the cash flows are received smoothly over the year. So the $500 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2.
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume an equal amount now (t=0) and in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end (t=1).
How much can you consume at each time?
Your neighbour asks you for a loan of $100 and offers to pay you back $120 in one year.
You don't actually have any money right now, but you can borrow and lend from the bank at a rate of 10% pa. Rates are given as effective annual rates.
Assume that your neighbour will definitely pay you back. Ignore interest tax shields and transaction costs.
The Net Present Value (NPV) of lending to your neighbour is $9.09. Describe what you would do to actually receive a $9.09 cash flow right now with zero net cash flows in the future.
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume an equal amount now (t=0), in one year (t=1) and in two years (t=2), and still have $50,000 in the bank after that (t=2).
How much can you consume at each time?
Jan asks you for a loan. He wants $100 now and offers to pay you back $120 in 1 year. You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Ignore credit risk. Remember:
### V_0 = \frac{V_t}{(1+r_\text{eff})^t} ###
Katya offers to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years (t=1,2,3,4,5) if you pay her $50 now (t=0). You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. Ignore credit risk.
The following equation is called the Dividend Discount Model (DDM), Gordon Growth Model or the perpetuity with growth formula: ### P_0 = \frac{ C_1 }{ r - g } ###
What is ##g##? The value ##g## is the long term expected:
This annuity formula ##\dfrac{C_1}{r}\left(1-\dfrac{1}{(1+r)^3} \right)## is equivalent to which of the following formulas? Note the 3.
In the below formulas, ##C_t## is a cash flow at time t. All of the cash flows are equal, but paid at different times.
Your friend overheard that you need some cash and asks if you would like to borrow some money. She can lend you $5,000 now (t=0), and in return she wants you to pay her back $1,000 in two years (t=2) and every year after that for the next 5 years, so there will be 6 payments of $1,000 from t=2 to t=7 inclusive.
What is the net present value (NPV) of borrowing from your friend?
Assume that banks loan funds at interest rates of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
A stock is just about to pay a dividend of $1 tonight. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. The next dividend of $1 will be paid tonight, and the year after that the dividend will be $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1), and a year later 1.0404 (=1*(1+0.04)^2) and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
###P_0=\frac{d_1}{r-g}###
A stock pays dividends annually. It just paid a dividend, but the next dividend (##d_1##) will be paid in one year.
According to the DDM, what is the correct formula for the expected price of the stock in 2.5 years?
The following is the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) used to price stocks:
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
If the assumptions of the DDM hold and the stock is fairly priced, which one of the following statements is NOT correct? The long term expected:
Question 50 DDM, stock pricing, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Most listed Australian companies pay dividends twice per year, the 'interim' and 'final' dividends, which are roughly 6 months apart.
You are an equities analyst trying to value the company BHP. You decide to use the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) as a starting point, so you study BHP's dividend history and you find that BHP tends to pay the same interim and final dividend each year, and that both grow by the same rate.
You expect BHP will pay a $0.55 interim dividend in six months and a $0.55 final dividend in one year. You expect each to grow by 4% next year and forever, so the interim and final dividends next year will be $0.572 each, and so on in perpetuity.
Assume BHP's cost of equity is 8% pa. All rates are quoted as nominal effective rates. The dividends are nominal cash flows and the inflation rate is 2.5% pa.
What is the current price of a BHP share?
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 1.15 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at 5% pa, so;
- the dividend at t=5 will be $1.15(1+0.05),
- the dividend at t=6 will be $1.15(1+0.05)^2, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates. What is the current price of the stock?
Question 31 DDM, perpetuity with growth, effective rate conversion
What is the NPV of the following series of cash flows when the discount rate is 5% given as an effective annual rate?
The first payment of $10 is in 4 years, followed by payments every 6 months forever after that which shrink by 2% every 6 months. That is, the growth rate every 6 months is actually negative 2%, given as an effective 6 month rate. So the payment at ## t=4.5 ## years will be ## 10(1-0.02)^1=9.80 ##, and so on.
The following is the Dividend Discount Model used to price stocks:
### p_0=\frac{d_1}{r-g} ###
Which of the following statements about the Dividend Discount Model is NOT correct?
Your friend wants to borrow $1,000 and offers to pay you back $100 in 6 months, with more $100 payments at the end of every month for another 11 months. So there will be twelve $100 payments in total. She says that 12 payments of $100 equals $1,200 so she's being generous.
If interest rates are 12% pa, given as an APR compounding monthly, what is the Net Present Value (NPV) of your friend's deal?
Estimate the US bank JP Morgan's share price using a price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only:
- The major US banks JP Morgan Chase (JPM), Citi Group (C) and Wells Fargo (WFC) are comparable companies;
- JP Morgan Chase's historical earnings per share (EPS) is $4.37;
- Citi Group's share price is $50.05 and historical EPS is $4.26;
- Wells Fargo's share price is $48.98 and historical EPS is $3.89.
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 24 March 2014.
Which firms tend to have low forward-looking price-earnings (PE) ratios?
Only consider firms with positive earnings, disregard firms with negative earnings and therefore negative PE ratios.
Which of the following investable assets are NOT suitable for valuation using PE multiples techniques?
You just borrowed $400,000 in the form of a 25 year interest-only mortgage with monthly payments of $3,000 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
You actually plan to pay more than the required interest payment. You plan to pay $3,300 in mortgage payments every month, which your mortgage lender allows. These extra payments will reduce the principal and the minimum interest payment required each month.
At the maturity of the mortgage, what will be the principal? That is, after the last (300th) interest payment of $3,300 in 25 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage?
Question 239 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, interest only loan
A bank grants a borrower an interest-only residential mortgage loan with a very large 50% deposit and a nominal interest rate of 6% that is not expected to change. Assume that inflation is expected to be a constant 2% pa over the life of the loan. Ignore credit risk.
From the bank's point of view, what is the long term expected nominal capital return of the loan asset?
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid semi-annually. So there are two coupons per year, paid in arrears every six months.
You're trying to save enough money to buy your first car which costs $2,500. You can save $100 at the end of each month starting from now. You currently have no money at all. You just opened a bank account with an interest rate of 6% pa payable monthly.
How many months will it take to save enough money to buy the car? Assume that the price of the car will stay the same over time.
Your main expense is fuel for your car which costs $100 per month. You just refueled, so you won't need any more fuel for another month (first payment at t=1 month).
You have $2,500 in a bank account which pays interest at a rate of 6% pa, payable monthly. Interest rates are not expected to change.
Assuming that you have no income, in how many months time will you not have enough money to fully refuel your car?
Question 35 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
A European company just issued two bonds, a
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the company's forward rate over the second year (from t=1 to t=2)? Give your answer as an effective annual rate, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 143 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds:
- A 6-month zero coupon bond at a yield of 6% pa, and
- A 12 month zero coupon bond at a yield of 7% pa.
What is the company's forward rate from 6 to 12 months? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 48 IRR, NPV, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds, market efficiency
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 56 income and capital returns, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds
Which of the following statements about risk free government bonds is NOT correct?
Hint: Total return can be broken into income and capital returns as follows:
###\begin{aligned} r_\text{total} &= \frac{c_1}{p_0} + \frac{p_1-p_0}{p_0} \\ &= r_\text{income} + r_\text{capital} \end{aligned} ###
The capital return is the growth rate of the price.
The income return is the periodic cash flow. For a bond this is the coupon payment.
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
In these tough economic times, central banks around the world have cut interest rates so low that they are practically zero. In some countries, government bond yields are also very close to zero.
A three year government bond with a face value of $100 and a coupon rate of 2% pa paid semi-annually was just issued at a yield of 0%. What is the price of the bond?
Find Sidebar Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Sidebar Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 405 | |
| COGS | 100 | |
| Depreciation | 34 | |
| Rent expense | 22 | |
| Interest expense | 39 | |
| Taxable Income | 210 | |
| Taxes at 30% | 63 | |
| Net income | 147 | |
| Sidebar Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Cash | 0 | 0 |
| Inventory | 70 | 50 |
| Trade debtors | 11 | 16 |
| Rent paid in advance | 4 | 3 |
| PPE | 700 | 680 |
| Total assets | 785 | 749 |
| Trade creditors | 11 | 19 |
| Bond liabilities | 400 | 390 |
| Contributed equity | 220 | 220 |
| Retained profits | 154 | 120 |
| Total L and OE | 785 | 749 |
Note: All figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
The cash flow from assets was:
Why is Capital Expenditure (CapEx) subtracted in the Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) formula?
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###
Diversification is achieved by investing in a large amount of stocks. What type of risk is reduced by diversification?
What is the correlation of a variable X with itself?
The corr(X, X) or ##\rho_{X,X}## equals:
Let the standard deviation of returns for a share per month be ##\sigma_\text{monthly}##.
What is the formula for the standard deviation of the share's returns per year ##(\sigma_\text{yearly})##?
Assume that returns are independently and identically distributed (iid) so they have zero auto correlation, meaning that if the return was higher than average today, it does not indicate that the return tomorrow will be higher or lower than average.
The covariance and correlation of two stocks X and Y's annual returns are calculated over a number of years. The units of the returns are in percent per annum ##(\% pa)##.
What are the units of the covariance ##(\sigma_{X,Y})## and correlation ##(\rho_{X,Y})## of returns respectively?
Hint: Visit Wikipedia to understand the difference between percentage points ##(\text{pp})## and percent ##(\%)##.
Question 556 portfolio risk, portfolio return, standard deviation
An investor wants to make a portfolio of two stocks A and B with a target expected portfolio return of 12% pa.
- Stock A has an expected return of 10% pa and a standard deviation of 20% pa.
- Stock B has an expected return of 15% pa and a standard deviation of 30% pa.
The correlation coefficient between stock A and B's expected returns is 70%.
What will be the annual standard deviation of the portfolio with this 12% pa target return?
Two years ago Fred bought a house for $300,000.
Now it's worth $500,000, based on recent similar sales in the area.
Fred's residential property has an expected total return of 8% pa.
He rents his house out for $2,000 per month, paid in advance. Every 12 months he plans to increase the rental payments.
The present value of 12 months of rental payments is $23,173.86.
The future value of 12 months of rental payments one year ahead is $25,027.77.
What is the expected annual growth rate of the rental payments? In other words, by what percentage increase will Fred have to raise the monthly rent by each year to sustain the expected annual total return of 8%?
One year ago you bought $100,000 of shares partly funded using a margin loan. The margin loan size was $70,000 and the other $30,000 was your own wealth or 'equity' in the share assets.
The interest rate on the margin loan was 7.84% pa.
Over the year, the shares produced a dividend yield of 4% pa and a capital gain of 5% pa.
What was the total return on your wealth? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and dividends) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates above are effective annual rates.
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
Interest expense (IntExp) is an important part of a company's income statement (or 'profit and loss' or 'statement of financial performance').
How does an accountant calculate the annual interest expense of a fixed-coupon bond that has a liquid secondary market? Select the most correct answer:
Annual interest expense is equal to:
A manufacturing company is considering a new project in the more risky services industry. The cash flows from assets (CFFA) are estimated for the new project, with interest expense excluded from the calculations. To get the levered value of the project, what should these unlevered cash flows be discounted by?
Assume that the manufacturing firm has a target debt-to-assets ratio that it sticks to.
The US firm Google operates in the online advertising business. In 2011 Google bought Motorola Mobility which manufactures mobile phones.
Assume the following:
- Google had a 10% after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC) before it bought Motorola.
- Motorola had a 20% after-tax WACC before it merged with Google.
- Google and Motorola have the same level of gearing.
- Both companies operate in a classical tax system.
You are a manager at Motorola. You must value a project for making mobile phones. Which method(s) will give the correct valuation of the mobile phone manufacturing project? Select the most correct answer.
The mobile phone manufacturing project's:
There are many ways to calculate a firm's free cash flow (FFCF), also called cash flow from assets (CFFA). Some include the annual interest tax shield in the cash flow and some do not.
Which of the below FFCF formulas include the interest tax shield in the cash flow?
###(1) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp### ###(2) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp.(1-t_c)### ###(3) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c )+ Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(4) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c) + Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(5) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(6) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(7) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(8) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c### ###(9) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(10) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c###The formulas for net income (NI also called earnings), EBIT and EBITDA are given below. Assume that depreciation and amortisation are both represented by 'Depr' and that 'FC' represents fixed costs such as rent.
###NI=(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###EBIT=Rev - COGS - FC-Depr### ###EBITDA=Rev - COGS - FC### ###Tax =(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).t_c= \dfrac{NI.t_c}{1-t_c}###A company issues a large amount of bonds to raise money for new projects of similar risk to the company's existing projects. The net present value (NPV) of the new projects is positive but small. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is NOT correct?
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 50%. The firm then issues a large amount of equity to raise money for new projects of similar systematic risk to the company's existing projects. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is correct?
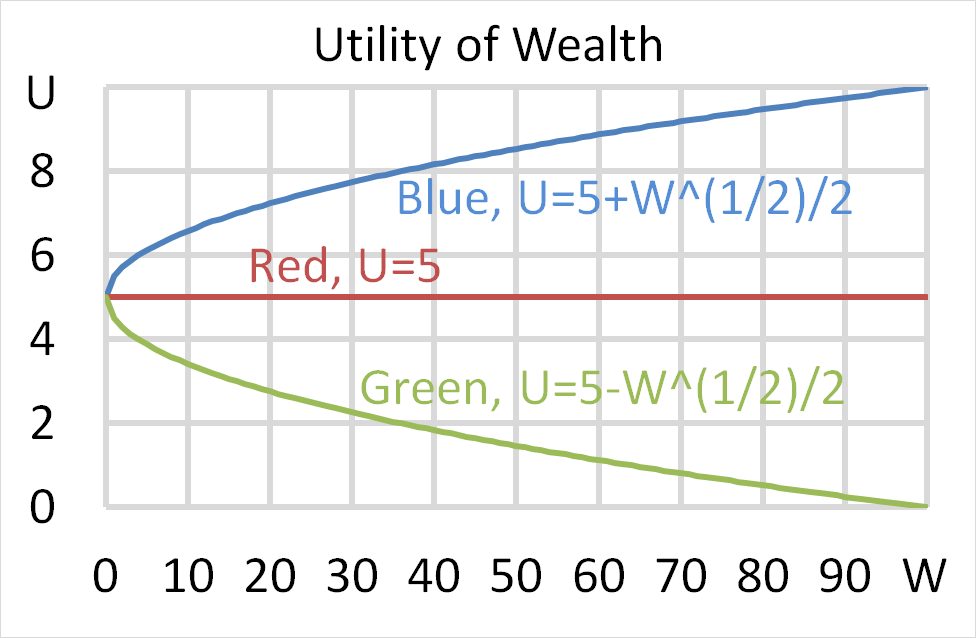
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
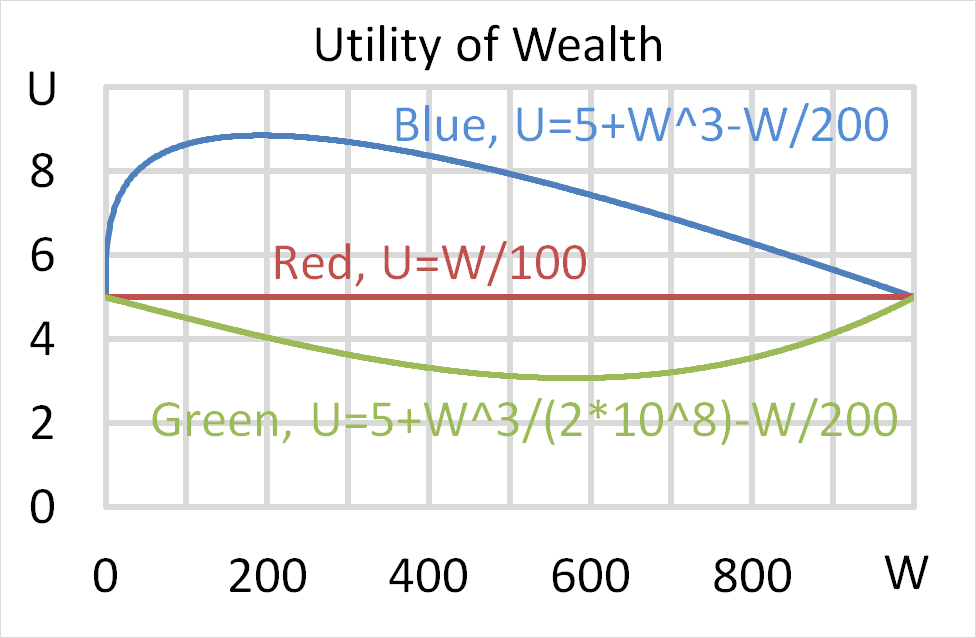
Question 704 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $256 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $256. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $256. If they flip tails then they will lose $256. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
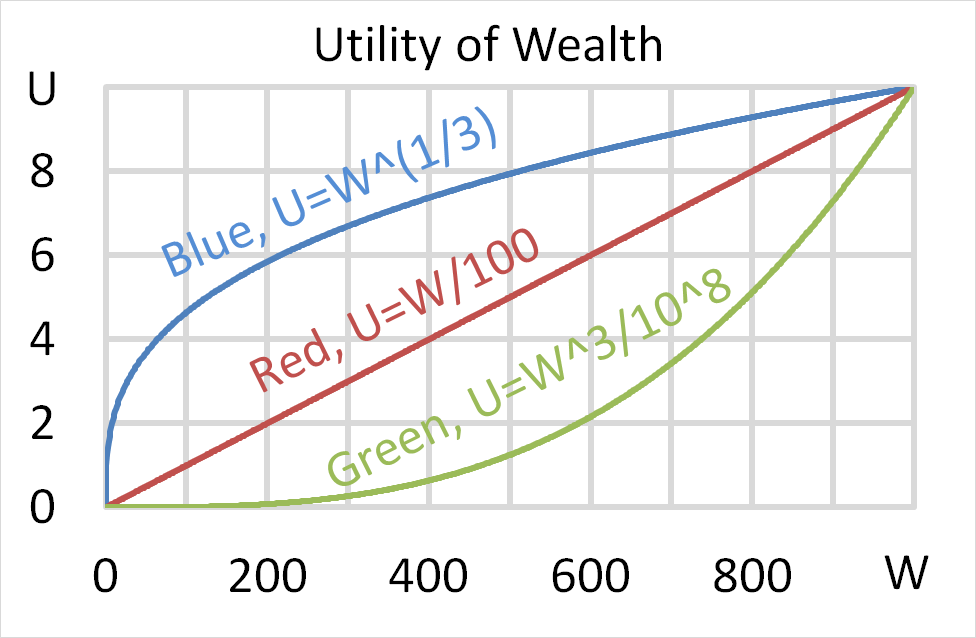
According to the theory of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), total risk can be broken into two components, systematic risk and idiosyncratic risk. Which of the following events would be considered a systematic, undiversifiable event according to the theory of the CAPM?
Stock A has a beta of 0.5 and stock B has a beta of 1. Which statement is NOT correct?
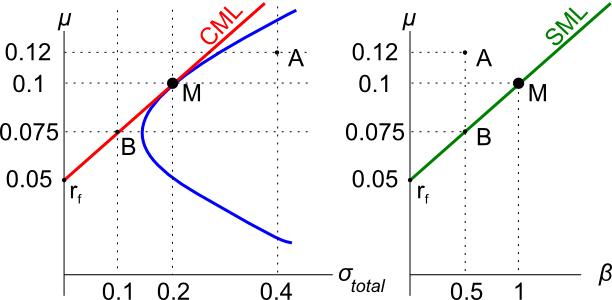
Assets A, B, M and ##r_f## are shown on the graphs above. Asset M is the market portfolio and ##r_f## is the risk free yield on government bonds. Assume that investors can borrow and lend at the risk free rate. Which of the below statements is NOT correct?
A stock has a beta of 1.5. The market's expected total return is 10% pa and the risk free rate is 5% pa, both given as effective annual rates.
In the last 5 minutes, bad economic news was released showing a higher chance of recession. Over this time the share market fell by 1%. The risk free rate was unchanged.
What do you think was the stock's historical return over the last 5 minutes, given as an effective 5 minute rate?
Which of the following statements about the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is NOT correct?
According to the theory of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), total variance can be broken into two components, systematic variance and idiosyncratic variance. Which of the following events would be considered the most diversifiable according to the theory of the CAPM?
Which statement(s) are correct?
(i) All stocks that plot on the Security Market Line (SML) are fairly priced.
(ii) All stocks that plot above the Security Market Line (SML) are overpriced.
(iii) All fairly priced stocks that plot on the Capital Market Line (CML) have zero idiosyncratic risk.
Select the most correct response:
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of debt and using the funds to repurchase shares. Its assets are unchanged. Ignore interest tax shields.
According to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which statement is correct?
Question 104 CAPM, payout policy, capital structure, Miller and Modigliani, risk
Assume that there exists a perfect world with no transaction costs, no asymmetric information, no taxes, no agency costs, equal borrowing rates for corporations and individual investors, the ability to short the risk free asset, semi-strong form efficient markets, the CAPM holds, investors are rational and risk-averse and there are no other market frictions.
For a firm operating in this perfect world, which statement(s) are correct?
(i) When a firm changes its capital structure and/or payout policy, share holders' wealth is unaffected.
(ii) When the idiosyncratic risk of a firm's assets increases, share holders do not expect higher returns.
(iii) When the systematic risk of a firm's assets increases, share holders do not expect higher returns.
Select the most correct response:
The total return of any asset can be broken down in different ways. One possible way is to use the dividend discount model (or Gordon growth model):
###p_0 = \frac{c_1}{r_\text{total}-r_\text{capital}}###
Which, since ##c_1/p_0## is the income return (##r_\text{income}##), can be expressed as:
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{income}+r_\text{capital}###
So the total return of an asset is the income component plus the capital or price growth component.
Another way to break up total return is to use the Capital Asset Pricing Model:
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{f}+β(r_\text{m}- r_\text{f})###
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{time value}+r_\text{risk premium}###
So the risk free rate is the time value of money and the term ##β(r_\text{m}- r_\text{f})## is the compensation for taking on systematic risk.
Using the above theory and your general knowledge, which of the below equations, if any, are correct?
(I) ##r_\text{income}=r_\text{time value}##
(II) ##r_\text{income}=r_\text{risk premium}##
(III) ##r_\text{capital}=r_\text{time value}##
(IV) ##r_\text{capital}=r_\text{risk premium}##
(V) ##r_\text{income}+r_\text{capital}=r_\text{time value}+r_\text{risk premium}##
Which of the equations are correct?
Question 271 CAPM, option, risk, systematic risk, systematic and idiosyncratic risk
All things remaining equal, according to the capital asset pricing model, if the systematic variance of an asset increases, its required return will increase and its price will decrease.
If the idiosyncratic variance of an asset increases, its price will be unchanged.
What is the relationship between the price of a call or put option and the total, systematic and idiosyncratic variance of the underlying asset that the option is based on? Select the most correct answer.
Call and put option prices increase when the:
The accounting identity states that the book value of a company's assets (A) equals its liabilities (L) plus owners equity (OE), so A = L + OE.
The finance version states that the market value of a company's assets (V) equals the market value of its debt (D) plus equity (E), so V = D + E.
Therefore a business's assets can be seen as a portfolio of the debt and equity that fund the assets.
Let ##\sigma_\text{V total}^2## be the total variance of returns on assets, ##\sigma_\text{V syst}^2## be the systematic variance of returns on assets, and ##\sigma_\text{V idio}^2## be the idiosyncratic variance of returns on assets, and ##\rho_\text{D idio, E idio}## be the correlation between the idiosyncratic returns on debt and equity.
Which of the following equations is NOT correct?
Question 338 market efficiency, CAPM, opportunity cost, technical analysis
A man inherits $500,000 worth of shares.
He believes that by learning the secrets of trading, keeping up with the financial news and doing complex trend analysis with charts that he can quit his job and become a self-employed day trader in the equities markets.
What is the expected gain from doing this over the first year? Measure the net gain in wealth received at the end of this first year due to the decision to become a day trader. Assume the following:
- He earns $60,000 pa in his current job, paid in a lump sum at the end of each year.
- He enjoys examining share price graphs and day trading just as much as he enjoys his current job.
- Stock markets are weak form and semi-strong form efficient.
- He has no inside information.
- He makes 1 trade every day and there are 250 trading days in the year. Trading costs are $20 per trade. His broker invoices him for the trading costs at the end of the year.
- The shares that he currently owns and the shares that he intends to trade have the same level of systematic risk as the market portfolio.
- The market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa.
Measure the net gain over the first year as an expected wealth increase at the end of the year.
Find Candys Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Candys Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 200 | |
| COGS | 50 | |
| Operating expense | 10 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Interest expense | 10 | |
| Income before tax | 110 | |
| Tax at 30% | 33 | |
| Net income | 77 | |
| Candys Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets | 220 | 180 |
| PPE | ||
| Cost | 300 | 340 |
| Accumul. depr. | 60 | 40 |
| Carrying amount | 240 | 300 |
| Total assets | 460 | 480 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | 175 | 190 |
| Non-current liabilities | 135 | 130 |
| Owners' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | 50 | 60 |
| Contributed equity | 100 | 100 |
| Total L and OE | 460 | 480 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
There are a number of ways that assets can be depreciated. Generally the government's tax office stipulates a certain method.
But if it didn't, what would be the ideal way to depreciate an asset from the perspective of a businesses owner?
A firm has forecast its Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) for this year and management is worried that it is too low. Which one of the following actions will lead to a higher CFFA for this year (t=0 to 1)? Only consider cash flows this year. Do not consider cash flows after one year, or the change in the NPV of the firm. Consider each action in isolation.
Find Scubar Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Scubar Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 200 | |
| COGS | 60 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Rent expense | 11 | |
| Interest expense | 19 | |
| Taxable Income | 90 | |
| Taxes at 30% | 27 | |
| Net income | 63 | |
| Scubar Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Inventory | 60 | 50 |
| Trade debtors | 19 | 6 |
| Rent paid in advance | 3 | 2 |
| PPE | 420 | 400 |
| Total assets | 502 | 458 |
| Trade creditors | 10 | 8 |
| Bond liabilities | 200 | 190 |
| Contributed equity | 130 | 130 |
| Retained profits | 162 | 130 |
| Total L and OE | 502 | 458 |
Note: All figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
The cash flow from assets was:
A new company's Firm Free Cash Flow (FFCF, same as CFFA) is forecast in the graph below.
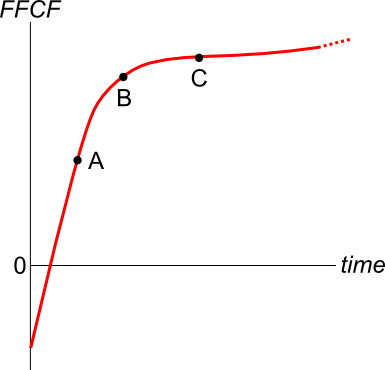
To value the firm's assets, the terminal value needs to be calculated using the perpetuity with growth formula:
###V_{\text{terminal, }t-1} = \dfrac{FFCF_{\text{terminal, }t}}{r-g}###
Which point corresponds to the best time to calculate the terminal value?
A new company's Firm Free Cash Flow (FFCF, same as CFFA) is forecast in the graph below.
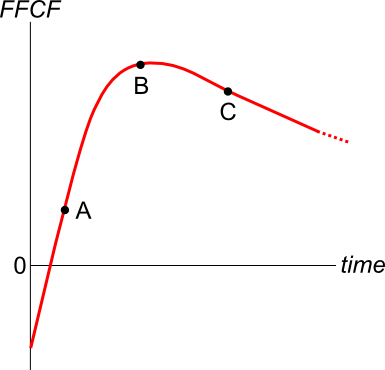
To value the firm's assets, the terminal value needs to be calculated using the perpetuity with growth formula:
###V_{\text{terminal, }t-1} = \dfrac{FFCF_{\text{terminal, }t}}{r-g}###
Which point corresponds to the best time to calculate the terminal value?
Which one of the following will have no effect on net income (NI) but decrease cash flow from assets (CFFA or FFCF) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - ΔNWC+IntExp###Your friend is trying to find the net present value of an investment which:
- Costs $1 million initially (t=0); and
- Pays a single positive cash flow of $1.1 million in one year (t=1).
The investment has a total required return of 10% pa due to its moderate level of undiversifiable risk.
Your friend is aware of the importance of opportunity costs and the time value of money, but he is unsure of how to find the NPV of the project.
He knows that the opportunity cost of investing the $1m in the project is the expected gain from investing the money in shares instead. Like the project, shares also have an expected return of 10% since they have moderate undiversifiable risk. This opportunity cost is $0.1m ##(=1m \times 10\%)## which occurs in one year (t=1).
He knows that the time value of money should be accounted for, and this can be done by finding the present value of the cash flows in one year.
Your friend has listed a few different ways to find the NPV which are written down below.
Method 1: ##-1m + \dfrac{1.1m}{(1+0.1)^1} ##
Method 2: ##-1m + 1.1m - 1m \times 0.1 ##
Method 3: ##-1m + \dfrac{1.1m}{(1+0.1)^1} - 1m \times 0.1 ##
Which of the above calculations give the correct NPV? Select the most correct answer.
A method commonly seen in textbooks for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is the following:
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp)(1-t_c) + \\ &\space\space\space+ Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp(1-t_c) \\ \end{aligned}###
Read the following financial statements and calculate the firm's free cash flow over the 2014 financial year.
| UBar Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2014 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 293 | |
| COGS | 200 | |
| Rent expense | 15 | |
| Gas expense | 8 | |
| Depreciation | 10 | |
| EBIT | 60 | |
| Interest expense | 0 | |
| Taxable income | 60 | |
| Taxes | 18 | |
| Net income | 42 | |
| UBar Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2014 | 2013 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | 30 | 29 |
| Accounts receivable | 5 | 7 |
| Pre-paid rent expense | 1 | 0 |
| Inventory | 50 | 46 |
| PPE | 290 | 300 |
| Total assets | 376 | 382 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Trade payables | 20 | 18 |
| Accrued gas expense | 3 | 2 |
| Non-current liabilities | 0 | 0 |
| Contributed equity | 212 | 212 |
| Retained profits | 136 | 150 |
| Asset revaluation reserve | 5 | 0 |
| Total L and OE | 376 | 382 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
The firm's free cash flow over the 2014 financial year was:
Question 69 interest tax shield, capital structure, leverage, WACC
Which statement about risk, required return and capital structure is the most correct?
A company has:
- 10 million common shares outstanding, each trading at a price of $90.
- 1 million preferred shares which have a face (or par) value of $100 and pay a constant dividend of 9% of par. They currently trade at a price of $120 each.
- Debentures that have a total face value of $60,000,000 and a yield to maturity of 6% per annum. They are publicly traded and their market price is equal to 90% of their face value.
- The risk-free rate is 5% and the market return is 10%.
- Market analysts estimate that the company's common stock has a beta of 1.2. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What is the company's after-tax Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)? Assume a classical tax system.
A firm can issue 5 year annual coupon bonds at a yield of 8% pa and a coupon rate of 12% pa.
The beta of its levered equity is 1. Five year government bonds yield 5% pa with a coupon rate of 6% pa. The market's expected dividend return is 4% pa and its expected capital return is 6% pa.
The firm's debt-to-equity ratio is 2:1. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What is the firm's after-tax WACC? Assume a classical tax system.
Question 237 WACC, Miller and Modigliani, interest tax shield
Which of the following discount rates should be the highest for a levered company? Ignore the costs of financial distress.
A company advertises an investment costing $1,000 which they say is underpriced. They say that it has an expected total return of 15% pa, but a required return of only 10% pa. Assume that there are no dividend payments so the entire 15% total return is all capital return.
Assuming that the company's statements are correct, what is the NPV of buying the investment if the 15% return lasts for the next 100 years (t=0 to 100), then reverts to 10% pa after that time? Also, what is the NPV of the investment if the 15% return lasts forever?
In both cases, assume that the required return of 10% remains constant. All returns are given as effective annual rates.
The answer choices below are given in the same order (15% for 100 years, and 15% forever):
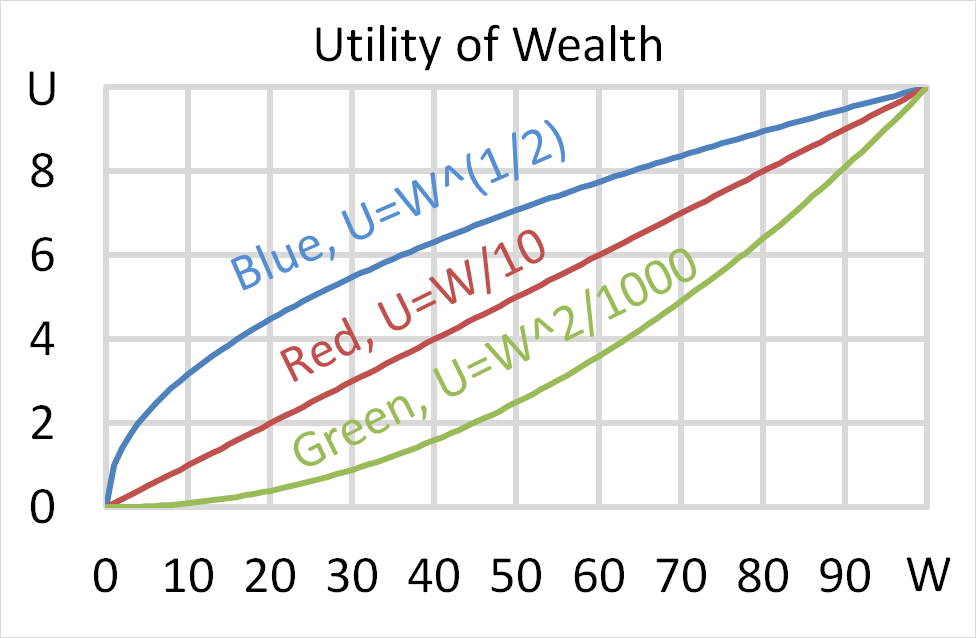
Which of the below statements about utility is NOT generally accepted by economists? Most people are thought to:
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions. Which of the statements about the 3 utility functions is NOT correct?
Question 699 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
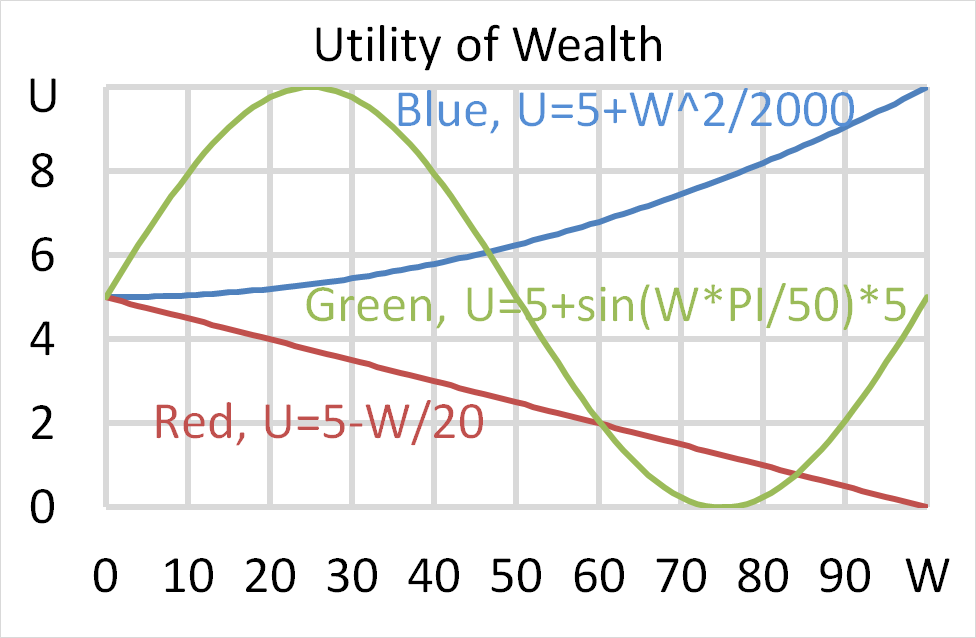
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 702 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 49 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, APR, effective rate
In Australia, nominal yields on semi-annual coupon paying Government Bonds with 2 years until maturity are currently 2.83% pa.
The inflation rate is currently 2.2% pa, given as an APR compounding per quarter. The inflation rate is not expected to change over the next 2 years.
What is the real yield on these bonds, given as an APR compounding every 6 months?
Question 180 equivalent annual cash flow, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Details of two different types of light bulbs are given below:
- Low-energy light bulbs cost $3.50, have a life of nine years, and use about $1.60 of electricity a year, paid at the end of each year.
- Conventional light bulbs cost only $0.50, but last only about a year and use about $6.60 of energy a year, paid at the end of each year.
The real discount rate is 5%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that all cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% given as an effective annual rate.
Find the Equivalent Annual Cost (EAC) of the low-energy and conventional light bulbs. The below choices are listed in that order.
Question 339 bond pricing, inflation, market efficiency, income and capital returns
Economic statistics released this morning were a surprise: they show a strong chance of consumer price inflation (CPI) reaching 5% pa over the next 2 years.
This is much higher than the previous forecast of 3% pa.
A vanilla fixed-coupon 2-year risk-free government bond was issued at par this morning, just before the economic news was released.
What is the expected change in bond price after the economic news this morning, and in the next 2 years? Assume that:
- Inflation remains at 5% over the next 2 years.
- Investors demand a constant real bond yield.
- The bond price falls by the (after-tax) value of the coupon the night before the ex-coupon date, as in real life.
In the 'Austin Powers' series of movies, the character Dr. Evil threatens to destroy the world unless the United Nations pays him a ransom (video 1, video 2). Dr. Evil makes the threat on two separate occasions:
- In 1969 he demands a ransom of $1 million (=10^6), and again;
- In 1997 he demands a ransom of $100 billion (=10^11).
If Dr. Evil's demands are equivalent in real terms, in other words $1 million will buy the same basket of goods in 1969 as $100 billion would in 1997, what was the implied inflation rate over the 28 years from 1969 to 1997?
The answer choices below are given as effective annual rates:
In Australia in the 1980's, inflation was around 8% pa, and residential mortgage loan interest rates were around 14%.
In 2013, inflation was around 2.5% pa, and residential mortgage loan interest rates were around 4.5%.
If a person can afford constant mortgage loan payments of $2,000 per month, how much more can they borrow when interest rates are 4.5% pa compared with 14.0% pa?
Give your answer as a proportional increase over the amount you could borrow when interest rates were high ##(V_\text{high rates})##, so:
###\text{Proportional increase} = \dfrac{V_\text{low rates}-V_\text{high rates}}{V_\text{high rates}} ###
Assume that:
- Interest rates are expected to be constant over the life of the loan.
- Loans are interest-only and have a life of 30 years.
- Mortgage loan payments are made every month in arrears and all interest rates are given as annualised percentage rates (APR's) compounding per month.
Question 574 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, NPV
What is the present value of a nominal payment of $100 in 5 years? The real discount rate is 10% pa and the inflation rate is 3% pa.
Question 578 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Which of the following statements about inflation is NOT correct?
Question 100 market efficiency, technical analysis, joint hypothesis problem
A company selling charting and technical analysis software claims that independent academic studies have shown that its software makes significantly positive abnormal returns. Assuming the claim is true, which statement(s) are correct?
(I) Weak form market efficiency is broken.
(II) Semi-strong form market efficiency is broken.
(III) Strong form market efficiency is broken.
(IV) The asset pricing model used to measure the abnormal returns (such as the CAPM) had mis-specification error so the returns may not be abnormal but rather fair for the level of risk.
Select the most correct response:
Fundamentalists who analyse company financial reports and news announcements (but who don't have inside information) will make positive abnormal returns if:
A company advertises an investment costing $1,000 which they say is underpriced. They say that it has an expected total return of 15% pa, but a required return of only 10% pa. Of the 15% pa total expected return, the dividend yield is expected to always be 7% pa and rest is the capital yield.
Assuming that the company's statements are correct, what is the NPV of buying the investment if the 15% total return lasts for the next 100 years (t=0 to 100), then reverts to 10% after that time? Also, what is the NPV of the investment if the 15% return lasts forever?
In both cases, assume that the required return of 10% remains constant, the dividends can only be re-invested at 10% pa and all returns are given as effective annual rates.
The answer choices below are given in the same order (15% for 100 years, and 15% forever):
Question 668 buy and hold, market efficiency, idiom
A quote from the famous investor Warren Buffet: "Much success can be attributed to inactivity. Most investors cannot resist the temptation to constantly buy and sell."
Buffet is referring to the buy-and-hold strategy which is to buy and never sell shares. Which of the following is a disadvantage of a buy-and-hold strategy? Assume that share markets are semi-strong form efficient. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of the strict buy-and-hold strategy? A disadvantage of the buy-and-hold strategy is that it reduces:
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Covariance ##(\sigma_{A,B})## | Beta | Dollars invested |
|
| A | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.12 | 0.5 | 40 | |
| B | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 80 | ||
What is the standard deviation (not variance) of the above portfolio? Note that the stocks' covariance is given, not correlation.
The standard deviation and variance of a stock's annual returns are calculated over a number of years. The units of the returns are percent per annum ##(\% pa)##.
What are the units of the standard deviation ##(\sigma)## and variance ##(\sigma^2)## of returns respectively?
Hint: Visit Wikipedia to understand the difference between percentage points ##(\text{pp})## and percent ##(\%)##.
The following cash flows are expected:
- 10 yearly payments of $80, with the first payment in 3 years from now (first payment at t=3).
- 1 payment of $600 in 5 years and 6 months (t=5.5) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
Question 498 NPV, Annuity, perpetuity with growth, multi stage growth model
A business project is expected to cost $100 now (t=0), then pay $10 at the end of the third (t=3), fourth, fifth and sixth years, and then grow by 5% pa every year forever. So the cash flow will be $10.5 at the end of the seventh year (t=7), then $11.025 at the end of the eighth year (t=8) and so on perpetually. The total required return is 10℅ pa.
Which of the following formulas will NOT give the correct net present value of the project?
The equations for Net Income (NI, also known as Earnings or Net Profit After Tax) and Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA, also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm) per year are:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c)###
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+IntExp###
For a firm with debt, what is the formula for the present value of interest tax shields if the tax shields occur in perpetuity?
You may assume:
- the value of debt (D) is constant through time,
- The cost of debt and the yield on debt are equal and given by ##r_D##.
- the appropriate rate to discount interest tax shields is ##r_D##.
- ##\text{IntExp}=D.r_D##
You believe that the price of a share will fall significantly very soon, but the rest of the market does not. The market thinks that the share price will remain the same. Assuming that your prediction will soon be true, which of the following trades is a bad idea? In other words, which trade will NOT make money or prevent losses?
Question 625 dividend re-investment plan, capital raising
Which of the following statements about dividend re-investment plans (DRP's) is NOT correct?
Question 469 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system, no explanation
A firm pays a fully franked cash dividend of $70 to one of its Australian shareholders who has a personal marginal tax rate of 45%. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What will be the shareholder's personal tax payable due to the dividend payment?
Question 624 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system, no explanation
Which of the following statements about Australian franking credits is NOT correct? Franking credits:
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.15 | 1.10 | 1.05 | 1.00 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at -5% pa. Note that this is a negative growth rate, so the dividend will actually shrink. So,
- the dividend at t=5 will be ##$1(1-0.05) = $0.95##,
- the dividend at t=6 will be ##$1(1-0.05)^2 = $0.9025##, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates.
What will be the price of the stock in four and a half years (t = 4.5)?
For certain shares, the forward-looking Price-Earnings Ratio (##P_0/EPS_1##) is equal to the inverse of the share's total expected return (##1/r_\text{total}##). For what shares is this true?
Use the general accounting definition of 'payout ratio' which is dividends per share (DPS) divided by earnings per share (EPS) and assume that all cash flows, earnings and rates are real rather than nominal.
A company's forward-looking PE ratio will be the inverse of its total expected return on equity when it has a:
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 10 | 3 | ... |
After year 4, the dividend will grow in perpetuity at 4% pa. The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates.
What is the current price of the stock?
A stock is expected to pay a dividend of $15 in one year (t=1), then $25 for 9 years after that (payments at t=2 ,3,...10), and on the 11th year (t=11) the dividend will be 2% less than at t=10, and will continue to shrink at the same rate every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10%. All rates are effective annual rates.
What is the price of the stock now?
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0 | 6 | 12 | 18 | 20 | ... |
After year 4, the dividend will grow in perpetuity at 5% pa. The required return of the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates.
What is the current price of the stock?
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0 | 6 | 12 | 18 | 20 | ... |
After year 4, the dividend will grow in perpetuity at 5% pa. The required return of the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates.
What will be the price of the stock in 7 years (t = 7), just after the dividend at that time has been paid?