Question 49 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, APR, effective rate
In Australia, nominal yields on semi-annual coupon paying Government Bonds with 2 years until maturity are currently 2.83% pa.
The inflation rate is currently 2.2% pa, given as an APR compounding per quarter. The inflation rate is not expected to change over the next 2 years.
What is the real yield on these bonds, given as an APR compounding every 6 months?
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 213 income and capital returns, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds
The coupon rate of a fixed annual-coupon bond is constant (always the same).
What can you say about the income return (##r_\text{income}##) of a fixed annual coupon bond? Remember that:
###r_\text{total} = r_\text{income} + r_\text{capital}###
###r_\text{total, 0 to 1} = \frac{c_1}{p_0} + \frac{p_1-p_0}{p_0}###
Assume that there is no change in the bond's total annual yield to maturity from when it is issued to when it matures.
Select the most correct statement.
From its date of issue until maturity, the income return of a fixed annual coupon:
Three important classes of investable risky assets are:
- Corporate debt which has low total risk,
- Real estate which has medium total risk,
- Equity which has high total risk.
Assume that the correlation between total returns on:
- Corporate debt and real estate is 0.1,
- Corporate debt and equity is 0.1,
- Real estate and equity is 0.5.
You are considering investing all of your wealth in one or more of these asset classes. Which portfolio will give the lowest total risk? You are restricted from shorting any of these assets. Disregard returns and the risk-return trade-off, pretend that you are only concerned with minimising risk.
Question 319 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
Investors expect the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to keep the policy rate steady at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 25 basis points due to fears that the economy is growing too fast and that inflation will be above their target rate of 2 to 3 per cent.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar is likely to:
Question 455 income and capital returns, payout policy, DDM, market efficiency
A fairly priced unlevered firm plans to pay a dividend of $1 next year (t=1) which is expected to grow by 3% pa every year after that. The firm's required return on equity is 8% pa.
The firm is thinking about reducing its future dividend payments by 10% so that it can use the extra cash to invest in more projects which are expected to return 8% pa, and have the same risk as the existing projects. Therefore, next year's dividend will be $0.90. No new equity or debt will be issued to fund the new projects, they'll all be funded by the cut in dividends.
What will be the stock's new annual capital return (proportional increase in price per year) if the change in payout policy goes ahead?
Assume that payout policy is irrelevant to firm value (so there's no signalling effects) and that all rates are effective annual rates.
Below is a graph of 3 peoples’ utility functions, Mr Blue (U=W^(1/2) ), Miss Red (U=W/10) and Mrs Green (U=W^2/1000). Assume that each of them currently have $50 of wealth.
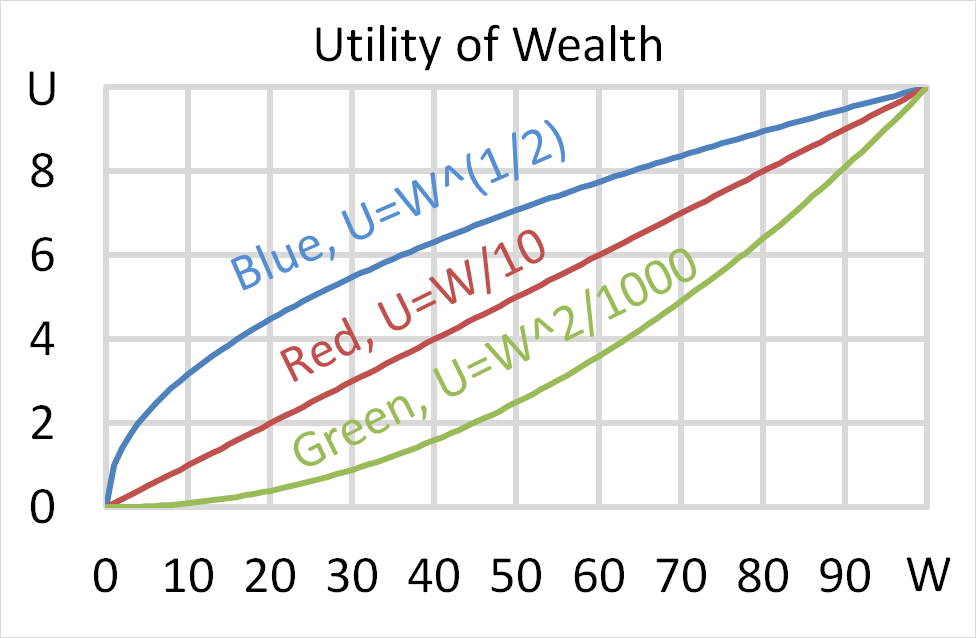
Which of the following statements about them is NOT correct?
(a) Mr Blue would prefer to invest his wealth in a well diversified portfolio of stocks rather than a single stock, assuming that all stocks had the same total risk and return.