A stock pays semi-annual dividends. It just paid a dividend of $10. The growth rate in the dividend is 1% every 6 months, given as an effective 6 month rate. You estimate that the stock's required return is 21% pa, as an effective annual rate.
Using the dividend discount model, what will be the share price?
Bonds A and B are issued by the same Australian company. Both bonds yield 7% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond A pays coupons of 10% pa and bond B pays coupons of 5% pa. Which of the following statements is true about the bonds' prices?
A share was bought for $10 (at t=0) and paid its annual dividend of $0.50 one year later (at t=1). Just after the dividend was paid, the share price was $11 (at t=1).
What was the total return, capital return and income return? Calculate your answers as effective annual rates. The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}##, ##r_\text{capital}##, ##r_\text{dividend}##.
An industrial chicken farmer grows chickens for their meat. Chickens:
- Cost $0.50 each to buy as chicks. They are bought on the day they’re born, at t=0.
- Grow at a rate of $0.70 worth of meat per chicken per week for the first 6 weeks (t=0 to t=6).
- Grow at a rate of $0.40 worth of meat per chicken per week for the next 4 weeks (t=6 to t=10) since they’re older and grow more slowly.
- Feed costs are $0.30 per chicken per week for their whole life. Chicken feed is bought and fed to the chickens once per week at the beginning of the week. So the first amount of feed bought for a chicken at t=0 costs $0.30, and so on.
- Can be slaughtered (killed for their meat) and sold at no cost at the end of the week. The price received for the chicken is their total value of meat (note that the chicken grows fast then slow, see above).
The required return of the chicken farm is 0.5% given as an effective weekly rate.
Ignore taxes and the fixed costs of the factory. Ignore the chicken’s welfare and other environmental and ethical concerns.
Find the equivalent weekly cash flow of slaughtering a chicken at 6 weeks and at 10 weeks so the farmer can figure out the best time to slaughter his chickens. The choices below are given in the same order, 6 and 10 weeks.
Which of the following statements about short-selling is NOT true?
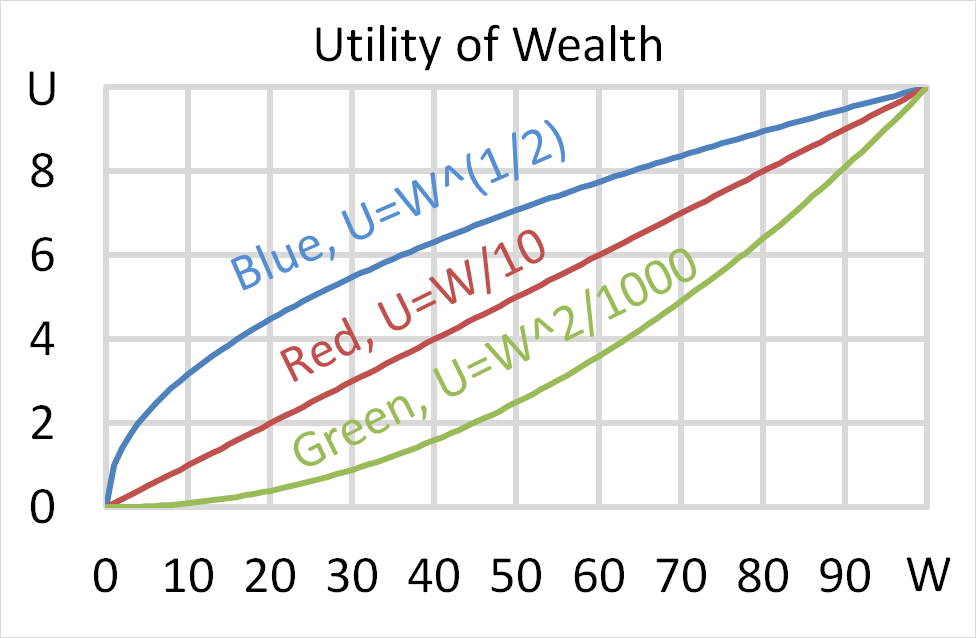
Question 699 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
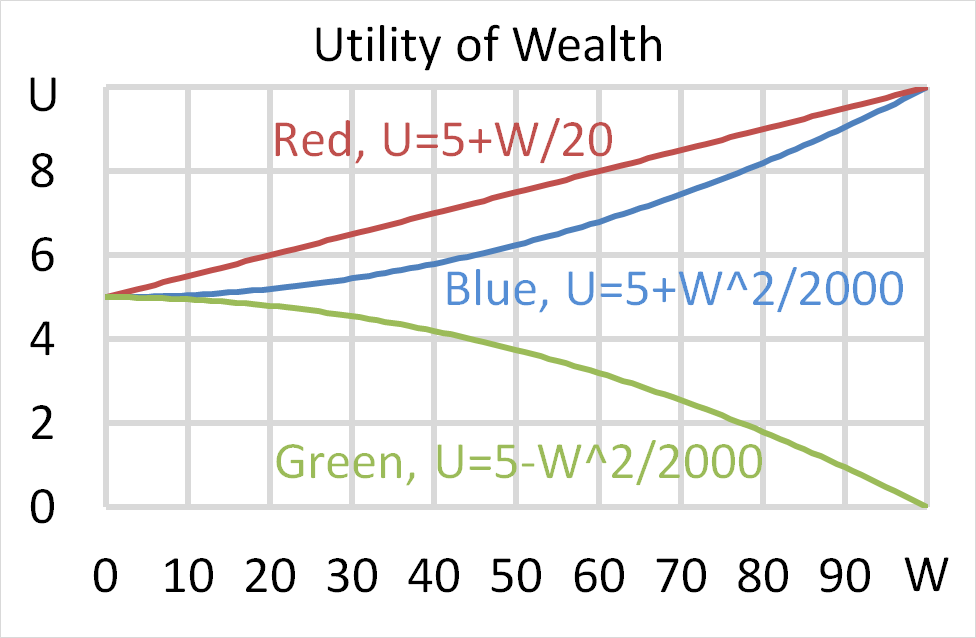
Question 701 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Use the below information to value a levered company with constant annual perpetual cash flows from assets. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now, so a perpetuity can be used to value this firm. Both the operating and firm free cash flows are constant (but not equal to each other).
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}## | $48.5m | Operating free cash flow |
| ##\text{FFCF or CFFA}## | $50m | Firm free cash flow or cash flow from assets |
| ##g## | 0% pa | Growth rate of OFCF and FFCF |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{BeforeTax}## | 10% pa | Weighted average cost of capital before tax |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{AfterTax}## | 9.7% pa | Weighted average cost of capital after tax |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 5% pa | Cost of debt |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 11.25% pa | Cost of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 20% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
What is the value of the levered firm including interest tax shields?
A stock has an expected return of 10% pa and you're 90% sure that over the next year, the return will be between -15% and 35%. The stock's returns are normally distributed. Note that the Z-statistic corresponding to a one-tail:
- 90% normal probability density function is 1.282.
- 95% normal probability density function is 1.645.
- 97.5% normal probability density function is 1.960.
What is the stock’s standard deviation of returns in percentage points per annum (pp pa)?
A New Zealand lady wants to calculate how many New Zealand Dollars (NZD) she needs to buy a 1 million Australian dollar (AUD) house in Sydney, Australia. The exchange rate is 0.69 USD per NZD and 0.72 USD per AUD. What is the AUD 1 million equivalent to in NZD?