A stock pays semi-annual dividends. It just paid a dividend of $10. The growth rate in the dividend is 1% every 6 months, given as an effective 6 month rate. You estimate that the stock's required return is 21% pa, as an effective annual rate.
Using the dividend discount model, what will be the share price?
Question 345 capital budgeting, break even, NPV
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 10 yrs | |
| Initial investment in factory | $10m | |
| Depreciation of factory per year | $1m | |
| Expected scrap value of factory at end of project | $0 | |
| Sale price per unit | $10 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $6 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $2m | |
| Interest expense per year | 0 | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Cost of capital per annum | 10% | |
Notes
- The firm's current liabilities are forecast to stay at $0.5m. The firm's current assets (mostly inventory) is currently $1m, but is forecast to grow by $0.1m at the end of each year due to the project.
At the end of the project, the current assets accumulated due to the project can be sold for the same price that they were bought. - A marketing survey was used to forecast sales. It cost $1.4m which was just paid. The cost has been capitalised by the accountants and is tax-deductible over the life of the project, regardless of whether the project goes ahead or not. This amortisation expense is not included in the depreciation expense listed in the table above.
Assumptions
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
Find the break even unit production (Q) per year to achieve a zero Net Income (NI) and Net Present Value (NPV), respectively. The answers below are listed in the same order.
Question 370 capital budgeting, NPV, interest tax shield, WACC, CFFA
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 2 yrs | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $600k | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $250k | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | $200k | |
| Revenue per job | $12k | |
| Variable cost per job | $4k | |
| Quantity of jobs per year | 120 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $100k | |
| Interest expense in first year (at t=1) | $16.091k | |
| Interest expense in second year (at t=2) | $9.711k | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Government treasury bond yield | 5% | |
| Bank loan debt yield | 6% | |
| Levered cost of equity | 12.5% | |
| Market portfolio return | 10% | |
| Beta of assets | 1.24 | |
| Beta of levered equity | 1.5 | |
| Firm's and project's debt-to-equity ratio | 25% | |
Notes
- The project will require an immediate purchase of $50k of inventory, which will all be sold at cost when the project ends. Current liabilities are negligible so they can be ignored.
Assumptions
- The debt-to-equity ratio will be kept constant throughout the life of the project. The amount of interest expense at the end of each period has been correctly calculated to maintain this constant debt-to-equity ratio. Note that interest expense is different in each year.
- Thousands are represented by 'k' (kilo).
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are nominal. The inflation rate is 2% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The 50% capital gains tax discount is not available since the project is undertaken by a firm, not an individual.
What is the net present value (NPV) of the project?
The below screenshot of Microsoft's (MSFT) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 28 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.
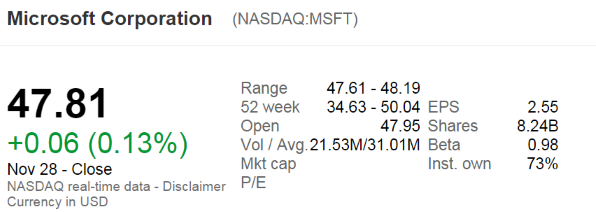
What was MSFT's approximate payout ratio over the last year?
Note that MSFT's past four quarterly dividends were $0.31, $0.28, $0.28 and $0.28.
Question 722 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
Here is a table of stock prices and returns. Which of the statements below the table is NOT correct?
| Price and Return Population Statistics | ||||
| Time | Prices | LGDR | GDR | NDR |
| 0 | 100 | |||
| 1 | 50 | -0.6931 | 0.5 | -0.5 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.6931 | 2 | 1 |
| Arithmetic average | 0 | 1.25 | 0.25 | |
| Arithmetic standard deviation | 0.9802 | 1.0607 | 1.0607 | |
Question 890 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, no explanation
The market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to increase the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting. The current exchange rate is 0.8 USD per AUD.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 50 basis points due to increased fears of inflation.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate on the day when the surprise announcement is made? The Australian dollar is likely to suddenly:
Question 892 foreign exchange reserve, foreign exchange rate, no explanation
The Chinese central bank has the largest amount of foreign currency reserves.
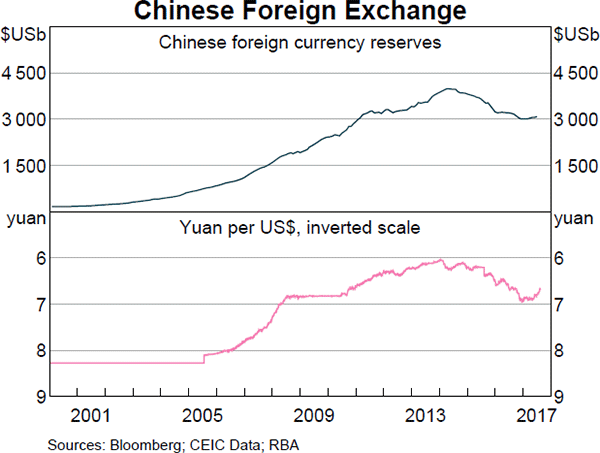
What could the large amounts of foreign exchange reserves held by the Chinese government be used for in a currency crisis? China's currency is called the Renminbi (RMB) or Yuan (CNY). In a Chinese currency crisis the Chinese government is likely to use its FX reserves to:
A stock's returns are normally distributed with a mean of 8% pa and a standard deviation of 15 percentage points pa. What is the 99% confidence interval of returns over the next year? Note that the Z-statistic corresponding to a one-tail:
- 90% normal probability density function is 1.282.
- 95% normal probability density function is 1.645.
- 97.5% normal probability density function is 1.960.
- 99% normal probability density function is 2.326.
- 99.5% normal probability density function is 2.576
The 99% confidence interval of annual returns is between:
Question 968 foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate, cross currency interest rate parity, no explanation
Below is a graph showing the spread or difference between government bond yields in different countries compared to the US. Assume that all governments have zero credit risk.
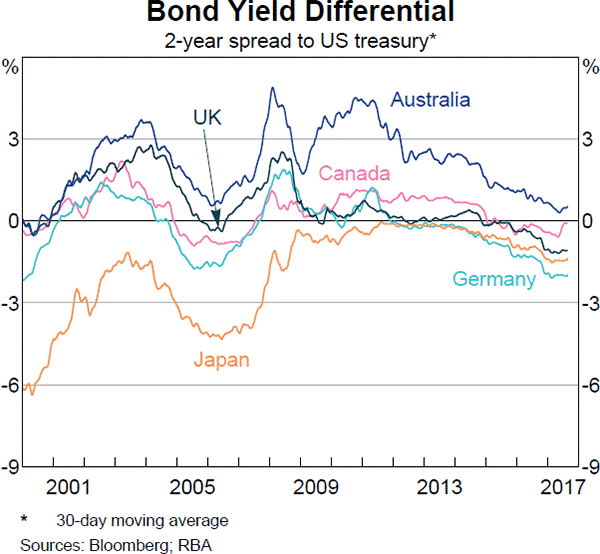
According to the principle of cross-currency interest rate parity, which country is likely to have the greatest expected currency appreciation against the USD over the next 2 years?
Assume that the market portfolio has a duration of 15 years and an individual stock has a duration of 20 years.
What can you say about the stock's (single factor CAPM) beta with respect to the market portfolio? The stock's beta is likely to be: