A two year Government bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 2.5% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 0.5% pa, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
A share was bought for $30 (at t=0) and paid its annual dividend of $6 one year later (at t=1).
Just after the dividend was paid, the share price fell to $27 (at t=1). What were the total, capital and income returns given as effective annual rates?
The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}## , ##r_\text{capital}## , ##r_\text{dividend}##.
A company increases the proportion of debt funding it uses to finance its assets by issuing bonds and using the cash to repurchase stock, leaving assets unchanged.
Ignoring the costs of financial distress, which of the following statements is NOT correct:
Question 345 capital budgeting, break even, NPV
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 10 yrs | |
| Initial investment in factory | $10m | |
| Depreciation of factory per year | $1m | |
| Expected scrap value of factory at end of project | $0 | |
| Sale price per unit | $10 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $6 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $2m | |
| Interest expense per year | 0 | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Cost of capital per annum | 10% | |
Notes
- The firm's current liabilities are forecast to stay at $0.5m. The firm's current assets (mostly inventory) is currently $1m, but is forecast to grow by $0.1m at the end of each year due to the project.
At the end of the project, the current assets accumulated due to the project can be sold for the same price that they were bought. - A marketing survey was used to forecast sales. It cost $1.4m which was just paid. The cost has been capitalised by the accountants and is tax-deductible over the life of the project, regardless of whether the project goes ahead or not. This amortisation expense is not included in the depreciation expense listed in the table above.
Assumptions
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
Find the break even unit production (Q) per year to achieve a zero Net Income (NI) and Net Present Value (NPV), respectively. The answers below are listed in the same order.
Question 398 financial distress, capital raising, leverage, capital structure, NPV
A levered firm has zero-coupon bonds which mature in one year and have a combined face value of $9.9m.
Investors are risk-neutral and therefore all debt and equity holders demand the same required return of 10% pa.
In one year the firm's assets will be worth:
- $13.2m with probability 0.5 in the good state of the world, or
- $6.6m with probability 0.5 in the bad state of the world.
A new project presents itself which requires an investment of $2m and will provide a certain cash flow of $3.3m in one year.
The firm doesn't have any excess cash to make the initial $2m investment, but the funds can be raised from shareholders through a fairly priced rights issue. Ignore all transaction costs.
Should shareholders vote to proceed with the project and equity raising? What will be the gain in shareholder wealth if they decide to proceed?
Acquirer firm plans to launch a takeover of Target firm. The deal is expected to create a present value of synergies totaling $105 million. A cash offer will be made that pays the fair price for the target's shares plus 75% of the total synergy value. The cash will be paid out of the firm's cash holdings, no new debt or equity will be raised.
| Firms Involved in the Takeover | ||
| Acquirer | Target | |
| Assets ($m) | 6,000 | 700 |
| Debt ($m) | 4,800 | 400 |
| Share price ($) | 40 | 20 |
| Number of shares (m) | 30 | 15 |
Ignore transaction costs and fees. Assume that the firms' debt and equity are fairly priced, and that each firms' debts' risk, yield and values remain constant. The acquisition is planned to occur immediately, so ignore the time value of money.
Calculate the merged firm's share price and total number of shares after the takeover has been completed.
Acquirer firm plans to launch a takeover of Target firm. The deal is expected to create a present value of synergies totaling $105 million. A 40% scrip and 60% cash offer will be made that pays the fair price for the target's shares plus 75% of the total synergy value. The cash will be paid out of the firm's cash holdings, no new debt or equity will be raised.
| Firms Involved in the Takeover | ||
| Acquirer | Target | |
| Assets ($m) | 6,000 | 700 |
| Debt ($m) | 4,800 | 400 |
| Share price ($) | 40 | 20 |
| Number of shares (m) | 30 | 15 |
Ignore transaction costs and fees. Assume that the firms' debt and equity are fairly priced, and that each firms' debts' risk, yield and values remain constant. The acquisition is planned to occur immediately, so ignore the time value of money.
Calculate the merged firm's share price and total number of shares after the takeover has been completed.
Question 727 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
The Australian Federal Government lends money to domestic students to pay for their university education. This is known as the Higher Education Contribution Scheme (HECS). The nominal interest rate on the HECS loan is set equal to the consumer price index (CPI) inflation rate. The interest is capitalised every year, which means that the interest is added to the principal. The interest and principal does not need to be repaid by students until they finish study and begin working.
Which of the following statements about HECS loans is NOT correct?
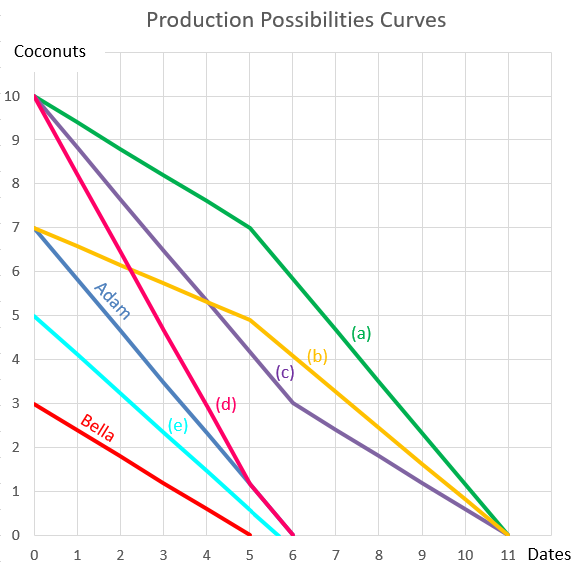
Question 898 comparative advantage in trade, production possibilities curve, no explanation
Adam and Bella are the only people on a remote island. Their production possibility curves are shown in the graph.
Assuming that Adam and Bella cooperate according to the principles of comparative advantage, what will be their combined production possibilities curve?