A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.15 | 1.10 | 1.05 | 1.00 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at -5% pa. Note that this is a negative growth rate, so the dividend will actually shrink. So,
- the dividend at t=5 will be ##$1(1-0.05) = $0.95##,
- the dividend at t=6 will be ##$1(1-0.05)^2 = $0.9025##, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates.
What will be the price of the stock in four and a half years (t = 4.5)?
A company issues a large amount of bonds to raise money for new projects of similar risk to the company's existing projects. The net present value (NPV) of the new projects is positive but small. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is NOT correct?
In Australia in the 1980's, inflation was around 8% pa, and residential mortgage loan interest rates were around 14%.
In 2013, inflation was around 2.5% pa, and residential mortgage loan interest rates were around 4.5%.
If a person can afford constant mortgage loan payments of $2,000 per month, how much more can they borrow when interest rates are 4.5% pa compared with 14.0% pa?
Give your answer as a proportional increase over the amount you could borrow when interest rates were high ##(V_\text{high rates})##, so:
###\text{Proportional increase} = \dfrac{V_\text{low rates}-V_\text{high rates}}{V_\text{high rates}} ###
Assume that:
- Interest rates are expected to be constant over the life of the loan.
- Loans are interest-only and have a life of 30 years.
- Mortgage loan payments are made every month in arrears and all interest rates are given as annualised percentage rates (APR's) compounding per month.
A Chinese man wishes to convert AUD 1 million into Chinese Renminbi (RMB, also called the Yuan (CNY)). The exchange rate is 6.35 RMB per USD, and 0.72 USD per AUD. How much is the AUD 1 million worth in RMB?
Question 624 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system, no explanation
Which of the following statements about Australian franking credits is NOT correct? Franking credits:
A firm wishes to raise $100 million now. The firm's current market value of equity is $300m and the market price per share is $5. They estimate that they'll be able to issue shares in a rights issue at a subscription price of $4. All answers are rounded to 6 decimal places. Ignore the time value of money and assume that all shareholders exercise their rights. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
The below graph from the RBA shows the phase-in of the Basel 3 minimum regulatory capital requirements under the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) on the left panel and in Australia under the Australian Prudential Regulatory Authority (APRA) on the right panel.
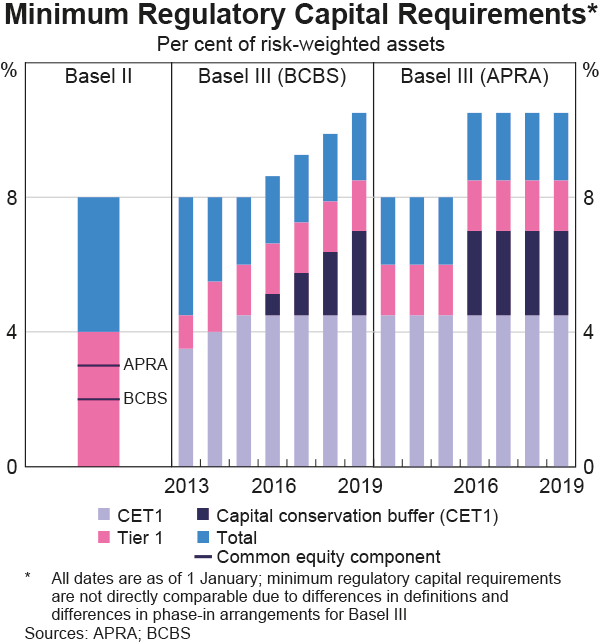
Which of the following statements about the Basel 3 minimum regulatory capital requirements as at 2019 is NOT correct? All minimum amounts exclude the 2.5% counter-cyclical buffer.
The Basel 3 minimum regulatory capital requirement as a percent of Risk Weighted Assets (RWA) is:
Question 918 duration, Macaulay duration, modified duration, bond convexity
A fixed coupon bond’s modified duration is 10 years, and yields are currently 5% pa compounded annually. Which of the following statements about the bond is NOT correct?
Question 926 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
The arithmetic average continuously compounded or log gross discrete return (AALGDR) on the ASX200 accumulation index over the 24 years from 31 Dec 1992 to 31 Dec 2016 is 9.49% pa.
The arithmetic standard deviation (SDLGDR) is 16.92 percentage points pa.
Assume that the log gross discrete returns are normally distributed and that the above estimates are true population statistics, not sample statistics, so there is no standard error in the sample mean or standard deviation estimates. Also assume that the standardised normal Z-statistic corresponding to a one-tail probability of 2.5% is exactly -1.96.
If you had a $1 million fund that replicated the ASX200 accumulation index, in how many years would the median dollar value of your fund first be expected to lie outside the 95% confidence interval forecast?