You just borrowed $400,000 in the form of a 25 year interest-only mortgage with monthly payments of $3,000 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
You actually plan to pay more than the required interest payment. You plan to pay $3,300 in mortgage payments every month, which your mortgage lender allows. These extra payments will reduce the principal and the minimum interest payment required each month.
At the maturity of the mortgage, what will be the principal? That is, after the last (300th) interest payment of $3,300 in 25 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage?
The below screenshot of Microsoft's (MSFT) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 28 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.
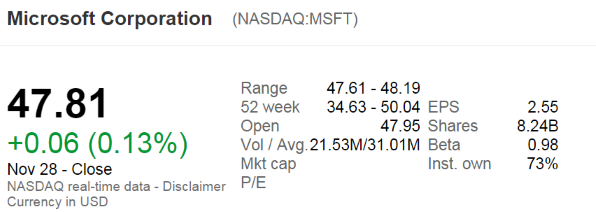
What was MSFT's backwards-looking price-earnings ratio?
A stock's total standard deviation of returns is 20% pa. The market portfolio's total standard deviation of returns is 15% pa. The beta of the stock is 0.8.
What is the stock's diversifiable standard deviation?
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 20%. What is its debt-to-equity ratio?
A company conducts a 2 for 3 rights issue at a subscription price of $8 when the pre-announcement stock price was $9. Assume that all investors use their rights to buy those extra shares.
What is the percentage increase in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order.
Use the below information to value a levered company with constant annual perpetual cash flows from assets. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now, so a perpetuity can be used to value this firm. Both the operating and firm free cash flows are constant (but not equal to each other).
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}## | $48.5m | Operating free cash flow |
| ##\text{FFCF or CFFA}## | $50m | Firm free cash flow or cash flow from assets |
| ##g## | 0% pa | Growth rate of OFCF and FFCF |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{BeforeTax}## | 10% pa | Weighted average cost of capital before tax |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{AfterTax}## | 9.7% pa | Weighted average cost of capital after tax |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 5% pa | Cost of debt |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 11.25% pa | Cost of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 20% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
What is the value of the levered firm including interest tax shields?
Question 780 mispriced asset, NPV, DDM, market efficiency, no explanation
A company advertises an investment costing $1,000 which they say is under priced. They say that it has an expected total return of 15% pa, but a required return of only 10% pa. Of the 15% pa total expected return, the dividend yield is expected to be 4% pa and the capital yield 11% pa. Assume that the company's statements are correct.
What is the NPV of buying the investment if the 15% total return lasts for the next 100 years (t=0 to 100), then reverts to 10% after that time? Also, what is the NPV of the investment if the 15% return lasts forever?
In both cases, assume that the required return of 10% remains constant, the dividends can only be re-invested at 10% pa and all returns are given as effective annual rates. The answer choices below are given in the same order (15% for 100 years, and 15% forever):
RBA analyst Adam Hamilton wrote in the December 2018 Bulletin article ‘Understanding Exchange Rates and Why They Are Important’ the following passage about bilateral exchange rates:
A bilateral exchange rate refers to the value of one currency relative to another. It is the most commonly referenced type of exchange rate. Most bilateral exchange rates are quoted against the US dollar (USD), as it is the most traded currency globally. Looking at the Australian dollar (AUD), the AUD/USD exchange rate gives you the amount of US dollars that you will receive for each Australian dollar that you convert (or sell). For example, an AUD/USD exchange rate of 0.75 means that you will get US75 cents for every 1 AUD.
An appreciation of the Australian dollar is an increase in its value compared with a foreign currency. This means that each Australian dollar buys you more foreign currency than before. Equivalently, if you are buying an item that is priced in foreign currency it will now cost you less in Australian dollars than before. If there is a depreciation of the Australian dollar, the opposite is true.
Based on this information, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 976 comparative advantage in trade, production possibilities curve, no explanation
Arthur and Bindi are the only people on a remote island. Their production possibility curves are shown in the graph.
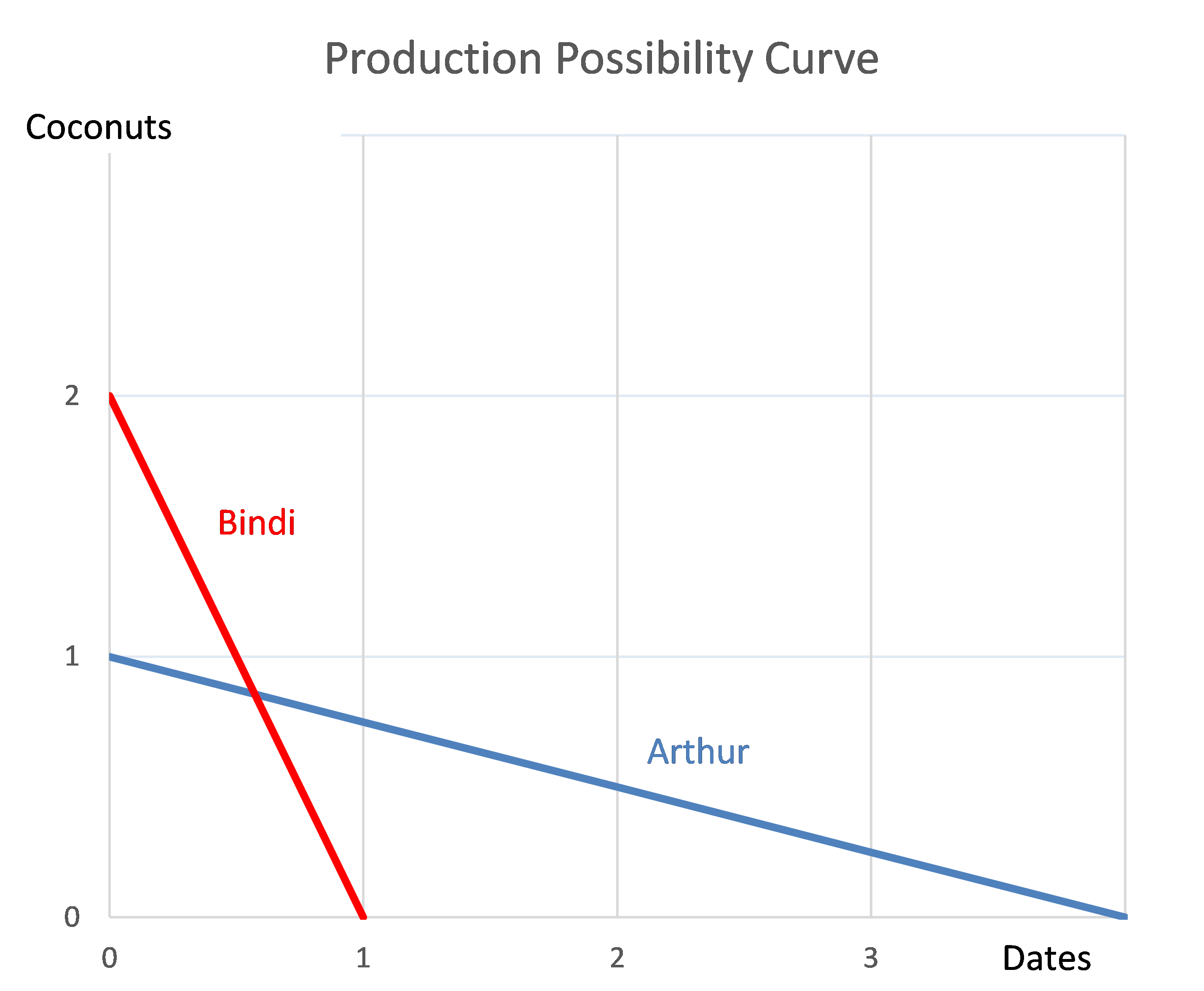
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 993 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
In February 2020, the RBA cash rate was 0.75% pa and the Australian CPI inflation rate was 1.8% pa.
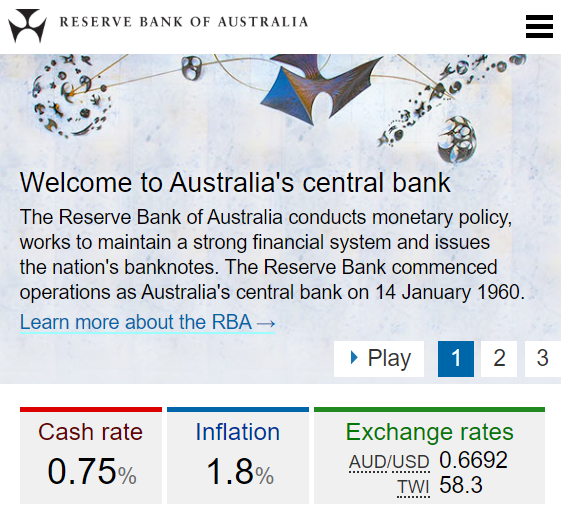
You currently have $100 in the bank which pays a 0.75% pa interest rate.
Apples currently cost $1 each at the shop and inflation is 1.8% pa which is the expected growth rate in the apple price.
This information is summarised in the table below, with some parts missing that correspond to the answer options. All rates are given as effective annual rates. Note that when payments are not specified as real, as in this question, they're conventionally assumed to be nominal.
| Wealth in Dollars and Apples | ||||
| Time (year) | Bank account wealth ($) | Apple price ($) | Wealth in apples | |
| 0 | 100 | 1 | 100 | |
| 1 | 100.75 | 1.018 | (a) | |
| 2 | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? Your: