Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions. Which of the statements about the 3 utility functions is NOT correct?
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions. Which of the statements about the 3 utility functions is NOT correct?
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions. Which of the statements about the 3 utility functions is NOT correct?
Question 699 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?

Question 701 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
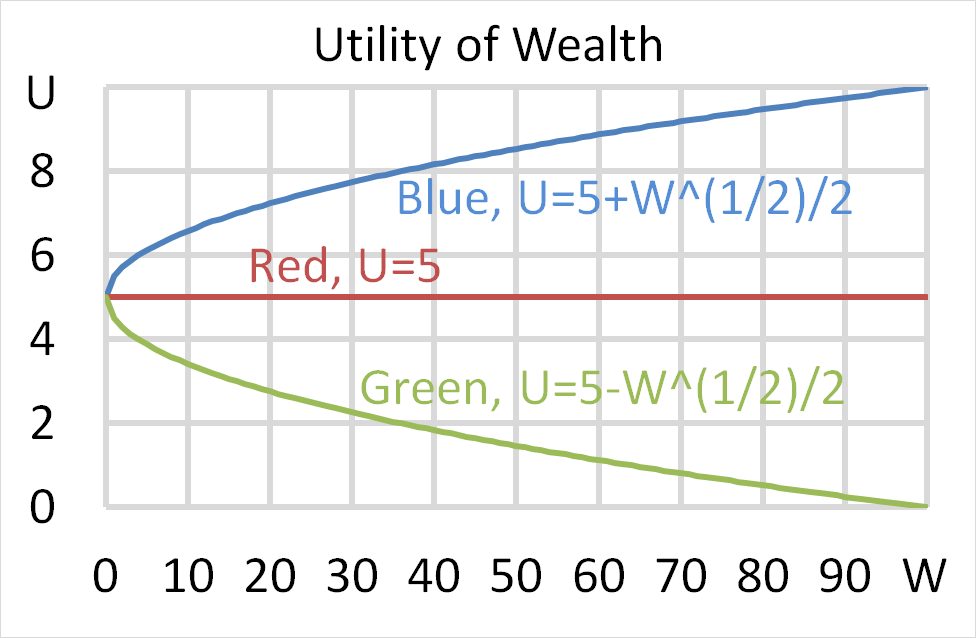
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?

Question 702 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
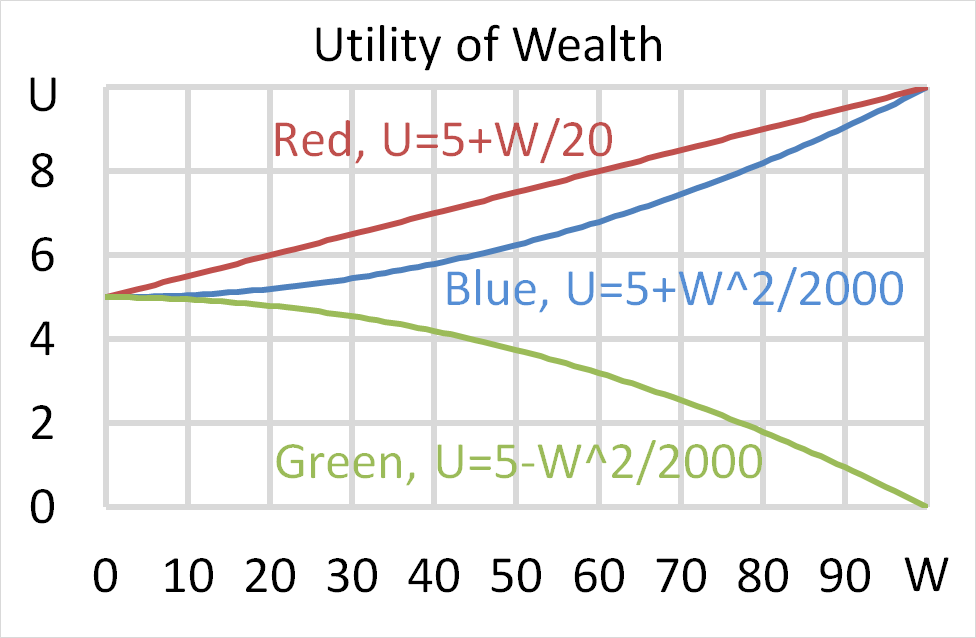
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 703 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
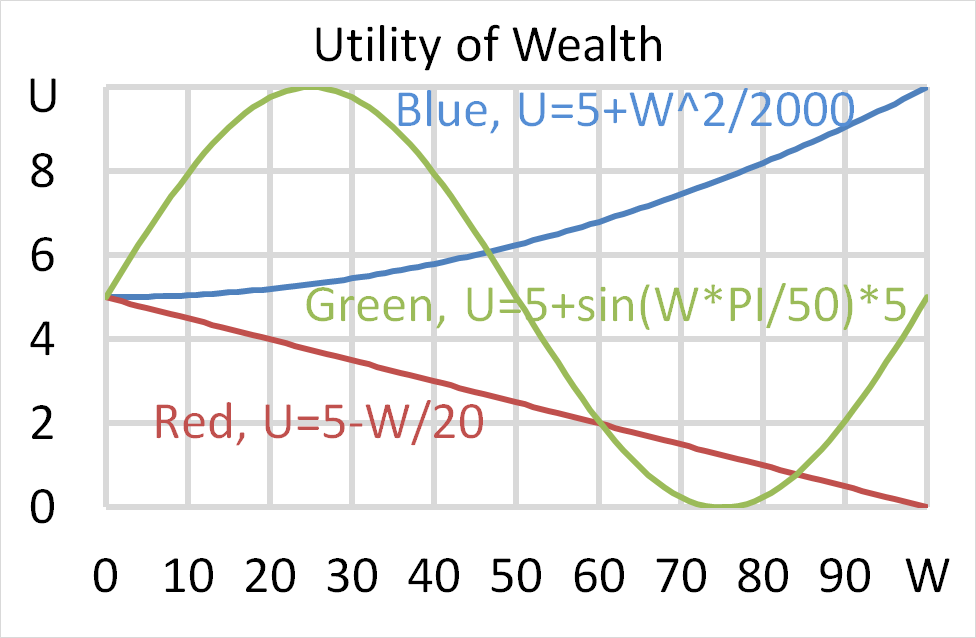
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $500 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $500. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $500. If they flip tails then they will lose $500. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
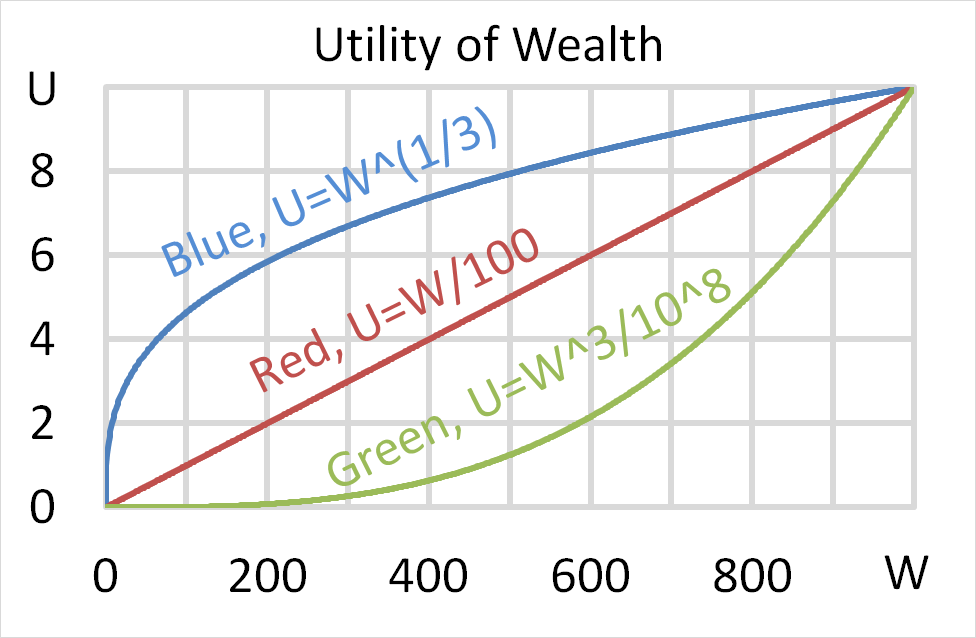
Question 704 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $256 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $256. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $256. If they flip tails then they will lose $256. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?

Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
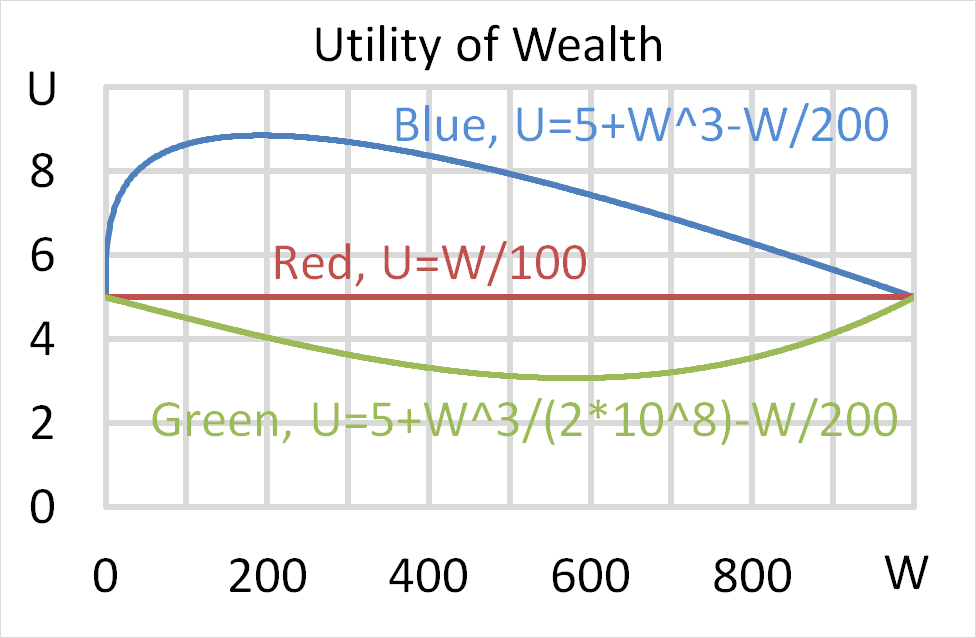
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Note that a fair gamble is a bet that has an expected value of zero, such as paying $0.50 to win $1 in a coin flip with heads or nothing if it lands tails. Fairly priced insurance is when the expected present value of the insurance premiums is equal to the expected loss from the disaster that the insurance protects against, such as the cost of rebuilding a home after a catastrophic fire.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?

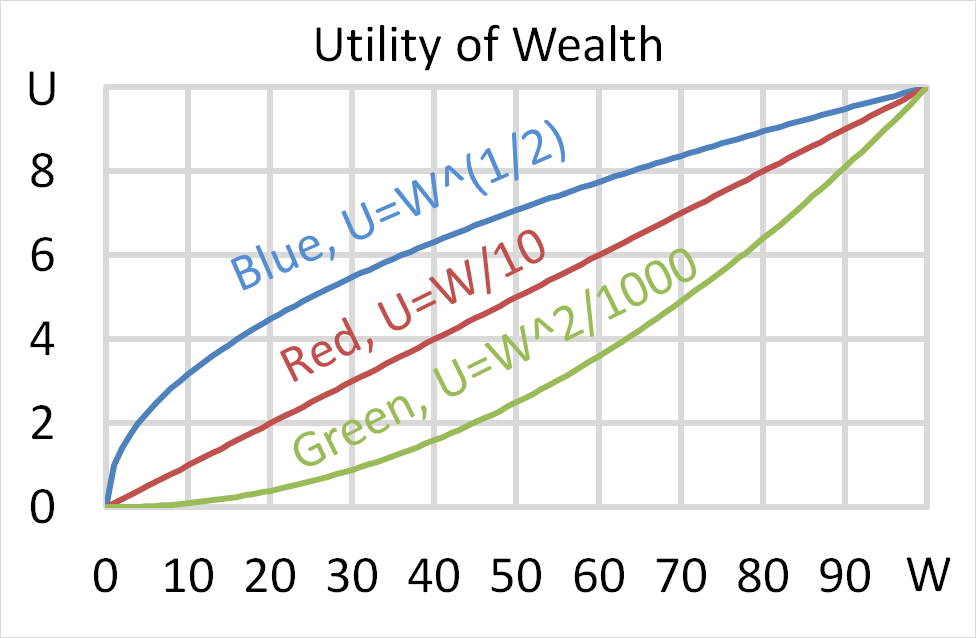
Below is a graph of 3 peoples’ utility functions, Mr Blue (U=W^(1/2) ), Miss Red (U=W/10) and Mrs Green (U=W^2/1000). Assume that each of them currently have $50 of wealth.

Which of the following statements about them is NOT correct?
(a) Mr Blue would prefer to invest his wealth in a well diversified portfolio of stocks rather than a single stock, assuming that all stocks had the same total risk and return.
Which of the following is NOT a valid method for estimating the beta of a company's stock? Assume that markets are efficient, a long history of past data is available, the stock possesses idiosyncratic and market risk. The variances and standard deviations below denote total risks.
A stock has a beta of 1.5. The market's expected total return is 10% pa and the risk free rate is 5% pa, both given as effective annual rates.
In the last 5 minutes, bad economic news was released showing a higher chance of recession. Over this time the share market fell by 1%. The risk free rate was unchanged.
What do you think was the stock's historical return over the last 5 minutes, given as an effective 5 minute rate?
Question 776 market efficiency, systematic and idiosyncratic risk, beta, income and capital returns
Which of the following statements about returns is NOT correct? A stock's:
The market's expected total return is 10% pa and the risk free rate is 5% pa, both given as effective annual rates.
A stock has a beta of 0.5.
In the last 5 minutes, the federal government unexpectedly raised taxes. Over this time the share market fell by 3%. The risk free rate was unchanged.
What do you think was the stock's historical return over the last 5 minutes, given as an effective 5 minute rate?
Question 513 stock split, reverse stock split, stock dividend, bonus issue, rights issue
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 566 capital structure, capital raising, rights issue, on market repurchase, dividend, stock split, bonus issue
A company's share price fell by 20% and its number of shares rose by 25%. Assume that there are no taxes, no signalling effects and no transaction costs.
Which one of the following corporate events may have happened?
A manufacturing company is considering a new project in the more risky services industry. The cash flows from assets (CFFA) are estimated for the new project, with interest expense excluded from the calculations. To get the levered value of the project, what should these unlevered cash flows be discounted by?
Assume that the manufacturing firm has a target debt-to-assets ratio that it sticks to.
The US firm Google operates in the online advertising business. In 2011 Google bought Motorola Mobility which manufactures mobile phones.
Assume the following:
- Google had a 10% after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC) before it bought Motorola.
- Motorola had a 20% after-tax WACC before it merged with Google.
- Google and Motorola have the same level of gearing.
- Both companies operate in a classical tax system.
You are a manager at Motorola. You must value a project for making mobile phones. Which method(s) will give the correct valuation of the mobile phone manufacturing project? Select the most correct answer.
The mobile phone manufacturing project's:
The hardest and most important aspect of business project valuation is the estimation of the:
A young lady is trying to decide if she should attend university or not.
The young lady's parents say that she must attend university because otherwise all of her hard work studying and attending school during her childhood was a waste.
What's the correct way to classify this item from a capital budgeting perspective when trying to decide whether to attend university?
The hard work studying at school in her childhood should be classified as:
The 'time value of money' is most closely related to which of the following concepts?
Question 568 rights issue, capital raising, capital structure
A company conducts a 1 for 5 rights issue at a subscription price of $7 when the pre-announcement stock price was $10. What is the percentage change in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order. Ignore all taxes, transaction costs and signalling effects.
A company conducts a 2 for 3 rights issue at a subscription price of $8 when the pre-announcement stock price was $9. Assume that all investors use their rights to buy those extra shares.
What is the percentage increase in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order.
A firm's weighted average cost of capital before tax (##r_\text{WACC before tax}##) would increase due to:
A company issues a large amount of bonds to raise money for new projects of similar risk to the company's existing projects. The net present value (NPV) of the new projects is positive but small. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is NOT correct?
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 50%. The firm then issues a large amount of equity to raise money for new projects of similar systematic risk to the company's existing projects. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is correct?
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of debt and using the funds to repurchase shares. Its assets are unchanged. Ignore interest tax shields.
According to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which statement is correct?
Question 99 capital structure, interest tax shield, Miller and Modigliani, trade off theory of capital structure
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of debt and using the funds to repurchase shares. Its assets are unchanged.
Assume that:
- The firm and individual investors can borrow at the same rate and have the same tax rates.
- The firm's debt and shares are fairly priced and the shares are repurchased at the market price, not at a premium.
- There are no market frictions relating to debt such as asymmetric information or transaction costs.
- Shareholders wealth is measured in terms of utiliity. Shareholders are wealth-maximising and risk-averse. They have a preferred level of overall leverage. Before the firm's capital restructure all shareholders were optimally levered.
According to Miller and Modigliani's theory, which statement is correct?
Question 104 CAPM, payout policy, capital structure, Miller and Modigliani, risk
Assume that there exists a perfect world with no transaction costs, no asymmetric information, no taxes, no agency costs, equal borrowing rates for corporations and individual investors, the ability to short the risk free asset, semi-strong form efficient markets, the CAPM holds, investors are rational and risk-averse and there are no other market frictions.
For a firm operating in this perfect world, which statement(s) are correct?
(i) When a firm changes its capital structure and/or payout policy, share holders' wealth is unaffected.
(ii) When the idiosyncratic risk of a firm's assets increases, share holders do not expect higher returns.
(iii) When the systematic risk of a firm's assets increases, share holders do not expect higher returns.
Select the most correct response:
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 50%. The firm then issues a large amount of debt to raise money for new projects of similar market risk to the company's existing projects. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is correct?
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of equity and using the funds to repay debt. Its assets are unchanged. Ignore interest tax shields.
According to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which statement is correct?
Question 121 capital structure, leverage, financial distress, interest tax shield
Fill in the missing words in the following sentence:
All things remaining equal, as a firm's amount of debt funding falls, benefits of interest tax shields __________ and the costs of financial distress __________.
A company conducts a 4 for 3 stock split. What is the percentage change in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order.
Stock A has a beta of 0.5 and stock B has a beta of 1. Which statement is NOT correct?
Diversification is achieved by investing in a large amount of stocks. What type of risk is reduced by diversification?
According to the theory of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), total variance can be broken into two components, systematic variance and idiosyncratic variance. Which of the following events would be considered the most diversifiable according to the theory of the CAPM?
Which statement(s) are correct?
(i) All stocks that plot on the Security Market Line (SML) are fairly priced.
(ii) All stocks that plot above the Security Market Line (SML) are overpriced.
(iii) All fairly priced stocks that plot on the Capital Market Line (CML) have zero idiosyncratic risk.
Select the most correct response:
A stock's correlation with the market portfolio increases while its total risk is unchanged. What will happen to the stock's expected return and systematic risk?
The security market line (SML) shows the relationship between beta and expected return.
Buying investment projects that plot above the SML would lead to:
Question 235 SML, NPV, CAPM, risk
The security market line (SML) shows the relationship between beta and expected return.
Investment projects that plot on the SML would have:
Question 244 CAPM, SML, NPV, risk
Examine the following graph which shows stocks' betas ##(\beta)## and expected returns ##(\mu)##:
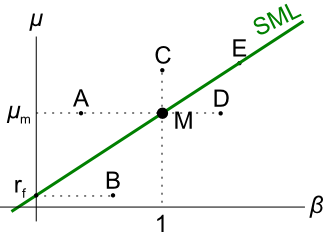
Assume that the CAPM holds and that future expectations of stocks' returns and betas are correctly measured. Which statement is NOT correct?
The total return of any asset can be broken down in different ways. One possible way is to use the dividend discount model (or Gordon growth model):
###p_0 = \frac{c_1}{r_\text{total}-r_\text{capital}}###
Which, since ##c_1/p_0## is the income return (##r_\text{income}##), can be expressed as:
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{income}+r_\text{capital}###
So the total return of an asset is the income component plus the capital or price growth component.
Another way to break up total return is to use the Capital Asset Pricing Model:
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{f}+β(r_\text{m}- r_\text{f})###
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{time value}+r_\text{risk premium}###
So the risk free rate is the time value of money and the term ##β(r_\text{m}- r_\text{f})## is the compensation for taking on systematic risk.
Using the above theory and your general knowledge, which of the below equations, if any, are correct?
(I) ##r_\text{income}=r_\text{time value}##
(II) ##r_\text{income}=r_\text{risk premium}##
(III) ##r_\text{capital}=r_\text{time value}##
(IV) ##r_\text{capital}=r_\text{risk premium}##
(V) ##r_\text{income}+r_\text{capital}=r_\text{time value}+r_\text{risk premium}##
Which of the equations are correct?
The CAPM can be used to find a business's expected opportunity cost of capital:
###r_i=r_f+β_i (r_m-r_f)###
What should be used as the risk free rate ##r_f##?
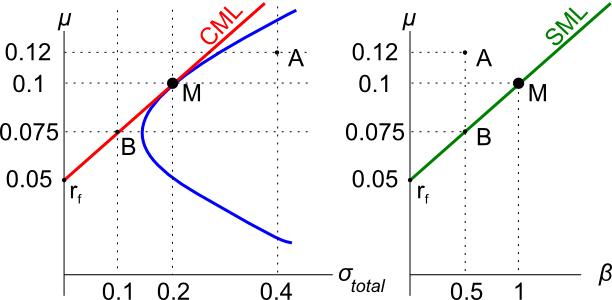
Assets A, B, M and ##r_f## are shown on the graphs above. Asset M is the market portfolio and ##r_f## is the risk free yield on government bonds. Which of the below statements is NOT correct?

Assets A, B, M and ##r_f## are shown on the graphs above. Asset M is the market portfolio and ##r_f## is the risk free yield on government bonds. Assume that investors can borrow and lend at the risk free rate. Which of the below statements is NOT correct?
Question 657 systematic and idiosyncratic risk, CAPM, no explanation
A stock's required total return will decrease when its:
A stock's total standard deviation of returns is 20% pa. The market portfolio's total standard deviation of returns is 15% pa. The beta of the stock is 0.8.
What is the stock's diversifiable standard deviation?
Question 778 CML, systematic and idiosyncratic risk, portfolio risk, CAPM
The capital market line (CML) is shown in the graph below. The total standard deviation is denoted by σ and the expected return is μ. Assume that markets are efficient so all assets are fairly priced.
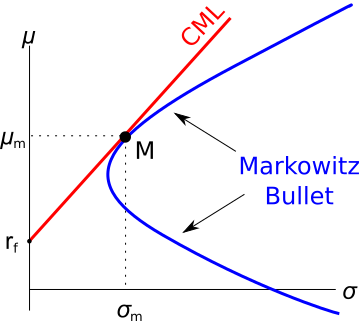
Which of the below statements is NOT correct?
Question 449 personal tax on dividends, classical tax system
A small private company has a single shareholder. This year the firm earned a $100 profit before tax. All of the firm's after tax profits will be paid out as dividends to the owner.
The corporate tax rate is 30% and the sole shareholder's personal marginal tax rate is 45%.
The United States' classical tax system applies because the company generates all of its income in the US and pays corporate tax to the Internal Revenue Service. The shareholder is also an American for tax purposes.
What will be the personal tax payable by the shareholder and the corporate tax payable by the company?
Question 691 continuously compounding rate, effective rate, continuously compounding rate conversion, no explanation
A bank quotes an interest rate of 6% pa with quarterly compounding. Note that another way of stating this rate is that it is an annual percentage rate (APR) compounding discretely every 3 months.
Which of the following statements about this rate is NOT correct? All percentages are given to 6 decimal places. The equivalent:
Question 707 continuously compounding rate, continuously compounding rate conversion
Convert a 10% effective annual rate ##(r_\text{eff annual})## into a continuously compounded annual rate ##(r_\text{cc annual})##. The equivalent continuously compounded annual rate is:
Question 708 continuously compounding rate, continuously compounding rate conversion
Convert a 10% continuously compounded annual rate ##(r_\text{cc annual})## into an effective annual rate ##(r_\text{eff annual})##. The equivalent effective annual rate is:
Question 710 continuously compounding rate, continuously compounding rate conversion
A continuously compounded monthly return of 1% ##(r_\text{cc monthly})## is equivalent to a continuously compounded annual return ##(r_\text{cc annual})## of:
Question 722 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
Here is a table of stock prices and returns. Which of the statements below the table is NOT correct?
| Price and Return Population Statistics | ||||
| Time | Prices | LGDR | GDR | NDR |
| 0 | 100 | |||
| 1 | 50 | -0.6931 | 0.5 | -0.5 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.6931 | 2 | 1 |
| Arithmetic average | 0 | 1.25 | 0.25 | |
| Arithmetic standard deviation | 0.9802 | 1.0607 | 1.0607 | |
Question 723 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
Here is a table of stock prices and returns. Which of the statements below the table is NOT correct?
| Price and Return Population Statistics | ||||
| Time | Prices | LGDR | GDR | NDR |
| 0 | 100 | |||
| 1 | 99 | -0.010050 | 0.990000 | -0.010000 |
| 2 | 180.40 | 0.600057 | 1.822222 | 0.822222 |
| 3 | 112.73 | 0.470181 | 0.624889 | 0.375111 |
| Arithmetic average | 0.0399 | 1.1457 | 0.1457 | |
| Arithmetic standard deviation | 0.4384 | 0.5011 | 0.5011 | |
Stock A and B's returns have a correlation of 0.3. Which statement is NOT correct?
All things remaining equal, the variance of a portfolio of two positively-weighted stocks rises as:
Diversification in a portfolio of two assets works best when the correlation between their returns is:
The following table shows a sample of historical total returns of shares in two different companies A and B.
| Stock Returns | ||
| Total effective annual returns | ||
| Year | ##r_A## | ##r_B## |
| 2007 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| 2008 | 0.04 | -0.2 |
| 2009 | -0.1 | -0.3 |
| 2010 | 0.18 | 0.5 |
What is the historical sample covariance (##\hat{\sigma}_{A,B}##) and correlation (##\rho_{A,B}##) of stock A and B's total effective annual returns?
All things remaining equal, the higher the correlation of returns between two stocks:
Question 559 variance, standard deviation, covariance, correlation
Which of the following statements about standard statistical mathematics notation is NOT correct?
The covariance and correlation of two stocks X and Y's annual returns are calculated over a number of years. The units of the returns are in percent per annum ##(\% pa)##.
What are the units of the covariance ##(\sigma_{X,Y})## and correlation ##(\rho_{X,Y})## of returns respectively?
Hint: Visit Wikipedia to understand the difference between percentage points ##(\text{pp})## and percent ##(\%)##.
What is the correlation of a variable X with a constant C?
The corr(X, C) or ##\rho_{X,C}## equals:
What is the covariance of a variable X with itself?
The cov(X, X) or ##\sigma_{X,X}## equals:
Which of the below statements about effective rates and annualised percentage rates (APR's) is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements about effective rates and annualised percentage rates (APR's) is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements is NOT equivalent to the yield on debt?
Assume that the debt being referred to is fairly priced, but do not assume that it's priced at par.
Question 539 debt terminology, fully amortising loan, bond pricing
A 'fully amortising' loan can also be called a:
You bought a house, primarily funded using a home loan from a bank. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 241 Miller and Modigliani, leverage, payout policy, diversification, NPV
One of Miller and Modigliani's (M&M's) important insights is that a firm's managers should not try to achieve a particular level of leverage in a world with zero taxes and perfect information since investors can make their own leverage. Therefore corporate capital structure policy is irrelevant since investors can achieve their own desired leverage at the personal level by borrowing or lending on their own.
This principal of 'home-made' or 'do-it-yourself' leverage can also be applied to other topics. Read the following statements to decide which are true:
(I) Payout policy: a firm's managers should not try to achieve a particular pattern of equity payout.
(II) Agency costs: a firm's managers should not try to minimise agency costs.
(III) Diversification: a firm's managers should not try to diversify across industries.
(IV) Shareholder wealth: a firm's managers should not try to maximise shareholders' wealth.
Which of the above statement(s) are true?
Question 572 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 573 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, liquidity premium theory, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 448 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system
A small private company has a single shareholder. This year the firm earned a $100 profit before tax. All of the firm's after tax profits will be paid out as dividends to the owner.
The corporate tax rate is 30% and the sole shareholder's personal marginal tax rate is 45%.
The Australian imputation tax system applies because the company generates all of its income in Australia and pays corporate tax to the Australian Tax Office. Therefore all of the company's dividends are fully franked. The sole shareholder is an Australian for tax purposes and can therefore use the franking credits to offset his personal income tax liability.
What will be the personal tax payable by the shareholder and the corporate tax payable by the company?
Question 469 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system, no explanation
A firm pays a fully franked cash dividend of $70 to one of its Australian shareholders who has a personal marginal tax rate of 45%. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What will be the shareholder's personal tax payable due to the dividend payment?
Question 494 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system
A firm pays a fully franked cash dividend of $100 to one of its Australian shareholders who has a personal marginal tax rate of 15%. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What will be the shareholder's personal tax payable due to the dividend payment?
Question 624 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system, no explanation
Which of the following statements about Australian franking credits is NOT correct? Franking credits:
Question 119 market efficiency, fundamental analysis, joint hypothesis problem
Your friend claims that by reading 'The Economist' magazine's economic news articles, she can identify shares that will have positive abnormal expected returns over the next 2 years. Assuming that her claim is true, which statement(s) are correct?
(i) Weak form market efficiency is broken.
(ii) Semi-strong form market efficiency is broken.
(iii) Strong form market efficiency is broken.
(iv) The asset pricing model used to measure the abnormal returns (such as the CAPM) is either wrong (mis-specification error) or is measured using the wrong inputs (data errors) so the returns may not be abnormal but rather fair for the level of risk.
Select the most correct response:
Fundamentalists who analyse company financial reports and news announcements (but who don't have inside information) will make positive abnormal returns if:
Question 658 CFFA, income statement, balance sheet, no explanation
To value a business's assets, the free cash flow of the firm (FCFF, also called CFFA) needs to be calculated. This requires figures from the firm's income statement and balance sheet. For what figures is the income statement needed? Note that the income statement is sometimes also called the profit and loss, P&L, or statement of financial performance.
Question 737 financial statement, balance sheet, income statement
Where can a publicly listed firm's book value of equity be found? It can be sourced from the company's:
Question 738 financial statement, balance sheet, income statement
Where can a private firm's market value of equity be found? It can be sourced from the company's:
Interest expense (IntExp) is an important part of a company's income statement (or 'profit and loss' or 'statement of financial performance').
How does an accountant calculate the annual interest expense of a fixed-coupon bond that has a liquid secondary market? Select the most correct answer:
Annual interest expense is equal to:
Here are the Net Income (NI) and Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) equations:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c)###
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+IntExp###
What is the formula for calculating annual interest expense (IntExp) which is used in the equations above?
Select one of the following answers. Note that D is the value of debt which is constant through time, and ##r_D## is the cost of debt.
The equations for Net Income (NI, also known as Earnings or Net Profit After Tax) and Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA, also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm) per year are:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c)###
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+IntExp###
For a firm with debt, what is the amount of the interest tax shield per year?
Which one of the following will increase the Cash Flow From Assets in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Question 237 WACC, Miller and Modigliani, interest tax shield
Which of the following discount rates should be the highest for a levered company? Ignore the costs of financial distress.
A company increases the proportion of debt funding it uses to finance its assets by issuing bonds and using the cash to repurchase stock, leaving assets unchanged.
Ignoring the costs of financial distress, which of the following statements is NOT correct:
Unrestricted negative gearing is allowed in Australia, New Zealand and Japan. Negative gearing laws allow income losses on investment properties to be deducted from a tax-payer's pre-tax personal income. Negatively geared investors benefit from this tax advantage. They also hope to benefit from capital gains which exceed the income losses.
For example, a property investor buys an apartment funded by an interest only mortgage loan. Interest expense is $2,000 per month. The rental payments received from the tenant living on the property are $1,500 per month. The investor can deduct this income loss of $500 per month from his pre-tax personal income. If his personal marginal tax rate is 46.5%, this saves $232.5 per month in personal income tax.
The advantage of negative gearing is an example of the benefits of:
Use the below information to value a levered company with constant annual perpetual cash flows from assets. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now, so a perpetuity can be used to value this firm. Both the operating and firm free cash flows are constant (but not equal to each other).
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}## | $48.5m | Operating free cash flow |
| ##\text{FFCF or CFFA}## | $50m | Firm free cash flow or cash flow from assets |
| ##g## | 0% pa | Growth rate of OFCF and FFCF |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{BeforeTax}## | 10% pa | Weighted average cost of capital before tax |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{AfterTax}## | 9.7% pa | Weighted average cost of capital after tax |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 5% pa | Cost of debt |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 11.25% pa | Cost of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 20% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
What is the value of the levered firm including interest tax shields?