Government bonds currently have a return of 5%. A stock has a beta of 2 and the market return is 7%. What is the expected return of the stock?
A 10 year Australian government bond was just issued at par with a yield of 3.9% pa. The fixed coupon payments are semi-annual. The bond has a face value of $1,000.
Six months later, just after the first coupon is paid, the yield of the bond decreases to 3.65% pa. What is the bond's new price?
Question 385 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
A risky firm will last for one period only (t=0 to 1), then it will be liquidated. So it's assets will be sold and the debt holders and equity holders will be paid out in that order. The firm has the following quantities:
##V## = Market value of assets.
##E## = Market value of (levered) equity.
##D## = Market value of zero coupon bonds.
##F_1## = Total face value of zero coupon bonds which is promised to be paid in one year.

The levered equity graph above contains bold labels a to e. Which of the following statements about those labels is NOT correct?
Question 418 capital budgeting, NPV, interest tax shield, WACC, CFFA, CAPM
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $8m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $8m | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | 0 | |
| Unit sales per year | 4m | |
| Sale price per unit | $10 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $5 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $2m | |
| Interest expense in first year (at t=1) | $0.562m | |
| Corporate tax rate | 30% | |
| Government treasury bond yield | 5% | |
| Bank loan debt yield | 9% | |
| Market portfolio return | 10% | |
| Covariance of levered equity returns with market | 0.32 | |
| Variance of market portfolio returns | 0.16 | |
| Firm's and project's debt-to-equity ratio | 50% | |
Notes
- Due to the project, current assets will increase by $6m now (t=0) and fall by $6m at the end (t=1). Current liabilities will not be affected.
Assumptions
- The debt-to-equity ratio will be kept constant throughout the life of the project. The amount of interest expense at the end of each period has been correctly calculated to maintain this constant debt-to-equity ratio.
- Millions are represented by 'm'.
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The project is undertaken by a firm, not an individual.
What is the net present value (NPV) of the project?
Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| Project Data | |
| Project life | 2 years |
| Initial investment in equipment | $8m |
| Depreciation of equipment per year for tax purposes | $3m |
| Unit sales per year | 10m |
| Sale price per unit | $9 |
| Variable cost per unit | $4 |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $2m |
| Tax rate | 30% |
Note 1: Due to the project, the firm will have to purchase $40m of inventory initially (at t=0). Half of this inventory will be sold at t=1 and the other half at t=2.
Note 2: The equipment will have a book value of $2m at the end of the project for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $1m when it is sold. Assume that the full capital loss is tax-deductible and taxed at the full corporate tax rate.
Note 3: The project will be fully funded by equity which investors will expect to pay dividends totaling $10m at the end of each year.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero, one and two. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Question 626 cross currency interest rate parity, foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate
The Australian cash rate is expected to be 2% pa over the next one year, while the Japanese cash rate is expected to be 0% pa, both given as nominal effective annual rates. The current exchange rate is 100 JPY per AUD.
What is the implied 1 year forward foreign exchange rate?
Which of the below formulas gives the profit ##(\pi)## from being short a call option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T##, the exercise price be ##X_T## and the option price be ##f_{LC,0}##. Note that ##S_T##, ##X_T## and ##f_{LC,0}## are all positive numbers.
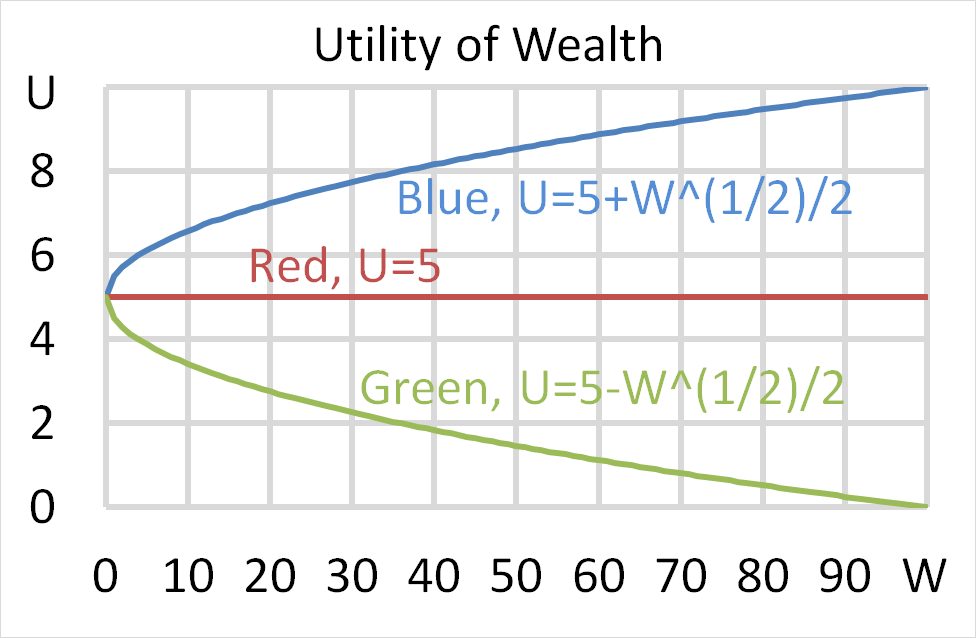
Question 700 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 903 option, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing, option on stock index
A six month European-style call option on the S&P500 stock index has a strike price of 2800 points.
The underlying S&P500 stock index currently trades at 2700 points, has a continuously compounded dividend yield of 2% pa and a standard deviation of continuously compounded returns of 25% pa.
The risk-free interest rate is 5% pa continuously compounded.
Use the Black-Scholes-Merton formula to calculate the option price. The call option price now is: