The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of the project?
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 121 |
What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of the project detailed in the table below?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time. All answers are given as effective annual rates.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 121 |
If a project's net present value (NPV) is zero, then its internal rate of return (IRR) will be:
The required return of a building project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time.
The building firm is just about to start the project and the client has signed the contract. Initially the firm will pay $100 to the sub-contractors to carry out the work and then will receive an $11 payment from the client in one year and $121 when the project is finished in 2 years. Ignore credit risk.
But the building company is considering selling the project to a competitor at different points in time and is pondering the minimum price that they should sell it for.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 11 |
| 2 | 121 |
Which of the below statements is NOT correct? The project is worth:
The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the payback period of the project in years?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are received smoothly over the year. So the $121 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 11 |
| 2 | 121 |
A project has the following cash flows:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 500 |
What is the payback period of the project in years?
Normally cash flows are assumed to happen at the given time. But here, assume that the cash flows are received smoothly over the year. So the $500 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2.
The below graph shows a project's net present value (NPV) against its annual discount rate.
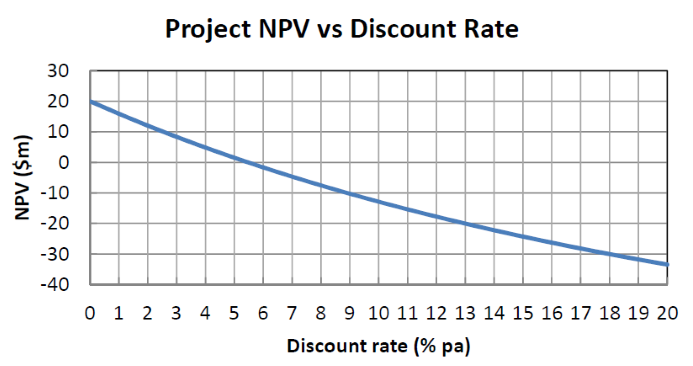
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume an equal amount now (t=0), in one year (t=1) and in two years (t=2), and still have $50,000 in the bank after that (t=2).
How much can you consume at each time?
The saying "buy low, sell high" suggests that investors should make a:
Total cash flows can be broken into income and capital cash flows. What is the name given to the income cash flow from owning shares?
An asset's total expected return over the next year is given by:
###r_\text{total} = \dfrac{c_1+p_1-p_0}{p_0} ###
Where ##p_0## is the current price, ##c_1## is the expected income in one year and ##p_1## is the expected price in one year. The total return can be split into the income return and the capital return.
Which of the following is the expected capital return?
A share was bought for $30 (at t=0) and paid its annual dividend of $6 one year later (at t=1).
Just after the dividend was paid, the share price fell to $27 (at t=1). What were the total, capital and income returns given as effective annual rates?
The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}## , ##r_\text{capital}## , ##r_\text{dividend}##.
One and a half years ago Frank bought a house for $600,000. Now it's worth only $500,000, based on recent similar sales in the area.
The expected total return on Frank's residential property is 7% pa.
He rents his house out for $1,600 per month, paid in advance. Every 12 months he plans to increase the rental payments.
The present value of 12 months of rental payments is $18,617.27.
The future value of 12 months of rental payments one year in the future is $19,920.48.
What is the expected annual rental yield of the property? Ignore the costs of renting such as maintenance, real estate agent fees and so on.
Question 542 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to double every 10 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
Question 278 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Imagine that the interest rate on your savings account was 1% per year and inflation was 2% per year.
Question 993 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
In February 2020, the RBA cash rate was 0.75% pa and the Australian CPI inflation rate was 1.8% pa.
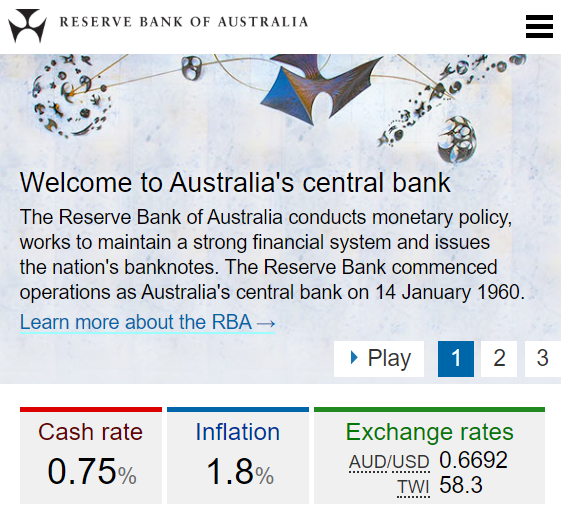
You currently have $100 in the bank which pays a 0.75% pa interest rate.
Apples currently cost $1 each at the shop and inflation is 1.8% pa which is the expected growth rate in the apple price.
This information is summarised in the table below, with some parts missing that correspond to the answer options. All rates are given as effective annual rates. Note that when payments are not specified as real, as in this question, they're conventionally assumed to be nominal.
| Wealth in Dollars and Apples | ||||
| Time (year) | Bank account wealth ($) | Apple price ($) | Wealth in apples | |
| 0 | 100 | 1 | 100 | |
| 1 | 100.75 | 1.018 | (a) | |
| 2 | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? Your:
Question 407 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
A stock has a real expected total return of 7% pa and a real expected capital return of 2% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What is the nominal expected total return, capital return and dividend yield? The answers below are given in the same order.
Question 525 income and capital returns, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation
Which of the following statements about cash in the form of notes and coins is NOT correct? Assume that inflation is positive.
Notes and coins:
Katya offers to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years (t=1,2,3,4,5) if you pay her $50 now (t=0). You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. Ignore credit risk.
Your friend overheard that you need some cash and asks if you would like to borrow some money. She can lend you $5,000 now (t=0), and in return she wants you to pay her back $1,000 in two years (t=2) and every year after that for the next 5 years, so there will be 6 payments of $1,000 from t=2 to t=7 inclusive.
What is the net present value (NPV) of borrowing from your friend?
Assume that banks loan funds at interest rates of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Discounted cash flow (DCF) valuation prices assets by finding the present value of the asset's future cash flows. The single cash flow, annuity, and perpetuity equations are very useful for this.
Which of the following equations is the 'perpetuity with growth' equation?
A stock is expected to pay its next dividend of $1 in one year. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. So the first dividend of $1 will be in one year, the year after that $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1), and a year later $1.0404 (=1*(1+0.02)^2) and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
For a price of $13, Carla will sell you a share paying a dividend of $1 in one year and every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
The perpetuity with growth formula, also known as the dividend discount model (DDM) or Gordon growth model, is appropriate for valuing a company's shares. ##P_0## is the current share price, ##C_1## is next year's expected dividend, ##r## is the total required return and ##g## is the expected growth rate of the dividend.
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
The below graph shows the expected future price path of the company's shares. Which of the following statements about the graph is NOT correct?
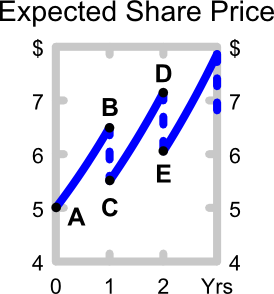
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
###P_0=\frac{d_1}{r-g}###
A stock pays dividends annually. It just paid a dividend, but the next dividend (##d_1##) will be paid in one year.
According to the DDM, what is the correct formula for the expected price of the stock in 2.5 years?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### P_{0} = \frac{C_1}{r_{\text{eff}} - g_{\text{eff}}} ###
What would you call the expression ## C_1/P_0 ##?
A home loan company advertises an interest rate of 6% pa, payable monthly. Which of the following statements about the interest rate is NOT correct? All rates are given to four decimal places.
Which of the below statements about effective rates and annualised percentage rates (APR's) is NOT correct?
A credit card offers an interest rate of 18% pa, compounding monthly.
Find the effective monthly rate, effective annual rate and the effective daily rate. Assume that there are 365 days in a year.
All answers are given in the same order:
### r_\text{eff monthly} , r_\text{eff yearly} , r_\text{eff daily} ###
Calculate the effective annual rates of the following three APR's:
- A credit card offering an interest rate of 18% pa, compounding monthly.
- A bond offering a yield of 6% pa, compounding semi-annually.
- An annual dividend-paying stock offering a return of 10% pa compounding annually.
All answers are given in the same order:
##r_\text{credit card, eff yrly}##, ##r_\text{bond, eff yrly}##, ##r_\text{stock, eff yrly}##
You want to buy an apartment priced at $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $30,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $270,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 12% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments? Remember that mortgage loan payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
You want to buy an apartment worth $400,000. You have saved a deposit of $80,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $320,000 as a fully amortising mortgage loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $2,000 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 5 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change.
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $1,500 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 10 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change.
You just agreed to a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $2,500. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 10 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change. The below choices are given in the same order.
You want to buy an apartment priced at $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $30,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $270,000 as an interest only loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 12% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments? Remember that mortgage payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
You just borrowed $400,000 in the form of a 25 year interest-only mortgage with monthly payments of $3,000 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
You actually plan to pay more than the required interest payment. You plan to pay $3,300 in mortgage payments every month, which your mortgage lender allows. These extra payments will reduce the principal and the minimum interest payment required each month.
At the maturity of the mortgage, what will be the principal? That is, after the last (300th) interest payment of $3,300 in 25 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage?
You want to buy an apartment worth $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $60,000.
The bank has agreed to lend you $240,000 as an interest only mortgage loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
Question 239 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, interest only loan
A bank grants a borrower an interest-only residential mortgage loan with a very large 50% deposit and a nominal interest rate of 6% that is not expected to change. Assume that inflation is expected to be a constant 2% pa over the life of the loan. Ignore credit risk.
From the bank's point of view, what is the long term expected nominal capital return of the loan asset?
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid annually. So there's only one coupon per year, paid in arrears every year.
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid semi-annually. So there are two coupons per year, paid in arrears every six months.
"Buy low, sell high" is a phrase commonly heard in financial markets. It states that traders should try to buy assets at low prices and sell at high prices.
Traders in the fixed-coupon bond markets often quote promised bond yields rather than prices. Fixed-coupon bond traders should try to:
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same US company. Both bonds yield 10% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X and Y's coupon rates are 8 and 12% pa respectively. Which of the following statements is true?
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A bond maturing in 10 years has a coupon rate of 4% pa, paid semi-annually. The bond's yield is currently 6% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. What is its price?
A three year bond has a fixed coupon rate of 12% pa, paid semi-annually. The bond's yield is currently 6% pa. The face value is $100. What is its price?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at a discount?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at a premium?
An investor bought two fixed-coupon bonds issued by the same company, a zero-coupon bond and a 7% pa semi-annual coupon bond. Both bonds have a face value of $1,000, mature in 10 years, and had a yield at the time of purchase of 8% pa.
A few years later, yields fell to 6% pa. Which of the following statements is correct? Note that a capital gain is an increase in price.
In these tough economic times, central banks around the world have cut interest rates so low that they are practically zero. In some countries, government bond yields are also very close to zero.
A three year government bond with a face value of $100 and a coupon rate of 2% pa paid semi-annually was just issued at a yield of 0%. What is the price of the bond?
A 10 year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 6% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 8% pa, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
Below are some statements about loans and bonds. The first descriptive sentence is correct. But one of the second sentences about the loans' or bonds' prices is not correct. Which statement is NOT correct? Assume that interest rates are positive.
Note that coupons or interest payments are the periodic payments made throughout a bond or loan's life. The face or par value of a bond or loan is the amount paid at the end when the debt matures.
Question 143 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds:
- A 6-month zero coupon bond at a yield of 6% pa, and
- A 12 month zero coupon bond at a yield of 7% pa.
What is the company's forward rate from 6 to 12 months? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 96 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds paying semi-annual coupons:
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
You really want to go on a back packing trip to Europe when you finish university. Currently you have $1,500 in the bank. Bank interest rates are 8% pa, given as an APR compounding per month. If the holiday will cost $2,000, how long will it take for your bank account to reach that amount?
A young lady is trying to decide if she should attend university or not.
The young lady's parents say that she must attend university because otherwise all of her hard work studying and attending school during her childhood was a waste.
What's the correct way to classify this item from a capital budgeting perspective when trying to decide whether to attend university?
The hard work studying at school in her childhood should be classified as:
What is the net present value (NPV) of undertaking a full-time Australian undergraduate business degree as an Australian citizen? Only include the cash flows over the duration of the degree, ignore any benefits or costs of the degree after it's completed.
Assume the following:
- The degree takes 3 years to complete and all students pass all subjects.
- There are 2 semesters per year and 4 subjects per semester.
- University fees per subject per semester are $1,277, paid at the start of each semester. Fees are expected to remain constant in real terms for the next 3 years.
- There are 52 weeks per year.
- The first semester is just about to start (t=0). The first semester lasts for 19 weeks (t=0 to 19).
- The second semester starts immediately afterwards (t=19) and lasts for another 19 weeks (t=19 to 38).
- The summer holidays begin after the second semester ends and last for 14 weeks (t=38 to 52). Then the first semester begins the next year, and so on.
- Working full time at the grocery store instead of studying full-time pays $20/hr and you can work 35 hours per week. Wages are paid at the end of each week and are expected to remain constant in real terms.
- Full-time students can work full-time during the summer holiday at the grocery store for the same rate of $20/hr for 35 hours per week.
- The discount rate is 9.8% pa. All rates and cash flows are real. Inflation is expected to be 3% pa. All rates are effective annual.
The NPV of costs from undertaking the university degree is:
Find Sidebar Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Sidebar Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 405 | |
| COGS | 100 | |
| Depreciation | 34 | |
| Rent expense | 22 | |
| Interest expense | 39 | |
| Taxable Income | 210 | |
| Taxes at 30% | 63 | |
| Net income | 147 | |
| Sidebar Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Cash | 0 | 0 |
| Inventory | 70 | 50 |
| Trade debtors | 11 | 16 |
| Rent paid in advance | 4 | 3 |
| PPE | 700 | 680 |
| Total assets | 785 | 749 |
| Trade creditors | 11 | 19 |
| Bond liabilities | 400 | 390 |
| Contributed equity | 220 | 220 |
| Retained profits | 154 | 120 |
| Total L and OE | 785 | 749 |
Note: All figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
The cash flow from assets was:
Why is Capital Expenditure (CapEx) subtracted in the Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) formula?
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###
A firm has forecast its Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) for this year and management is worried that it is too low. Which one of the following actions will lead to a higher CFFA for this year (t=0 to 1)? Only consider cash flows this year. Do not consider cash flows after one year, or the change in the NPV of the firm. Consider each action in isolation.
Over the next year, the management of an unlevered company plans to:
- Achieve firm free cash flow (FFCF or CFFA) of $1m.
- Pay dividends of $1.8m
- Complete a $1.3m share buy-back.
- Spend $0.8m on new buildings without buying or selling any other fixed assets. This capital expenditure is included in the CFFA figure quoted above.
Assume that:
- All amounts are received and paid at the end of the year so you can ignore the time value of money.
- The firm has sufficient retained profits to pay the dividend and complete the buy back.
- The firm plans to run a very tight ship, with no excess cash above operating requirements currently or over the next year.
How much new equity financing will the company need? In other words, what is the value of new shares that will need to be issued?
Over the next year, the management of an unlevered company plans to:
- Make $5m in sales, $1.9m in net income and $2m in equity free cash flow (EFCF).
- Pay dividends of $1m.
- Complete a $1.3m share buy-back.
Assume that:
- All amounts are received and paid at the end of the year so you can ignore the time value of money.
- The firm has sufficient retained profits to legally pay the dividend and complete the buy back.
- The firm plans to run a very tight ship, with no excess cash above operating requirements currently or over the next year.
How much new equity financing will the company need? In other words, what is the value of new shares that will need to be issued?
Your friend just bought a house for $400,000. He financed it using a $320,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $80,000.
In the context of residential housing and mortgages, the 'equity' tied up in the value of a person's house is the value of the house less the value of the mortgage. So the initial equity your friend has in his house is $80,000. Let this amount be E, let the value of the mortgage be D and the value of the house be V. So ##V=D+E##.
If house prices suddenly fall by 10%, what would be your friend's percentage change in equity (E)? Assume that the value of the mortgage is unchanged and that no income (rent) was received from the house during the short time over which house prices fell.
Remember:
### r_{0\rightarrow1}=\frac{p_1-p_0+c_1}{p_0} ###
where ##r_{0-1}## is the return (percentage change) of an asset with price ##p_0## initially, ##p_1## one period later, and paying a cash flow of ##c_1## at time ##t=1##.
Your friend just bought a house for $1,000,000. He financed it using a $900,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $100,000.
In the context of residential housing and mortgages, the 'equity' or 'net wealth' tied up in a house is the value of the house less the value of the mortgage loan. Assuming that your friend's only asset is his house, his net wealth is $100,000.
If house prices suddenly fall by 15%, what would be your friend's percentage change in net wealth?
Assume that:
- No income (rent) was received from the house during the short time over which house prices fell.
- Your friend will not declare bankruptcy, he will always pay off his debts.
One year ago you bought $100,000 of shares partly funded using a margin loan. The margin loan size was $70,000 and the other $30,000 was your own wealth or 'equity' in the share assets.
The interest rate on the margin loan was 7.84% pa.
Over the year, the shares produced a dividend yield of 4% pa and a capital gain of 5% pa.
What was the total return on your wealth? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and dividends) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates above are effective annual rates.
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
Here are the Net Income (NI) and Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) equations:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c)###
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+IntExp###
What is the formula for calculating annual interest expense (IntExp) which is used in the equations above?
Select one of the following answers. Note that D is the value of debt which is constant through time, and ##r_D## is the cost of debt.
Interest expense (IntExp) is an important part of a company's income statement (or 'profit and loss' or 'statement of financial performance').
How does an accountant calculate the annual interest expense of a fixed-coupon bond that has a liquid secondary market? Select the most correct answer:
Annual interest expense is equal to:
Which one of the following will increase the Cash Flow From Assets in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Which one of the following will decrease net income (NI) but increase cash flow from assets (CFFA) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - ΔNWC+IntExp###A manufacturing company is considering a new project in the more risky services industry. The cash flows from assets (CFFA) are estimated for the new project, with interest expense excluded from the calculations. To get the levered value of the project, what should these unlevered cash flows be discounted by?
Assume that the manufacturing firm has a target debt-to-assets ratio that it sticks to.
A retail furniture company buys furniture wholesale and distributes it through its retail stores. The owner believes that she has some good ideas for making stylish new furniture. She is considering a project to buy a factory and employ workers to manufacture the new furniture she's designed. Furniture manufacturing has more systematic risk than furniture retailing.
Her furniture retailing firm's after-tax WACC is 20%. Furniture manufacturing firms have an after-tax WACC of 30%. Both firms are optimally geared. Assume a classical tax system.
Which method(s) will give the correct valuation of the new furniture-making project? Select the most correct answer.
The US firm Google operates in the online advertising business. In 2011 Google bought Motorola Mobility which manufactures mobile phones.
Assume the following:
- Google had a 10% after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC) before it bought Motorola.
- Motorola had a 20% after-tax WACC before it merged with Google.
- Google and Motorola have the same level of gearing.
- Both companies operate in a classical tax system.
You are a manager at Motorola. You must value a project for making mobile phones. Which method(s) will give the correct valuation of the mobile phone manufacturing project? Select the most correct answer.
The mobile phone manufacturing project's:
There are many ways to calculate a firm's free cash flow (FFCF), also called cash flow from assets (CFFA). Some include the annual interest tax shield in the cash flow and some do not.
Which of the below FFCF formulas include the interest tax shield in the cash flow?
###(1) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp### ###(2) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp.(1-t_c)### ###(3) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c )+ Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(4) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c) + Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(5) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(6) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(7) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(8) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c### ###(9) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(10) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c###The formulas for net income (NI also called earnings), EBIT and EBITDA are given below. Assume that depreciation and amortisation are both represented by 'Depr' and that 'FC' represents fixed costs such as rent.
###NI=(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###EBIT=Rev - COGS - FC-Depr### ###EBITDA=Rev - COGS - FC### ###Tax =(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).t_c= \dfrac{NI.t_c}{1-t_c}###A method commonly seen in textbooks for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is the following:
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp)(1-t_c) + \\ &\space\space\space+ Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp(1-t_c) \\ \end{aligned}###
One formula for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to use earnings before interest and tax (EBIT).
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (EBIT)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ \end{aligned} \\###
One method for calculating a firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to ignore interest expense. That is, pretend that interest expense ##(IntExp)## is zero:
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - 0)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC - 0\\ \end{aligned}###
One formula for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to use net operating profit after tax (NOPAT).
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= NOPAT + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC \\ \end{aligned} \\###
Which of the following equations is NOT equal to the total return of an asset?
Let ##p_0## be the current price, ##p_1## the expected price in one year and ##c_1## the expected income in one year.
Total cash flows can be broken into income and capital cash flows.
What is the name given to the cash flow generated from selling shares at a higher price than they were bought?
Question 543 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to triple every 5 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
A newly floated farming company is financed with senior bonds, junior bonds, cumulative non-voting preferred stock and common stock. The new company has no retained profits and due to floods it was unable to record any revenues this year, leading to a loss. The firm is not bankrupt yet since it still has substantial contributed equity (same as paid-up capital).
On which securities must it pay interest or dividend payments in this terrible financial year?
Question 452 limited liability, expected and historical returns
What is the lowest and highest expected share price and expected return from owning shares in a company over a finite period of time?
Let the current share price be ##p_0##, the expected future share price be ##p_1##, the expected future dividend be ##d_1## and the expected return be ##r##. Define the expected return as:
##r=\dfrac{p_1-p_0+d_1}{p_0} ##
The answer choices are stated using inequalities. As an example, the first answer choice "(a) ##0≤p<∞## and ##0≤r< 1##", states that the share price must be larger than or equal to zero and less than positive infinity, and that the return must be larger than or equal to zero and less than one.
A young lady is trying to decide if she should attend university. Her friends say that she should go to university because she is more likely to meet a clever young man than if she begins full time work straight away.
What's the correct way to classify this item from a capital budgeting perspective when trying to find the Net Present Value of going to university rather than working?
The opportunity to meet a desirable future spouse should be classified as:
A man is thinking about taking a day off from his casual painting job to relax.
He just woke up early in the morning and he's about to call his boss to say that he won't be coming in to work.
But he's thinking about the hours that he could work today (in the future) which are:
A man has taken a day off from his casual painting job to relax.
It's the end of the day and he's thinking about the hours that he could have spent working (in the past) which are now:
Find Candys Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Candys Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 200 | |
| COGS | 50 | |
| Operating expense | 10 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Interest expense | 10 | |
| Income before tax | 110 | |
| Tax at 30% | 33 | |
| Net income | 77 | |
| Candys Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets | 220 | 180 |
| PPE | ||
| Cost | 300 | 340 |
| Accumul. depr. | 60 | 40 |
| Carrying amount | 240 | 300 |
| Total assets | 460 | 480 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | 175 | 190 |
| Non-current liabilities | 135 | 130 |
| Owners' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | 50 | 60 |
| Contributed equity | 100 | 100 |
| Total L and OE | 460 | 480 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Find Ching-A-Lings Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Ching-A-Lings Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 100 | |
| COGS | 20 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Rent expense | 11 | |
| Interest expense | 19 | |
| Taxable Income | 30 | |
| Taxes at 30% | 9 | |
| Net income | 21 | |
| Ching-A-Lings Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Inventory | 49 | 38 |
| Trade debtors | 14 | 2 |
| Rent paid in advance | 5 | 5 |
| PPE | 400 | 400 |
| Total assets | 468 | 445 |
| Trade creditors | 4 | 10 |
| Bond liabilities | 200 | 190 |
| Contributed equity | 145 | 145 |
| Retained profits | 119 | 100 |
| Total L and OE | 468 | 445 |
Note: All figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
The cash flow from assets was:
To value a business's assets, the free cash flow of the firm (FCFF, also called CFFA) needs to be calculated. This requires figures from the firm's income statement and balance sheet. For what figures is the balance sheet needed? Note that the balance sheet is sometimes also called the statement of financial position.
Which one of the following will decrease net income (NI) but increase cash flow from assets (CFFA) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI = (Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###Which one of the following will have no effect on net income (NI) but decrease cash flow from assets (CFFA or FFCF) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - ΔNWC+IntExp###Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| One Year Mining Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in building mine and equipment | $9m | |
| Depreciation of mine and equipment over the year | $8m | |
| Kilograms of gold mined at end of year | 1,000 | |
| Sale price per kilogram | $0.05m | |
| Variable cost per kilogram | $0.03m | |
| Before-tax cost of closing mine at end of year | $4m | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
Note 1: Due to the project, the firm also anticipates finding some rare diamonds which will give before-tax revenues of $1m at the end of the year.
Note 2: The land that will be mined actually has thermal springs and a family of koalas that could be sold to an eco-tourist resort for an after-tax amount of $3m right now. However, if the mine goes ahead then this natural beauty will be destroyed.
Note 3: The mining equipment will have a book value of $1m at the end of the year for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $2.5m when it is sold.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero and one. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m), with the first cash flow at time zero, and the second at time one.
A credit card company advertises an interest rate of 18% pa, payable monthly. Which of the following statements about the interest rate is NOT correct? All rates are given to four decimal places.
Which of the following statements about effective rates and annualised percentage rates (APR's) is NOT correct?
A European bond paying annual coupons of 6% offers a yield of 10% pa.
Convert the yield into an effective monthly rate, an effective annual rate and an effective daily rate. Assume that there are 365 days in a year.
All answers are given in the same order:
### r_\text{eff, monthly} , r_\text{eff, yearly} , r_\text{eff, daily} ###
You want to buy an apartment priced at $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $1,500 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
To your surprise, you can actually afford to pay $2,000 per month and your mortgage allows early repayments without fees. If you maintain these higher monthly payments, how long will it take to pay off your mortgage?
Use the below information to value a levered company with constant annual perpetual cash flows from assets. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now, so a perpetuity can be used to value this firm. Both the operating and firm free cash flows are constant (but not equal to each other).
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}## | $48.5m | Operating free cash flow |
| ##\text{FFCF or CFFA}## | $50m | Firm free cash flow or cash flow from assets |
| ##g## | 0% pa | Growth rate of OFCF and FFCF |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{BeforeTax}## | 10% pa | Weighted average cost of capital before tax |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{AfterTax}## | 9.7% pa | Weighted average cost of capital after tax |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 5% pa | Cost of debt |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 11.25% pa | Cost of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 20% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
What is the value of the levered firm including interest tax shields?
A firm has a debt-to-equity ratio of 60%. What is its debt-to-assets ratio?
In the home loan market, the acronym LVR stands for Loan to Valuation Ratio. If you bought a house worth one million dollars, partly funded by an $800,000 home loan, then your LVR was 80%. The LVR is equivalent to which of the following ratios?
There are a number of ways that assets can be depreciated. Generally the government's tax office stipulates a certain method.
But if it didn't, what would be the ideal way to depreciate an asset from the perspective of a businesses owner?
The hardest and most important aspect of business project valuation is the estimation of the:
Question 658 CFFA, income statement, balance sheet, no explanation
To value a business's assets, the free cash flow of the firm (FCFF, also called CFFA) needs to be calculated. This requires figures from the firm's income statement and balance sheet. For what figures is the income statement needed? Note that the income statement is sometimes also called the profit and loss, P&L, or statement of financial performance.
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 50%. The firm then issues a large amount of debt to raise money for new projects of similar market risk to the company's existing projects. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is correct?
Question 241 Miller and Modigliani, leverage, payout policy, diversification, NPV
One of Miller and Modigliani's (M&M's) important insights is that a firm's managers should not try to achieve a particular level of leverage in a world with zero taxes and perfect information since investors can make their own leverage. Therefore corporate capital structure policy is irrelevant since investors can achieve their own desired leverage at the personal level by borrowing or lending on their own.
This principal of 'home-made' or 'do-it-yourself' leverage can also be applied to other topics. Read the following statements to decide which are true:
(I) Payout policy: a firm's managers should not try to achieve a particular pattern of equity payout.
(II) Agency costs: a firm's managers should not try to minimise agency costs.
(III) Diversification: a firm's managers should not try to diversify across industries.
(IV) Shareholder wealth: a firm's managers should not try to maximise shareholders' wealth.
Which of the above statement(s) are true?
The following table shows a sample of historical total returns of shares in two different companies A and B.
| Stock Returns | ||
| Total effective annual returns | ||
| Year | ##r_A## | ##r_B## |
| 2007 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| 2008 | 0.04 | -0.2 |
| 2009 | -0.1 | -0.3 |
| 2010 | 0.18 | 0.5 |
What is the historical sample covariance (##\hat{\sigma}_{A,B}##) and correlation (##\rho_{A,B}##) of stock A and B's total effective annual returns?
Stock A and B's returns have a correlation of 0.3. Which statement is NOT correct?
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Correlation | Dollars invested |
||
| A | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 60 | ||
| B | 0.2 | 0.6 | 140 | |||
What is the expected return of the above portfolio?
Question 282 expected and historical returns, income and capital returns
You're the boss of an investment bank's equities research team. Your five analysts are each trying to find the expected total return over the next year of shares in a mining company. The mining firm:
- Is regarded as a mature company since it's quite stable in size and was floated around 30 years ago. It is not a high-growth company;
- Share price is very sensitive to changes in the price of the market portfolio, economic growth, the exchange rate and commodities prices. Due to this, its standard deviation of total returns is much higher than that of the market index;
- Experienced tough times in the last 10 years due to unexpected falls in commodity prices.
- Shares are traded in an active liquid market.
- The analysts' source data is correct and true, but their inferences might be wrong;
- All returns and yields are given as effective annual nominal rates.
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Covariance ##(\sigma_{A,B})## | Beta | Dollars invested |
|
| A | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.12 | 0.5 | 40 | |
| B | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 80 | ||
What is the standard deviation (not variance) of the above portfolio? Note that the stocks' covariance is given, not correlation.
Which of the following statements about short-selling is NOT true?
Question 558 portfolio weights, portfolio return, short selling
An investor wants to make a portfolio of two stocks A and B with a target expected portfolio return of 16% pa.
- Stock A has an expected return of 8% pa.
- Stock B has an expected return of 12% pa.
What portfolio weights should the investor have in stocks A and B respectively?
What is the covariance of a variable X with itself?
The cov(X, X) or ##\sigma_{X,X}## equals:
In 2014 the median starting salaries of male and female Australian bachelor degree accounting graduates aged less than 25 years in their first full-time industry job was $50,000 before tax, according to Graduate Careers Australia. See page 9 of this report. Personal income tax rates published by the Australian Tax Office are reproduced for the 2014-2015 financial year in the table below.
| Taxable income | Tax on this income |
|---|---|
| 0 – $18,200 | Nil |
| $18,201 – $37,000 | 19c for each $1 over $18,200 |
| $37,001 – $80,000 | $3,572 plus 32.5c for each $1 over $37,000 |
| $80,001 – $180,000 | $17,547 plus 37c for each $1 over $80,000 |
| $180,001 and over | $54,547 plus 45c for each $1 over $180,000 |
The above rates do not include the Medicare levy of 2%. Exclude the Medicare levy from your calculations
How much personal income tax would you have to pay per year if you earned $50,000 per annum before-tax?
Question 494 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system
A firm pays a fully franked cash dividend of $100 to one of its Australian shareholders who has a personal marginal tax rate of 15%. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What will be the shareholder's personal tax payable due to the dividend payment?
Due to floods overseas, there is a cut in the supply of the mineral iron ore and its price increases dramatically. An Australian iron ore mining company therefore expects a large but temporary increase in its profit and cash flows. The mining company does not have any positive NPV projects to begin, so what should it do? Select the most correct answer.
A pharmaceutical firm has just discovered a valuable new drug. So far the news has been kept a secret.
The net present value of making and commercialising the drug is $200 million, but $600 million of bonds will need to be issued to fund the project and buy the necessary plant and equipment.
The firm will release the news of the discovery and bond raising to shareholders simultaneously in the same announcement. The bonds will be issued shortly after.
Once the announcement is made and the bonds are issued, what is the expected increase in the value of the firm's assets (ΔV), market capitalisation of debt (ΔD) and market cap of equity (ΔE)?
The triangle symbol is the Greek letter capital delta which means change or increase in mathematics.
Ignore the benefit of interest tax shields from having more debt.
Remember: ##ΔV = ΔD+ΔE##
Question 513 stock split, reverse stock split, stock dividend, bonus issue, rights issue
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A company conducts a 4 for 3 stock split. What is the percentage change in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order.
Question 566 capital structure, capital raising, rights issue, on market repurchase, dividend, stock split, bonus issue
A company's share price fell by 20% and its number of shares rose by 25%. Assume that there are no taxes, no signalling effects and no transaction costs.
Which one of the following corporate events may have happened?
In mid 2009 the listed mining company Rio Tinto announced a 21-for-40 renounceable rights issue. Below is the chronology of events:
- 04/06/2009. Share price opens at $69.00 and closes at $66.90.
- 05/06/2009. 21-for-40 rights issue announced at a subscription price of $28.29.
- 16/06/2009. Last day that shares trade cum-rights. Share price opens at $76.40 and closes at $75.50.
- 17/06/2009. Shares trade ex-rights. Rights trading commences.
All things remaining equal, what would you expect Rio Tinto's stock price to open at on the first day that it trades ex-rights (17/6/2009)? Ignore the time value of money since time is negligibly short. Also ignore taxes.
Question 455 income and capital returns, payout policy, DDM, market efficiency
A fairly priced unlevered firm plans to pay a dividend of $1 next year (t=1) which is expected to grow by 3% pa every year after that. The firm's required return on equity is 8% pa.
The firm is thinking about reducing its future dividend payments by 10% so that it can use the extra cash to invest in more projects which are expected to return 8% pa, and have the same risk as the existing projects. Therefore, next year's dividend will be $0.90. No new equity or debt will be issued to fund the new projects, they'll all be funded by the cut in dividends.
What will be the stock's new annual capital return (proportional increase in price per year) if the change in payout policy goes ahead?
Assume that payout policy is irrelevant to firm value (so there's no signalling effects) and that all rates are effective annual rates.
Question 577 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
What is the present value of a real payment of $500 in 2 years? The nominal discount rate is 7% pa and the inflation rate is 4% pa.
Question 554 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
On his 20th birthday, a man makes a resolution. He will put $30 cash under his bed at the end of every month starting from today. His birthday today is the first day of the month. So the first addition to his cash stash will be in one month. He will write in his will that when he dies the cash under the bed should be given to charity.
If the man lives for another 60 years, how much money will be under his bed if he dies just after making his last (720th) addition?
Also, what will be the real value of that cash in today's prices if inflation is expected to 2.5% pa? Assume that the inflation rate is an effective annual rate and is not expected to change.
The answers are given in the same order, the amount of money under his bed in 60 years, and the real value of that money in today's prices.
Question 745 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, income and capital returns
If the nominal gold price is expected to increase at the same rate as inflation which is 3% pa, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
You're considering making an investment in a particular company. They have preference shares, ordinary shares, senior debt and junior debt.
Which is the safest investment? Which has the highest expected returns?
Which business structure or structures have the advantage of limited liability for equity investors?
The below screenshot of Commonwealth Bank of Australia's (CBA) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 7 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.
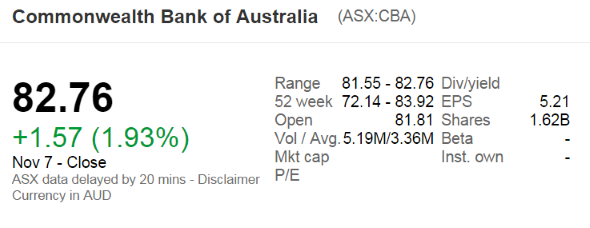
What was CBA's market capitalisation of equity?
Question 445 financing decision, corporate financial decision theory
The financing decision primarily affects which part of a business?
Question 443 corporate financial decision theory, investment decision, financing decision, working capital decision, payout policy
Business people make lots of important decisions. Which of the following is the most important long term decision?
The expression 'you have to spend money to make money' relates to which business decision?
The standard deviation and variance of a stock's annual returns are calculated over a number of years. The units of the returns are percent per annum ##(\% pa)##.
What are the units of the standard deviation ##(\sigma)## and variance ##(\sigma^2)## of returns respectively?
Hint: Visit Wikipedia to understand the difference between percentage points ##(\text{pp})## and percent ##(\%)##.
Let the variance of returns for a share per month be ##\sigma_\text{monthly}^2##.
What is the formula for the variance of the share's returns per year ##(\sigma_\text{yearly}^2)##?
Assume that returns are independently and identically distributed (iid) so they have zero auto correlation, meaning that if the return was higher than average today, it does not indicate that the return tomorrow will be higher or lower than average.
Question 708 continuously compounding rate, continuously compounding rate conversion
Convert a 10% continuously compounded annual rate ##(r_\text{cc annual})## into an effective annual rate ##(r_\text{eff annual})##. The equivalent effective annual rate is:
Which of the following interest rate quotes is NOT equivalent to a 10% effective annual rate of return? Assume that each year has 12 months, each month has 30 days, each day has 24 hours, each hour has 60 minutes and each minute has 60 seconds. APR stands for Annualised Percentage Rate.
Question 710 continuously compounding rate, continuously compounding rate conversion
A continuously compounded monthly return of 1% ##(r_\text{cc monthly})## is equivalent to a continuously compounded annual return ##(r_\text{cc annual})## of:
An effective monthly return of 1% ##(r_\text{eff monthly})## is equivalent to an effective annual return ##(r_\text{eff annual})## of:
Which of the following quantities is commonly assumed to be normally distributed?
The below three graphs show probability density functions (PDF) of three different random variables Red, Green and Blue.
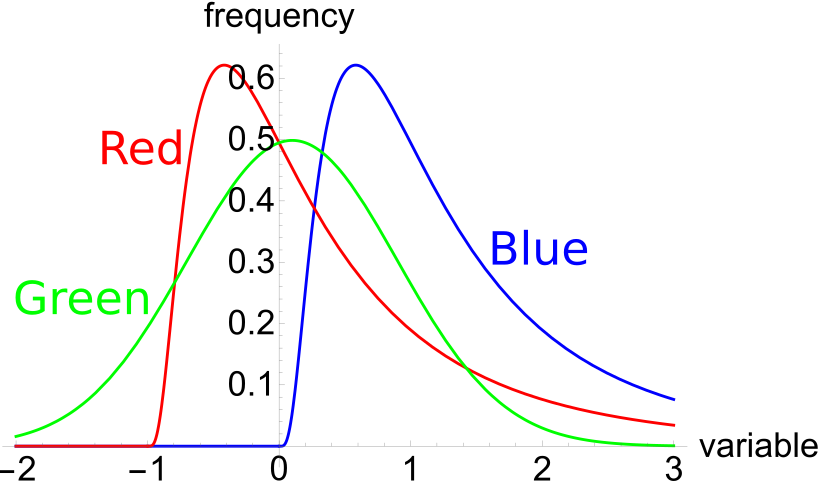
Which of the below statements is NOT correct?
The symbol ##\text{GDR}_{0\rightarrow 1}## represents a stock's gross discrete return per annum over the first year. ##\text{GDR}_{0\rightarrow 1} = P_1/P_0##. The subscript indicates the time period that the return is mentioned over. So for example, ##\text{AAGDR}_{1 \rightarrow 3}## is the arithmetic average GDR measured over the two year period from years 1 to 3, but it is expressed as a per annum rate.
Which of the below statements about the arithmetic and geometric average GDR is NOT correct?
Question 811 log-normal distribution, mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages
Which of the following statements about probability distributions is NOT correct?
Question 722 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
Here is a table of stock prices and returns. Which of the statements below the table is NOT correct?
| Price and Return Population Statistics | ||||
| Time | Prices | LGDR | GDR | NDR |
| 0 | 100 | |||
| 1 | 50 | -0.6931 | 0.5 | -0.5 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.6931 | 2 | 1 |
| Arithmetic average | 0 | 1.25 | 0.25 | |
| Arithmetic standard deviation | 0.9802 | 1.0607 | 1.0607 | |
When someone says that they're "buying American dollars" (USD), what type of asset are they probably buying? They're probably buying:
An Indonesian lady wishes to convert 1 million Indonesian rupiah (IDR) to Australian dollars (AUD). Exchange rates are 13,125 IDR per USD and 0.79 USD per AUD. How many AUD is the IDR 1 million worth?
Question 315 foreign exchange rate, American and European terms
If the current AUD exchange rate is USD 0.9686 = AUD 1, what is the European terms quote of the AUD against the USD?
Question 319 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
Investors expect the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to keep the policy rate steady at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 25 basis points due to fears that the economy is growing too fast and that inflation will be above their target rate of 2 to 3 per cent.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar is likely to:
Question 321 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
The market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to increase the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 50 basis points due to high future GDP and inflation forecasts.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar will:
Question 626 cross currency interest rate parity, foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate
The Australian cash rate is expected to be 2% pa over the next one year, while the Japanese cash rate is expected to be 0% pa, both given as nominal effective annual rates. The current exchange rate is 100 JPY per AUD.
What is the implied 1 year forward foreign exchange rate?
Question 246 foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate, cross currency interest rate parity
Suppose the Australian cash rate is expected to be 8.15% pa and the US federal funds rate is expected to be 3.00% pa over the next 2 years, both given as nominal effective annual rates. The current exchange rate is at parity, so 1 USD = 1 AUD.
What is the implied 2 year forward foreign exchange rate?
The Chinese government attempts to fix its exchange rate against the US dollar and at the same time use monetary policy to fix its interest rate at a set level.
To be able to fix its exchange rate and interest rate in this way, what does the Chinese government actually do?
- Adopts capital controls to prevent financial arbitrage by private firms and individuals.
- Adopts the same interest rate (monetary policy) as the United States.
- Fixes inflation so that the domestic real interest rate is equal to the United States' real interest rate.
Which of the above statements is or are true?
A firm has a debt-to-equity ratio of 25%. What is its debt-to-assets ratio?
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 20%. What is its debt-to-equity ratio?
One year ago you bought a $1,000,000 house partly funded using a mortgage loan. The loan size was $800,000 and the other $200,000 was your wealth or 'equity' in the house asset.
The interest rate on the home loan was 4% pa.
Over the year, the house produced a net rental yield of 2% pa and a capital gain of 2.5% pa.
Assuming that all cash flows (interest payments and net rental payments) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates are given as effective annual rates, what was the total return on your wealth over the past year?
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
Use the below information to value a levered company with constant annual perpetual cash flows from assets. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now, so a perpetuity can be used to value this firm. Both the operating and firm free cash flows are constant (but not equal to each other).
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}## | $100m | Operating free cash flow |
| ##\text{FFCF or CFFA}## | $112m | Firm free cash flow or cash flow from assets (includes interest tax shields) |
| ##g## | 0% pa | Growth rate of OFCF and FFCF |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{BeforeTax}## | 7% pa | Weighted average cost of capital before tax |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{AfterTax}## | 6.25% pa | Weighted average cost of capital after tax |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 5% pa | Cost of debt |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 9% pa | Cost of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 50% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
What is the value of the levered firm including interest tax shields?
Use the below information to value a levered company with annual perpetual cash flows from assets that grow. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now. Note that ‘k’ means kilo or 1,000. So the $30k is $30,000.
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}## | $30k | Operating free cash flow |
| ##g## | 1.5% pa | Growth rate of OFCF |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 4% pa | Cost of debt |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 16.3% pa | Cost of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 80% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
| ##n_\text{shares}## | 100k | Number of shares |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 772 interest tax shield, capital structure, leverage
A firm issues debt and uses the funds to buy back equity. Assume that there are no costs of financial distress or transactions costs. Which of the following statements about interest tax shields is NOT correct?