The saying "buy low, sell high" suggests that investors should make a:
Question 490 expected and historical returns, accounting ratio
Which of the following is NOT a synonym of 'required return'?
Total cash flows can be broken into income and capital cash flows. What is the name given to the income cash flow from owning shares?
Which of the following equations is NOT equal to the total return of an asset?
Let ##p_0## be the current price, ##p_1## the expected price in one year and ##c_1## the expected income in one year.
An asset's total expected return over the next year is given by:
###r_\text{total} = \dfrac{c_1+p_1-p_0}{p_0} ###
Where ##p_0## is the current price, ##c_1## is the expected income in one year and ##p_1## is the expected price in one year. The total return can be split into the income return and the capital return.
Which of the following is the expected capital return?
A stock was bought for $8 and paid a dividend of $0.50 one year later (at t=1 year). Just after the dividend was paid, the stock price was $7 (at t=1 year).
What were the total, capital and dividend returns given as effective annual rates? The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}##, ##r_\text{capital}##, ##r_\text{dividend}##.
A share was bought for $30 (at t=0) and paid its annual dividend of $6 one year later (at t=1).
Just after the dividend was paid, the share price fell to $27 (at t=1). What were the total, capital and income returns given as effective annual rates?
The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}## , ##r_\text{capital}## , ##r_\text{dividend}##.
A fixed coupon bond was bought for $90 and paid its annual coupon of $3 one year later (at t=1 year). Just after the coupon was paid, the bond price was $92 (at t=1 year). What was the total return, capital return and income return? Calculate your answers as effective annual rates.
The choices are given in the same order: ## r_\text{total},r_\text{capital},r_\text{income} ##.
One and a half years ago Frank bought a house for $600,000. Now it's worth only $500,000, based on recent similar sales in the area.
The expected total return on Frank's residential property is 7% pa.
He rents his house out for $1,600 per month, paid in advance. Every 12 months he plans to increase the rental payments.
The present value of 12 months of rental payments is $18,617.27.
The future value of 12 months of rental payments one year in the future is $19,920.48.
What is the expected annual rental yield of the property? Ignore the costs of renting such as maintenance, real estate agent fees and so on.
Question 278 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Imagine that the interest rate on your savings account was 1% per year and inflation was 2% per year.
Question 295 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, NPV
When valuing assets using discounted cash flow (net present value) methods, it is important to consider inflation. To properly deal with inflation:
(I) Discount nominal cash flows by nominal discount rates.
(II) Discount nominal cash flows by real discount rates.
(III) Discount real cash flows by nominal discount rates.
(IV) Discount real cash flows by real discount rates.
Which of the above statements is or are correct?
In the 'Austin Powers' series of movies, the character Dr. Evil threatens to destroy the world unless the United Nations pays him a ransom (video 1, video 2). Dr. Evil makes the threat on two separate occasions:
- In 1969 he demands a ransom of $1 million (=10^6), and again;
- In 1997 he demands a ransom of $100 billion (=10^11).
If Dr. Evil's demands are equivalent in real terms, in other words $1 million will buy the same basket of goods in 1969 as $100 billion would in 1997, what was the implied inflation rate over the 28 years from 1969 to 1997?
The answer choices below are given as effective annual rates:
Question 353 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 6% pa and nominal capital return of 3% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns? The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Question 363 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 8% pa and nominal capital return of 3% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns? The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Question 407 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
A stock has a real expected total return of 7% pa and a real expected capital return of 2% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What is the nominal expected total return, capital return and dividend yield? The answers below are given in the same order.
Question 155 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, Loan, effective rate conversion
You are a banker about to grant a 2 year loan to a customer. The loan's principal and interest will be repaid in a single payment at maturity, sometimes called a zero-coupon loan, discount loan or bullet loan.
You require a real return of 6% pa over the two years, given as an effective annual rate. Inflation is expected to be 2% this year and 4% next year, both given as effective annual rates.
You judge that the customer can afford to pay back $1,000,000 in 2 years, given as a nominal cash flow. How much should you lend to her right now?
You're considering making an investment in a particular company. They have preference shares, ordinary shares, senior debt and junior debt.
Which is the safest investment? Which has the highest expected returns?
A newly floated farming company is financed with senior bonds, junior bonds, cumulative non-voting preferred stock and common stock. The new company has no retained profits and due to floods it was unable to record any revenues this year, leading to a loss. The firm is not bankrupt yet since it still has substantial contributed equity (same as paid-up capital).
On which securities must it pay interest or dividend payments in this terrible financial year?
Which business structure or structures have the advantage of limited liability for equity investors?
Question 452 limited liability, expected and historical returns
What is the lowest and highest expected share price and expected return from owning shares in a company over a finite period of time?
Let the current share price be ##p_0##, the expected future share price be ##p_1##, the expected future dividend be ##d_1## and the expected return be ##r##. Define the expected return as:
##r=\dfrac{p_1-p_0+d_1}{p_0} ##
The answer choices are stated using inequalities. As an example, the first answer choice "(a) ##0≤p<∞## and ##0≤r< 1##", states that the share price must be larger than or equal to zero and less than positive infinity, and that the return must be larger than or equal to zero and less than one.
Which of the following statements about book and market equity is NOT correct?
Question 461 book and market values, ROE, ROA, market efficiency
One year ago a pharmaceutical firm floated by selling its 1 million shares for $100 each. Its book and market values of equity were both $100m. Its debt totalled $50m. The required return on the firm's assets was 15%, equity 20% and debt 5% pa.
In the year since then, the firm:
- Earned net income of $29m.
- Paid dividends totaling $10m.
- Discovered a valuable new drug that will lead to a massive 1,000 times increase in the firm's net income in 10 years after the research is commercialised. News of the discovery was publicly announced. The firm's systematic risk remains unchanged.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? All statements are about current figures, not figures one year ago.
Hint: Book return on assets (ROA) and book return on equity (ROE) are ratios that accountants like to use to measure a business's past performance.
###\text{ROA}= \dfrac{\text{Net income}}{\text{Book value of assets}}###
###\text{ROE}= \dfrac{\text{Net income}}{\text{Book value of equity}}###
The required return on assets ##r_V## is a return that financiers like to use to estimate a business's future required performance which compensates them for the firm's assets' risks. If the business were to achieve realised historical returns equal to its required returns, then investment into the business's assets would have been a zero-NPV decision, which is neither good nor bad but fair.
###r_\text{V, 0 to 1}= \dfrac{\text{Cash flow from assets}_\text{1}}{\text{Market value of assets}_\text{0}} = \dfrac{CFFA_\text{1}}{V_\text{0}}###
Similarly for equity and debt.
The below screenshot of Commonwealth Bank of Australia's (CBA) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 7 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.
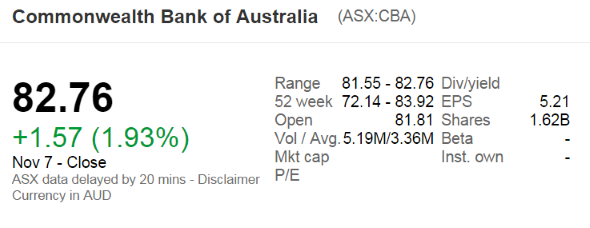
What was CBA's market capitalisation of equity?
The below screenshot of Microsoft's (MSFT) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 28 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.
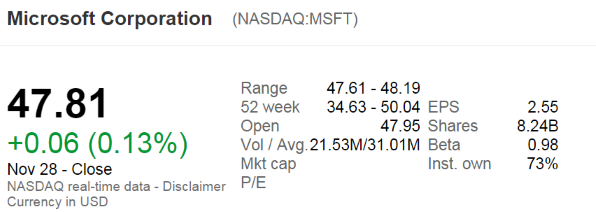
What was MSFT's market capitalisation of equity?
Question 444 investment decision, corporate financial decision theory
The investment decision primarily affects which part of a business?
Question 446 working capital decision, corporate financial decision theory
The working capital decision primarily affects which part of a business?
Question 445 financing decision, corporate financial decision theory
The financing decision primarily affects which part of a business?
Question 447 payout policy, corporate financial decision theory
Payout policy is most closely related to which part of a business?
Question 443 corporate financial decision theory, investment decision, financing decision, working capital decision, payout policy
Business people make lots of important decisions. Which of the following is the most important long term decision?
Katya offers to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years (t=1,2,3,4,5) if you pay her $50 now (t=0). You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. Ignore credit risk.
This annuity formula ##\dfrac{C_1}{r}\left(1-\dfrac{1}{(1+r)^3} \right)## is equivalent to which of the following formulas? Note the 3.
In the below formulas, ##C_t## is a cash flow at time t. All of the cash flows are equal, but paid at different times.
Some countries' interest rates are so low that they're zero.
If interest rates are 0% pa and are expected to stay at that level for the foreseeable future, what is the most that you would be prepared to pay a bank now if it offered to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years?
In other words, what is the present value of five $10 payments at time 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 if interest rates are 0% pa?
The following equation is called the Dividend Discount Model (DDM), Gordon Growth Model or the perpetuity with growth formula: ### P_0 = \frac{ C_1 }{ r - g } ###
What is ##g##? The value ##g## is the long term expected:
The first payment of a constant perpetual annual cash flow is received at time 5. Let this cash flow be ##C_5## and the required return be ##r##.
So there will be equal annual cash flows at time 5, 6, 7 and so on forever, and all of the cash flows will be equal so ##C_5 = C_6 = C_7 = ...##
When the perpetuity formula is used to value this stream of cash flows, it will give a value (V) at time:
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### P_{0} = \frac{C_1}{r_{\text{eff}} - g_{\text{eff}}} ###
What would you call the expression ## C_1/P_0 ##?
A stock just paid its annual dividend of $9. The share price is $60. The required return of the stock is 10% pa as an effective annual rate.
What is the implied growth rate of the dividend per year?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
###P_0=\frac{d_1}{r-g}###
A stock pays dividends annually. It just paid a dividend, but the next dividend (##d_1##) will be paid in one year.
According to the DDM, what is the correct formula for the expected price of the stock in 2.5 years?
Two years ago Fred bought a house for $300,000.
Now it's worth $500,000, based on recent similar sales in the area.
Fred's residential property has an expected total return of 8% pa.
He rents his house out for $2,000 per month, paid in advance. Every 12 months he plans to increase the rental payments.
The present value of 12 months of rental payments is $23,173.86.
The future value of 12 months of rental payments one year ahead is $25,027.77.
What is the expected annual growth rate of the rental payments? In other words, by what percentage increase will Fred have to raise the monthly rent by each year to sustain the expected annual total return of 8%?
A share just paid its semi-annual dividend of $10. The dividend is expected to grow at 2% every 6 months forever. This 2% growth rate is an effective 6 month rate. Therefore the next dividend will be $10.20 in six months. The required return of the stock 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the price of the share now?
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 1.15 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at 5% pa, so;
- the dividend at t=5 will be $1.15(1+0.05),
- the dividend at t=6 will be $1.15(1+0.05)^2, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates. What is the current price of the stock?
The following is the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) used to price stocks:
### P_0 = \frac{d_1}{r-g} ###Assume that the assumptions of the DDM hold and that the time period is measured in years.
Which of the following is equal to the expected dividend in 3 years, ## d_3 ##?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
###p_0=\frac{d_1}{r_\text{eff}-g_\text{eff}}###
Which expression is NOT equal to the expected capital return?
A stock pays semi-annual dividends. It just paid a dividend of $10. The growth rate in the dividend is 1% every 6 months, given as an effective 6 month rate. You estimate that the stock's required return is 21% pa, as an effective annual rate.
Using the dividend discount model, what will be the share price?
You own an apartment which you rent out as an investment property.
What is the price of the apartment using discounted cash flow (DCF, same as NPV) valuation?
Assume that:
- You just signed a contract to rent the apartment out to a tenant for the next 12 months at $2,000 per month, payable in advance (at the start of the month, t=0). The tenant is just about to pay you the first $2,000 payment.
- The contract states that monthly rental payments are fixed for 12 months. After the contract ends, you plan to sign another contract but with rental payment increases of 3%. You intend to do this every year.
So rental payments will increase at the start of the 13th month (t=12) to be $2,060 (=2,000(1+0.03)), and then they will be constant for the next 12 months.
Rental payments will increase again at the start of the 25th month (t=24) to be $2,121.80 (=2,000(1+0.03)2), and then they will be constant for the next 12 months until the next year, and so on. - The required return of the apartment is 8.732% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
- Ignore all taxes, maintenance, real estate agent, council and strata fees, periods of vacancy and other costs. Assume that the apartment will last forever and so will the rental payments.
The boss of WorkingForTheManCorp has a wicked (and unethical) idea. He plans to pay his poor workers one week late so that he can get more interest on his cash in the bank.
Every week he is supposed to pay his 1,000 employees $1,000 each. So $1 million is paid to employees every week.
The boss was just about to pay his employees today, until he thought of this idea so he will actually pay them one week (7 days) later for the work they did last week and every week in the future, forever.
Bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as a real effective annual rate. So ##r_\text{eff annual, real} = 0.1## and the real effective weekly rate is therefore ##r_\text{eff weekly, real} = (1+0.1)^{1/52}-1 = 0.001834569##
All rates and cash flows are real, the inflation rate is 3% pa and there are 52 weeks per year. The boss will always pay wages one week late. The business will operate forever with constant real wages and the same number of employees.
What is the net present value (NPV) of the boss's decision to pay later?
Question 498 NPV, Annuity, perpetuity with growth, multi stage growth model
A business project is expected to cost $100 now (t=0), then pay $10 at the end of the third (t=3), fourth, fifth and sixth years, and then grow by 5% pa every year forever. So the cash flow will be $10.5 at the end of the seventh year (t=7), then $11.025 at the end of the eighth year (t=8) and so on perpetually. The total required return is 10℅ pa.
Which of the following formulas will NOT give the correct net present value of the project?
What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of the project detailed in the table below?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time. All answers are given as effective annual rates.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 121 |
Your neighbour asks you for a loan of $100 and offers to pay you back $120 in one year.
You don't actually have any money right now, but you can borrow and lend from the bank at a rate of 10% pa. Rates are given as effective annual rates.
Assume that your neighbour will definitely pay you back. Ignore interest tax shields and transaction costs.
The Net Present Value (NPV) of lending to your neighbour is $9.09. Describe what you would do to actually receive a $9.09 cash flow right now with zero net cash flows in the future.
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume an equal amount now (t=0), in one year (t=1) and in two years (t=2), and still have $50,000 in the bank after that (t=2).
How much can you consume at each time?
The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the payback period of the project in years?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are received smoothly over the year. So the $121 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 11 |
| 2 | 121 |
A project to build a toll road will take 3 years to complete, costing three payments of $50 million, paid at the start of each year (at times 0, 1, and 2).
After completion, the toll road will yield a constant $10 million at the end of each year forever with no costs. So the first payment will be at t=4.
The required return of the project is 10% pa given as an effective nominal rate. All cash flows are nominal.
What is the payback period?
A project has the following cash flows:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 200 |
| 2 | 250 |
What is the Profitability Index (PI) of the project? Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time. The required return is 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
A project has the following cash flows:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -90 |
| 1 | 30 |
| 2 | 105 |
The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time.
What is the Profitability Index (PI) of the project?
Estimate the Chinese bank ICBC's share price using a backward-looking price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only. Note that the renminbi (RMB) is the Chinese currency, also known as the yuan (CNY).
- The 4 major Chinese banks ICBC, China Construction Bank (CCB), Bank of China (BOC) and Agricultural Bank of China (ABC) are comparable companies;
- ICBC 's historical earnings per share (EPS) is RMB 0.74;
- CCB's backward-looking PE ratio is 4.59;
- BOC 's backward-looking PE ratio is 4.78;
- ABC's backward-looking PE ratio is also 4.78;
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 25 March 2014. Share prices are from the Shanghai stock exchange.
Which of the following investable assets are NOT suitable for valuation using PE multiples techniques?
Which of the following investable assets are NOT suitable for valuation using PE multiples techniques?
Which firms tend to have low forward-looking price-earnings (PE) ratios? Only consider firms with positive PE ratios.
Which of the following statements about effective rates and annualised percentage rates (APR's) is NOT correct?
A European bond paying annual coupons of 6% offers a yield of 10% pa.
Convert the yield into an effective monthly rate, an effective annual rate and an effective daily rate. Assume that there are 365 days in a year.
All answers are given in the same order:
### r_\text{eff, monthly} , r_\text{eff, yearly} , r_\text{eff, daily} ###
Question 49 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, APR, effective rate
In Australia, nominal yields on semi-annual coupon paying Government Bonds with 2 years until maturity are currently 2.83% pa.
The inflation rate is currently 2.2% pa, given as an APR compounding per quarter. The inflation rate is not expected to change over the next 2 years.
What is the real yield on these bonds, given as an APR compounding every 6 months?
On his 20th birthday, a man makes a resolution. He will deposit $30 into a bank account at the end of every month starting from now, which is the start of the month. So the first payment will be in one month. He will write in his will that when he dies the money in the account should be given to charity.
The bank account pays interest at 6% pa compounding monthly, which is not expected to change.
If the man lives for another 60 years, how much money will be in the bank account if he dies just after making his last (720th) payment?
You want to buy an apartment worth $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as a fully amortising mortgage loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments?
You want to buy an apartment priced at $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage with monthly payments of $1,000 per month. The interest rate is 6% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 20 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 6% and is not expected to change.
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $1,500 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
To your surprise, you can actually afford to pay $2,000 per month and your mortgage allows early repayments without fees. If you maintain these higher monthly payments, how long will it take to pay off your mortgage?
You want to buy a house priced at $400,000. You have saved a deposit of $40,000. The bank has agreed to lend you $360,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 8% pa payable monthly and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments?
You just signed up for a 30 year interest-only mortgage with monthly payments of $3,000 per month. The interest rate is 6% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 15 years, just after the 180th payment at that time, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 6% and is not expected to change. Remember that the mortgage is interest-only and that mortgage payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
You want to buy an apartment worth $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $60,000.
The bank has agreed to lend you $240,000 as an interest only mortgage loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
Question 239 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, interest only loan
A bank grants a borrower an interest-only residential mortgage loan with a very large 50% deposit and a nominal interest rate of 6% that is not expected to change. Assume that inflation is expected to be a constant 2% pa over the life of the loan. Ignore credit risk.
From the bank's point of view, what is the long term expected nominal capital return of the loan asset?
In Australia in the 1980's, inflation was around 8% pa, and residential mortgage loan interest rates were around 14%.
In 2013, inflation was around 2.5% pa, and residential mortgage loan interest rates were around 4.5%.
If a person can afford constant mortgage loan payments of $2,000 per month, how much more can they borrow when interest rates are 4.5% pa compared with 14.0% pa?
Give your answer as a proportional increase over the amount you could borrow when interest rates were high ##(V_\text{high rates})##, so:
###\text{Proportional increase} = \dfrac{V_\text{low rates}-V_\text{high rates}}{V_\text{high rates}} ###
Assume that:
- Interest rates are expected to be constant over the life of the loan.
- Loans are interest-only and have a life of 30 years.
- Mortgage loan payments are made every month in arrears and all interest rates are given as annualised percentage rates (APR's) compounding per month.
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid annually. So there's only one coupon per year, paid in arrears every year.
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid semi-annually. So there are two coupons per year, paid in arrears every six months.
Bonds A and B are issued by the same company. They have the same face value, maturity, seniority and coupon payment frequency. The only difference is that bond A has a 5% coupon rate, while bond B has a 10% coupon rate. The yield curve is flat, which means that yields are expected to stay the same.
Which bond would have the higher current price?
Bonds A and B are issued by the same Australian company. Both bonds yield 7% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond A pays coupons of 10% pa and bond B pays coupons of 5% pa. Which of the following statements is true about the bonds' prices?
A firm wishes to raise $20 million now. They will issue 8% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 5 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 6% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at a premium?
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same company. Both bonds yield 10% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X pays coupons of 6% pa and bond Y pays coupons of 8% pa. Which of the following statements is true?
A 10 year Australian government bond was just issued at par with a yield of 3.9% pa. The fixed coupon payments are semi-annual. The bond has a face value of $1,000.
Six months later, just after the first coupon is paid, the yield of the bond decreases to 3.65% pa. What is the bond's new price?
You're trying to save enough money to buy your first car which costs $2,500. You can save $100 at the end of each month starting from now. You currently have no money at all. You just opened a bank account with an interest rate of 6% pa payable monthly.
How many months will it take to save enough money to buy the car? Assume that the price of the car will stay the same over time.
You really want to go on a back packing trip to Europe when you finish university. Currently you have $1,500 in the bank. Bank interest rates are 8% pa, given as an APR compounding per month. If the holiday will cost $2,000, how long will it take for your bank account to reach that amount?
When using the dividend discount model, care must be taken to avoid using a nominal dividend growth rate that exceeds the country's nominal GDP growth rate. Otherwise the firm is forecast to take over the country since it grows faster than the average business forever.
Suppose a firm's nominal dividend grows at 10% pa forever, and nominal GDP growth is 5% pa forever. The firm's total dividends are currently $1 billion (t=0). The country's GDP is currently $1,000 billion (t=0).
In approximately how many years will the company's total dividends be as large as the country's GDP?
A low-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $1,000 and will last for 1 year before it will be scrapped for nothing.
A high-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $4,900 and it will last for 5 years before it will be scrapped for nothing.
What is the equivalent annual cost of each car? Assume a discount rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
The answer choices are given as the equivalent annual cost of the low-quality car and then the high quality car.
You're advising your superstar client 40-cent who is weighing up buying a private jet or a luxury yacht. 40-cent is just as happy with either, but he wants to go with the more cost-effective option. These are the cash flows of the two options:
- The private jet can be bought for $6m now, which will cost $12,000 per month in fuel, piloting and airport costs, payable at the end of each month. The jet will last for 12 years.
- Or the luxury yacht can be bought for $4m now, which will cost $20,000 per month in fuel, crew and berthing costs, payable at the end of each month. The yacht will last for 20 years.
What's unusual about 40-cent is that he is so famous that he will actually be able to sell his jet or yacht for the same price as it was bought since the next generation of superstar musicians will buy it from him as a status symbol.
Bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. You can assume that 40-cent will live for another 60 years and that when the jet or yacht's life is at an end, he will buy a new one with the same details as above.
Would you advise 40-cent to buy the or the ?
Note that the effective monthly rate is ##r_\text{eff monthly}=(1+0.1)^{1/12}-1=0.00797414##
Which of the below statements about effective rates and annualised percentage rates (APR's) is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements is NOT equivalent to the yield on debt?
Assume that the debt being referred to is fairly priced, but do not assume that it's priced at par.
When someone says that they're "buying American dollars" (USD), what type of asset are they probably buying? They're probably buying:
An American wishes to convert USD 1 million to Australian dollars (AUD). The exchange rate is 0.8 USD per AUD. How much is the USD 1 million worth in AUD?
Question 315 foreign exchange rate, American and European terms
If the current AUD exchange rate is USD 0.9686 = AUD 1, what is the European terms quote of the AUD against the USD?
Question 319 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
Investors expect the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to keep the policy rate steady at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 25 basis points due to fears that the economy is growing too fast and that inflation will be above their target rate of 2 to 3 per cent.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar is likely to:
Question 320 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
Investors expect the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to decrease the overnight cash rate at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will keep the policy rate unchanged.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar is likely to:
Question 321 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
The market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to increase the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 50 basis points due to high future GDP and inflation forecasts.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar will:
Question 323 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
The market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to increase the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting.
As expected, the RBA increases the policy rate by 25 basis points.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar will:
Question 246 foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate, cross currency interest rate parity
Suppose the Australian cash rate is expected to be 8.15% pa and the US federal funds rate is expected to be 3.00% pa over the next 2 years, both given as nominal effective annual rates. The current exchange rate is at parity, so 1 USD = 1 AUD.
What is the implied 2 year forward foreign exchange rate?
Question 100 market efficiency, technical analysis, joint hypothesis problem
A company selling charting and technical analysis software claims that independent academic studies have shown that its software makes significantly positive abnormal returns. Assuming the claim is true, which statement(s) are correct?
(I) Weak form market efficiency is broken.
(II) Semi-strong form market efficiency is broken.
(III) Strong form market efficiency is broken.
(IV) The asset pricing model used to measure the abnormal returns (such as the CAPM) had mis-specification error so the returns may not be abnormal but rather fair for the level of risk.
Select the most correct response:
Question 119 market efficiency, fundamental analysis, joint hypothesis problem
Your friend claims that by reading 'The Economist' magazine's economic news articles, she can identify shares that will have positive abnormal expected returns over the next 2 years. Assuming that her claim is true, which statement(s) are correct?
(i) Weak form market efficiency is broken.
(ii) Semi-strong form market efficiency is broken.
(iii) Strong form market efficiency is broken.
(iv) The asset pricing model used to measure the abnormal returns (such as the CAPM) is either wrong (mis-specification error) or is measured using the wrong inputs (data errors) so the returns may not be abnormal but rather fair for the level of risk.
Select the most correct response:
Select the most correct statement from the following.
'Chartists', also known as 'technical traders', believe that:
Fundamentalists who analyse company financial reports and news announcements (but who don't have inside information) will make positive abnormal returns if:
Question 48 IRR, NPV, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds, market efficiency
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A person is thinking about borrowing $100 from the bank at 7% pa and investing it in shares with an expected return of 10% pa. One year later the person intends to sell the shares and pay back the loan in full. Both the loan and the shares are fairly priced.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of this one year investment? Note that you are asked to find the present value (##V_0##), not the value in one year (##V_1##).
Question 339 bond pricing, inflation, market efficiency, income and capital returns
Economic statistics released this morning were a surprise: they show a strong chance of consumer price inflation (CPI) reaching 5% pa over the next 2 years.
This is much higher than the previous forecast of 3% pa.
A vanilla fixed-coupon 2-year risk-free government bond was issued at par this morning, just before the economic news was released.
What is the expected change in bond price after the economic news this morning, and in the next 2 years? Assume that:
- Inflation remains at 5% over the next 2 years.
- Investors demand a constant real bond yield.
- The bond price falls by the (after-tax) value of the coupon the night before the ex-coupon date, as in real life.
Question 338 market efficiency, CAPM, opportunity cost, technical analysis
A man inherits $500,000 worth of shares.
He believes that by learning the secrets of trading, keeping up with the financial news and doing complex trend analysis with charts that he can quit his job and become a self-employed day trader in the equities markets.
What is the expected gain from doing this over the first year? Measure the net gain in wealth received at the end of this first year due to the decision to become a day trader. Assume the following:
- He earns $60,000 pa in his current job, paid in a lump sum at the end of each year.
- He enjoys examining share price graphs and day trading just as much as he enjoys his current job.
- Stock markets are weak form and semi-strong form efficient.
- He has no inside information.
- He makes 1 trade every day and there are 250 trading days in the year. Trading costs are $20 per trade. His broker invoices him for the trading costs at the end of the year.
- The shares that he currently owns and the shares that he intends to trade have the same level of systematic risk as the market portfolio.
- The market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa.
Measure the net gain over the first year as an expected wealth increase at the end of the year.
Question 416 real estate, market efficiency, income and capital returns, DDM, CAPM
A residential real estate investor believes that house prices will grow at a rate of 5% pa and that rents will grow by 2% pa forever.
All rates are given as nominal effective annual returns. Assume that:
- His forecast is true.
- Real estate is and always will be fairly priced and the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is true.
- Ignore all costs such as taxes, agent fees, maintenance and so on.
- All rental income cash flow is paid out to the owner, so there is no re-investment and therefore no additions or improvements made to the property.
- The non-monetary benefits of owning real estate and renting remain constant.
Which one of the following statements is NOT correct? Over time:
A company advertises an investment costing $1,000 which they say is underpriced. They say that it has an expected total return of 15% pa, but a required return of only 10% pa. Assume that there are no dividend payments so the entire 15% total return is all capital return.
Assuming that the company's statements are correct, what is the NPV of buying the investment if the 15% return lasts for the next 100 years (t=0 to 100), then reverts to 10% pa after that time? Also, what is the NPV of the investment if the 15% return lasts forever?
In both cases, assume that the required return of 10% remains constant. All returns are given as effective annual rates.
The answer choices below are given in the same order (15% for 100 years, and 15% forever):
A managed fund charges fees based on the amount of money that you keep with them. The fee is 2% of the start-of-year amount, but it is paid at the end of every year.
This fee is charged regardless of whether the fund makes gains or losses on your money.
The fund offers to invest your money in shares which have an expected return of 10% pa before fees.
You are thinking of investing $100,000 in the fund and keeping it there for 40 years when you plan to retire.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of investing your money in the fund? Note that the question is not asking how much money you will have in 40 years, it is asking: what is the NPV of investing in the fund? Assume that:
- The fund has no private information.
- Markets are weak and semi-strong form efficient.
- The fund's transaction costs are negligible.
- The cost and trouble of investing your money in shares by yourself, without the managed fund, is negligible.
Question 572 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 573 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, liquidity premium theory, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 35 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
A European company just issued two bonds, a
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the company's forward rate over the second year (from t=1 to t=2)? Give your answer as an effective annual rate, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 25 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
A European company just issued two bonds, a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 3 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the company's forward rate over the third year (from t=2 to t=3)? Give your answer as an effective annual rate, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
A European company just issued two bonds, a
- 3 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 6% pa, and a
- 4 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 6.5% pa.
What is the company's forward rate over the fourth year (from t=3 to t=4)? Give your answer as an effective annual rate, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 143 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds:
- A 6-month zero coupon bond at a yield of 6% pa, and
- A 12 month zero coupon bond at a yield of 7% pa.
What is the company's forward rate from 6 to 12 months? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 96 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds paying semi-annual coupons:
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 108 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds:
- A 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa, and
- A 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
For a price of $100, Vera will sell you a 2 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 10% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with similar risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 8% pa.
For a price of $100, Carol will sell you a 5 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 16% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with similar risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 12% pa.
For a price of $100, Rad will sell you a 5 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 16% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with the same risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 6% pa.
For a price of $100, Andrea will sell you a 2 year bond paying annual coupons of 10% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with the same risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 6% pa.
A three year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 10% and a fixed coupon rate of 5%, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same US company. Both bonds yield 10% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X and Y's coupon rates are 8 and 12% pa respectively. Which of the following statements is true?
A two year Government bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 2.5% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 0.5% pa, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
Question 56 income and capital returns, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds
Which of the following statements about risk free government bonds is NOT correct?
Hint: Total return can be broken into income and capital returns as follows:
###\begin{aligned} r_\text{total} &= \frac{c_1}{p_0} + \frac{p_1-p_0}{p_0} \\ &= r_\text{income} + r_\text{capital} \end{aligned} ###
The capital return is the growth rate of the price.
The income return is the periodic cash flow. For a bond this is the coupon payment.
A bond maturing in 10 years has a coupon rate of 4% pa, paid semi-annually. The bond's yield is currently 6% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. What is its price?
Bonds X and Y are issued by different companies, but they both pay a semi-annual coupon of 10% pa and they have the same face value ($100) and maturity (3 years).
The only difference is that bond X and Y's yields are 8 and 12% pa respectively. Which of the following statements is true?
A three year bond has a fixed coupon rate of 12% pa, paid semi-annually. The bond's yield is currently 6% pa. The face value is $100. What is its price?
Bonds X and Y are issued by different companies, but they both pay a semi-annual coupon of 10% pa and they have the same face value ($100), maturity (3 years) and yield (10%) as each other.
Which of the following statements is true?
A four year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 6% and a fixed coupon rate of 12%, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at a discount?
A five year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 12% and a fixed coupon rate of 6%, paid semi-annually.
What is the bond's price?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at par?
A firm wishes to raise $8 million now. They will issue 7% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 10 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 10% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
Question 207 income and capital returns, bond pricing, coupon rate, no explanation
For a bond that pays fixed semi-annual coupons, how is the annual coupon rate defined, and how is the bond's annual income yield from time 0 to 1 defined mathematically?
Let: ##P_0## be the bond price now,
##F_T## be the bond's face value,
##T## be the bond's maturity in years,
##r_\text{total}## be the bond's total yield,
##r_\text{income}## be the bond's income yield,
##r_\text{capital}## be the bond's capital yield, and
##C_t## be the bond's coupon at time t in years. So ##C_{0.5}## is the coupon in 6 months, ##C_1## is the coupon in 1 year, and so on.
Question 213 income and capital returns, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds
The coupon rate of a fixed annual-coupon bond is constant (always the same).
What can you say about the income return (##r_\text{income}##) of a fixed annual coupon bond? Remember that:
###r_\text{total} = r_\text{income} + r_\text{capital}###
###r_\text{total, 0 to 1} = \frac{c_1}{p_0} + \frac{p_1-p_0}{p_0}###
Assume that there is no change in the bond's total annual yield to maturity from when it is issued to when it matures.
Select the most correct statement.
From its date of issue until maturity, the income return of a fixed annual coupon:
An investor bought two fixed-coupon bonds issued by the same company, a zero-coupon bond and a 7% pa semi-annual coupon bond. Both bonds have a face value of $1,000, mature in 10 years, and had a yield at the time of purchase of 8% pa.
A few years later, yields fell to 6% pa. Which of the following statements is correct? Note that a capital gain is an increase in price.
A firm wishes to raise $10 million now. They will issue 6% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 8 years and have a face value of $1,000 each. Bond yields are 10% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue? All numbers are rounded up.
A four year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 9% and a fixed coupon rate of 6%, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
In these tough economic times, central banks around the world have cut interest rates so low that they are practically zero. In some countries, government bond yields are also very close to zero.
A three year government bond with a face value of $100 and a coupon rate of 2% pa paid semi-annually was just issued at a yield of 0%. What is the price of the bond?
A 10 year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 6% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 8% pa, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
A 30 year Japanese government bond was just issued at par with a yield of 1.7% pa. The fixed coupon payments are semi-annual. The bond has a face value of $100.
Six months later, just after the first coupon is paid, the yield of the bond increases to 2% pa. What is the bond's new price?
There are many different ways to value a firm's assets. Which of the following will NOT give the correct market value of a levered firm's assets ##(V_L)##? Assume that:
- The firm is financed by listed common stock and vanilla annual fixed coupon bonds, which are both traded in a liquid market.
- The bonds' yield is equal to the coupon rate, so the bonds are issued at par. The yield curve is flat and yields are not expected to change. When bonds mature they will be rolled over by issuing the same number of new bonds with the same expected yield and coupon rate, and so on forever.
- Tax rates on the dividends and capital gains received by investors are equal, and capital gains tax is paid every year, even on unrealised gains regardless of when the asset is sold.
- There is no re-investment of the firm's cash back into the business. All of the firm's excess cash flow is paid out as dividends so real growth is zero.
- The firm operates in a mature industry with zero real growth.
- All cash flows and rates in the below equations are real (not nominal) and are expected to be stable forever. Therefore the perpetuity equation with no growth is suitable for valuation.
Where:
###r_\text{WACC before tax} = r_D.\frac{D}{V_L} + r_{EL}.\frac{E_L}{V_L} = \text{Weighted average cost of capital before tax}### ###r_\text{WACC after tax} = r_D.(1-t_c).\frac{D}{V_L} + r_{EL}.\frac{E_L}{V_L} = \text{Weighted average cost of capital after tax}### ###NI_L=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-\mathbf{IntExp}).(1-t_c) = \text{Net Income Levered}### ###CFFA_L=NI_L+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+\mathbf{IntExp} = \text{Cash Flow From Assets Levered}### ###NI_U=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr).(1-t_c) = \text{Net Income Unlevered}### ###CFFA_U=NI_U+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC= \text{Cash Flow From Assets Unlevered}###Bonds X and Y are issued by the same US company. Both bonds yield 6% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X pays coupons of 8% pa and bond Y pays coupons of 12% pa. Which of the following statements is true?
Below are some statements about loans and bonds. The first descriptive sentence is correct. But one of the second sentences about the loans' or bonds' prices is not correct. Which statement is NOT correct? Assume that interest rates are positive.
Note that coupons or interest payments are the periodic payments made throughout a bond or loan's life. The face or par value of a bond or loan is the amount paid at the end when the debt matures.
Question 536 idiom, bond pricing, capital structure, leverage
The expression 'my word is my bond' is often used in everyday language to make a serious promise.
Why do you think this expression uses the metaphor of a bond rather than a share?
Question 538 bond pricing, income and capital returns, no explanation
Risk-free government bonds that have coupon rates greater than their yields:
Question 539 debt terminology, fully amortising loan, bond pricing
A 'fully amortising' loan can also be called a:
A firm wishes to raise $10 million now. They will issue 6% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 3 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 5% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
An investor bought a 10 year 2.5% pa fixed coupon government bond priced at par. The face value is $100. Coupons are paid semi-annually and the next one is in 6 months.
Six months later, just after the coupon at that time was paid, yields suddenly and unexpectedly fell to 2% pa. Note that all yields above are given as APR's compounding semi-annually.
What was the bond investors' historical total return over that first 6 month period, given as an effective semi-annual rate?
An investor bought a 20 year 5% pa fixed coupon government bond priced at par. The face value is $100. Coupons are paid semi-annually and the next one is in 6 months.
Six months later, just after the coupon at that time was paid, yields suddenly and unexpectedly rose to 5.5% pa. Note that all yields above are given as APR's compounding semi-annually.
What was the bond investors' historical total return over that first 6 month period, given as an effective semi-annual rate?
Your friend is trying to find the net present value of an investment which:
- Costs $1 million initially (t=0); and
- Pays a single positive cash flow of $1.1 million in one year (t=1).
The investment has a total required return of 10% pa due to its moderate level of undiversifiable risk.
Your friend is aware of the importance of opportunity costs and the time value of money, but he is unsure of how to find the NPV of the project.
He knows that the opportunity cost of investing the $1m in the project is the expected gain from investing the money in shares instead. Like the project, shares also have an expected return of 10% since they have moderate undiversifiable risk. This opportunity cost is $0.1m ##(=1m \times 10\%)## which occurs in one year (t=1).
He knows that the time value of money should be accounted for, and this can be done by finding the present value of the cash flows in one year.
Your friend has listed a few different ways to find the NPV which are written down below.
Method 1: ##-1m + \dfrac{1.1m}{(1+0.1)^1} ##
Method 2: ##-1m + 1.1m - 1m \times 0.1 ##
Method 3: ##-1m + \dfrac{1.1m}{(1+0.1)^1} - 1m \times 0.1 ##
Which of the above calculations give the correct NPV? Select the most correct answer.
A young lady is trying to decide if she should attend university or not.
The young lady's parents say that she must attend university because otherwise all of her hard work studying and attending school during her childhood was a waste.
What's the correct way to classify this item from a capital budgeting perspective when trying to decide whether to attend university?
The hard work studying at school in her childhood should be classified as:
A young lady is trying to decide if she should attend university. Her friends say that she should go to university because she is more likely to meet a clever young man than if she begins full time work straight away.
What's the correct way to classify this item from a capital budgeting perspective when trying to find the Net Present Value of going to university rather than working?
The opportunity to meet a desirable future spouse should be classified as:
A man is thinking about taking a day off from his casual painting job to relax.
He just woke up early in the morning and he's about to call his boss to say that he won't be coming in to work.
But he's thinking about the hours that he could work today (in the future) which are:
A man has taken a day off from his casual painting job to relax.
It's the end of the day and he's thinking about the hours that he could have spent working (in the past) which are now:
Find Candys Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Candys Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 200 | |
| COGS | 50 | |
| Operating expense | 10 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Interest expense | 10 | |
| Income before tax | 110 | |
| Tax at 30% | 33 | |
| Net income | 77 | |
| Candys Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets | 220 | 180 |
| PPE | ||
| Cost | 300 | 340 |
| Accumul. depr. | 60 | 40 |
| Carrying amount | 240 | 300 |
| Total assets | 460 | 480 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | 175 | 190 |
| Non-current liabilities | 135 | 130 |
| Owners' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | 50 | 60 |
| Contributed equity | 100 | 100 |
| Total L and OE | 460 | 480 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Why is Capital Expenditure (CapEx) subtracted in the Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) formula?
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###
A firm has forecast its Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) for this year and management is worried that it is too low. Which one of the following actions will lead to a higher CFFA for this year (t=0 to 1)? Only consider cash flows this year. Do not consider cash flows after one year, or the change in the NPV of the firm. Consider each action in isolation.
A company increases the proportion of debt funding it uses to finance its assets by issuing bonds and using the cash to repurchase stock, leaving assets unchanged.
Ignoring the costs of financial distress, which of the following statements is NOT correct:
Which one of the following will decrease net income (NI) but increase cash flow from assets (CFFA) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI = (Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###Over the next year, the management of an unlevered company plans to:
- Achieve firm free cash flow (FFCF or CFFA) of $1m.
- Pay dividends of $1.8m
- Complete a $1.3m share buy-back.
- Spend $0.8m on new buildings without buying or selling any other fixed assets. This capital expenditure is included in the CFFA figure quoted above.
Assume that:
- All amounts are received and paid at the end of the year so you can ignore the time value of money.
- The firm has sufficient retained profits to pay the dividend and complete the buy back.
- The firm plans to run a very tight ship, with no excess cash above operating requirements currently or over the next year.
How much new equity financing will the company need? In other words, what is the value of new shares that will need to be issued?
Which one of the following will have no effect on net income (NI) but decrease cash flow from assets (CFFA or FFCF) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - ΔNWC+IntExp###Find Ching-A-Lings Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Ching-A-Lings Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 100 | |
| COGS | 20 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Rent expense | 11 | |
| Interest expense | 19 | |
| Taxable Income | 30 | |
| Taxes at 30% | 9 | |
| Net income | 21 | |
| Ching-A-Lings Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Inventory | 49 | 38 |
| Trade debtors | 14 | 2 |
| Rent paid in advance | 5 | 5 |
| PPE | 400 | 400 |
| Total assets | 468 | 445 |
| Trade creditors | 4 | 10 |
| Bond liabilities | 200 | 190 |
| Contributed equity | 145 | 145 |
| Retained profits | 119 | 100 |
| Total L and OE | 468 | 445 |
Note: All figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
The cash flow from assets was:
Over the next year, the management of an unlevered company plans to:
- Make $5m in sales, $1.9m in net income and $2m in equity free cash flow (EFCF).
- Pay dividends of $1m.
- Complete a $1.3m share buy-back.
Assume that:
- All amounts are received and paid at the end of the year so you can ignore the time value of money.
- The firm has sufficient retained profits to legally pay the dividend and complete the buy back.
- The firm plans to run a very tight ship, with no excess cash above operating requirements currently or over the next year.
How much new equity financing will the company need? In other words, what is the value of new shares that will need to be issued?
Read the following financial statements and calculate the firm's free cash flow over the 2014 financial year.
| UBar Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2014 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 293 | |
| COGS | 200 | |
| Rent expense | 15 | |
| Gas expense | 8 | |
| Depreciation | 10 | |
| EBIT | 60 | |
| Interest expense | 0 | |
| Taxable income | 60 | |
| Taxes | 18 | |
| Net income | 42 | |
| UBar Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2014 | 2013 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | 30 | 29 |
| Accounts receivable | 5 | 7 |
| Pre-paid rent expense | 1 | 0 |
| Inventory | 50 | 46 |
| PPE | 290 | 300 |
| Total assets | 376 | 382 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Trade payables | 20 | 18 |
| Accrued gas expense | 3 | 2 |
| Non-current liabilities | 0 | 0 |
| Contributed equity | 212 | 212 |
| Retained profits | 136 | 150 |
| Asset revaluation reserve | 5 | 0 |
| Total L and OE | 376 | 382 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
The firm's free cash flow over the 2014 financial year was:
Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| One Year Mining Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in building mine and equipment | $9m | |
| Depreciation of mine and equipment over the year | $8m | |
| Kilograms of gold mined at end of year | 1,000 | |
| Sale price per kilogram | $0.05m | |
| Variable cost per kilogram | $0.03m | |
| Before-tax cost of closing mine at end of year | $4m | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
Note 1: Due to the project, the firm also anticipates finding some rare diamonds which will give before-tax revenues of $1m at the end of the year.
Note 2: The land that will be mined actually has thermal springs and a family of koalas that could be sold to an eco-tourist resort for an after-tax amount of $3m right now. However, if the mine goes ahead then this natural beauty will be destroyed.
Note 3: The mining equipment will have a book value of $1m at the end of the year for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $2.5m when it is sold.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero and one. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m), with the first cash flow at time zero, and the second at time one.
Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 2 years | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $6m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year for tax purposes | $1m | |
| Unit sales per year | 4m | |
| Sale price per unit | $8 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $3 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $1.5m | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
Note 1: The equipment will have a book value of $4m at the end of the project for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $0.9 million when it is sold at t=2.
Note 2: Due to the project, the firm will have to purchase $0.8m of inventory initially, which it will sell at t=1. The firm will buy another $0.8m at t=1 and sell it all again at t=2 with zero inventory left. The project will have no effect on the firm's current liabilities.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero, one and two. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Value the following business project to manufacture a new product.
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 2 yrs | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $6m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $3m | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | $0.6m | |
| Unit sales per year | 4m | |
| Sale price per unit | $8 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $5 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $1m | |
| Interest expense per year | 0 | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Weighted average cost of capital after tax per annum | 10% | |
Notes
- The firm's current assets and current liabilities are $3m and $2m respectively right now. This net working capital will not be used in this project, it will be used in other unrelated projects.
Due to the project, current assets (mostly inventory) will grow by $2m initially (at t = 0), and then by $0.2m at the end of the first year (t=1).
Current liabilities (mostly trade creditors) will increase by $0.1m at the end of the first year (t=1).
At the end of the project, the net working capital accumulated due to the project can be sold for the same price that it was bought. - The project cost $0.5m to research which was incurred one year ago.
Assumptions
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The business considering the project is run as a 'sole tradership' (run by an individual without a company) and is therefore eligible for a 50% capital gains tax discount when the equipment is sold, as permitted by the Australian Tax Office.
What is the expected net present value (NPV) of the project?
Your friend just bought a house for $400,000. He financed it using a $320,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $80,000.
In the context of residential housing and mortgages, the 'equity' tied up in the value of a person's house is the value of the house less the value of the mortgage. So the initial equity your friend has in his house is $80,000. Let this amount be E, let the value of the mortgage be D and the value of the house be V. So ##V=D+E##.
If house prices suddenly fall by 10%, what would be your friend's percentage change in equity (E)? Assume that the value of the mortgage is unchanged and that no income (rent) was received from the house during the short time over which house prices fell.
Remember:
### r_{0\rightarrow1}=\frac{p_1-p_0+c_1}{p_0} ###
where ##r_{0-1}## is the return (percentage change) of an asset with price ##p_0## initially, ##p_1## one period later, and paying a cash flow of ##c_1## at time ##t=1##.
Your friend just bought a house for $1,000,000. He financed it using a $900,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $100,000.
In the context of residential housing and mortgages, the 'equity' or 'net wealth' tied up in a house is the value of the house less the value of the mortgage loan. Assuming that your friend's only asset is his house, his net wealth is $100,000.
If house prices suddenly fall by 15%, what would be your friend's percentage change in net wealth?
Assume that:
- No income (rent) was received from the house during the short time over which house prices fell.
- Your friend will not declare bankruptcy, he will always pay off his debts.
One year ago you bought $100,000 of shares partly funded using a margin loan. The margin loan size was $70,000 and the other $30,000 was your own wealth or 'equity' in the share assets.
The interest rate on the margin loan was 7.84% pa.
Over the year, the shares produced a dividend yield of 4% pa and a capital gain of 5% pa.
What was the total return on your wealth? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and dividends) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates above are effective annual rates.
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
Here are the Net Income (NI) and Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) equations:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c)###
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+IntExp###
What is the formula for calculating annual interest expense (IntExp) which is used in the equations above?
Select one of the following answers. Note that D is the value of debt which is constant through time, and ##r_D## is the cost of debt.
Interest expense (IntExp) is an important part of a company's income statement (or 'profit and loss' or 'statement of financial performance').
How does an accountant calculate the annual interest expense of a fixed-coupon bond that has a liquid secondary market? Select the most correct answer:
Annual interest expense is equal to:
Which one of the following will increase the Cash Flow From Assets in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Which one of the following will decrease net income (NI) but increase cash flow from assets (CFFA) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - ΔNWC+IntExp###A manufacturing company is considering a new project in the more risky services industry. The cash flows from assets (CFFA) are estimated for the new project, with interest expense excluded from the calculations. To get the levered value of the project, what should these unlevered cash flows be discounted by?
Assume that the manufacturing firm has a target debt-to-assets ratio that it sticks to.
A retail furniture company buys furniture wholesale and distributes it through its retail stores. The owner believes that she has some good ideas for making stylish new furniture. She is considering a project to buy a factory and employ workers to manufacture the new furniture she's designed. Furniture manufacturing has more systematic risk than furniture retailing.
Her furniture retailing firm's after-tax WACC is 20%. Furniture manufacturing firms have an after-tax WACC of 30%. Both firms are optimally geared. Assume a classical tax system.
Which method(s) will give the correct valuation of the new furniture-making project? Select the most correct answer.
The US firm Google operates in the online advertising business. In 2011 Google bought Motorola Mobility which manufactures mobile phones.
Assume the following:
- Google had a 10% after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC) before it bought Motorola.
- Motorola had a 20% after-tax WACC before it merged with Google.
- Google and Motorola have the same level of gearing.
- Both companies operate in a classical tax system.
You are a manager at Motorola. You must value a project for making mobile phones. Which method(s) will give the correct valuation of the mobile phone manufacturing project? Select the most correct answer.
The mobile phone manufacturing project's:
There are many ways to calculate a firm's free cash flow (FFCF), also called cash flow from assets (CFFA). Some include the annual interest tax shield in the cash flow and some do not.
Which of the below FFCF formulas include the interest tax shield in the cash flow?
###(1) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp### ###(2) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp.(1-t_c)### ###(3) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c )+ Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(4) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c) + Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(5) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(6) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(7) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(8) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c### ###(9) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(10) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c###The formulas for net income (NI also called earnings), EBIT and EBITDA are given below. Assume that depreciation and amortisation are both represented by 'Depr' and that 'FC' represents fixed costs such as rent.
###NI=(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###EBIT=Rev - COGS - FC-Depr### ###EBITDA=Rev - COGS - FC### ###Tax =(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).t_c= \dfrac{NI.t_c}{1-t_c}###A method commonly seen in textbooks for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is the following:
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp)(1-t_c) + \\ &\space\space\space+ Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp(1-t_c) \\ \end{aligned}###
One formula for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to use earnings before interest and tax (EBIT).
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (EBIT)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ \end{aligned} \\###
One method for calculating a firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to ignore interest expense. That is, pretend that interest expense ##(IntExp)## is zero:
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - 0)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC - 0\\ \end{aligned}###
One formula for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to use net operating profit after tax (NOPAT).
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= NOPAT + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC \\ \end{aligned} \\###
Question 413 CFFA, interest tax shield, depreciation tax shield
There are many ways to calculate a firm's free cash flow (FFCF), also called cash flow from assets (CFFA).
One method is to use the following formulas to transform net income (NI) into FFCF including interest and depreciation tax shields:
###FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp###
###NI=(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).(1-t_c )###
Another popular method is to use EBITDA rather than net income. EBITDA is defined as:
###EBITDA=Rev - COGS - FC###
One of the below formulas correctly calculates FFCF from EBITDA, including interest and depreciation tax shields, giving an identical answer to that above. Which formula is correct?
Question 69 interest tax shield, capital structure, leverage, WACC
Which statement about risk, required return and capital structure is the most correct?
A company issues a large amount of bonds to raise money for new projects of similar risk to the company's existing projects. The net present value (NPV) of the new projects is positive but small. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is NOT correct?
A firm is considering a new project of similar risk to the current risk of the firm. This project will expand its existing business. The cash flows of the project have been calculated assuming that there is no interest expense. In other words, the cash flows assume that the project is all-equity financed.
In fact the firm has a target debt-to-equity ratio of 1, so the project will be financed with 50% debt and 50% equity. To find the levered value of the firm's assets, what discount rate should be applied to the project's unlevered cash flows? Assume a classical tax system.
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 50%. The firm then issues a large amount of equity to raise money for new projects of similar systematic risk to the company's existing projects. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is correct?
Question 99 capital structure, interest tax shield, Miller and Modigliani, trade off theory of capital structure
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of debt and using the funds to repurchase shares. Its assets are unchanged.
Assume that:
- The firm and individual investors can borrow at the same rate and have the same tax rates.
- The firm's debt and shares are fairly priced and the shares are repurchased at the market price, not at a premium.
- There are no market frictions relating to debt such as asymmetric information or transaction costs.
- Shareholders wealth is measured in terms of utiliity. Shareholders are wealth-maximising and risk-averse. They have a preferred level of overall leverage. Before the firm's capital restructure all shareholders were optimally levered.
According to Miller and Modigliani's theory, which statement is correct?
Question 121 capital structure, leverage, financial distress, interest tax shield
Fill in the missing words in the following sentence:
All things remaining equal, as a firm's amount of debt funding falls, benefits of interest tax shields __________ and the costs of financial distress __________.
Question 337 capital structure, interest tax shield, leverage, real and nominal returns and cash flows, multi stage growth model
A fast-growing firm is suitable for valuation using a multi-stage growth model.
It's nominal unlevered cash flow from assets (##CFFA_U##) at the end of this year (t=1) is expected to be $1 million. After that it is expected to grow at a rate of:
- 12% pa for the next two years (from t=1 to 3),
- 5% over the fourth year (from t=3 to 4), and
- -1% forever after that (from t=4 onwards). Note that this is a negative one percent growth rate.
Assume that:
- The nominal WACC after tax is 9.5% pa and is not expected to change.
- The nominal WACC before tax is 10% pa and is not expected to change.
- The firm has a target debt-to-equity ratio that it plans to maintain.
- The inflation rate is 3% pa.
- All rates are given as nominal effective annual rates.
What is the levered value of this fast growing firm's assets?
A firm plans to issue equity and use the cash raised to pay off its debt. No assets will be bought or sold. Ignore the costs of financial distress.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct, all things remaining equal?
Diversification is achieved by investing in a large amount of stocks. What type of risk is reduced by diversification?
According to the theory of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), total variance can be broken into two components, systematic variance and idiosyncratic variance. Which of the following events would be considered the most diversifiable according to the theory of the CAPM?
According to the theory of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), total risk can be broken into two components, systematic risk and idiosyncratic risk. Which of the following events would be considered a systematic, undiversifiable event according to the theory of the CAPM?
Treasury bonds currently have a return of 5% pa. A stock has a beta of 0.5 and the market return is 10% pa. What is the expected return of the stock?
A fairly priced stock has an expected return equal to the market's. Treasury bonds yield 5% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa. What is the stock's beta?
A stock has a beta of 0.5. Its next dividend is expected to be $3, paid one year from now. Dividends are expected to be paid annually and grow by 2% pa forever. Treasury bonds yield 5% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa. All returns are effective annual rates.
What is the price of the stock now?
Question 244 CAPM, SML, NPV, risk
Examine the following graph which shows stocks' betas ##(\beta)## and expected returns ##(\mu)##:
Assume that the CAPM holds and that future expectations of stocks' returns and betas are correctly measured. Which statement is NOT correct?
Question 235 SML, NPV, CAPM, risk
The security market line (SML) shows the relationship between beta and expected return.
Investment projects that plot on the SML would have:
The security market line (SML) shows the relationship between beta and expected return.
Buying investment projects that plot above the SML would lead to:
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Correlation | Beta | Dollars invested |
|
| A | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.12 | 0.5 | 40 | |
| B | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 80 | ||
What is the beta of the above portfolio?
Stock A has a beta of 0.5 and stock B has a beta of 1. Which statement is NOT correct?
Which statement(s) are correct?
(i) All stocks that plot on the Security Market Line (SML) are fairly priced.
(ii) All stocks that plot above the Security Market Line (SML) are overpriced.
(iii) All fairly priced stocks that plot on the Capital Market Line (CML) have zero idiosyncratic risk.
Select the most correct response:
A stock's correlation with the market portfolio increases while its total risk is unchanged. What will happen to the stock's expected return and systematic risk?
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of debt and using the funds to repurchase shares. Its assets are unchanged. Ignore interest tax shields.
According to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which statement is correct?
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of equity and using the funds to repay debt. Its assets are unchanged. Ignore interest tax shields.
According to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which statement is correct?
The total return of any asset can be broken down in different ways. One possible way is to use the dividend discount model (or Gordon growth model):
###p_0 = \frac{c_1}{r_\text{total}-r_\text{capital}}###
Which, since ##c_1/p_0## is the income return (##r_\text{income}##), can be expressed as:
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{income}+r_\text{capital}###
So the total return of an asset is the income component plus the capital or price growth component.
Another way to break up total return is to use the Capital Asset Pricing Model:
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{f}+β(r_\text{m}- r_\text{f})###
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{time value}+r_\text{risk premium}###
So the risk free rate is the time value of money and the term ##β(r_\text{m}- r_\text{f})## is the compensation for taking on systematic risk.
Using the above theory and your general knowledge, which of the below equations, if any, are correct?
(I) ##r_\text{income}=r_\text{time value}##
(II) ##r_\text{income}=r_\text{risk premium}##
(III) ##r_\text{capital}=r_\text{time value}##
(IV) ##r_\text{capital}=r_\text{risk premium}##
(V) ##r_\text{income}+r_\text{capital}=r_\text{time value}+r_\text{risk premium}##
Which of the equations are correct?
The CAPM can be used to find a business's expected opportunity cost of capital:
###r_i=r_f+β_i (r_m-r_f)###
What should be used as the risk free rate ##r_f##?
Question 408 leverage, portfolio beta, portfolio risk, real estate, CAPM
You just bought a house worth $1,000,000. You financed it with an $800,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $200,000.
You estimate that:
- The house has a beta of 1;
- The mortgage loan has a beta of 0.2.
What is the beta of the equity (the $200,000 deposit) that you have in your house?
Also, if the risk free rate is 5% pa and the market portfolio's return is 10% pa, what is the expected return on equity in your house? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and rent) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates are effective annual rates.
A firm can issue 5 year annual coupon bonds at a yield of 8% pa and a coupon rate of 12% pa.
The beta of its levered equity is 1. Five year government bonds yield 5% pa with a coupon rate of 6% pa. The market's expected dividend return is 4% pa and its expected capital return is 6% pa.
The firm's debt-to-equity ratio is 2:1. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What is the firm's after-tax WACC? Assume a classical tax system.
Which of the following statements about the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is NOT correct?
Question 559 variance, standard deviation, covariance, correlation
Which of the following statements about standard statistical mathematics notation is NOT correct?
Diversification in a portfolio of two assets works best when the correlation between their returns is:
Stock A and B's returns have a correlation of 0.3. Which statement is NOT correct?
All things remaining equal, the variance of a portfolio of two positively-weighted stocks rises as:
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Correlation | Dollars invested |
||
| A | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 60 | ||
| B | 0.2 | 0.6 | 140 | |||
What is the expected return of the above portfolio?
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Correlation ##(\rho_{A,B})## | Dollars invested |
||
| A | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 60 | ||
| B | 0.2 | 0.6 | 140 | |||
What is the standard deviation (not variance) of returns of the above portfolio?
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Covariance ##(\sigma_{A,B})## | Beta | Dollars invested |
|
| A | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.12 | 0.5 | 40 | |
| B | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 80 | ||
What is the standard deviation (not variance) of the above portfolio? Note that the stocks' covariance is given, not correlation.
Question 282 expected and historical returns, income and capital returns
You're the boss of an investment bank's equities research team. Your five analysts are each trying to find the expected total return over the next year of shares in a mining company. The mining firm:
- Is regarded as a mature company since it's quite stable in size and was floated around 30 years ago. It is not a high-growth company;
- Share price is very sensitive to changes in the price of the market portfolio, economic growth, the exchange rate and commodities prices. Due to this, its standard deviation of total returns is much higher than that of the market index;
- Experienced tough times in the last 10 years due to unexpected falls in commodity prices.
- Shares are traded in an active liquid market.
- The analysts' source data is correct and true, but their inferences might be wrong;
- All returns and yields are given as effective annual nominal rates.
Two risky stocks A and B comprise an equal-weighted portfolio. The correlation between the stocks' returns is 70%.
If the variance of stock A's returns increases but the:
- Prices and expected returns of each stock stays the same,
- Variance of stock B's returns stays the same,
- Correlation of returns between the stocks stays the same.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
All things remaining equal, the higher the correlation of returns between two stocks:
Which of the following statements about short-selling is NOT true?
An investor wants to make a portfolio of two stocks A and B with a target expected portfolio return of 6% pa.
- Stock A has an expected return of 5% pa.
- Stock B has an expected return of 10% pa.
What portfolio weights should the investor have in stocks A and B respectively?
Question 558 portfolio weights, portfolio return, short selling
An investor wants to make a portfolio of two stocks A and B with a target expected portfolio return of 16% pa.
- Stock A has an expected return of 8% pa.
- Stock B has an expected return of 12% pa.
What portfolio weights should the investor have in stocks A and B respectively?
Question 556 portfolio risk, portfolio return, standard deviation
An investor wants to make a portfolio of two stocks A and B with a target expected portfolio return of 12% pa.
- Stock A has an expected return of 10% pa and a standard deviation of 20% pa.
- Stock B has an expected return of 15% pa and a standard deviation of 30% pa.
The correlation coefficient between stock A and B's expected returns is 70%.
What will be the annual standard deviation of the portfolio with this 12% pa target return?
What is the covariance of a variable X with itself?
The cov(X, X) or ##\sigma_{X,X}## equals:
What is the correlation of a variable X with itself?
The corr(X, X) or ##\rho_{X,X}## equals:
What is the covariance of a variable X with a constant C?
The cov(X, C) or ##\sigma_{X,C}## equals:
What is the correlation of a variable X with a constant C?
The corr(X, C) or ##\rho_{X,C}## equals:
The standard deviation and variance of a stock's annual returns are calculated over a number of years. The units of the returns are percent per annum ##(\% pa)##.
What are the units of the standard deviation ##(\sigma)## and variance ##(\sigma^2)## of returns respectively?
Hint: Visit Wikipedia to understand the difference between percentage points ##(\text{pp})## and percent ##(\%)##.
The covariance and correlation of two stocks X and Y's annual returns are calculated over a number of years. The units of the returns are in percent per annum ##(\% pa)##.
What are the units of the covariance ##(\sigma_{X,Y})## and correlation ##(\rho_{X,Y})## of returns respectively?
Hint: Visit Wikipedia to understand the difference between percentage points ##(\text{pp})## and percent ##(\%)##.
Let the variance of returns for a share per month be ##\sigma_\text{monthly}^2##.
What is the formula for the variance of the share's returns per year ##(\sigma_\text{yearly}^2)##?
Assume that returns are independently and identically distributed (iid) so they have zero auto correlation, meaning that if the return was higher than average today, it does not indicate that the return tomorrow will be higher or lower than average.
Let the standard deviation of returns for a share per month be ##\sigma_\text{monthly}##.
What is the formula for the standard deviation of the share's returns per year ##(\sigma_\text{yearly})##?
Assume that returns are independently and identically distributed (iid) so they have zero auto correlation, meaning that if the return was higher than average today, it does not indicate that the return tomorrow will be higher or lower than average.
The average weekly earnings of an Australian adult worker before tax was $1,542.40 per week in November 2014 according to the Australian Bureau of Statistics. Therefore average annual earnings before tax were $80,204.80 assuming 52 weeks per year. Personal income tax rates published by the Australian Tax Office are reproduced for the 2014-2015 financial year in the table below:
| Taxable income | Tax on this income |
|---|---|
| 0 – $18,200 | Nil |
| $18,201 – $37,000 | 19c for each $1 over $18,200 |
| $37,001 – $80,000 | $3,572 plus 32.5c for each $1 over $37,000 |
| $80,001 – $180,000 | $17,547 plus 37c for each $1 over $80,000 |
| $180,001 and over | $54,547 plus 45c for each $1 over $180,000 |
The above rates do not include the Medicare levy of 2%. Exclude the Medicare levy from your calculations
How much personal income tax would you have to pay per year if you earned $80,204.80 per annum before-tax?
Question 448 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system
A small private company has a single shareholder. This year the firm earned a $100 profit before tax. All of the firm's after tax profits will be paid out as dividends to the owner.
The corporate tax rate is 30% and the sole shareholder's personal marginal tax rate is 45%.
The Australian imputation tax system applies because the company generates all of its income in Australia and pays corporate tax to the Australian Tax Office. Therefore all of the company's dividends are fully franked. The sole shareholder is an Australian for tax purposes and can therefore use the franking credits to offset his personal income tax liability.
What will be the personal tax payable by the shareholder and the corporate tax payable by the company?
Question 449 personal tax on dividends, classical tax system
A small private company has a single shareholder. This year the firm earned a $100 profit before tax. All of the firm's after tax profits will be paid out as dividends to the owner.
The corporate tax rate is 30% and the sole shareholder's personal marginal tax rate is 45%.
The United States' classical tax system applies because the company generates all of its income in the US and pays corporate tax to the Internal Revenue Service. The shareholder is also an American for tax purposes.
What will be the personal tax payable by the shareholder and the corporate tax payable by the company?
Question 494 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system
A firm pays a fully franked cash dividend of $100 to one of its Australian shareholders who has a personal marginal tax rate of 15%. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What will be the shareholder's personal tax payable due to the dividend payment?
A company announces that it will pay a dividend, as the market expected. The company's shares trade on the stock exchange which is open from 10am in the morning to 4pm in the afternoon each weekday. When would the share price be expected to fall by the amount of the dividend? Ignore taxes.
The share price is expected to fall during the:
A pharmaceutical firm has just discovered a valuable new drug. So far the news has been kept a secret.
The net present value of making and commercialising the drug is $200 million, but $600 million of bonds will need to be issued to fund the project and buy the necessary plant and equipment.
The firm will release the news of the discovery and bond raising to shareholders simultaneously in the same announcement. The bonds will be issued shortly after.
Once the announcement is made and the bonds are issued, what is the expected increase in the value of the firm's assets (ΔV), market capitalisation of debt (ΔD) and market cap of equity (ΔE)?
The triangle symbol is the Greek letter capital delta which means change or increase in mathematics.
Ignore the benefit of interest tax shields from having more debt.
Remember: ##ΔV = ΔD+ΔE##
Currently, a mining company has a share price of $6 and pays constant annual dividends of $0.50. The next dividend will be paid in 1 year. Suddenly and unexpectedly the mining company announces that due to higher than expected profits, all of these windfall profits will be paid as a special dividend of $0.30 in 1 year.
If investors believe that the windfall profits and dividend is a one-off event, what will be the new share price? If investors believe that the additional dividend is actually permanent and will continue to be paid, what will be the new share price? Assume that the required return on equity is unchanged. Choose from the following, where the first share price includes the one-off increase in earnings and dividends for the first year only ##(P_\text{0 one-off})## , and the second assumes that the increase is permanent ##(P_\text{0 permanent})##:
Note: When a firm makes excess profits they sometimes pay them out as special dividends. Special dividends are just like ordinary dividends but they are one-off and investors do not expect them to continue, unlike ordinary dividends which are expected to persist.
A mining firm has just discovered a new mine. So far the news has been kept a secret.
The net present value of digging the mine and selling the minerals is $250 million, but $500 million of new equity and $300 million of new bonds will need to be issued to fund the project and buy the necessary plant and equipment.
The firm will release the news of the discovery and equity and bond raising to shareholders simultaneously in the same announcement. The shares and bonds will be issued shortly after.
Once the announcement is made and the new shares and bonds are issued, what is the expected increase in the value of the firm's assets ##(\Delta V)##, market capitalisation of debt ##(\Delta D)## and market cap of equity ##(\Delta E)##? Assume that markets are semi-strong form efficient.
The triangle symbol ##\Delta## is the Greek letter capital delta which means change or increase in mathematics.
Ignore the benefit of interest tax shields from having more debt.
Remember: ##\Delta V = \Delta D+ \Delta E##
Question 513 stock split, reverse stock split, stock dividend, bonus issue, rights issue
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 566 capital structure, capital raising, rights issue, on market repurchase, dividend, stock split, bonus issue
A company's share price fell by 20% and its number of shares rose by 25%. Assume that there are no taxes, no signalling effects and no transaction costs.
Which one of the following corporate events may have happened?
A company conducts a 4 for 3 stock split. What is the percentage change in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order.
Question 568 rights issue, capital raising, capital structure
A company conducts a 1 for 5 rights issue at a subscription price of $7 when the pre-announcement stock price was $10. What is the percentage change in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order. Ignore all taxes, transaction costs and signalling effects.
In mid 2009 the listed mining company Rio Tinto announced a 21-for-40 renounceable rights issue. Below is the chronology of events:
- 04/06/2009. Share price opens at $69.00 and closes at $66.90.
- 05/06/2009. 21-for-40 rights issue announced at a subscription price of $28.29.
- 16/06/2009. Last day that shares trade cum-rights. Share price opens at $76.40 and closes at $75.50.
- 17/06/2009. Shares trade ex-rights. Rights trading commences.
All things remaining equal, what would you expect Rio Tinto's stock price to open at on the first day that it trades ex-rights (17/6/2009)? Ignore the time value of money since time is negligibly short. Also ignore taxes.
In late 2003 the listed bank ANZ announced a 2-for-11 rights issue to fund the takeover of New Zealand bank NBNZ. Below is the chronology of events:
- 23/10/2003. Share price closes at $18.30.
- 24/10/2003. 2-for-11 rights issue announced at a subscription price of $13. The proceeds of the rights issue will be used to acquire New Zealand bank NBNZ. Trading halt announced in morning before market opens.
- 28/10/2003. Trading halt lifted. Last (and only) day that shares trade cum-rights. Share price opens at $18.00 and closes at $18.14.
- 29/10/2003. Shares trade ex-rights.
All things remaining equal, what would you expect ANZ's stock price to open at on the first day that it trades ex-rights (29/10/2003)? Ignore the time value of money since time is negligibly short. Also ignore taxes.
Question 455 income and capital returns, payout policy, DDM, market efficiency
A fairly priced unlevered firm plans to pay a dividend of $1 next year (t=1) which is expected to grow by 3% pa every year after that. The firm's required return on equity is 8% pa.
The firm is thinking about reducing its future dividend payments by 10% so that it can use the extra cash to invest in more projects which are expected to return 8% pa, and have the same risk as the existing projects. Therefore, next year's dividend will be $0.90. No new equity or debt will be issued to fund the new projects, they'll all be funded by the cut in dividends.
What will be the stock's new annual capital return (proportional increase in price per year) if the change in payout policy goes ahead?
Assume that payout policy is irrelevant to firm value (so there's no signalling effects) and that all rates are effective annual rates.
Government bonds currently have a return of 5% pa. A stock has an expected return of 6% pa and the market return is 7% pa. What is the beta of the stock?
A firm's weighted average cost of capital before tax (##r_\text{WACC before tax}##) would increase due to:
A company has:
- 50 million shares outstanding.
- The market price of one share is currently $6.
- The risk-free rate is 5% and the market return is 10%.
- Market analysts believe that the company's ordinary shares have a beta of 2.
- The company has 1 million preferred stock which have a face (or par) value of $100 and pay a constant dividend of 10% of par. They currently trade for $80 each.
- The company's debentures are publicly traded and their market price is equal to 90% of their face value.
- The debentures have a total face value of $60,000,000 and the current yield to maturity of corporate debentures is 10% per annum. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What is the company's after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC)? Assume a classical tax system.
Government bonds currently have a return of 5%. A stock has a beta of 2 and the market return is 7%. What is the expected return of the stock?
A company has:
- 140 million shares outstanding.
- The market price of one share is currently $2.
- The company's debentures are publicly traded and their market price is equal to 93% of the face value.
- The debentures have a total face value of $50,000,000 and the current yield to maturity of corporate debentures is 12% per annum.
- The risk-free rate is 8.50% and the market return is 13.7%.
- Market analysts estimated that the company's stock has a beta of 0.90.
- The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What is the company's after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC) in a classical tax system?
A firm can issue 3 year annual coupon bonds at a yield of 10% pa and a coupon rate of 8% pa.
The beta of its levered equity is 2. The market's expected return is 10% pa and 3 year government bonds yield 6% pa with a coupon rate of 4% pa.
The market value of equity is $1 million and the market value of debt is $1 million. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What is the firm's after-tax WACC? Assume a classical tax system.
Question 104 CAPM, payout policy, capital structure, Miller and Modigliani, risk
Assume that there exists a perfect world with no transaction costs, no asymmetric information, no taxes, no agency costs, equal borrowing rates for corporations and individual investors, the ability to short the risk free asset, semi-strong form efficient markets, the CAPM holds, investors are rational and risk-averse and there are no other market frictions.
For a firm operating in this perfect world, which statement(s) are correct?
(i) When a firm changes its capital structure and/or payout policy, share holders' wealth is unaffected.
(ii) When the idiosyncratic risk of a firm's assets increases, share holders do not expect higher returns.
(iii) When the systematic risk of a firm's assets increases, share holders do not expect higher returns.
Select the most correct response:
A fairly priced stock has an expected return of 15% pa. Treasury bonds yield 5% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa. What is the beta of the stock?
A fairly priced stock has a beta that is the same as the market portfolio's beta. Treasury bonds yield 5% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa. What is the expected return of the stock?
Question 418 capital budgeting, NPV, interest tax shield, WACC, CFFA, CAPM
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $8m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $8m | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | 0 | |
| Unit sales per year | 4m | |
| Sale price per unit | $10 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $5 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $2m | |
| Interest expense in first year (at t=1) | $0.562m | |
| Corporate tax rate | 30% | |
| Government treasury bond yield | 5% | |
| Bank loan debt yield | 9% | |
| Market portfolio return | 10% | |
| Covariance of levered equity returns with market | 0.32 | |
| Variance of market portfolio returns | 0.16 | |
| Firm's and project's debt-to-equity ratio | 50% | |
Notes
- Due to the project, current assets will increase by $6m now (t=0) and fall by $6m at the end (t=1). Current liabilities will not be affected.
Assumptions
- The debt-to-equity ratio will be kept constant throughout the life of the project. The amount of interest expense at the end of each period has been correctly calculated to maintain this constant debt-to-equity ratio.
- Millions are represented by 'm'.
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The project is undertaken by a firm, not an individual.
What is the net present value (NPV) of the project?
Question 419 capital budgeting, NPV, interest tax shield, WACC, CFFA, CAPM, no explanation
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $6m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $6m | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | 0 | |
| Unit sales per year | 9m | |
| Sale price per unit | $8 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $6 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $1m | |
| Interest expense in first year (at t=1) | $0.53m | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Government treasury bond yield | 5% | |
| Bank loan debt yield | 6% | |
| Market portfolio return | 10% | |
| Covariance of levered equity returns with market | 0.08 | |
| Variance of market portfolio returns | 0.16 | |
| Firm's and project's debt-to-assets ratio | 50% | |
Notes
- Due to the project, current assets will increase by $5m now (t=0) and fall by $5m at the end (t=1). Current liabilities will not be affected.
Assumptions
- The debt-to-assets ratio will be kept constant throughout the life of the project. The amount of interest expense at the end of each period has been correctly calculated to maintain this constant debt-to-equity ratio.
- Millions are represented by 'm'.
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 2% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The 50% capital gains tax discount is not available since the project is undertaken by a firm, not an individual.
What is the net present value (NPV) of the project?
The accounting identity states that the book value of a company's assets (A) equals its liabilities (L) plus owners equity (OE), so A = L + OE.
The finance version states that the market value of a company's assets (V) equals the market value of its debt (D) plus equity (E), so V = D + E.
Therefore a business's assets can be seen as a portfolio of the debt and equity that fund the assets.
Let ##\sigma_\text{V total}^2## be the total variance of returns on assets, ##\sigma_\text{V syst}^2## be the systematic variance of returns on assets, and ##\sigma_\text{V idio}^2## be the idiosyncratic variance of returns on assets, and ##\rho_\text{D idio, E idio}## be the correlation between the idiosyncratic returns on debt and equity.
Which of the following equations is NOT correct?
A new company's Firm Free Cash Flow (FFCF, same as CFFA) is forecast in the graph below.
To value the firm's assets, the terminal value needs to be calculated using the perpetuity with growth formula:
###V_{\text{terminal, }t-1} = \dfrac{FFCF_{\text{terminal, }t}}{r-g}###
Which point corresponds to the best time to calculate the terminal value?
An old company's Firm Free Cash Flow (FFCF, same as CFFA) is forecast in the graph below.
To value the firm's assets, the terminal value needs to be calculated using the perpetuity with growth formula:
###V_{\text{terminal, }t-1} = \dfrac{FFCF_{\text{terminal, }t}}{r-g}###
Which point corresponds to the best time to calculate the terminal value?
A new company's Firm Free Cash Flow (FFCF, same as CFFA) is forecast in the graph below.
To value the firm's assets, the terminal value needs to be calculated using the perpetuity with growth formula:
###V_{\text{terminal, }t-1} = \dfrac{FFCF_{\text{terminal, }t}}{r-g}###
Which point corresponds to the best time to calculate the terminal value?
Question 370 capital budgeting, NPV, interest tax shield, WACC, CFFA
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 2 yrs | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $600k | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $250k | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | $200k | |
| Revenue per job | $12k | |
| Variable cost per job | $4k | |
| Quantity of jobs per year | 120 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $100k | |
| Interest expense in first year (at t=1) | $16.091k | |
| Interest expense in second year (at t=2) | $9.711k | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Government treasury bond yield | 5% | |
| Bank loan debt yield | 6% | |
| Levered cost of equity | 12.5% | |
| Market portfolio return | 10% | |
| Beta of assets | 1.24 | |
| Beta of levered equity | 1.5 | |
| Firm's and project's debt-to-equity ratio | 25% | |
Notes
- The project will require an immediate purchase of $50k of inventory, which will all be sold at cost when the project ends. Current liabilities are negligible so they can be ignored.
Assumptions
- The debt-to-equity ratio will be kept constant throughout the life of the project. The amount of interest expense at the end of each period has been correctly calculated to maintain this constant debt-to-equity ratio. Note that interest expense is different in each year.
- Thousands are represented by 'k' (kilo).
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are nominal. The inflation rate is 2% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The 50% capital gains tax discount is not available since the project is undertaken by a firm, not an individual.
What is the net present value (NPV) of the project?
The hardest and most important aspect of business project valuation is the estimation of the:
A young lady is trying to decide if she should attend university or begin working straight away in her home town.
The young lady's grandma says that she should not go to university because she is less likely to marry the local village boy whom she likes because she will spend less time with him if she attends university.
What's the correct way to classify this item from a capital budgeting perspective when trying to decide whether to attend university?
The cost of not marrying the local village boy should be classified as:
Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| Project Data | |
| Project life | 2 years |
| Initial investment in equipment | $8m |
| Depreciation of equipment per year for tax purposes | $3m |
| Unit sales per year | 10m |
| Sale price per unit | $9 |
| Variable cost per unit | $4 |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $2m |
| Tax rate | 30% |
Note 1: Due to the project, the firm will have to purchase $40m of inventory initially (at t=0). Half of this inventory will be sold at t=1 and the other half at t=2.
Note 2: The equipment will have a book value of $2m at the end of the project for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $1m when it is sold. Assume that the full capital loss is tax-deductible and taxed at the full corporate tax rate.
Note 3: The project will be fully funded by equity which investors will expect to pay dividends totaling $10m at the end of each year.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero, one and two. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Three important classes of investable risky assets are:
- Corporate debt which has low total risk,
- Real estate which has medium total risk,
- Equity which has high total risk.
Assume that the correlation between total returns on:
- Corporate debt and real estate is 0.1,
- Corporate debt and equity is 0.1,
- Real estate and equity is 0.5.
You are considering investing all of your wealth in one or more of these asset classes. Which portfolio will give the lowest total risk? You are restricted from shorting any of these assets. Disregard returns and the risk-return trade-off, pretend that you are only concerned with minimising risk.
The following table shows a sample of historical total returns of shares in two different companies A and B.
| Stock Returns | ||
| Total effective annual returns | ||
| Year | ##r_A## | ##r_B## |
| 2007 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| 2008 | 0.04 | -0.2 |
| 2009 | -0.1 | -0.3 |
| 2010 | 0.18 | 0.5 |
What is the historical sample covariance (##\hat{\sigma}_{A,B}##) and correlation (##\rho_{A,B}##) of stock A and B's total effective annual returns?
Question 469 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system, no explanation
A firm pays a fully franked cash dividend of $70 to one of its Australian shareholders who has a personal marginal tax rate of 45%. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What will be the shareholder's personal tax payable due to the dividend payment?
You want to buy an apartment priced at $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $30,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $270,000 as an interest only loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 12% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments? Remember that mortgage payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
You just borrowed $400,000 in the form of a 25 year interest-only mortgage with monthly payments of $3,000 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
You actually plan to pay more than the required interest payment. You plan to pay $3,300 in mortgage payments every month, which your mortgage lender allows. These extra payments will reduce the principal and the minimum interest payment required each month.
At the maturity of the mortgage, what will be the principal? That is, after the last (300th) interest payment of $3,300 in 25 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage?
You want to buy an apartment priced at $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as an interest only loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
A prospective home buyer can afford to pay $2,000 per month in mortgage loan repayments. The central bank recently lowered its policy rate by 0.25%, and residential home lenders cut their mortgage loan rates from 4.74% to 4.49%.
How much more can the prospective home buyer borrow now that interest rates are 4.49% rather than 4.74%? Give your answer as a proportional increase over the original amount he could borrow (##V_\text{before}##), so:
###\text{Proportional increase} = \frac{V_\text{after}-V_\text{before}}{V_\text{before}} ###Assume that:
- Interest rates are expected to be constant over the life of the loan.
- Loans are interest-only and have a life of 30 years.
- Mortgage loan payments are made every month in arrears and all interest rates are given as annualised percentage rates compounding per month.
Question 546 income and capital returns, interest only loan, no explanation
Which of the following statements about the capital and income returns of an interest-only loan is correct?
Assume that the yield curve (which shows total returns over different maturities) is flat and is not expected to change.
An interest-only loan's expected:
Many Australian home loans that are interest-only actually require payments to be made on a fully amortising basis after a number of years.
You decide to borrow $600,000 from the bank at an interest rate of 4.25% pa for 25 years. The payments will be interest-only for the first 10 years (t=0 to 10 years), then they will have to be paid on a fully amortising basis for the last 15 years (t=10 to 25 years).
Assuming that interest rates will remain constant, what will be your monthly payments over the first 10 years from now, and then the next 15 years after that? The answer options are given in the same order.
Question 241 Miller and Modigliani, leverage, payout policy, diversification, NPV
One of Miller and Modigliani's (M&M's) important insights is that a firm's managers should not try to achieve a particular level of leverage in a world with zero taxes and perfect information since investors can make their own leverage. Therefore corporate capital structure policy is irrelevant since investors can achieve their own desired leverage at the personal level by borrowing or lending on their own.
This principal of 'home-made' or 'do-it-yourself' leverage can also be applied to other topics. Read the following statements to decide which are true:
(I) Payout policy: a firm's managers should not try to achieve a particular pattern of equity payout.
(II) Agency costs: a firm's managers should not try to minimise agency costs.
(III) Diversification: a firm's managers should not try to diversify across industries.
(IV) Shareholder wealth: a firm's managers should not try to maximise shareholders' wealth.
Which of the above statement(s) are true?
Question 247 cross currency interest rate parity, no explanation
In the so called 'Swiss Loans Affair' of the 1980's, Australian banks offered loans denominated in Swiss Francs to Australian farmers at interest rates as low as 4% pa. This was far lower than interest rates on Australian Dollar loans which were above 10% due to very high inflation in Australia at the time.
In the late-1980's there was a large depreciation in the Australian Dollar. The Australian Dollar nearly halved in value against the Swiss Franc. Many Australian farmers went bankrupt since they couldn't afford the interest payments on the Swiss Franc loans because the Australian Dollar value of those payments nearly doubled. The farmers accused the banks of promoting Swiss Franc loans without making them aware of the risks.
What fundamental principal of finance did the Australian farmers (and the bankers) fail to understand?
Question 245 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, foreign exchange rate direct quote, no explanation
Investors expect Australia's central bank, the RBA, to leave the policy rate unchanged at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the policy rate is reduced due to fears that Australia's GDP growth is slowing.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate? Direct and indirect quotes are given from the perspective of an Australian.
The Australian dollar will:
Question 312 foreign exchange rate, American and European terms
If the current AUD exchange rate is USD 0.9686 = AUD 1, what is the American terms quote of the AUD against the USD?
Question 322 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
The market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to decrease the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will decrease the policy rate by 50 basis points due to fears of a recession and deflation.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate? The Australian dollar will:
The Chinese government attempts to fix its exchange rate against the US dollar and at the same time use monetary policy to fix its interest rate at a set level.
To be able to fix its exchange rate and interest rate in this way, what does the Chinese government actually do?
- Adopts capital controls to prevent financial arbitrage by private firms and individuals.
- Adopts the same interest rate (monetary policy) as the United States.
- Fixes inflation so that the domestic real interest rate is equal to the United States' real interest rate.
Which of the above statements is or are true?
Question 335 foreign exchange rate, American and European terms
Investors expect Australia's central bank, the RBA, to reduce the policy rate at their next meeting due to fears that the economy is slowing. Then unexpectedly, the policy rate is actually kept unchanged.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate?
An Indonesian lady wishes to convert 1 million Indonesian rupiah (IDR) to Australian dollars (AUD). Exchange rates are 13,125 IDR per USD and 0.79 USD per AUD. How many AUD is the IDR 1 million worth?
In the 1997 Asian financial crisis many countries' exchange rates depreciated rapidly against the US dollar (USD). The Thai, Indonesian, Malaysian, Korean and Filipino currencies were severely affected. The below graph shows these Asian countries' currencies in USD per one unit of their currency, indexed to 100 in June 1997.
Of the statements below, which is NOT correct? The Asian countries':
A firm has a debt-to-equity ratio of 25%. What is its debt-to-assets ratio?
A firm has a debt-to-equity ratio of 60%. What is its debt-to-assets ratio?
Question 237 WACC, Miller and Modigliani, interest tax shield
Which of the following discount rates should be the highest for a levered company? Ignore the costs of financial distress.
The expression 'cash is king' emphasizes the importance of having enough cash to pay your short term debts to avoid bankruptcy. Which business decision is this expression most closely related to?
The expression 'you have to spend money to make money' relates to which business decision?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### p_{0} = \frac{c_1}{r_{\text{eff}} - g_{\text{eff}}} ###
What is the discount rate '## r_\text{eff} ##' in this equation?
A share was bought for $20 (at t=0) and paid its annual dividend of $3 one year later (at t=1). Just after the dividend was paid, the share price was $16 (at t=1). What was the total return, capital return and income return? Calculate your answers as effective annual rates.
The choices are given in the same order: ## r_\text{total},r_\text{capital},r_\text{income} ##.
When using the dividend discount model to price a stock:
### p_{0} = \frac{d_1}{r - g} ###
The growth rate of dividends (g):
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### p_0 = \frac{d_1}{r - g} ###
Which expression is NOT equal to the expected dividend yield?
A share was bought for $10 (at t=0) and paid its annual dividend of $0.50 one year later (at t=1). Just after the dividend was paid, the share price was $11 (at t=1).
What was the total return, capital return and income return? Calculate your answers as effective annual rates. The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}##, ##r_\text{capital}##, ##r_\text{dividend}##.
The following is the Dividend Discount Model used to price stocks:
### p_0=\frac{d_1}{r-g} ###
Which of the following statements about the Dividend Discount Model is NOT correct?
Here's the Dividend Discount Model, used to price stocks:
### p_0=\frac{d_1}{r-g} ###
All rates are effective annual rates and the cash flows (##d_1##) are received every year. Note that the r and g terms in the above DDM could also be labelled: ###r = r_{\text{total, 0}\rightarrow\text{1yr, eff 1yr}}### ###g = r_{\text{capital, 0}\rightarrow\text{1yr, eff 1yr}}### Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
The following is the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) used to price stocks:
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
If the assumptions of the DDM hold and the stock is fairly priced, which one of the following statements is NOT correct? The long term expected:
A credit card offers an interest rate of 18% pa, compounding monthly.
Find the effective monthly rate, effective annual rate and the effective daily rate. Assume that there are 365 days in a year.
All answers are given in the same order:
### r_\text{eff monthly} , r_\text{eff yearly} , r_\text{eff daily} ###
Question 497 income and capital returns, DDM, ex dividend date
A stock will pay you a dividend of $10 tonight if you buy it today. Thereafter the annual dividend is expected to grow by 5% pa, so the next dividend after the $10 one tonight will be $10.50 in one year, then in two years it will be $11.025 and so on. The stock's required return is 10% pa.
What is the stock price today and what do you expect the stock price to be tomorrow, approximately?
For a price of $13, Carla will sell you a share paying a dividend of $1 in one year and every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
For a price of $6, Carlos will sell you a share which will pay a dividend of $1 in one year and every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
For a price of $102, Andrea will sell you a share which just paid a dividend of $10 yesterday, and is expected to pay dividends every year forever, growing at a rate of 5% pa.
So the next dividend will be ##10(1+0.05)^1=$10.50## in one year from now, and the year after it will be ##10(1+0.05)^2=11.025## and so on.
The required return of the stock is 15% pa.
For a price of $1040, Camille will sell you a share which just paid a dividend of $100, and is expected to pay dividends every year forever, growing at a rate of 5% pa.
So the next dividend will be ##100(1+0.05)^1=$105.00##, and the year after it will be ##100(1+0.05)^2=110.25## and so on.
The required return of the stock is 15% pa.
For a price of $10.20 each, Renee will sell you 100 shares. Each share is expected to pay dividends in perpetuity, growing at a rate of 5% pa. The next dividend is one year away (t=1) and is expected to be $1 per share.
The required return of the stock is 15% pa.
For a price of $129, Joanne will sell you a share which is expected to pay a $30 dividend in one year, and a $10 dividend every year after that forever. So the stock's dividends will be $30 at t=1, $10 at t=2, $10 at t=3, and $10 forever onwards.
The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
For a price of $95, Sherylanne will sell you a share which is expected to pay its first dividend of $10 in 7 years (t=7), and will continue to pay the same $10 dividend every year after that forever.
The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
A three year project's NPV is negative. The cash flows of the project include a negative cash flow at the very start and positive cash flows over its short life. The required return of the project is 10% pa. Select the most correct statement.
A project has the following cash flows. Normally cash flows are assumed to happen at the given time. But here, assume that the cash flows are received smoothly over the year. So the $250 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 200 |
| 2 | 250 |
What is the payback period of the project in years?
If a project's net present value (NPV) is zero, then its internal rate of return (IRR) will be:
A project has an internal rate of return (IRR) which is greater than its required return. Select the most correct statement.
A project's net present value (NPV) is negative. Select the most correct statement.
A project's NPV is positive. Select the most correct statement:
A project has the following cash flows:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 500 |
The required return on the project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of this project? The following choices are effective annual rates. Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time.
A project's Profitability Index (PI) is less than 1. Select the most correct statement:
Question 218 NPV, IRR, profitability index, average accounting return
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A firm is considering a business project which costs $11m now and is expected to pay a constant $1m at the end of every year forever.
Assume that the initial $11m cost is funded using the firm's existing cash so no new equity or debt will be raised. The cost of capital is 10% pa.
Which of the following statements about net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR) and payback period is NOT correct?
A firm is considering a business project which costs $10m now and is expected to pay a single cash flow of $12.1m in two years.
Assume that the initial $10m cost is funded using the firm's existing cash so no new equity or debt will be raised. The cost of capital is 10% pa.
Which of the following statements about net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR) and payback period is NOT correct?
The below graph shows a project's net present value (NPV) against its annual discount rate.
For what discount rate or range of discount rates would you accept and commence the project?
All answer choices are given as approximations from reading off the graph.
The below graph shows a project's net present value (NPV) against its annual discount rate.

Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
An investor owns an empty block of land that has local government approval to be developed into a petrol station, car wash or car park. The council will only allow a single development so the projects are mutually exclusive.
All of the development projects have the same risk and the required return of each is 10% pa. Each project has an immediate cost and once construction is finished in one year the land and development will be sold. The table below shows the estimated costs payable now, expected sale prices in one year and the internal rates of returns (IRR's).
| Mutually Exclusive Projects | |||
| Project | Cost now ($) |
Sale price in one year ($) |
IRR (% pa) |
| Petrol station | 9,000,000 | 11,000,000 | 22.22 |
| Car wash | 800,000 | 1,100,000 | 37.50 |
| Car park | 70,000 | 110,000 | 57.14 |
Which project should the investor accept?
Which of the following decisions relates to the current assets and current liabilities of the firm?
A stock is expected to pay its next dividend of $1 in one year. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. So the first dividend of $1 will be in one year, the year after that $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1), and a year later $1.0404 (=1*(1+0.02)^2) and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
A stock just paid a dividend of $1. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. The next dividend of $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1) will be in one year, and the year after that the dividend will be $1.0404 (=1*(1+0.02)^2), and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
A stock is just about to pay a dividend of $1 tonight. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. The next dividend of $1 will be paid tonight, and the year after that the dividend will be $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1), and a year later 1.0404 (=1*(1+0.04)^2) and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
The following cash flows are expected:
- Constant perpetual yearly payments of $70, with the first payment in 2.5 years from now (first payment at t=2.5).
- A single payment of $600 in 3 years and 9 months (t=3.75) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
The following cash flows are expected:
- 10 yearly payments of $80, with the first payment in 6.5 years from now (first payment at t=6.5).
- A single payment of $500 in 4 years and 3 months (t=4.25) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
Question 522 income and capital returns, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 6% pa and nominal capital return of 2.5% pa. Inflation is expected to be 2.5% pa.
All of the above are effective nominal rates and investors believe that they will stay the same in perpetuity.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns?
The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Question 523 income and capital returns, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation
A low-growth mature stock has an expected nominal total return of 6% pa and nominal capital return of 2% pa. Inflation is expected to be 3% pa.
All of the above are effective nominal rates and investors believe that they will stay the same in perpetuity.
What are the stock's expected real total, capital and income returns?
The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Question 524 risk, expected and historical returns, bankruptcy or insolvency, capital structure, corporate financial decision theory, limited liability
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 525 income and capital returns, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation
Which of the following statements about cash in the form of notes and coins is NOT correct? Assume that inflation is positive.
Notes and coins:
Question 526 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, no explanation
How can a nominal cash flow be precisely converted into a real cash flow?
Total cash flows can be broken into income and capital cash flows.
What is the name given to the cash flow generated from selling shares at a higher price than they were bought?
The perpetuity with growth formula, also known as the dividend discount model (DDM) or Gordon growth model, is appropriate for valuing a company's shares. ##P_0## is the current share price, ##C_1## is next year's expected dividend, ##r## is the total required return and ##g## is the expected growth rate of the dividend.
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
The below graph shows the expected future price path of the company's shares. Which of the following statements about the graph is NOT correct?
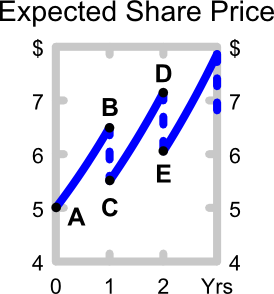
Question 529 DDM, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, real estate, no explanation
If housing rents are constrained from growing more than the maximum target inflation rate, and houses can be priced as a perpetuity of growing net rental cash flows, then what is the implication for house prices, all things remaining equal? Select the most correct answer.
Background: Since 1990, many central banks across the world have become 'inflation targeters'. They have adopted a policy of trying to keep inflation in a predictable narrow range, with the hope of encouraging long-term lending to fund more investment and maintain higher GDP growth.
Australia's central bank, the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA), has specifically stated their inflation target range is between 2 and 3% pa.
Some Australian residential property market commentators suggest that because rental costs comprise a large part of the Australian consumer price index (CPI), rent costs across the nation cannot significantly exceed the maximum inflation target range of 3% pa without the prices of other goods growing by less than the target range for long periods, which is unlikely.
You are promised 20 payments of $100, where the first payment is immediate (t=0) and the last is at the end of the 19th year (t=19). The effective annual discount rate is ##r##.
Which of the following equations does NOT give the correct present value of these 20 payments?
Question 531 bankruptcy or insolvency, capital structure, risk, limited liability
Who is most in danger of being personally bankrupt? Assume that all of their businesses' assets are highly liquid and can therefore be sold immediately.
Question 535 DDM, real and nominal returns and cash flows, stock pricing
You are an equities analyst trying to value the equity of the Australian telecoms company Telstra, with ticker TLS. In Australia, listed companies like Telstra tend to pay dividends every 6 months. The payment around August is called the final dividend and the payment around February is called the interim dividend. Both occur annually.
- Today is mid-March 2015.
- TLS's last interim dividend of $0.15 was one month ago in mid-February 2015.
- TLS's last final dividend of $0.15 was seven months ago in mid-August 2014.
Judging by TLS's dividend history and prospects, you estimate that the nominal dividend growth rate will be 1% pa. Assume that TLS's total nominal cost of equity is 6% pa. The dividends are nominal cash flows and the inflation rate is 2.5% pa. All rates are quoted as nominal effective annual rates. Assume that each month is exactly one twelfth (1/12) of a year, so you can ignore the number of days in each month.
Calculate the current TLS share price.
Estimate the French bank Societe Generale's share price using a backward-looking price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only. Note that EUR is the euro, the European monetary union's currency.
- The 4 major European banks Credit Agricole (ACA), Deutsche Bank AG (DBK), UniCredit (UCG) and Banco Santander (SAN) are comparable companies to Societe Generale (GLE);
- Societe Generale's (GLE's) historical earnings per share (EPS) is EUR 2.92;
- ACA's backward-looking PE ratio is 16.29 and historical EPS is EUR 0.84;
- DBK's backward-looking PE ratio is 25.01 and historical EPS is EUR 1.26;
- SAN's backward-looking PE ratio is 14.71 and historical EPS is EUR 0.47;
- UCG's backward-looking PE ratio is 15.78 and historical EPS is EUR 0.40;
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 27 March 2015.
Which one of the below statements about effective rates and annualised percentage rates (APR's) is NOT correct?
Question 542 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to double every 10 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
Question 543 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to triple every 5 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
Question 545 income and capital returns, fully amortising loan, no explanation
Which of the following statements about the capital and income returns of a 25 year fully amortising loan asset is correct?
Assume that the yield curve (which shows total returns over different maturities) is flat and is not expected to change.
Over the 25 years from issuance to maturity, a fully amortising loan's expected annual effective:
Question 547 PE ratio, Multiples valuation, DDM, income and capital returns, no explanation
A firm pays out all of its earnings as dividends. Because of this, the firm has no real growth in earnings, dividends or stock price since there is no re-investment back into the firm to buy new assets and make higher earnings. The dividend discount model is suitable to value this company.
The firm's revenues and costs are expected to increase by inflation in the foreseeable future. The firm has no debt. It operates in the services industry and has few physical assets so there is negligible depreciation expense and negligible net working capital required.
Which of the following statements about this firm's PE ratio is NOT correct? The PE ratio should:
Note: The inverse of x is 1/x.
Question 554 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
On his 20th birthday, a man makes a resolution. He will put $30 cash under his bed at the end of every month starting from today. His birthday today is the first day of the month. So the first addition to his cash stash will be in one month. He will write in his will that when he dies the cash under the bed should be given to charity.
If the man lives for another 60 years, how much money will be under his bed if he dies just after making his last (720th) addition?
Also, what will be the real value of that cash in today's prices if inflation is expected to 2.5% pa? Assume that the inflation rate is an effective annual rate and is not expected to change.
The answers are given in the same order, the amount of money under his bed in 60 years, and the real value of that money in today's prices.
In the dividend discount model:
###P_0 = \dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
The return ##r## is supposed to be the:
In the dividend discount model:
### P_0= \frac{d_1}{r-g} ###
The pronumeral ##g## is supposed to be the:
For certain shares, the forward-looking Price-Earnings Ratio (##P_0/EPS_1##) is equal to the inverse of the share's total expected return (##1/r_\text{total}##). For what shares is this true?
Use the general accounting definition of 'payout ratio' which is dividends per share (DPS) divided by earnings per share (EPS) and assume that all cash flows, earnings and rates are real rather than nominal.
A company's forward-looking PE ratio will be the inverse of its total expected return on equity when it has a:
Estimate Microsoft's (MSFT) share price using a price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only:
- Apple, Google and Microsoft are comparable companies,
- Apple's (AAPL) share price is $526.24 and historical EPS is $40.32.
- Google's (GOOG) share price is $1,215.65 and historical EPS is $36.23.
- Micrsoft's (MSFT) historical earnings per share (EPS) is $2.71.
Source: Google Finance 28 Feb 2014.
Estimate the US bank JP Morgan's share price using a price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only:
- The major US banks JP Morgan Chase (JPM), Citi Group (C) and Wells Fargo (WFC) are comparable companies;
- JP Morgan Chase's historical earnings per share (EPS) is $4.37;
- Citi Group's share price is $50.05 and historical EPS is $4.26;
- Wells Fargo's share price is $48.98 and historical EPS is $3.89.
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 24 March 2014.
Which firms tend to have low forward-looking price-earnings (PE) ratios?
Only consider firms with positive earnings, disregard firms with negative earnings and therefore negative PE ratios.
Which firms tend to have high forward-looking price-earnings (PE) ratios?
Which of the following companies is most suitable for valuation using PE multiples techniques?
Which of the following investable assets is the LEAST suitable for valuation using PE multiples techniques?
A mature firm has constant expected future earnings and dividends. Both amounts are equal. So earnings and dividends are expected to be equal and unchanging.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Private equity firms are known to buy medium sized private companies operating in the same industry, merge them together into a larger company, and then sell it off in a public float (initial public offering, IPO).
If medium-sized private companies trade at PE ratios of 5 and larger listed companies trade at PE ratios of 15, what return can be achieved from this strategy?
Assume that:
- The medium-sized companies can be bought, merged and sold in an IPO instantaneously.
- There are no costs of finding, valuing, merging and restructuring the medium sized companies. Also, there is no competition to buy the medium-sized companies from other private equity firms.
- The large merged firm's earnings are the sum of the medium firms' earnings.
- The only reason for the difference in medium and large firm's PE ratios is due to the illiquidity of the medium firms' shares.
- Return is defined as: ##r_{0→1} = (p_1-p_0+c_1)/p_0## , where time zero is just before the merger and time one is just after.
A firm has 1 million shares which trade at a price of $30 each. The firm is expected to announce earnings of $3 million at the end of the year and pay an annual dividend of $1.50 per share.
What is the firm's (forward looking) price/earnings (PE) ratio?
The below screenshot of Commonwealth Bank of Australia's (CBA) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 7 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.

What was CBA's backwards-looking price-earnings ratio?
The below screenshot of Microsoft's (MSFT) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 28 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.

What was MSFT's backwards-looking price-earnings ratio?
A firm has 2m shares and a market capitalisation of equity of $30m. The firm just announced earnings of $5m and paid an annual dividend of $0.75 per share.
What is the firm's (backward looking) price/earnings (PE) ratio?
Question 22 NPV, perpetuity with growth, effective rate, effective rate conversion
What is the NPV of the following series of cash flows when the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
The first payment of $90 is in 3 years, followed by payments every 6 months in perpetuity after that which shrink by 3% every 6 months. That is, the growth rate every 6 months is actually negative 3%, given as an effective 6 month rate. So the payment at ## t=3.5 ## years will be ## 90(1-0.03)^1=87.3 ##, and so on.
A stock pays annual dividends which are expected to continue forever. It just paid a dividend of $10. The growth rate in the dividend is 2% pa. You estimate that the stock's required return is 10% pa. Both the discount rate and growth rate are given as effective annual rates. Using the dividend discount model, what will be the share price?
Suppose you had $100 in a savings account and the interest rate was 2% per year.
After 5 years, how much do you think you would have in the account if you left the money to grow?
A home loan company advertises an interest rate of 6% pa, payable monthly. Which of the following statements about the interest rate is NOT correct? All rates are given to four decimal places.
Jan asks you for a loan. He wants $100 now and offers to pay you back $120 in 1 year. You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Ignore credit risk. Remember:
### V_0 = \frac{V_t}{(1+r_\text{eff})^t} ###
Assets A, B, M and ##r_f## are shown on the graphs above. Asset M is the market portfolio and ##r_f## is the risk free yield on government bonds. Which of the below statements is NOT correct?
In general, stock prices tend to rise. What does this mean for futures on equity?
Which of the following statements about futures contracts on shares is NOT correct, assuming that markets are efficient?
When an equity future is first negotiated (at t=0):
After doing extensive fundamental analysis of a company, you believe that their shares are overpriced and will soon fall significantly. The market believes that there will be no such fall.
Which of the following strategies is NOT a good idea, assuming that your prediction is true?
A trader buys one December futures contract on orange juice. Each contract is for the delivery of 10,000 pounds. The current futures price is $1.20 per pound. The initial margin is $5,000 per contract, and the maintenance margin is $4,000 per contract.
What is the smallest price change would that would lead to a margin call for the buyer?
The price of gold is currently $700 per ounce. The forward price for delivery in 1 year is $800. An arbitrageur can borrow money at 10% per annum given as an effective discrete annual rate. Assume that gold is fairly priced and the cost of storing gold is zero.
What is the best way to conduct an arbitrage in this situation? The best arbitrage strategy requires zero capital, has zero risk and makes money straight away. An arbitrageur should sell 1 forward on gold and:
The current gold price is $700, gold storage costs are 2% pa and the risk free rate is 10% pa, both with continuous compounding.
What should be the 3 year gold futures price?
A 2-year futures contract on a stock paying a continuous dividend yield of 3% pa was bought when the underlying stock price was $10 and the risk free rate was 10% per annum with continuous compounding. Assume that investors are risk-neutral, so the stock's total required return is the risk free rate.
Find the forward price ##(F_2)## and value of the contract ##(V_0)## initially. Also find the value of the contract in 6 months ##(V_{0.5})## if the stock price rose to $12.
An equity index is currently at 5,000 points. The 2 year futures price is 5,400 points and the total required return is 8% pa with continuous compounding. Each index point is worth $25.
What is the implied continuous dividend yield as a continuously compounded rate per annum?
A stock is expected to pay a dividend of $5 per share in 1 month and $5 again in 7 months.
The stock price is $100, and the risk-free rate of interest is 10% per annum with continuous compounding. The yield curve is flat. Assume that investors are risk-neutral.
An investor has just taken a short position in a one year forward contract on the stock.
Find the forward price ##(F_1)## and value of the contract ##(V_0)## initially. Also find the value of the short futures contract in 6 months ##(V_\text{0.5, SF})## if the stock price fell to $90.
Question 598 future, tailing the hedge, cross hedging
The standard deviation of monthly changes in the spot price of lamb is $0.015 per pound. The standard deviation of monthly changes in the futures price of live cattle is $0.012 per pound. The correlation between the spot price of lamb and the futures price of cattle is 0.4.
It is now January. A lamb producer is committed to selling 1,000,000 pounds of lamb in May. The spot price of live cattle is $0.30 per pound and the June futures price is $0.32 per pound. The spot price of lamb is $0.60 per pound.
The producer wants to use the June live cattle futures contracts to hedge his risk. Each futures contract is for the delivery of 50,000 pounds of cattle.
How many live cattle futures should the lamb farmer sell to hedge his risk? Round your answer to the nearest whole number of contracts.
Which one of the below option and futures contracts gives the possibility of potentially unlimited gains?
Which of the below formulas gives the payoff at maturity ##(f_T)## from being long a future? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T## and the locked-in futures price be ##K_T##.
Which of the below formulas gives the payoff at maturity ##(f_T)## from being short a future? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T## and the locked-in futures price be ##K_T##.
A trader buys one crude oil futures contract on the CME expiring in one year with a locked-in futures price of $38.94 per barrel. If the trader doesn’t close out her contract before expiry then in one year she will have the:
A trader sells one crude oil futures contract on the CME expiring in one year with a locked-in futures price of $38.94 per barrel. The crude oil spot price is $40.33. If the trader doesn’t close out her contract before expiry then in one year she will have the:
Alice, Bob, Chris and Delta are traders in the futures market. The following trades occur over a single day in a newly-opened equity index future that matures in one year which the exchange just made available.
1. Alice buys a future from Bob.
2. Chris buys a future from Delta.
3. Delta buys a future from Alice.
These were the only trades made in this equity index future. What was the trading volume and what is the open interest?
A trader buys a one year futures contract on crude oil. The contract is for the delivery of 1,000 barrels. The current futures price is $38.94 per barrel. The initial margin is $3,410 per contract, and the maintenance margin is $3,100 per contract.
What is the smallest price change that would lead to a margin call for the buyer?
A trader sells a one year futures contract on crude oil. The contract is for the delivery of 1,000 barrels. The current futures price is $38.94 per barrel. The initial margin is $3,410 per contract, and the maintenance margin is $3,100 per contract.
What is the smallest price change that would lead to a margin call for the seller?
In February a company sold one December 40,000 pound (about 18 metric tons) lean hog futures contract. It closed out its position in May.
The spot price was $0.68 per pound in February. The December futures price was $0.70 per pound when the trader entered into the contract in February, $0.60 when he closed out his position in May, and $0.55 when the contract matured in December.
What was the total profit?
An equity index is currently at 5,200 points. The 6 month futures price is 5,300 points and the total required return is 6% pa with continuous compounding. Each index point is worth $25.
What is the implied dividend yield as a continuously compounded rate per annum?
An equity index is currently at 4,800 points. The 1.5 year futures price is 5,100 points and the total required return is 6% pa with continuous compounding. Each index point is worth $25.
What is the implied dividend yield as a continuously compounded rate per annum?
Which of the following statements about futures and forward contracts is NOT correct?
Alice, Bob, Chris and Delta are traders in the futures market. The following trades occur over a single day in a newly-opened equity index future that matures in one year which the exchange just made available.
1. Alice buys a future from Bob.
2. Chris buys a future from Delta.
3. Bob buys a future from Chris.
These were the only trades made in this equity index future. What was the trading volume and what is the open interest?
Alice, Bob, Chris and Delta are traders in the futures market. The following trades occur over a single day in a newly-opened equity index future that matures in one year which the exchange just made available.
1. Alice buys a future from Bob.
2. Chris buys a future from Delta.
3. Alice buys a future from Chris.
These were the only trades made in this equity index future. What was the trading volume and what is the open interest?
An equity index stands at 100 points and the one year equity futures price is 107.
The equity index is expected to have a dividend yield of 3% pa. Assume that investors are risk-neutral so their total required return on the shares is the same as the risk free Treasury bond yield which is 10% pa. Both are given as discrete effective annual rates.
Assuming that the equity index is fairly priced, an arbitrageur would recognise that the equity futures are:
An equity index stands at 100 points and the one year equity futures price is 102.
The equity index is expected to have a dividend yield of 4% pa. Assume that investors are risk-neutral so their total required return on the shares is the same as the risk free Treasury bond yield which is 10% pa. Both are given as discrete effective annual rates.
Assuming that the equity index is fairly priced, an arbitrageur would recognise that the equity futures are:
A pig farmer in the US is worried about the price of hogs falling and wants to lock in a price now. In one year the pig farmer intends to sell 1,000,000 pounds of hogs. Luckily, one year CME lean hog futures expire on the exact day that he wishes to sell his pigs. The futures have a notional principal of 40,000 pounds (about 18 metric tons) and currently trade at a price of 63.85 cents per pound. The underlying lean hogs spot price is 77.15 cents per pound. The correlation between the futures price and the underlying hogs price is one and the standard deviations are both 4 cents per pound. The initial margin is USD1,500 and the maintenance margin is USD1,200 per futures contract.
Which of the below statements is NOT correct?
An equity index fund manager controls a USD1 billion diversified equity portfolio with a beta of 1.3. The equity manager fears that a global recession will begin in the next year, causing equity prices to tumble. The market does not think that this will happen. If the fund manager wishes to reduce her portfolio beta to 0.5, how many S&P500 futures should she sell?
The US market equity index is the S&P500. One year CME futures on the S&P500 currently trade at 2,062 points and the spot price is 2,091 points. Each point is worth $250. How many one year S&P500 futures contracts should the fund manager sell?
The standard deviation of monthly changes in the spot price of corn is 50 cents per bushel. The standard deviation of monthly changes in the futures price of corn is 40 cents per bushel. The correlation between the spot price of corn and the futures price of corn is 0.9.
It is now March. A corn chip manufacturer is committed to buying 250,000 bushels of corn in May. The spot price of corn is 381 cents per bushel and the June futures price is 399 cents per bushel.
The corn chip manufacturer wants to use the June corn futures contracts to hedge his risk. Each futures contract is for the delivery of 5,000 bushels of corn. One bushel is about 127 metric tons.
How many corn futures should the corn chip manufacturer buy to hedge his risk? Round your answer to the nearest whole number of contracts. Remember to tail the hedge.
A company runs a number of slaughterhouses which supply hamburger meat to McDonalds. The company is afraid that live cattle prices will increase over the next year, even though there is widespread belief in the market that they will be stable. What can the company do to hedge against the risk of increasing live cattle prices? Which statement(s) are correct?
(i) buy call options on live cattle.
(ii) buy put options on live cattle.
(iii) sell call options on live cattle.
Select the most correct response:
Below are 4 option graphs. Note that the y-axis is payoff at maturity (T). What options do they depict? List them in the order that they are numbered.
You have just sold an 'in the money' 6 month European put option on the mining company BHP at an exercise price of $40 for a premium of $3.
Which of the following statements best describes your situation?
Below are 4 option graphs. Note that the y-axis is payoff at maturity (T). What options do they depict? List them in the order that they are numbered
You operate a cattle farm that supplies hamburger meat to the big fast food chains. You buy a lot of grain to feed your cattle, and you sell the fully grown cattle on the livestock market.
You're afraid of adverse movements in grain and livestock prices. What options should you buy to hedge your exposures in the grain and cattle livestock markets?
Select the most correct response:
Suppose that the US government recently announced that subsidies for fresh milk producers will be gradually phased out over the next year. Newspapers say that there are expectations of a 40% increase in the spot price of fresh milk over the next year.
Option prices on fresh milk trading on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) reflect expectations of this 40% increase in spot prices over the next year. Similarly to the rest of the market, you believe that prices will rise by 40% over the next year.
What option trades are likely to be profitable, or to be more specific, result in a positive Net Present Value (NPV)?
Assume that:
- Only the spot price is expected to increase and there is no change in expected volatility or other variables that affect option prices.
- No taxes, transaction costs, information asymmetry, bid-ask spreads or other market frictions.
Question 271 CAPM, option, risk, systematic risk, systematic and idiosyncratic risk
All things remaining equal, according to the capital asset pricing model, if the systematic variance of an asset increases, its required return will increase and its price will decrease.
If the idiosyncratic variance of an asset increases, its price will be unchanged.
What is the relationship between the price of a call or put option and the total, systematic and idiosyncratic variance of the underlying asset that the option is based on? Select the most correct answer.
Call and put option prices increase when the:
Which one of the following is NOT usually considered an 'investable' asset for long-term wealth creation?
You believe that the price of a share will fall significantly very soon, but the rest of the market does not. The market thinks that the share price will remain the same. Assuming that your prediction will soon be true, which of the following trades is a bad idea? In other words, which trade will NOT make money or prevent losses?
Question 381 Merton model of corporate debt, option, real option
In the Merton model of corporate debt, buying a levered company's debt is equivalent to buying risk free government bonds and:
Question 382 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
In the Merton model of corporate debt, buying a levered company's shares is equivalent to:
Question 383 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
In the Merton model of corporate debt, buying a levered company's debt is equivalent to buying the company's assets and:
Which of the following is the least useful method or model to calculate the value of a real option in a project?
Question 385 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
A risky firm will last for one period only (t=0 to 1), then it will be liquidated. So it's assets will be sold and the debt holders and equity holders will be paid out in that order. The firm has the following quantities:
##V## = Market value of assets.
##E## = Market value of (levered) equity.
##D## = Market value of zero coupon bonds.
##F_1## = Total face value of zero coupon bonds which is promised to be paid in one year.

The levered equity graph above contains bold labels a to e. Which of the following statements about those labels is NOT correct?
Question 386 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
A risky firm will last for one period only (t=0 to 1), then it will be liquidated. So it's assets will be sold and the debt holders and equity holders will be paid out in that order. The firm has the following quantities:
##V## = Market value of assets.
##E## = Market value of (levered) equity.
##D## = Market value of zero coupon bonds.
##F_1## = Total face value of zero coupon bonds which is promised to be paid in one year.

The risky corporate debt graph above contains bold labels a to e. Which of the following statements about those labels is NOT correct?
One of the reasons why firms may not begin projects with relatively small positive net present values (NPV's) is because they wish to maximise the value of their:
A moped is a bicycle with pedals and a little motor that can be switched on to assist the rider. Mopeds are useful for quick transport using the motor, and for physical exercise when using the pedals unassisted. This offers the rider:
You're thinking of starting a new cafe business, but you're not sure if it will be profitable.
You have to decide what type of cups, mugs and glasses you wish to buy. You can pay to have your cafe's name printed on them, or just buy the plain un-marked ones. For marketing reasons it's better to have the cafe name printed. But the plain un-marked cups, mugs and glasses maximise your:
Some financially minded people insist on a prenuptial agreement before committing to marry their partner. This agreement states how the couple's assets should be divided in case they divorce. Prenuptial agreements are designed to give the richer partner more of the couples' assets if they divorce, thus maximising the richer partner's:
The cheapest mobile phones available tend to be those that are 'locked' into a cell phone operator's network. Locked phones can not be used with other cell phone operators' networks.
Locked mobile phones are cheaper than unlocked phones because the locked-in network operator helps create a monopoly by:
Your firm's research scientists can begin an exciting new project at a cost of $10m now, after which there’s a:
- 70% chance that cash flows will be $1m per year forever, starting in 5 years (t=5). This is the A state of the world.
- 20% chance that cash flows will be $3m per year forever, starting in 5 years (t=5). This is the B state of the world.
- 10% chance of a major break through in which case the cash flows will be $20m per year forever starting in 5 years (t=5), or instead, the project can be expanded by investing another $10m (at t=5) which is expected to give cash flows of $60m per year forever, starting at year 9 (t=9). Note that the perpetual cash flows are either the $20m from year 4 onwards, or the $60m from year 9 onwards after the additional $10m year 5 investment, but not both. This is the C state of the world.
The firm's cost of capital is 10% pa.
What's the present value (at t=0) of the option to expand in year 5?
A European call option will mature in ##T## years with a strike price of ##K## dollars. The underlying asset has a price of ##S## dollars.
What is an expression for the payoff at maturity ##(f_T)## in dollars from owning (being long) the call option?
A European put option will mature in ##T## years with a strike price of ##K## dollars. The underlying asset has a price of ##S## dollars.
What is an expression for the payoff at maturity ##(f_T)## in dollars from having written (being short) the put option?
Question 432 option, option intrinsic value, no explanation
An American style call option with a strike price of ##K## dollars will mature in ##T## years. The underlying asset has a price of ##S## dollars.
What is an expression for the current intrinsic value in dollars from owning (being long) the American style call option? Note that the intrinsic value of an option does not subtract the premium paid to buy the option.
Question 433 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option, no explanation
A risky firm will last for one period only (t=0 to 1), then it will be liquidated. So it's assets will be sold and the debt holders and equity holders will be paid out in that order. The firm has the following quantities:
##V## = Market value of assets.
##E## = Market value of (levered) equity.
##D## = Market value of zero coupon bonds.
##F_1## = Total face value of zero coupon bonds which is promised to be paid in one year.
What is the payoff to equity holders at maturity, assuming that they keep their shares until maturity?
Question 434 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
A risky firm will last for one period only (t=0 to 1), then it will be liquidated. So it's assets will be sold and the debt holders and equity holders will be paid out in that order. The firm has the following quantities:
##V## = Market value of assets.
##E## = Market value of (levered) equity.
##D## = Market value of zero coupon bonds.
##F_1## = Total face value of zero coupon bonds which is promised to be paid in one year.
What is the payoff to debt holders at maturity, assuming that they keep their debt until maturity?
Question 584 option, option payoff at maturity, option profit
Which of the following statements about European call options on non-dividend paying stocks is NOT correct?
A man just sold a call option to his counterparty, a lady. The man has just now:
Which of the following statements about option contracts is NOT correct? For every:
If trader A has sold the right that allows counterparty B to buy the underlying asset from him at maturity if counterparty B wants then trader A is:
Question 636 option, option payoff at maturity, no explanation
Which of the below formulas gives the payoff ##(f)## at maturity ##(T)## from being long a call option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T## and the exercise price be ##X_T##.
Question 638 option, option payoff at maturity, no explanation
Which of the below formulas gives the payoff ##(f)## at maturity ##(T)## from being long a put option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T## and the exercise price be ##X_T##.
Question 639 option, option payoff at maturity, no explanation
Which of the below formulas gives the payoff ##(f)## at maturity ##(T)## from being short a put option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T## and the exercise price be ##X_T##.
A trader buys one crude oil European style call option contract on the CME expiring in one year with an exercise price of $44 per barrel for a price of $6.64. The crude oil spot price is $40.33. If the trader doesn’t close out her contract before maturity, then at maturity she will have the:
Which of the below formulas gives the profit ##(\pi)## from being long a call option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T##, the exercise price be ##X_T## and the option price be ##f_{LC,0}##. Note that ##S_T##, ##X_T## and ##f_{LC,0}## are all positive numbers.
Which of the below formulas gives the profit ##(\pi)## from being short a call option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T##, the exercise price be ##X_T## and the option price be ##f_{LC,0}##. Note that ##S_T##, ##X_T## and ##f_{LC,0}## are all positive numbers.
Which of the below formulas gives the profit ##(\pi)## from being long a put option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T##, the exercise price be ##X_T## and the option price be ##f_{LP,0}##. Note that ##S_T##, ##X_T## and ##f_{LP,0}## are all positive numbers.
Which of the below formulas gives the profit ##(\pi)## from being short a put option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T##, the exercise price be ##X_T## and the option price be ##f_{LP,0}##. Note that ##S_T##, ##X_T## and ##f_{LP,0}## are all positive numbers.
A trader sells one crude oil European style call option contract on the CME expiring in one year with an exercise price of $44 per barrel for a price of $6.64. The crude oil spot price is $40.33. If the trader doesn’t close out her contract before maturity, then at maturity she will have the:
A trader buys one crude oil European style put option contract on the CME expiring in one year with an exercise price of $44 per barrel for a price of $6.64. The crude oil spot price is $40.33. If the trader doesn’t close out her contract before maturity, then at maturity she will have the:
Which of the following statements about call options is NOT correct?
A trader just bought a European style put option on CBA stock. The current option premium is $2, the exercise price is $75, the option matures in one year and the spot CBA stock price is $74.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Which of the following is NOT a valid method for estimating the beta of a company's stock? Assume that markets are efficient, a long history of past data is available, the stock possesses idiosyncratic and market risk. The variances and standard deviations below denote total risks.
A stock has a beta of 1.5. The market's expected total return is 10% pa and the risk free rate is 5% pa, both given as effective annual rates.
What do you think will be the stock's expected return over the next year, given as an effective annual rate?
A stock has a beta of 1.5. The market's expected total return is 10% pa and the risk free rate is 5% pa, both given as effective annual rates.
In the last 5 minutes, bad economic news was released showing a higher chance of recession. Over this time the share market fell by 1%. The risk free rate was unchanged.
What do you think was the stock's historical return over the last 5 minutes, given as an effective 5 minute rate?
A stock has a beta of 1.5. The market's expected total return is 10% pa and the risk free rate is 5% pa, both given as effective annual rates.
Over the last year, bad economic news was released showing a higher chance of recession. Over this time the share market fell by 1%. So ##r_{m} = (P_{0} - P_{-1})/P_{-1} = -0.01##, where the current time is zero and one year ago is time -1. The risk free rate was unchanged.
What do you think was the stock's historical return over the last year, given as an effective annual rate?
Question 699 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
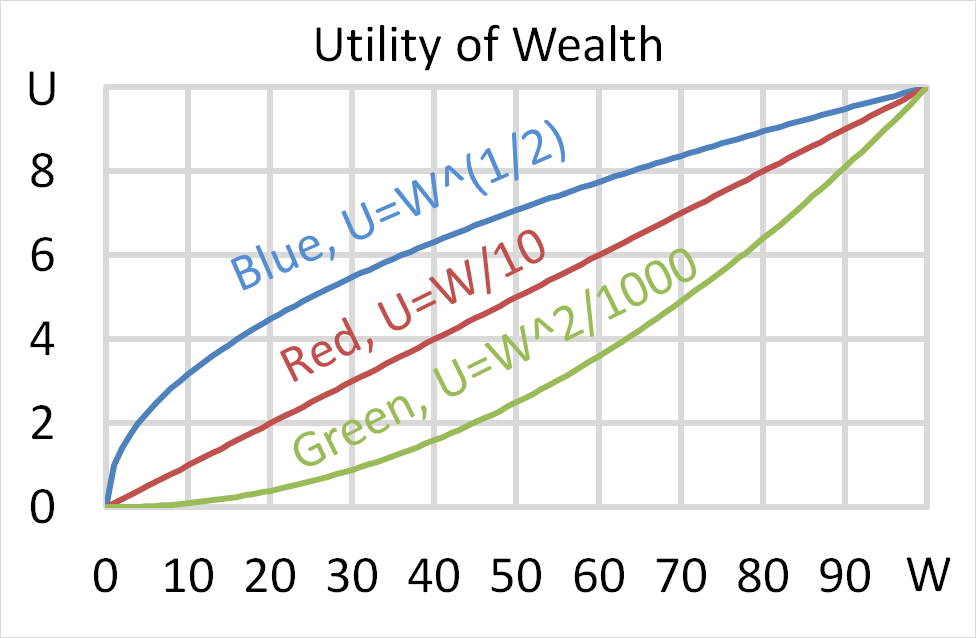
Question 700 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 701 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 702 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 703 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $500 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $500. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $500. If they flip tails then they will lose $500. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
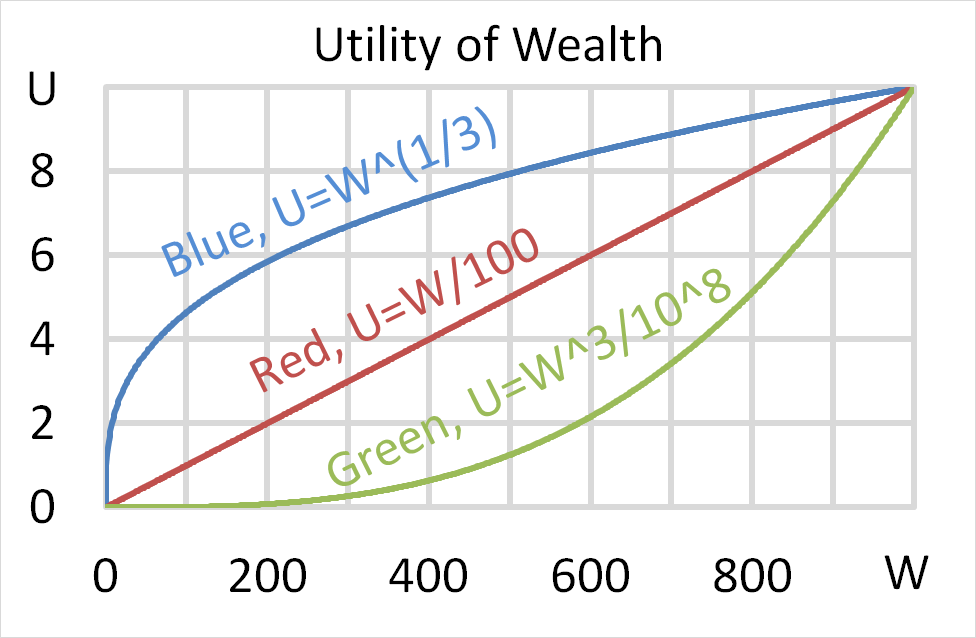
Question 704 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $256 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $256. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $256. If they flip tails then they will lose $256. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?

A 180-day Bank Accepted Bill has a face value of $1,000,000. The interest rate is 8% pa and there are 365 days in the year. What is its price now?
A 90-day Bank Accepted Bill (BAB) has a face value of $1,000,000. The simple interest rate is 10% pa and there are 365 days in the year. What is its price now?
Question 147 bill pricing, simple interest rate, no explanation
A 30-day Bank Accepted Bill has a face value of $1,000,000. The interest rate is 8% pa and there are 365 days in the year. What is its price now?
Question 157 bill pricing, simple interest rate, no explanation
A 90-day Bank Accepted Bill has a face value of $1,000,000. The interest rate is 6% pa and there are 365 days in the year. What is its price?
A 60-day Bank Accepted Bill has a face value of $1,000,000. The interest rate is 8% pa and there are 365 days in the year. What is its price now?
A 30-day Bank Accepted Bill has a face value of $1,000,000. The interest rate is 2.5% pa and there are 365 days in the year. What is its price now?
"Buy low, sell high" is a phrase commonly heard in financial markets. It states that traders should try to buy assets at low prices and sell at high prices.
Traders in the fixed-coupon bond markets often quote promised bond yields rather than prices. Fixed-coupon bond traders should try to: