Question 35 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
A European company just issued two bonds, a
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the company's forward rate over the second year (from t=1 to t=2)? Give your answer as an effective annual rate, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Using the term structure of interest rates equation, also known as the expectations hypothesis theory of interest rates,
###(1+r_{0-2})^2 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2}) ### ###(1+0.1)^2 = (1+0.08)(1+r_{1-2}) ### ###1+r_{1-2} = \frac{(1+0.1)^2}{1+0.08} ### ###\begin{aligned} r_{1-2} =& \frac{(1+0.1)^2}{1+0.08} - 1 \\ =& 0.12037037 \\ \end{aligned} ###Question 25 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
A European company just issued two bonds, a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 3 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the company's forward rate over the third year (from t=2 to t=3)? Give your answer as an effective annual rate, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Using the term structure of interest rates equation, also known as the expectations hypothesis theory of interest rates,
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-2})^2(1+r_{2-3}) ### ###(1+0.1)^3 = (1+0.08)^2(1+r_{2-3}) ### ###1+r_{2-3} = \frac{(1+0.1)^3}{(1+0.08)^2} ### ###\begin{aligned} r_{2-3} =& \frac{(1+0.1)^3}{(1+0.08)^2} - 1 \\ =& 0.14111797 \\ \end{aligned} ###Question 96 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds paying semi-annual coupons:
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Using the term structure of interest rates equation, also known as the expectations hypothesis theory of interest rates,
###\left(1+r_\text{0-2yrs, eff 6mth}\right)^4 = \left(1+r_\text{0-1yrs, eff 6mth}\right)^2\left(1+r_\text{1-2yrs, eff 6mth}\right)^2 ### ###\left(1+\frac{r_\text{0-2yrs, apr 6mth}}{2}\right)^4 = \left(1+\frac{r_\text{0-1yrs, apr 6mth}}{2}\right)^2\left(1+\frac{r_\text{1-2yrs, apr 6mth}}{2}\right)^2 ### ###\left(1+\frac{0.1}{2}\right)^4 = \left(1+\frac{0.08}{2}\right)^2\left(1+\frac{r_\text{1-2yrs, apr 6mth}}{2}\right)^2 ### ###\left(1+\frac{r_\text{1-2yrs, apr 6mth}}{2}\right)^2 = \frac{\left(1+\frac{0.1}{2}\right)^4}{\left(1+\frac{0.08}{2}\right)^2} ### ###\begin{aligned} r_\text{1-2yrs, apr 6mth} &= \left( \left( \frac{\left(1+\frac{0.1}{2}\right)^4}{\left(1+\frac{0.08}{2}\right)^2} \right)^{1/2} - 1 \right) \times 2\\ &= 0.1202 \\ \end{aligned} ###Question 572 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
All statements are true except b. This is because ##r_{0-1}## is the one year spot rate, not the forward rate. Spot interest rates are apply straight away 'on the spot', so they begin at time zero. Borrowers can borrow at the spot rate straight away.
Forward rates start at a future time, so they can't be borrowed at straight away. Forward rates can be locked-in using forward rate agreements (FRA's) which allow you to borrow in the future at an interest rate agreed to now, usually with a bank.
Question 573 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, liquidity premium theory, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Statement b is false. If the liquidity premium theory is true, then the forward rates are higher than the expected future spot rates due to the liquidity premium, not lower.
Which of the following statements about yield curves is NOT correct?
A yield curve is a graph of spot rates.
Question 862 yield curve, bond pricing, bill pricing, monetary policy, no explanation
Refer to the below graph when answering the questions.
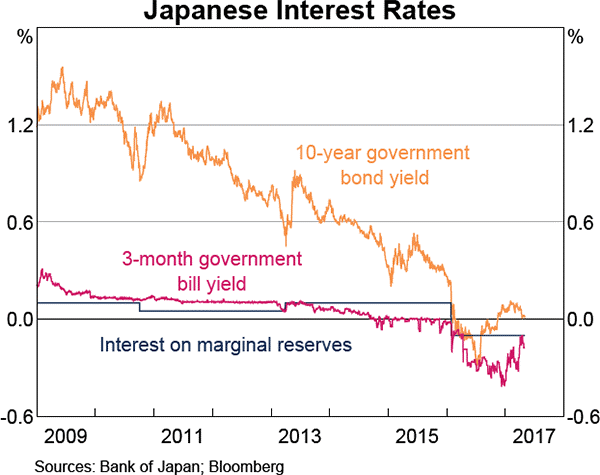
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
No explanation provided.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? An inverted US government bond yield curve indicates that:
An inverted government yield curve indicates that bond market participants believe that future monetary policy will be more expansionary than it is now. They believe that the central bank will lower interest rates in the future to encourage people to borrow and spend rather than save, which will increase consumption and GDP (=C+I+G+X-M), creating more jobs.
An inverted yield curve indicates that the market believe that there is a higher chance of recession in the future compared to when yield curves were normal (upward sloping). This would typically lead to expectations of expansionary fiscal policy. But expansionary fiscal policy would be carried out by the government raising their spending or lowering taxes, not cutting spending.