For a price of $100, Vera will sell you a 2 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 10% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with similar risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 8% pa.
Question 49 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, APR, effective rate
In Australia, nominal yields on semi-annual coupon paying Government Bonds with 2 years until maturity are currently 2.83% pa.
The inflation rate is currently 2.2% pa, given as an APR compounding per quarter. The inflation rate is not expected to change over the next 2 years.
What is the real yield on these bonds, given as an APR compounding every 6 months?
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $1,500 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
To your surprise, you can actually afford to pay $2,000 per month and your mortgage allows early repayments without fees. If you maintain these higher monthly payments, how long will it take to pay off your mortgage?
Question 246 foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate, cross currency interest rate parity
Suppose the Australian cash rate is expected to be 8.15% pa and the US federal funds rate is expected to be 3.00% pa over the next 2 years, both given as nominal effective annual rates. The current exchange rate is at parity, so 1 USD = 1 AUD.
What is the implied 2 year forward foreign exchange rate?
The total return of any asset can be broken down in different ways. One possible way is to use the dividend discount model (or Gordon growth model):
###p_0 = \frac{c_1}{r_\text{total}-r_\text{capital}}###
Which, since ##c_1/p_0## is the income return (##r_\text{income}##), can be expressed as:
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{income}+r_\text{capital}###
So the total return of an asset is the income component plus the capital or price growth component.
Another way to break up total return is to use the Capital Asset Pricing Model:
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{f}+β(r_\text{m}- r_\text{f})###
###r_\text{total}=r_\text{time value}+r_\text{risk premium}###
So the risk free rate is the time value of money and the term ##β(r_\text{m}- r_\text{f})## is the compensation for taking on systematic risk.
Using the above theory and your general knowledge, which of the below equations, if any, are correct?
(I) ##r_\text{income}=r_\text{time value}##
(II) ##r_\text{income}=r_\text{risk premium}##
(III) ##r_\text{capital}=r_\text{time value}##
(IV) ##r_\text{capital}=r_\text{risk premium}##
(V) ##r_\text{income}+r_\text{capital}=r_\text{time value}+r_\text{risk premium}##
Which of the equations are correct?
Which business structure or structures have the advantage of limited liability for equity investors?
The perpetuity with growth formula, also known as the dividend discount model (DDM) or Gordon growth model, is appropriate for valuing a company's shares. ##P_0## is the current share price, ##C_1## is next year's expected dividend, ##r## is the total required return and ##g## is the expected growth rate of the dividend.
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
The below graph shows the expected future price path of the company's shares. Which of the following statements about the graph is NOT correct?
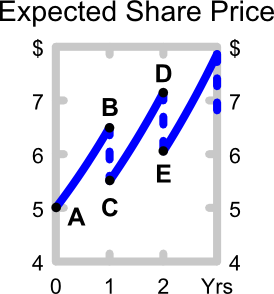
"Buy low, sell high" is a phrase commonly heard in financial markets. It states that traders should try to buy assets at low prices and sell at high prices.
Traders in the fixed-coupon bond markets often quote promised bond yields rather than prices. Fixed-coupon bond traders should try to:
A share will pay its next dividend of ##C_1## in one year, and will continue to pay a dividend every year after that forever, growing at a rate of ##g##. So the next dividend will be ##C_2=C_1 (1+g)^1##, then ##C_3=C_2 (1+g)^1##, and so on forever.
The current price of the share is ##P_0## and its required return is ##r##
Which of the following is NOT equal to the expected share price in 2 years ##(P_2)## just after the dividend at that time ##(C_2)## has been paid?
Calculate Australia’s GDP over the 2016 calendar year using the below table:
| Australian Gross Domestic Product Components | ||||
| A$ billion, 2016 Calendar Year from 1 Jan 2016 to 31 Dec 2016 inclusive | ||||
| Consumption | Investment | Government spending | Exports | Imports |
| 971 | 421 | 320 | 328 | 344 |
Source: ABS 5206.0 Australian National Accounts: National Income, Expenditure and Product. Table 3. Expenditure on Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Current prices.
Over the 2016 calendar year, Australia’s GDP was: