A European bond paying annual coupons of 6% offers a yield of 10% pa.
Convert the yield into an effective monthly rate, an effective annual rate and an effective daily rate. Assume that there are 365 days in a year.
All answers are given in the same order:
### r_\text{eff, monthly} , r_\text{eff, yearly} , r_\text{eff, daily} ###
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.15 | 1.10 | 1.05 | 1.00 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at -5% pa. Note that this is a negative growth rate, so the dividend will actually shrink. So,
- the dividend at t=5 will be ##$1(1-0.05) = $0.95##,
- the dividend at t=6 will be ##$1(1-0.05)^2 = $0.9025##, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates.
What is the current price of the stock?
Question 65 annuity with growth, needs refinement
Which of the below formulas gives the present value of an annuity with growth?
Hint: The equation of a perpetuity without growth is: ###V_\text{0, perp without growth} = \frac{C_\text{1}}{r}###
The formula for the present value of an annuity without growth is derived from the formula for a perpetuity without growth.
The idea is than an annuity with T payments from t=1 to T inclusive is equivalent to a perpetuity starting at t=1 with fixed positive cash flows, plus a perpetuity starting T periods later (t=T+1) with fixed negative cash flows. The positive and negative cash flows after time period T cancel each other out, leaving the positive cash flows between t=1 to T, which is the annuity.
###\begin{aligned} V_\text{0, annuity} &= V_\text{0, perp without growth from t=1} - V_\text{0, perp without growth from t=T+1} \\ &= \dfrac{C_\text{1}}{r} - \dfrac{ \left( \dfrac{C_\text{T+1}}{r} \right) }{(1+r)^T} \\ &= \dfrac{C_\text{1}}{r} - \dfrac{ \left( \dfrac{C_\text{1}}{r} \right) }{(1+r)^T} \\ &= \dfrac{C_\text{1}}{r}\left(1 - \dfrac{1}{(1+r)^T}\right) \\ \end{aligned}###
The equation of a perpetuity with growth is:
###V_\text{0, perp with growth} = \dfrac{C_\text{1}}{r-g}###A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 50%. The firm then issues a large amount of debt to raise money for new projects of similar market risk to the company's existing projects. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is correct?
Question 154 implicit interest rate in wholesale credit, no explanation
A wholesale vitamin supplements store offers credit to its customers. Customers are given 30 days to pay for their goods, but if they pay within 5 days they will get a 1% discount.
What is the effective interest rate implicit in the discount being offered? Assume 365 days in a year and that all customers pay on either the 5th day or the 30th day. All of the below answer choices are given as effective annual interest rates.
Let the standard deviation of returns for a share per month be ##\sigma_\text{monthly}##.
What is the formula for the standard deviation of the share's returns per year ##(\sigma_\text{yearly})##?
Assume that returns are independently and identically distributed (iid) so they have zero auto correlation, meaning that if the return was higher than average today, it does not indicate that the return tomorrow will be higher or lower than average.
Question 338 market efficiency, CAPM, opportunity cost, technical analysis
A man inherits $500,000 worth of shares.
He believes that by learning the secrets of trading, keeping up with the financial news and doing complex trend analysis with charts that he can quit his job and become a self-employed day trader in the equities markets.
What is the expected gain from doing this over the first year? Measure the net gain in wealth received at the end of this first year due to the decision to become a day trader. Assume the following:
- He earns $60,000 pa in his current job, paid in a lump sum at the end of each year.
- He enjoys examining share price graphs and day trading just as much as he enjoys his current job.
- Stock markets are weak form and semi-strong form efficient.
- He has no inside information.
- He makes 1 trade every day and there are 250 trading days in the year. Trading costs are $20 per trade. His broker invoices him for the trading costs at the end of the year.
- The shares that he currently owns and the shares that he intends to trade have the same level of systematic risk as the market portfolio.
- The market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa.
Measure the net gain over the first year as an expected wealth increase at the end of the year.
A stock is expected to pay its next dividend of $1 in one year. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. So the first dividend of $1 will be in one year, the year after that $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1), and a year later $1.0404 (=1*(1+0.02)^2) and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
A firm wishes to raise $50 million now. They will issue 5% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 10 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 5% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
Examine the graph of the AUD versus the USD, EUR and JPY. Note that RHS means right hand side and LHS left hand side which indicates which axis each line corresponds to. Assume inflation rates in each country were equal over the time period 1984 to 2018.
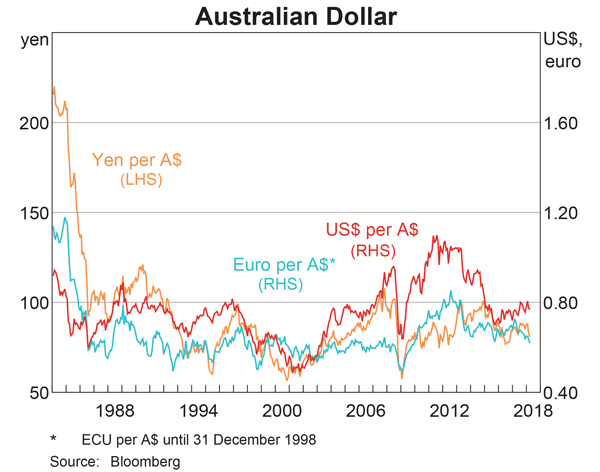
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?