A manufacturing company is considering a new project in the more risky services industry. The cash flows from assets (CFFA) are estimated for the new project, with interest expense excluded from the calculations. To get the levered value of the project, what should these unlevered cash flows be discounted by?
Assume that the manufacturing firm has a target debt-to-assets ratio that it sticks to.
You have just sold an 'in the money' 6 month European put option on the mining company BHP at an exercise price of $40 for a premium of $3.
Which of the following statements best describes your situation?
A stock was bought for $8 and paid a dividend of $0.50 one year later (at t=1 year). Just after the dividend was paid, the stock price was $7 (at t=1 year).
What were the total, capital and dividend returns given as effective annual rates? The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}##, ##r_\text{capital}##, ##r_\text{dividend}##.
Unrestricted negative gearing is allowed in Australia, New Zealand and Japan. Negative gearing laws allow income losses on investment properties to be deducted from a tax-payer's pre-tax personal income. Negatively geared investors benefit from this tax advantage. They also hope to benefit from capital gains which exceed the income losses.
For example, a property investor buys an apartment funded by an interest only mortgage loan. Interest expense is $2,000 per month. The rental payments received from the tenant living on the property are $1,500 per month. The investor can deduct this income loss of $500 per month from his pre-tax personal income. If his personal marginal tax rate is 46.5%, this saves $232.5 per month in personal income tax.
The advantage of negative gearing is an example of the benefits of:
A 2 year corporate bond yields 3% pa with a coupon rate of 5% pa, paid semi-annually.
Find the effective monthly rate, effective six month rate, and effective annual rate.
##r_\text{eff monthly}##, ##r_\text{eff 6 month}##, ##r_\text{eff annual}##.
One year ago you bought $100,000 of shares partly funded using a margin loan. The margin loan size was $70,000 and the other $30,000 was your own wealth or 'equity' in the share assets.
The interest rate on the margin loan was 7.84% pa.
Over the year, the shares produced a dividend yield of 4% pa and a capital gain of 5% pa.
What was the total return on your wealth? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and dividends) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates above are effective annual rates.
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
Question 522 income and capital returns, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 6% pa and nominal capital return of 2.5% pa. Inflation is expected to be 2.5% pa.
All of the above are effective nominal rates and investors believe that they will stay the same in perpetuity.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns?
The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Which of the below statements about utility is NOT generally accepted by economists? Most people are thought to:
Examine the below graphs. The first graph shows daily FX turnover in the world by both the public (government) and private sectors. The second graph 'Official Reserve Assets' shows the FX reserves of the Australian central bank, the RBA. The third graph's top panel shows the FX reserves of the Chinese central bank, the PBoC.
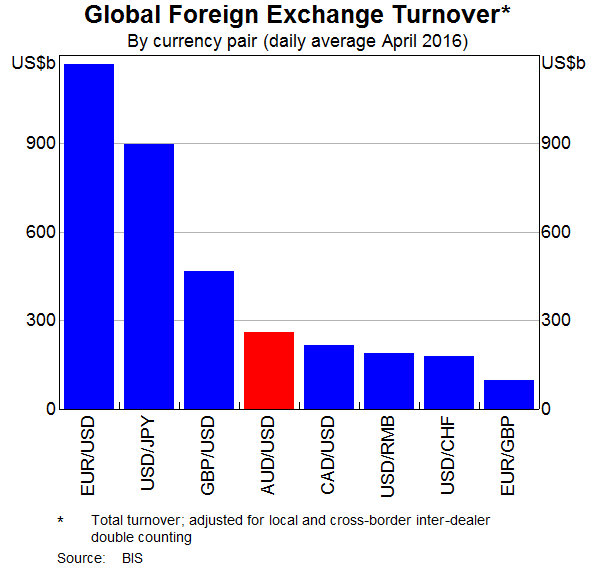
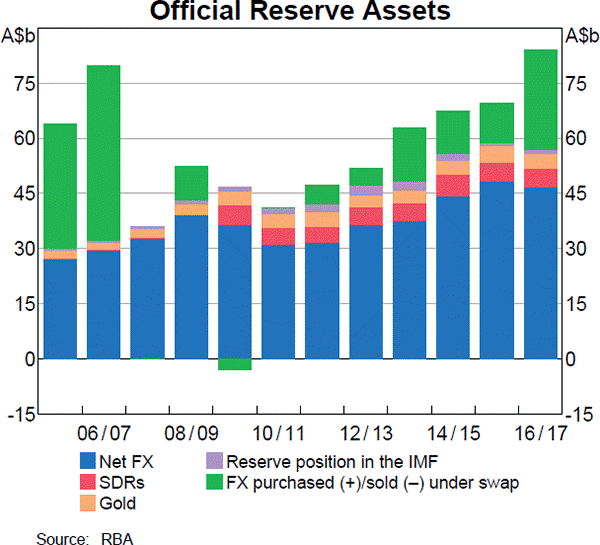
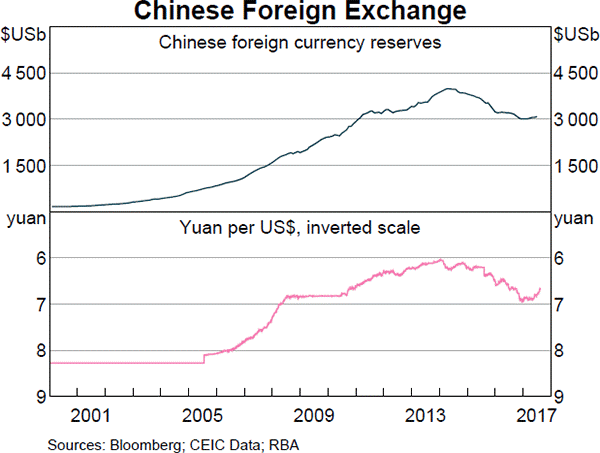
Assume that the AUD and USD are priced at parity so 1 AUD = 1 USD.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Which type of business organisation has the most checks and balances against the detrimental effects of the principal-agent problem since it's potentially the most exposed?