Question 96 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds paying semi-annual coupons:
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Calculate the effective annual rates of the following three APR's:
- A credit card offering an interest rate of 18% pa, compounding monthly.
- A bond offering a yield of 6% pa, compounding semi-annually.
- An annual dividend-paying stock offering a return of 10% pa compounding annually.
All answers are given in the same order:
##r_\text{credit card, eff yrly}##, ##r_\text{bond, eff yrly}##, ##r_\text{stock, eff yrly}##
The following cash flows are expected:
- 10 yearly payments of $60, with the first payment in 3 years from now (first payment at t=3 and last at t=12).
- 1 payment of $400 in 5 years and 6 months (t=5.5) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
A fairly priced stock has a beta that is the same as the market portfolio's beta. Treasury bonds yield 5% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa. What is the expected return of the stock?
Your firm's research scientists can begin an exciting new project at a cost of $10m now, after which there’s a:
- 70% chance that cash flows will be $1m per year forever, starting in 5 years (t=5). This is the A state of the world.
- 20% chance that cash flows will be $3m per year forever, starting in 5 years (t=5). This is the B state of the world.
- 10% chance of a major break through in which case the cash flows will be $20m per year forever starting in 5 years (t=5), or instead, the project can be expanded by investing another $10m (at t=5) which is expected to give cash flows of $60m per year forever, starting at year 9 (t=9). Note that the perpetual cash flows are either the $20m from year 4 onwards, or the $60m from year 9 onwards after the additional $10m year 5 investment, but not both. This is the C state of the world.
The firm's cost of capital is 10% pa.
What's the present value (at t=0) of the option to expand in year 5?
A young lady is trying to decide if she should attend university or not.
The young lady's parents say that she must attend university because otherwise all of her hard work studying and attending school during her childhood was a waste.
What's the correct way to classify this item from a capital budgeting perspective when trying to decide whether to attend university?
The hard work studying at school in her childhood should be classified as:
Which Australian institution is in charge of monetary policy?
Question 876 foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate, cross currency interest rate parity
Suppose the yield curve in the USA and Germany is flat and the:
- USD federal funds rate at the Federal Reserve is 1% pa;
- EUR deposit facility at the European Central Bank is -0.4% pa (note the negative sign);
- Spot EUR exchange rate is 1 USD per EUR;
- One year forward EUR exchange rate is 1.011 USD per EUR.
You suspect that there’s an arbitrage opportunity. Which one of the following statements about the potential arbitrage opportunity is NOT correct?
The below graph from the RBA shows the phase-in of the Basel 3 minimum regulatory capital requirements under the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) on the left panel and in Australia under the Australian Prudential Regulatory Authority (APRA) on the right panel.
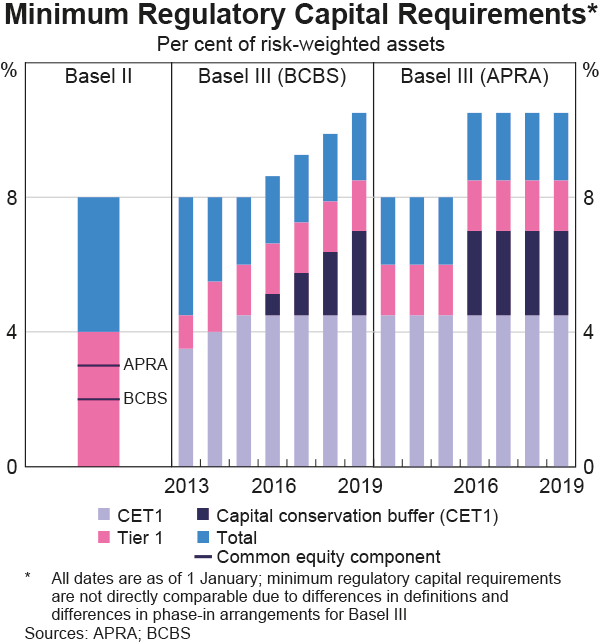
Which of the following statements about the Basel 3 minimum regulatory capital requirements as at 2019 is NOT correct? All minimum amounts exclude the 2.5% counter-cyclical buffer.
The Basel 3 minimum regulatory capital requirement as a percent of Risk Weighted Assets (RWA) is: