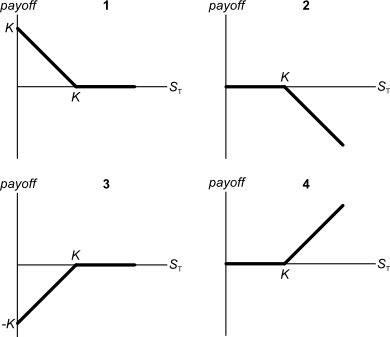
Below are 4 option graphs. Note that the y-axis is payoff at maturity (T). What options do they depict? List them in the order that they are numbered.
A stock pays annual dividends. It just paid a dividend of $3. The growth rate in the dividend is 4% pa. You estimate that the stock's required return is 10% pa. Both the discount rate and growth rate are given as effective annual rates. Using the dividend discount model, what will be the share price?
A student won $1m in a lottery. Currently the money is in a bank account which pays interest at 6% pa, given as an APR compounding per month.
She plans to spend $20,000 at the beginning of every month from now on (so the first withdrawal will be at t=0). After each withdrawal, she will check how much money is left in the account. When there is less than $500,000 left, she will donate that remaining amount to charity.
In how many months will she make her last withdrawal and donate the remainder to charity?
Your firm's research scientists can begin an exciting new project at a cost of $10m now, after which there’s a:
- 70% chance that cash flows will be $1m per year forever, starting in 5 years (t=5). This is the A state of the world.
- 20% chance that cash flows will be $3m per year forever, starting in 5 years (t=5). This is the B state of the world.
- 10% chance of a major break through in which case the cash flows will be $20m per year forever starting in 5 years (t=5), or instead, the project can be expanded by investing another $10m (at t=5) which is expected to give cash flows of $60m per year forever, starting at year 9 (t=9). Note that the perpetual cash flows are either the $20m from year 4 onwards, or the $60m from year 9 onwards after the additional $10m year 5 investment, but not both. This is the C state of the world.
The firm's cost of capital is 10% pa.
What's the present value (at t=0) of the option to expand in year 5?
An asset's total expected return over the next year is given by:
###r_\text{total} = \dfrac{c_1+p_1-p_0}{p_0} ###
Where ##p_0## is the current price, ##c_1## is the expected income in one year and ##p_1## is the expected price in one year. The total return can be split into the income return and the capital return.
Which of the following is the expected capital return?
Question 498 NPV, Annuity, perpetuity with growth, multi stage growth model
A business project is expected to cost $100 now (t=0), then pay $10 at the end of the third (t=3), fourth, fifth and sixth years, and then grow by 5% pa every year forever. So the cash flow will be $10.5 at the end of the seventh year (t=7), then $11.025 at the end of the eighth year (t=8) and so on perpetually. The total required return is 10℅ pa.
Which of the following formulas will NOT give the correct net present value of the project?
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid semi-annually. So there are two coupons per year, paid in arrears every six months.
Question 825 future, hedging, tailing the hedge, speculation, no explanation
An equity index fund manager controls a USD500 million diversified equity portfolio with a beta of 0.9. The equity manager expects a significant rally in equity prices next year. The market does not think that this will happen. If the fund manager wishes to increase his portfolio beta to 1.5, how many S&P500 futures should he buy?
The US market equity index is the S&P500. One year CME futures on the S&P500 currently trade at 2,155 points and the spot price is 2,180 points. Each point is worth $250.
The number of one year S&P500 futures contracts that the fund manager should buy is:
Question 834 option, delta, theta, gamma, standard deviation, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing
Which of the following statements about an option (either a call or put) and its underlying stock is NOT correct?
| European Call Option | ||
| on a non-dividend paying stock | ||
| Description | Symbol | Quantity |
| Spot price ($) | ##S_0## | 20 |
| Strike price ($) | ##K_T## | 18 |
| Risk free cont. comp. rate (pa) | ##r## | 0.05 |
| Standard deviation of the stock's cont. comp. returns (pa) | ##\sigma## | 0.3 |
| Option maturity (years) | ##T## | 1 |
| Call option price ($) | ##c_0## | 3.939488 |
| Delta | ##\Delta = N[d_1]## | 0.747891 |
| ##N[d_2]## | ##N[d_2]## | 0.643514 |
| Gamma | ##\Gamma## | 0.053199 |
| Theta ($/year) | ##\Theta = \partial c / \partial T## | 1.566433 |
Question 884 monetary policy, impossible trinity, foreign exchange rate, no explanation
According to the impossible trinity, a currency can only have two of these three desirable traits: be fixed against the USD; convertible to and from USD for traders and investors so there are open goods, services and capital markets; and allow independent monetary policy set by the country’s central bank, independent of the US central bank.
Which of the following exchange rate regimes sacrifices fixing the exchange rate to the USD? In other words, which regime uses a floating exchange rate?