Question 108 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds:
- A 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa, and
- A 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
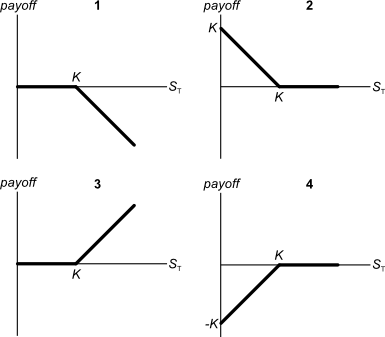
Below are 4 option graphs. Note that the y-axis is payoff at maturity (T). What options do they depict? List them in the order that they are numbered
The hardest and most important aspect of business project valuation is the estimation of the:
What is the covariance of a variable X with a constant C?
The cov(X, C) or ##\sigma_{X,C}## equals:
A credit card company advertises an interest rate of 18% pa, payable monthly. Which of the following statements about the interest rate is NOT correct? All rates are given to four decimal places.
A trader buys one crude oil European style put option contract on the CME expiring in one year with an exercise price of $44 per barrel for a price of $6.64. The crude oil spot price is $40.33. If the trader doesn’t close out her contract before maturity, then at maturity she will have the:
A share will pay its next dividend of ##C_1## in one year, and will continue to pay a dividend every year after that forever, growing at a rate of ##g##. So the next dividend will be ##C_2=C_1 (1+g)^1##, then ##C_3=C_2 (1+g)^1##, and so on forever.
The current price of the share is ##P_0## and its required return is ##r##
Which of the following is NOT equal to the expected share price in 2 years ##(P_2)## just after the dividend at that time ##(C_2)## has been paid?
A 4.5% fixed coupon Australian Government bond was issued at par in mid-April 2009. Coupons are paid semi-annually in arrears in mid-April and mid-October each year. The face value is $1,000. The bond will mature in mid-April 2020, so the bond had an original tenor of 11 years.
Today is mid-September 2015 and similar bonds now yield 1.9% pa.
What is the bond's new price? Note: there are 10 semi-annual coupon payments remaining from now (mid-September 2015) until maturity (mid-April 2020); both yields are given as APR's compounding semi-annually; assume that the yield curve was flat before the change in yields, and remained flat afterwards as well.