For a price of $100, Andrea will sell you a 2 year bond paying annual coupons of 10% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with the same risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 6% pa.
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.15 | 1.10 | 1.05 | 1.00 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at -5% pa. Note that this is a negative growth rate, so the dividend will actually shrink. So,
- the dividend at t=5 will be ##$1(1-0.05) = $0.95##,
- the dividend at t=6 will be ##$1(1-0.05)^2 = $0.9025##, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates.
What is the current price of the stock?
According to the theory of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), total risk can be broken into two components, systematic risk and idiosyncratic risk. Which of the following events would be considered a systematic, undiversifiable event according to the theory of the CAPM?
A project's net present value (NPV) is negative. Select the most correct statement.
Interest expense (IntExp) is an important part of a company's income statement (or 'profit and loss' or 'statement of financial performance').
How does an accountant calculate the annual interest expense of a fixed-coupon bond that has a liquid secondary market? Select the most correct answer:
Annual interest expense is equal to:
Question 381 Merton model of corporate debt, option, real option
In the Merton model of corporate debt, buying a levered company's debt is equivalent to buying risk free government bonds and:
Question 443 corporate financial decision theory, investment decision, financing decision, working capital decision, payout policy
Business people make lots of important decisions. Which of the following is the most important long term decision?
Question 452 limited liability, expected and historical returns
What is the lowest and highest expected share price and expected return from owning shares in a company over a finite period of time?
Let the current share price be ##p_0##, the expected future share price be ##p_1##, the expected future dividend be ##d_1## and the expected return be ##r##. Define the expected return as:
##r=\dfrac{p_1-p_0+d_1}{p_0} ##
The answer choices are stated using inequalities. As an example, the first answer choice "(a) ##0≤p<∞## and ##0≤r< 1##", states that the share price must be larger than or equal to zero and less than positive infinity, and that the return must be larger than or equal to zero and less than one.
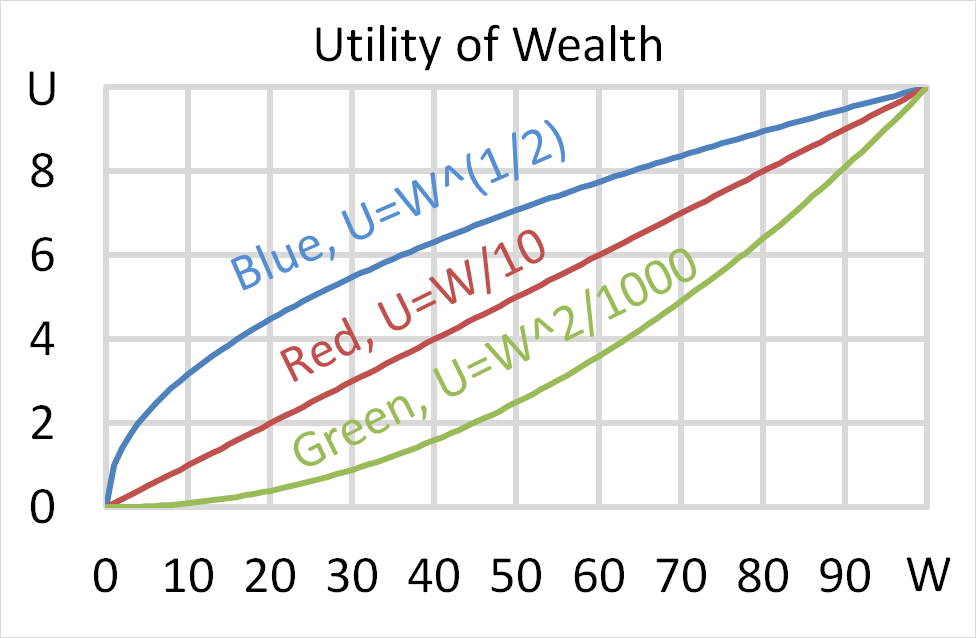
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions. Which of the statements about the 3 utility functions is NOT correct?
Question 889 cross currency interest rate parity, no explanation
Judging by the graph, in 2018 the USD short term interest rate set by the US Federal Reserve is higher than the JPY short term interest rate set by the Bank of Japan, which is higher than the EUR short term interest rate set by the European central bank.
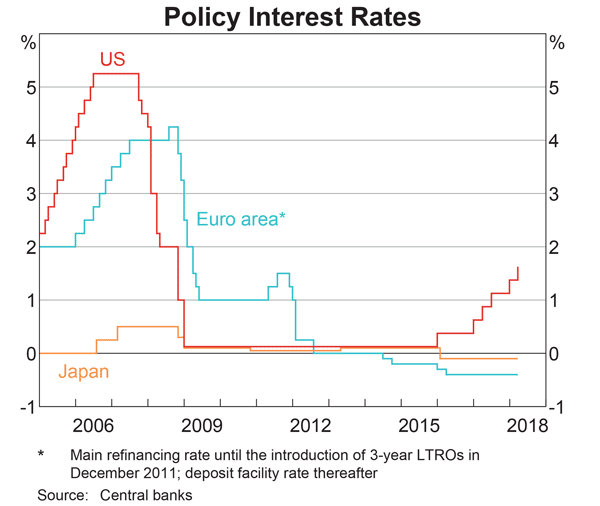
At the latest date shown in 2018: ##r_{USD}>r_{JPY}>r_{EUR}##
Assume that each currency’s yield curve is flat at the latest date shown in 2018, so interest rates are expected to remain at their current level into the future.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Over time you would expect the: