Question 245 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, foreign exchange rate direct quote, no explanation
Investors expect Australia's central bank, the RBA, to leave the policy rate unchanged at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the policy rate is reduced due to fears that Australia's GDP growth is slowing.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate? Direct and indirect quotes are given from the perspective of an Australian.
The Australian dollar will:
Question 319 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
Investors expect the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to keep the policy rate steady at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 25 basis points due to fears that the economy is growing too fast and that inflation will be above their target rate of 2 to 3 per cent.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar is likely to:
Question 320 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
Investors expect the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to decrease the overnight cash rate at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will keep the policy rate unchanged.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar is likely to:
Question 321 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
The market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to increase the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 50 basis points due to high future GDP and inflation forecasts.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar will:
Question 322 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
The market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to decrease the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will decrease the policy rate by 50 basis points due to fears of a recession and deflation.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate? The Australian dollar will:
Question 323 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
The market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to increase the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting.
As expected, the RBA increases the policy rate by 25 basis points.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar will:
Which Australian institution is in charge of monetary policy?
The Australian central bank implements monetary policy by directly controlling which interest rate?
Below is the Australian central bank’s cash rate.
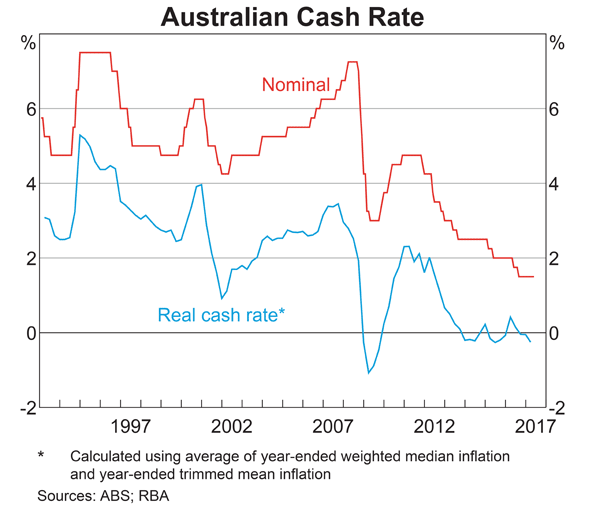
From 2011 to 2017 the Australian central bank has implemented:
Below is the Australian federal government’s budget balance as a percent of GDP. Note that the columns to the right of the vertical black line were a forecast at the time. The x-axis shows financial years, so for example the 06/07 financial year represents the time period from 1 July 2006 to 30 June 2007.
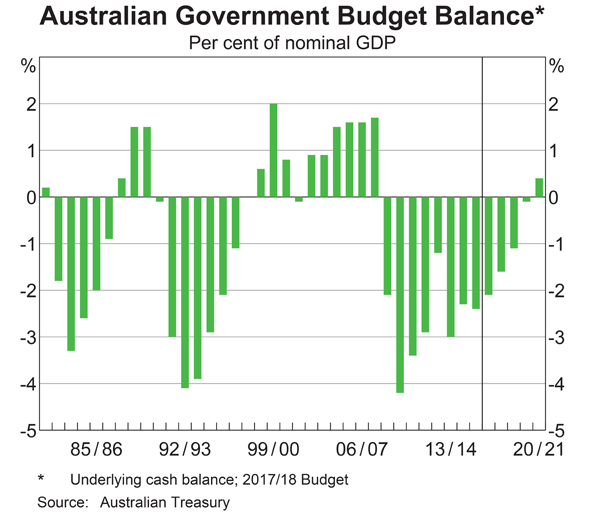
Comparing the 2008/09 financial year to the previous one, the Australian federal government implemented:
Which of the following is NOT the Australian central bank’s responsibility?
Question 862 yield curve, bond pricing, bill pricing, monetary policy, no explanation
Refer to the below graph when answering the questions.
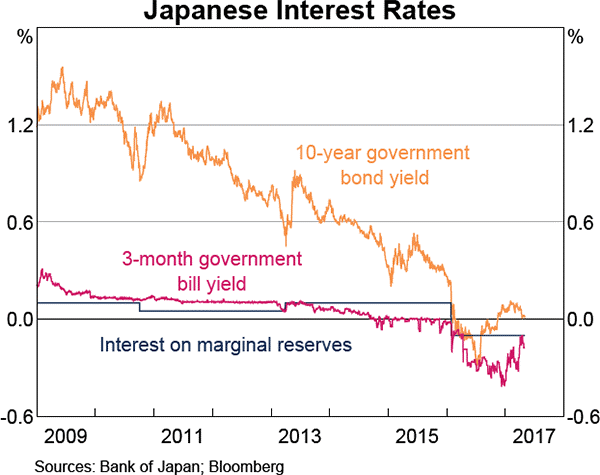
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 883 monetary policy, impossible trinity, foreign exchange rate
It’s often thought that the ideal currency or exchange rate regime would:
1. Be fixed against the USD;
2. Be convertible to and from USD for traders and investors so there are open goods, services and capital markets, and;
3. Allow independent monetary policy set by the country’s central bank, independent of the US central bank. So the country can set its own interest rate independent of the US Federal Reserve’s USD interest rate.
However, not all of these characteristics can be achieved. One must be sacrificed. This is the 'impossible trinity'.
Which of the following exchange rate regimes sacrifices convertibility?
Question 884 monetary policy, impossible trinity, foreign exchange rate, no explanation
According to the impossible trinity, a currency can only have two of these three desirable traits: be fixed against the USD; convertible to and from USD for traders and investors so there are open goods, services and capital markets; and allow independent monetary policy set by the country’s central bank, independent of the US central bank.
Which of the following exchange rate regimes sacrifices fixing the exchange rate to the USD? In other words, which regime uses a floating exchange rate?
Question 890 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, no explanation
The market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to increase the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting. The current exchange rate is 0.8 USD per AUD.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 50 basis points due to increased fears of inflation.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate on the day when the surprise announcement is made? The Australian dollar is likely to suddenly:
Question 891 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, no explanation
Suppose the market expects the Bank of Japan (BoJ) to decrease their short term interest rate by 15 basis points at their next meeting. The current short term interest rate is -0.1% pa and the exchange rate is 100 JPY per USD.
Then unexpectedly, the BoJ announce that they will leave the short term interest rate unchanged.
What do you expect to happen to Japan’s exchange rate on the day when the surprise announcement is made? The Japanese Yen (JPY) is likely to suddenly:
Question 964 monetary policy, impossible trinity, foreign exchange rate
It’s often thought that the ideal currency or exchange rate regime would:
1. Be fixed against the USD;
2. Be convertible to and from USD for traders and investors so there are open goods, services and capital markets, and;
3. Allow independent monetary policy set by the country’s central bank, independent of the US central bank. So the country can set its own interest rate independent of the US Federal Reserve’s USD interest rate.
However, not all of these characteristics can be achieved. One must be sacrificed. This is the 'impossible trinity'.
Which of the following exchange rate regimes sacrifices independent monetary policy?
Question 973 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, no explanation
Suppose the market expects the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to increase the policy rate by 25 basis points at their next meeting. The current exchange rate is 0.8 USD per AUD.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will leave the policy rate unchanged due to increasing unemployment and fears of a potential recession.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate on the day when the surprise announcement is made? The Australian dollar is likely to:
Question 974 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, no explanation
Suppose the market expects the Bank of Japan (BoJ) to increase their short term interest rate by 15 basis points at their next meeting. The current short term interest rate is -0.1% pa and the exchange rate is 100 JPY per USD.
As expected, the BoJ announce that they will increase short term interest rate by 15 basis points.
What do you expect to happen to Japan’s exchange rate on the day when the announcement is made? The Japanese Yen (JPY) is likely to:
Former Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) Governor Phil Lowe says that the RBA cash rate is the interest rate in the Australian:
Former RBA Governor Phil Lowe says that if the economy is growing very strongly, then goods and services prices might be growing too:
Former RBA Governor Phil Lowe says that when the RBA raise interest rates, homeowners' mortgage loan interest expense will be:
Question 1018 RBA cash rate, monetary policy, foreign exchange rate
RBA Governor Phil Lowe says that when the RBA raises the cash rate (by surprise), the Australian dollar (AUD) tends to:
Question 1019 RBA cash rate, monetary policy, wealth effect
Former RBA Governor Phil Lowe says that when the RBA raises the cash rate, asset prices tend to:
Question 1020 Federal funds rate, monetary policy, dot plot
US Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell showed the 'dot plot' of Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) members' estimated future Fed fund rates following their quarterly summary of economic projections on 15 Dec 2021. The dot plot shows that committee members intended to make monetary policy more:
Question 1021 Federal funds rate, monetary policy, quantitative easing, tapering
US Fed Chair Jerome Powell held a news conference following the 25-26 January 2022 FOMC meeting.
Nick Timiraos reporting for The Wall Street Journal asked: "Raising rates and reducing the balance sheet both restrain the economy, both tighten monetary policy. How should we think about the relationship between the two? For example, how much passive runoff is equal to every quarter percentage point increase in your benchmark rate?"
Jerome Powell replied: "So, again, we think of the balance sheet as moving in a predictable manner, sort of in the background, and that the active tool meeting to meeting is not -- both of them, it's the federal funds rate. There are rules of thumbs. I'm reluctant to land on one of them that equate this. And there's also an element of uncertainty around the balance sheet. I think we have a much better sense, frankly, of how rate increases affect financial conditions and, hence, economic conditions. Balance sheet is still a relatively new thing for the markets and for us, so we're less certain about that." (US Fed, 2022)
When Nick Timiraos mentioned 'reducing the balance sheet', he's referring to:
Question 1023 monetary policy, inflation, breakeven inflation rate
If the breakeven inflation rate was far above the US Fed's long term 2% average inflation target, the Fed would be expected to:
Question 1034 duration, monetary policy, inflation, market efficiency
On 18 March 2022 the AFR's James Thomson wrote: "In a world where the bombs are still falling in Ukraine and the Fed is just getting started on what looks likely to be a year-long cycle of rising interest rates, it would take a certain amount of bravery to embrace the sort of high-tech, long duration plays that Wood favours" (Thomson, 2022).
Which of the following US macro-economic data releases is most likely to cause Cathie Wood's ARK ETF share price to fall?
Question 1051 monetary policy, equilibrium real interest rate, inequality, marginal propensity to consume, gross domestic product, bond pricing
Read the below quote for background, or skip it to answer the question immediately.
In his 31 August 2021 article 'The rich get richer and rates get lower', Robert Armstrong states that:
"Atif Mian, Ludwig Straub and Amir Sufi agree with partisans of the demographic view, such as the economists Charles Goodhart and Manoj Pradhan, that a key contributor to falling rates is higher savings.
Mian, Straub and Sufi disagree, however, about why there are ever more savings sloshing around. It is not because the huge baby-boom generation is getting older and saving more (a trend that will change direction soon, when they are all retired). Rather, it’s because a larger and larger slice of national income is going to the top decile of earners. Because a person can only consume so much, the wealthy few tend to save much of this income rather than spend it. This pushes rates down directly, when those savings are invested, driving asset prices up and yields down; and indirectly, by sapping aggregate demand.
Why doesn’t all the cash that the rich push into markets get converted, ultimately, into productive investment, either at home or abroad? Tricky question. For present purposes it is enough to note that this is not happening — the savings of the American rich reappear, instead, as debt, owed by the government or by lower-income US households. (In another paper, MS&S have pointed out that this means the high share of income going to the rich hurts aggregate demand in two ways: the rich have a lower marginal propensity to consume, and governments and the non-rich are forced to shift dollars from consumption to debt service. Economically speaking, high inequality is a real buzzkill.)
MS&S prefer the inequality explanation for two reasons. Using data from the Fed’s Survey of Consumer Finances (which goes back to 1950) they show that differences in savings rates are much greater within any given age cohort than across age cohorts. That is, savings are building up faster because the rich are getting richer, not because the baby boomers are getting older."
Which of the following statements about this quote is NOT correct?
Question 1052 monetary policy, equilibrium real interest rate, marginal propensity to consume, gross domestic product, bond pricing
In the below chart by Rachel and Summers (2019), the red dotted line depicts the decline in advanced economies’ (AE) equilibrium real interest rate (R*) in percentage points since the 1970’s. The authors attribute this to the factors represented by columns above and below the x-axis. The sum of these columns is given by the black line labelled 'Total response of R* in the GE (general equilibrium) models'.
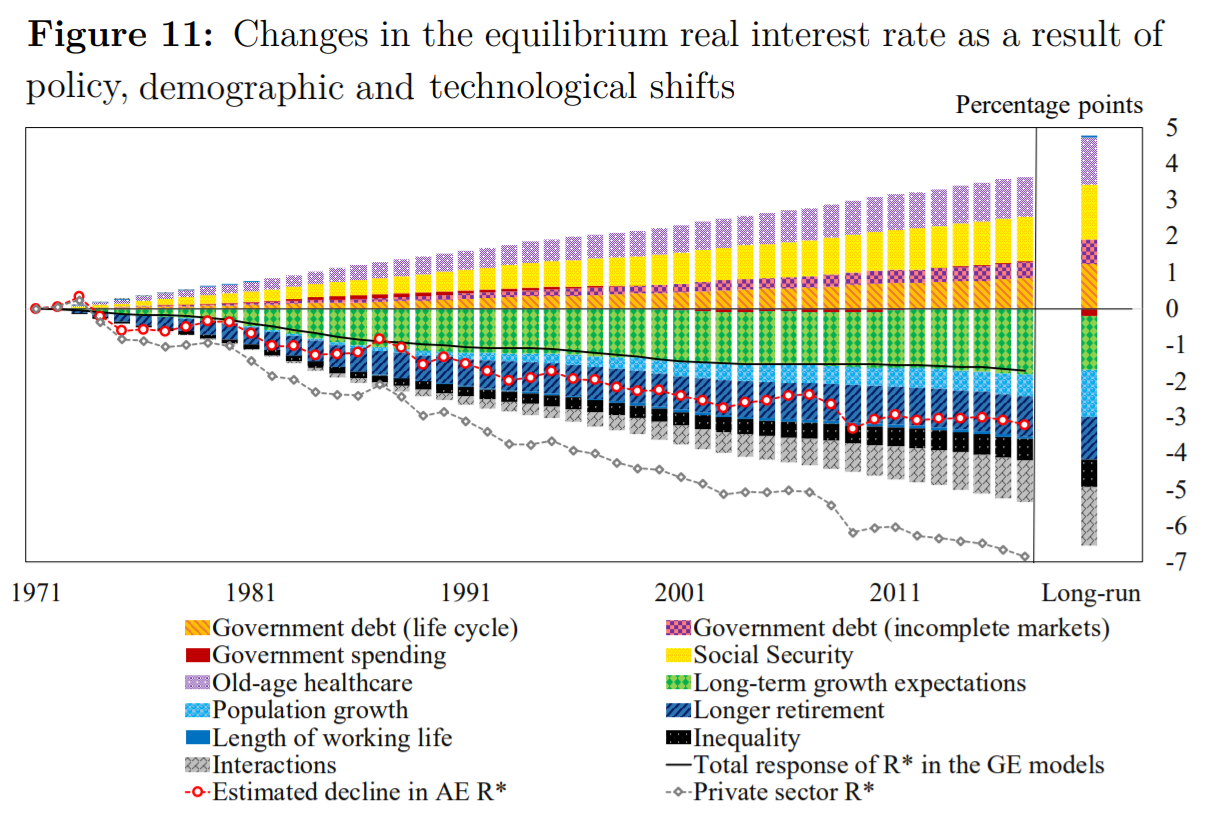
Which of the below statements about this graph is NOT correct?
Question 1053 bond pricing, monetary policy, supply and demand
In his 31 August 2021 article 'The rich get richer and rates get lower', Robert Armstrong states that: "Savings chase returns, so when there are more savings and the same number of places to put them, rates of return must fall" (Armstrong, 2021).
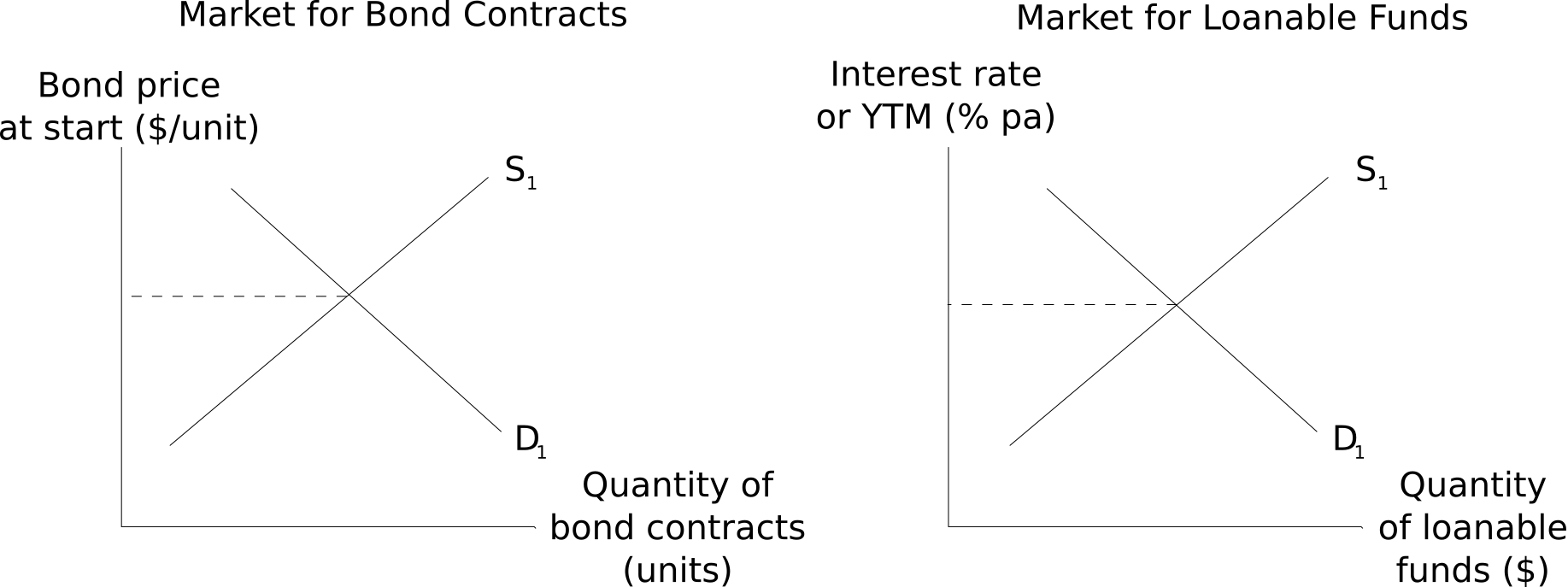
Another way of saying that "rates of return must fall" when there are more savings (loanable funds) invested into fixed coupon government and corporate bonds, is that increased:
View this great video from former RBA Governor Glenn Stevens from 0:22 to 1:30:
Select which of the following RBA objectives was introduced in the early 1990’s?
From 2:31 up to 4:00, Glenn Stevens discusses different shocks and how they affect inflation:
Which of the following shocks might reduce Australian inflation?