For a price of $13, Carla will sell you a share paying a dividend of $1 in one year and every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
A newly floated farming company is financed with senior bonds, junior bonds, cumulative non-voting preferred stock and common stock. The new company has no retained profits and due to floods it was unable to record any revenues this year, leading to a loss. The firm is not bankrupt yet since it still has substantial contributed equity (same as paid-up capital).
On which securities must it pay interest or dividend payments in this terrible financial year?
Question 447 payout policy, corporate financial decision theory
Payout policy is most closely related to which part of a business?
Question 723 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
Here is a table of stock prices and returns. Which of the statements below the table is NOT correct?
| Price and Return Population Statistics | ||||
| Time | Prices | LGDR | GDR | NDR |
| 0 | 100 | |||
| 1 | 99 | -0.010050 | 0.990000 | -0.010000 |
| 2 | 180.40 | 0.600057 | 1.822222 | 0.822222 |
| 3 | 112.73 | 0.470181 | 0.624889 | 0.375111 |
| Arithmetic average | 0.0399 | 1.1457 | 0.1457 | |
| Arithmetic standard deviation | 0.4384 | 0.5011 | 0.5011 | |
In the dividend discount model (DDM), share prices fall when dividends are paid. Let the high price before the fall be called the peak, and the low price after the fall be called the trough.
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
Which of the following statements about the DDM is NOT correct?
One year ago you bought a $1,000,000 house partly funded using a mortgage loan. The loan size was $800,000 and the other $200,000 was your wealth or 'equity' in the house asset.
The interest rate on the home loan was 4% pa.
Over the year, the house produced a net rental yield of 2% pa and a capital gain of 2.5% pa.
Assuming that all cash flows (interest payments and net rental payments) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates are given as effective annual rates, what was the total return on your wealth over the past year?
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
Question 862 yield curve, bond pricing, bill pricing, monetary policy, no explanation
Refer to the below graph when answering the questions.
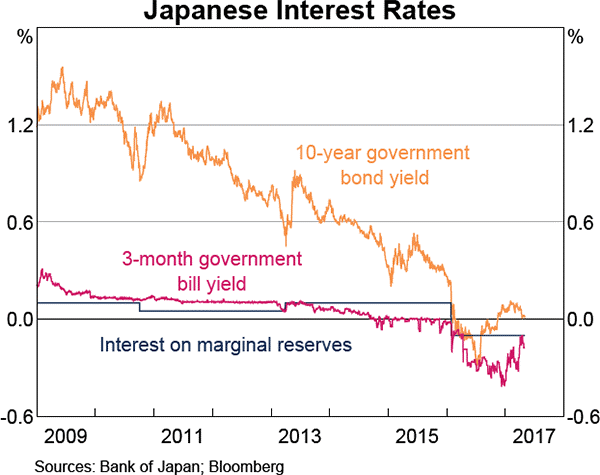
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 928 mean and median returns, mode return, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate, no explanation
The arithmetic average continuously compounded or log gross discrete return (AALGDR) on the ASX200 accumulation index over the 24 years from 31 Dec 1992 to 31 Dec 2016 is 9.49% pa.
The arithmetic standard deviation (SDLGDR) is 16.92 percentage points pa.
Assume that the log gross discrete returns are normally distributed and that the above estimates are true population statistics, not sample statistics, so there is no standard error in the sample mean or standard deviation estimates. Also assume that the standardised normal Z-statistic corresponding to a one-tail probability of 2.5% is exactly -1.96.
If you had a $1 million fund that replicated the ASX200 accumulation index, in how many years would the mode dollar value of your fund first be expected to lie outside the 95% confidence interval forecast?
Note that the mode of a log-normally distributed future price is: ##P_{T \text{ mode}} = P_0.e^{(\text{AALGDR} - \text{SDLGDR}^2 ).T} ##
Question 1000 duration, duration of a perpetuity with growth, needs refinement
An unlevered firm cuts its dividends and re-invests in zero-NPV projects with the same risk as its existing projects. This decreases the dividend yield, but increases the firm's equity's dividend growth rate and duration, while its total required return on equity remains unchanged. The equity can be valued as a perpetuity and the duration of a perpetuity is given below:
###D_\text{Macaulay} = \dfrac{1+r}{r-g}###What will be the effect on the stock's CAPM beta? Assume that there's no change in the risk free rate or market risk premium. The company's equity beta will: