Question 64 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, APR, effective rate
In Germany, nominal yields on semi-annual coupon paying Government Bonds with 2 years until maturity are currently 0.04% pa.
The inflation rate is currently 1.4% pa, given as an APR compounding per quarter. The inflation rate is not expected to change over the next 2 years.
What is the real yield on these bonds, given as an APR compounding every 6 months?
A prospective home buyer can afford to pay $2,000 per month in mortgage loan repayments. The central bank recently lowered its policy rate by 0.25%, and residential home lenders cut their mortgage loan rates from 4.74% to 4.49%.
How much more can the prospective home buyer borrow now that interest rates are 4.49% rather than 4.74%? Give your answer as a proportional increase over the original amount he could borrow (##V_\text{before}##), so:
###\text{Proportional increase} = \frac{V_\text{after}-V_\text{before}}{V_\text{before}} ###Assume that:
- Interest rates are expected to be constant over the life of the loan.
- Loans are interest-only and have a life of 30 years.
- Mortgage loan payments are made every month in arrears and all interest rates are given as annualised percentage rates compounding per month.
For a price of $95, Nicole will sell you a 10 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 8% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with the same risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 8% pa.
Your main expense is fuel for your car which costs $100 per month. You just refueled, so you won't need any more fuel for another month (first payment at t=1 month).
You have $2,500 in a bank account which pays interest at a rate of 6% pa, payable monthly. Interest rates are not expected to change.
Assuming that you have no income, in how many months time will you not have enough money to fully refuel your car?
A student won $1m in a lottery. Currently the money is in a bank account which pays interest at 6% pa, given as an APR compounding per month.
She plans to spend $20,000 at the beginning of every month from now on (so the first withdrawal will be at t=0). After each withdrawal, she will check how much money is left in the account. When there is less than $500,000 left, she will donate that remaining amount to charity.
In how many months will she make her last withdrawal and donate the remainder to charity?
Question 180 equivalent annual cash flow, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Details of two different types of light bulbs are given below:
- Low-energy light bulbs cost $3.50, have a life of nine years, and use about $1.60 of electricity a year, paid at the end of each year.
- Conventional light bulbs cost only $0.50, but last only about a year and use about $6.60 of energy a year, paid at the end of each year.
The real discount rate is 5%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that all cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% given as an effective annual rate.
Find the Equivalent Annual Cost (EAC) of the low-energy and conventional light bulbs. The below choices are listed in that order.
You own a nice suit which you wear once per week on nights out. You bought it one year ago for $600. In your experience, suits used once per week last for 6 years. So you expect yours to last for another 5 years.
Your younger brother said that retro is back in style so he wants to wants to borrow your suit once a week when he goes out. With the increased use, your suit will only last for another 4 years rather than 5.
What is the present value of the cost of letting your brother use your current suit for the next 4 years?
Assume: that bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate; you will buy a new suit when your current one wears out and your brother will not use the new one; your brother will only use your current suit so he will only use it for the next four years; and the price of a new suit never changes.
Question 249 equivalent annual cash flow, effective rate conversion
Details of two different types of desserts or edible treats are given below:
- High-sugar treats like candy, chocolate and ice cream make a person very happy. High sugar treats are cheap at only $2 per day.
- Low-sugar treats like nuts, cheese and fruit make a person equally happy if these foods are of high quality. Low sugar treats are more expensive at $4 per day.
The advantage of low-sugar treats is that a person only needs to pay the dentist $2,000 for fillings and root canal therapy once every 15 years. Whereas with high-sugar treats, that treatment needs to be done every 5 years.
The real discount rate is 10%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that there are 365 days in every year and that all cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% given as an effective annual rate.
Find the equivalent annual cash flow (EAC) of the high-sugar treats and low-sugar treats, including dental costs. The below choices are listed in that order.
Ignore the pain of dental therapy, personal preferences and other factors.
A manufacturing company is considering a new project in the more risky services industry. The cash flows from assets (CFFA) are estimated for the new project, with interest expense excluded from the calculations. To get the levered value of the project, what should these unlevered cash flows be discounted by?
Assume that the manufacturing firm has a target debt-to-assets ratio that it sticks to.
The US firm Google operates in the online advertising business. In 2011 Google bought Motorola Mobility which manufactures mobile phones.
Assume the following:
- Google had a 10% after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC) before it bought Motorola.
- Motorola had a 20% after-tax WACC before it merged with Google.
- Google and Motorola have the same level of gearing.
- Both companies operate in a classical tax system.
You are a manager at Motorola. You must value a project for making mobile phones. Which method(s) will give the correct valuation of the mobile phone manufacturing project? Select the most correct answer.
The mobile phone manufacturing project's:
A company increases the proportion of debt funding it uses to finance its assets by issuing bonds and using the cash to repurchase stock, leaving assets unchanged.
Ignoring the costs of financial distress, which of the following statements is NOT correct:
Value the following business project to manufacture a new product.
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 2 yrs | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $6m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $3m | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | $0.6m | |
| Unit sales per year | 4m | |
| Sale price per unit | $8 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $5 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $1m | |
| Interest expense per year | 0 | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Weighted average cost of capital after tax per annum | 10% | |
Notes
- The firm's current assets and current liabilities are $3m and $2m respectively right now. This net working capital will not be used in this project, it will be used in other unrelated projects.
Due to the project, current assets (mostly inventory) will grow by $2m initially (at t = 0), and then by $0.2m at the end of the first year (t=1).
Current liabilities (mostly trade creditors) will increase by $0.1m at the end of the first year (t=1).
At the end of the project, the net working capital accumulated due to the project can be sold for the same price that it was bought. - The project cost $0.5m to research which was incurred one year ago.
Assumptions
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The business considering the project is run as a 'sole tradership' (run by an individual without a company) and is therefore eligible for a 50% capital gains tax discount when the equipment is sold, as permitted by the Australian Tax Office.
What is the expected net present value (NPV) of the project?
There are many ways to calculate a firm's free cash flow (FFCF), also called cash flow from assets (CFFA). Some include the annual interest tax shield in the cash flow and some do not.
Which of the below FFCF formulas include the interest tax shield in the cash flow?
###(1) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp### ###(2) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp.(1-t_c)### ###(3) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c )+ Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(4) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c) + Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(5) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(6) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(7) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(8) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c### ###(9) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(10) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c###The formulas for net income (NI also called earnings), EBIT and EBITDA are given below. Assume that depreciation and amortisation are both represented by 'Depr' and that 'FC' represents fixed costs such as rent.
###NI=(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###EBIT=Rev - COGS - FC-Depr### ###EBITDA=Rev - COGS - FC### ###Tax =(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).t_c= \dfrac{NI.t_c}{1-t_c}###A firm plans to issue equity and use the cash raised to pay off its debt. No assets will be bought or sold. Ignore the costs of financial distress.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct, all things remaining equal?
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Correlation | Dollars invested |
||
| A | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 60 | ||
| B | 0.2 | 0.6 | 140 | |||
What is the expected return of the above portfolio?
According to the theory of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), total risk can be broken into two components, systematic risk and idiosyncratic risk. Which of the following events would be considered a systematic, undiversifiable event according to the theory of the CAPM?
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Correlation | Beta | Dollars invested |
|
| A | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.12 | 0.5 | 40 | |
| B | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 80 | ||
What is the beta of the above portfolio?
Stock A has a beta of 0.5 and stock B has a beta of 1. Which statement is NOT correct?
Question 408 leverage, portfolio beta, portfolio risk, real estate, CAPM
You just bought a house worth $1,000,000. You financed it with an $800,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $200,000.
You estimate that:
- The house has a beta of 1;
- The mortgage loan has a beta of 0.2.
What is the beta of the equity (the $200,000 deposit) that you have in your house?
Also, if the risk free rate is 5% pa and the market portfolio's return is 10% pa, what is the expected return on equity in your house? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and rent) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates are effective annual rates.
You just entered into a fully amortising home loan with a principal of $600,000, a variable interest rate of 4.25% pa and a term of 25 years.
Immediately after settling the loan, the variable interest rate suddenly falls to 4% pa! You can't believe your luck. Despite this, you plan to continue paying the same home loan payments as you did before. How long will it now take to pay off your home loan?
Assume that the lower interest rate was granted immediately and that rates were and are now again expected to remain constant. Round your answer up to the nearest whole month.
Question 573 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, liquidity premium theory, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 143 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds:
- A 6-month zero coupon bond at a yield of 6% pa, and
- A 12 month zero coupon bond at a yield of 7% pa.
What is the company's forward rate from 6 to 12 months? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 96 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds paying semi-annual coupons:
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
When someone says that they're "buying American dollars" (USD), what type of asset are they probably buying? They're probably buying:
Question 319 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
Investors expect the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to keep the policy rate steady at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 25 basis points due to fears that the economy is growing too fast and that inflation will be above their target rate of 2 to 3 per cent.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar is likely to:
In the 1997 Asian financial crisis many countries' exchange rates depreciated rapidly against the US dollar (USD). The Thai, Indonesian, Malaysian, Korean and Filipino currencies were severely affected. The below graph shows these Asian countries' currencies in USD per one unit of their currency, indexed to 100 in June 1997.
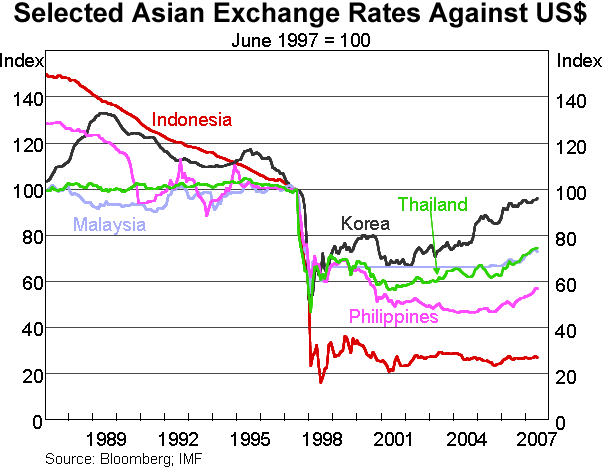
Of the statements below, which is NOT correct? The Asian countries':
The Chinese government attempts to fix its exchange rate against the US dollar and at the same time use monetary policy to fix its interest rate at a set level.
To be able to fix its exchange rate and interest rate in this way, what does the Chinese government actually do?
- Adopts capital controls to prevent financial arbitrage by private firms and individuals.
- Adopts the same interest rate (monetary policy) as the United States.
- Fixes inflation so that the domestic real interest rate is equal to the United States' real interest rate.
Which of the above statements is or are true?
Select the most correct statement from the following.
'Chartists', also known as 'technical traders', believe that:
Which of the following statements about short-selling is NOT true?
An investor wants to make a portfolio of two stocks A and B with a target expected portfolio return of 6% pa.
- Stock A has an expected return of 5% pa.
- Stock B has an expected return of 10% pa.
What portfolio weights should the investor have in stocks A and B respectively?
A firm can issue 5 year annual coupon bonds at a yield of 8% pa and a coupon rate of 12% pa.
The beta of its levered equity is 1. Five year government bonds yield 5% pa with a coupon rate of 6% pa. The market's expected dividend return is 4% pa and its expected capital return is 6% pa.
The firm's debt-to-equity ratio is 2:1. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What is the firm's after-tax WACC? Assume a classical tax system.
There are many different ways to value a firm's assets. Which of the following will NOT give the correct market value of a levered firm's assets ##(V_L)##? Assume that:
- The firm is financed by listed common stock and vanilla annual fixed coupon bonds, which are both traded in a liquid market.
- The bonds' yield is equal to the coupon rate, so the bonds are issued at par. The yield curve is flat and yields are not expected to change. When bonds mature they will be rolled over by issuing the same number of new bonds with the same expected yield and coupon rate, and so on forever.
- Tax rates on the dividends and capital gains received by investors are equal, and capital gains tax is paid every year, even on unrealised gains regardless of when the asset is sold.
- There is no re-investment of the firm's cash back into the business. All of the firm's excess cash flow is paid out as dividends so real growth is zero.
- The firm operates in a mature industry with zero real growth.
- All cash flows and rates in the below equations are real (not nominal) and are expected to be stable forever. Therefore the perpetuity equation with no growth is suitable for valuation.
Where:
###r_\text{WACC before tax} = r_D.\frac{D}{V_L} + r_{EL}.\frac{E_L}{V_L} = \text{Weighted average cost of capital before tax}### ###r_\text{WACC after tax} = r_D.(1-t_c).\frac{D}{V_L} + r_{EL}.\frac{E_L}{V_L} = \text{Weighted average cost of capital after tax}### ###NI_L=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-\mathbf{IntExp}).(1-t_c) = \text{Net Income Levered}### ###CFFA_L=NI_L+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+\mathbf{IntExp} = \text{Cash Flow From Assets Levered}### ###NI_U=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr).(1-t_c) = \text{Net Income Unlevered}### ###CFFA_U=NI_U+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC= \text{Cash Flow From Assets Unlevered}###What is the net present value (NPV) of undertaking a full-time Australian undergraduate business degree as an Australian citizen? Only include the cash flows over the duration of the degree, ignore any benefits or costs of the degree after it's completed.
Assume the following:
- The degree takes 3 years to complete and all students pass all subjects.
- There are 2 semesters per year and 4 subjects per semester.
- University fees per subject per semester are $1,277, paid at the start of each semester. Fees are expected to remain constant in real terms for the next 3 years.
- There are 52 weeks per year.
- The first semester is just about to start (t=0). The first semester lasts for 19 weeks (t=0 to 19).
- The second semester starts immediately afterwards (t=19) and lasts for another 19 weeks (t=19 to 38).
- The summer holidays begin after the second semester ends and last for 14 weeks (t=38 to 52). Then the first semester begins the next year, and so on.
- Working full time at the grocery store instead of studying full-time pays $20/hr and you can work 35 hours per week. Wages are paid at the end of each week and are expected to remain constant in real terms.
- Full-time students can work full-time during the summer holiday at the grocery store for the same rate of $20/hr for 35 hours per week.
- The discount rate is 9.8% pa. All rates and cash flows are real. Inflation is expected to be 3% pa. All rates are effective annual.
The NPV of costs from undertaking the university degree is:
Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| One Year Mining Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in building mine and equipment | $9m | |
| Depreciation of mine and equipment over the year | $8m | |
| Kilograms of gold mined at end of year | 1,000 | |
| Sale price per kilogram | $0.05m | |
| Variable cost per kilogram | $0.03m | |
| Before-tax cost of closing mine at end of year | $4m | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
Note 1: Due to the project, the firm also anticipates finding some rare diamonds which will give before-tax revenues of $1m at the end of the year.
Note 2: The land that will be mined actually has thermal springs and a family of koalas that could be sold to an eco-tourist resort for an after-tax amount of $3m right now. However, if the mine goes ahead then this natural beauty will be destroyed.
Note 3: The mining equipment will have a book value of $1m at the end of the year for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $2.5m when it is sold.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero and one. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m), with the first cash flow at time zero, and the second at time one.
Find Candys Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Candys Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 200 | |
| COGS | 50 | |
| Operating expense | 10 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Interest expense | 10 | |
| Income before tax | 110 | |
| Tax at 30% | 33 | |
| Net income | 77 | |
| Candys Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets | 220 | 180 |
| PPE | ||
| Cost | 300 | 340 |
| Accumul. depr. | 60 | 40 |
| Carrying amount | 240 | 300 |
| Total assets | 460 | 480 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | 175 | 190 |
| Non-current liabilities | 135 | 130 |
| Owners' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | 50 | 60 |
| Contributed equity | 100 | 100 |
| Total L and OE | 460 | 480 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Why is Capital Expenditure (CapEx) subtracted in the Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) formula?
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###
A firm has forecast its Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) for this year and management is worried that it is too low. Which one of the following actions will lead to a higher CFFA for this year (t=0 to 1)? Only consider cash flows this year. Do not consider cash flows after one year, or the change in the NPV of the firm. Consider each action in isolation.
Over the next year, the management of an unlevered company plans to:
- Achieve firm free cash flow (FFCF or CFFA) of $1m.
- Pay dividends of $1.8m
- Complete a $1.3m share buy-back.
- Spend $0.8m on new buildings without buying or selling any other fixed assets. This capital expenditure is included in the CFFA figure quoted above.
Assume that:
- All amounts are received and paid at the end of the year so you can ignore the time value of money.
- The firm has sufficient retained profits to pay the dividend and complete the buy back.
- The firm plans to run a very tight ship, with no excess cash above operating requirements currently or over the next year.
How much new equity financing will the company need? In other words, what is the value of new shares that will need to be issued?
Over the next year, the management of an unlevered company plans to:
- Make $5m in sales, $1.9m in net income and $2m in equity free cash flow (EFCF).
- Pay dividends of $1m.
- Complete a $1.3m share buy-back.
Assume that:
- All amounts are received and paid at the end of the year so you can ignore the time value of money.
- The firm has sufficient retained profits to legally pay the dividend and complete the buy back.
- The firm plans to run a very tight ship, with no excess cash above operating requirements currently or over the next year.
How much new equity financing will the company need? In other words, what is the value of new shares that will need to be issued?
Which of the following decisions relates to the current assets and current liabilities of the firm?
Question 119 market efficiency, fundamental analysis, joint hypothesis problem
Your friend claims that by reading 'The Economist' magazine's economic news articles, she can identify shares that will have positive abnormal expected returns over the next 2 years. Assuming that her claim is true, which statement(s) are correct?
(i) Weak form market efficiency is broken.
(ii) Semi-strong form market efficiency is broken.
(iii) Strong form market efficiency is broken.
(iv) The asset pricing model used to measure the abnormal returns (such as the CAPM) is either wrong (mis-specification error) or is measured using the wrong inputs (data errors) so the returns may not be abnormal but rather fair for the level of risk.
Select the most correct response:
A person is thinking about borrowing $100 from the bank at 7% pa and investing it in shares with an expected return of 10% pa. One year later the person intends to sell the shares and pay back the loan in full. Both the loan and the shares are fairly priced.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of this one year investment? Note that you are asked to find the present value (##V_0##), not the value in one year (##V_1##).
Question 338 market efficiency, CAPM, opportunity cost, technical analysis
A man inherits $500,000 worth of shares.
He believes that by learning the secrets of trading, keeping up with the financial news and doing complex trend analysis with charts that he can quit his job and become a self-employed day trader in the equities markets.
What is the expected gain from doing this over the first year? Measure the net gain in wealth received at the end of this first year due to the decision to become a day trader. Assume the following:
- He earns $60,000 pa in his current job, paid in a lump sum at the end of each year.
- He enjoys examining share price graphs and day trading just as much as he enjoys his current job.
- Stock markets are weak form and semi-strong form efficient.
- He has no inside information.
- He makes 1 trade every day and there are 250 trading days in the year. Trading costs are $20 per trade. His broker invoices him for the trading costs at the end of the year.
- The shares that he currently owns and the shares that he intends to trade have the same level of systematic risk as the market portfolio.
- The market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa.
Measure the net gain over the first year as an expected wealth increase at the end of the year.
A managed fund charges fees based on the amount of money that you keep with them. The fee is 2% of the start-of-year amount, but it is paid at the end of every year.
This fee is charged regardless of whether the fund makes gains or losses on your money.
The fund offers to invest your money in shares which have an expected return of 10% pa before fees.
You are thinking of investing $100,000 in the fund and keeping it there for 40 years when you plan to retire.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of investing your money in the fund? Note that the question is not asking how much money you will have in 40 years, it is asking: what is the NPV of investing in the fund? Assume that:
- The fund has no private information.
- Markets are weak and semi-strong form efficient.
- The fund's transaction costs are negligible.
- The cost and trouble of investing your money in shares by yourself, without the managed fund, is negligible.
Question 416 real estate, market efficiency, income and capital returns, DDM, CAPM
A residential real estate investor believes that house prices will grow at a rate of 5% pa and that rents will grow by 2% pa forever.
All rates are given as nominal effective annual returns. Assume that:
- His forecast is true.
- Real estate is and always will be fairly priced and the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is true.
- Ignore all costs such as taxes, agent fees, maintenance and so on.
- All rental income cash flow is paid out to the owner, so there is no re-investment and therefore no additions or improvements made to the property.
- The non-monetary benefits of owning real estate and renting remain constant.
Which one of the following statements is NOT correct? Over time:
Question 370 capital budgeting, NPV, interest tax shield, WACC, CFFA
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 2 yrs | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $600k | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $250k | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | $200k | |
| Revenue per job | $12k | |
| Variable cost per job | $4k | |
| Quantity of jobs per year | 120 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $100k | |
| Interest expense in first year (at t=1) | $16.091k | |
| Interest expense in second year (at t=2) | $9.711k | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Government treasury bond yield | 5% | |
| Bank loan debt yield | 6% | |
| Levered cost of equity | 12.5% | |
| Market portfolio return | 10% | |
| Beta of assets | 1.24 | |
| Beta of levered equity | 1.5 | |
| Firm's and project's debt-to-equity ratio | 25% | |
Notes
- The project will require an immediate purchase of $50k of inventory, which will all be sold at cost when the project ends. Current liabilities are negligible so they can be ignored.
Assumptions
- The debt-to-equity ratio will be kept constant throughout the life of the project. The amount of interest expense at the end of each period has been correctly calculated to maintain this constant debt-to-equity ratio. Note that interest expense is different in each year.
- Thousands are represented by 'k' (kilo).
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are nominal. The inflation rate is 2% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The 50% capital gains tax discount is not available since the project is undertaken by a firm, not an individual.
What is the net present value (NPV) of the project?
Question 69 interest tax shield, capital structure, leverage, WACC
Which statement about risk, required return and capital structure is the most correct?
A company issues a large amount of bonds to raise money for new projects of similar risk to the company's existing projects. The net present value (NPV) of the new projects is positive but small. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is NOT correct?
Question 99 capital structure, interest tax shield, Miller and Modigliani, trade off theory of capital structure
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of debt and using the funds to repurchase shares. Its assets are unchanged.
Assume that:
- The firm and individual investors can borrow at the same rate and have the same tax rates.
- The firm's debt and shares are fairly priced and the shares are repurchased at the market price, not at a premium.
- There are no market frictions relating to debt such as asymmetric information or transaction costs.
- Shareholders wealth is measured in terms of utiliity. Shareholders are wealth-maximising and risk-averse. They have a preferred level of overall leverage. Before the firm's capital restructure all shareholders were optimally levered.
According to Miller and Modigliani's theory, which statement is correct?