The following cash flows are expected:
- 10 yearly payments of $60, with the first payment in 3 years from now (first payment at t=3 and last at t=12).
- 1 payment of $400 in 5 years and 6 months (t=5.5) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
Your friend overheard that you need some cash and asks if you would like to borrow some money. She can lend you $5,000 now (t=0), and in return she wants you to pay her back $1,000 in two years (t=2) and every year after that for the next 5 years, so there will be 6 payments of $1,000 from t=2 to t=7 inclusive.
What is the net present value (NPV) of borrowing from your friend?
Assume that banks loan funds at interest rates of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Some countries' interest rates are so low that they're zero.
If interest rates are 0% pa and are expected to stay at that level for the foreseeable future, what is the most that you would be prepared to pay a bank now if it offered to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years?
In other words, what is the present value of five $10 payments at time 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 if interest rates are 0% pa?
For a price of $1040, Camille will sell you a share which just paid a dividend of $100, and is expected to pay dividends every year forever, growing at a rate of 5% pa.
So the next dividend will be ##100(1+0.05)^1=$105.00##, and the year after it will be ##100(1+0.05)^2=110.25## and so on.
The required return of the stock is 15% pa.
A stock just paid its annual dividend of $9. The share price is $60. The required return of the stock is 10% pa as an effective annual rate.
What is the implied growth rate of the dividend per year?
Question 497 income and capital returns, DDM, ex dividend date
A stock will pay you a dividend of $10 tonight if you buy it today. Thereafter the annual dividend is expected to grow by 5% pa, so the next dividend after the $10 one tonight will be $10.50 in one year, then in two years it will be $11.025 and so on. The stock's required return is 10% pa.
What is the stock price today and what do you expect the stock price to be tomorrow, approximately?
Two years ago Fred bought a house for $300,000.
Now it's worth $500,000, based on recent similar sales in the area.
Fred's residential property has an expected total return of 8% pa.
He rents his house out for $2,000 per month, paid in advance. Every 12 months he plans to increase the rental payments.
The present value of 12 months of rental payments is $23,173.86.
The future value of 12 months of rental payments one year ahead is $25,027.77.
What is the expected annual growth rate of the rental payments? In other words, by what percentage increase will Fred have to raise the monthly rent by each year to sustain the expected annual total return of 8%?
The following is the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) used to price stocks:
### P_0 = \frac{d_1}{r-g} ###Assume that the assumptions of the DDM hold and that the time period is measured in years.
Which of the following is equal to the expected dividend in 3 years, ## d_3 ##?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### p_0 = \frac{d_1}{r - g} ###
Which expression is NOT equal to the expected dividend yield?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
###p_0=\frac{d_1}{r_\text{eff}-g_\text{eff}}###
Which expression is NOT equal to the expected capital return?
Question 50 DDM, stock pricing, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Most listed Australian companies pay dividends twice per year, the 'interim' and 'final' dividends, which are roughly 6 months apart.
You are an equities analyst trying to value the company BHP. You decide to use the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) as a starting point, so you study BHP's dividend history and you find that BHP tends to pay the same interim and final dividend each year, and that both grow by the same rate.
You expect BHP will pay a $0.55 interim dividend in six months and a $0.55 final dividend in one year. You expect each to grow by 4% next year and forever, so the interim and final dividends next year will be $0.572 each, and so on in perpetuity.
Assume BHP's cost of equity is 8% pa. All rates are quoted as nominal effective rates. The dividends are nominal cash flows and the inflation rate is 2.5% pa.
What is the current price of a BHP share?
You own an apartment which you rent out as an investment property.
What is the price of the apartment using discounted cash flow (DCF, same as NPV) valuation?
Assume that:
- You just signed a contract to rent the apartment out to a tenant for the next 12 months at $2,000 per month, payable in advance (at the start of the month, t=0). The tenant is just about to pay you the first $2,000 payment.
- The contract states that monthly rental payments are fixed for 12 months. After the contract ends, you plan to sign another contract but with rental payment increases of 3%. You intend to do this every year.
So rental payments will increase at the start of the 13th month (t=12) to be $2,060 (=2,000(1+0.03)), and then they will be constant for the next 12 months.
Rental payments will increase again at the start of the 25th month (t=24) to be $2,121.80 (=2,000(1+0.03)2), and then they will be constant for the next 12 months until the next year, and so on. - The required return of the apartment is 8.732% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
- Ignore all taxes, maintenance, real estate agent, council and strata fees, periods of vacancy and other costs. Assume that the apartment will last forever and so will the rental payments.
The boss of WorkingForTheManCorp has a wicked (and unethical) idea. He plans to pay his poor workers one week late so that he can get more interest on his cash in the bank.
Every week he is supposed to pay his 1,000 employees $1,000 each. So $1 million is paid to employees every week.
The boss was just about to pay his employees today, until he thought of this idea so he will actually pay them one week (7 days) later for the work they did last week and every week in the future, forever.
Bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as a real effective annual rate. So ##r_\text{eff annual, real} = 0.1## and the real effective weekly rate is therefore ##r_\text{eff weekly, real} = (1+0.1)^{1/52}-1 = 0.001834569##
All rates and cash flows are real, the inflation rate is 3% pa and there are 52 weeks per year. The boss will always pay wages one week late. The business will operate forever with constant real wages and the same number of employees.
What is the net present value (NPV) of the boss's decision to pay later?
Carlos and Edwin are brothers and they both love Holden Commodore cars.
Carlos likes to buy the latest Holden Commodore car for $40,000 every 4 years as soon as the new model is released. As soon as he buys the new car, he sells the old one on the second hand car market for $20,000. Carlos never has to bother with paying for repairs since his cars are brand new.
Edwin also likes Commodores, but prefers to buy 4-year old cars for $20,000 and keep them for 11 years until the end of their life (new ones last for 15 years in total but the 4-year old ones only last for another 11 years). Then he sells the old car for $2,000 and buys another 4-year old second hand car, and so on.
Every time Edwin buys a second hand 4 year old car he immediately has to spend $1,000 on repairs, and then $1,000 every year after that for the next 10 years. So there are 11 payments in total from when the second hand car is bought at t=0 to the last payment at t=10. One year later (t=11) the old car is at the end of its total 15 year life and can be scrapped for $2,000.
Assuming that Carlos and Edwin maintain their love of Commodores and keep up their habits of buying new ones and second hand ones respectively, how much larger is Carlos' equivalent annual cost of car ownership compared with Edwin's?
The real discount rate is 10% pa. All cash flows are real and are expected to remain constant. Inflation is forecast to be 3% pa. All rates are effective annual. Ignore capital gains tax and tax savings from depreciation since cars are tax-exempt for individuals.
You own a nice suit which you wear once per week on nights out. You bought it one year ago for $600. In your experience, suits used once per week last for 6 years. So you expect yours to last for another 5 years.
Your younger brother said that retro is back in style so he wants to wants to borrow your suit once a week when he goes out. With the increased use, your suit will only last for another 4 years rather than 5.
What is the present value of the cost of letting your brother use your current suit for the next 4 years?
Assume: that bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate; you will buy a new suit when your current one wears out and your brother will not use the new one; your brother will only use your current suit so he will only use it for the next four years; and the price of a new suit never changes.
You own some nice shoes which you use once per week on date nights. You bought them 2 years ago for $500. In your experience, shoes used once per week last for 6 years. So you expect yours to last for another 4 years.
Your younger sister said that she wants to borrow your shoes once per week. With the increased use, your shoes will only last for another 2 years rather than 4.
What is the present value of the cost of letting your sister use your current shoes for the next 2 years?
Assume: that bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate; you will buy a new pair of shoes when your current pair wears out and your sister will not use the new ones; your sister will only use your current shoes so she will only use it for the next 2 years; and the price of new shoes never changes.
An industrial chicken farmer grows chickens for their meat. Chickens:
- Cost $0.50 each to buy as chicks. They are bought on the day they’re born, at t=0.
- Grow at a rate of $0.70 worth of meat per chicken per week for the first 6 weeks (t=0 to t=6).
- Grow at a rate of $0.40 worth of meat per chicken per week for the next 4 weeks (t=6 to t=10) since they’re older and grow more slowly.
- Feed costs are $0.30 per chicken per week for their whole life. Chicken feed is bought and fed to the chickens once per week at the beginning of the week. So the first amount of feed bought for a chicken at t=0 costs $0.30, and so on.
- Can be slaughtered (killed for their meat) and sold at no cost at the end of the week. The price received for the chicken is their total value of meat (note that the chicken grows fast then slow, see above).
The required return of the chicken farm is 0.5% given as an effective weekly rate.
Ignore taxes and the fixed costs of the factory. Ignore the chicken’s welfare and other environmental and ethical concerns.
Find the equivalent weekly cash flow of slaughtering a chicken at 6 weeks and at 10 weeks so the farmer can figure out the best time to slaughter his chickens. The choices below are given in the same order, 6 and 10 weeks.
Question 575 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
You expect a nominal payment of $100 in 5 years. The real discount rate is 10% pa and the inflation rate is 3% pa. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 461 book and market values, ROE, ROA, market efficiency
One year ago a pharmaceutical firm floated by selling its 1 million shares for $100 each. Its book and market values of equity were both $100m. Its debt totalled $50m. The required return on the firm's assets was 15%, equity 20% and debt 5% pa.
In the year since then, the firm:
- Earned net income of $29m.
- Paid dividends totaling $10m.
- Discovered a valuable new drug that will lead to a massive 1,000 times increase in the firm's net income in 10 years after the research is commercialised. News of the discovery was publicly announced. The firm's systematic risk remains unchanged.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? All statements are about current figures, not figures one year ago.
Hint: Book return on assets (ROA) and book return on equity (ROE) are ratios that accountants like to use to measure a business's past performance.
###\text{ROA}= \dfrac{\text{Net income}}{\text{Book value of assets}}###
###\text{ROE}= \dfrac{\text{Net income}}{\text{Book value of equity}}###
The required return on assets ##r_V## is a return that financiers like to use to estimate a business's future required performance which compensates them for the firm's assets' risks. If the business were to achieve realised historical returns equal to its required returns, then investment into the business's assets would have been a zero-NPV decision, which is neither good nor bad but fair.
###r_\text{V, 0 to 1}= \dfrac{\text{Cash flow from assets}_\text{1}}{\text{Market value of assets}_\text{0}} = \dfrac{CFFA_\text{1}}{V_\text{0}}###
Similarly for equity and debt.
When using the dividend discount model, care must be taken to avoid using a nominal dividend growth rate that exceeds the country's nominal GDP growth rate. Otherwise the firm is forecast to take over the country since it grows faster than the average business forever.
Suppose a firm's nominal dividend grows at 10% pa forever, and nominal GDP growth is 5% pa forever. The firm's total dividends are currently $1 billion (t=0). The country's GDP is currently $1,000 billion (t=0).
In approximately how many years will the company's total dividends be as large as the country's GDP?
A project to build a toll road will take 3 years to complete, costing three payments of $50 million, paid at the start of each year (at times 0, 1, and 2).
After completion, the toll road will yield a constant $10 million at the end of each year forever with no costs. So the first payment will be at t=4.
The required return of the project is 10% pa given as an effective nominal rate. All cash flows are nominal.
What is the payback period?
The phone company Telstra have 2 mobile service plans on offer which both have the same amount of phone call, text message and internet data credit. Both plans have a contract length of 24 months and the monthly cost is payable in advance. The only difference between the two plans is that one is a:
- 'Bring Your Own' (BYO) mobile service plan, costing $50 per month. There is no phone included in this plan. The other plan is a:
- 'Bundled' mobile service plan that comes with the latest smart phone, costing $71 per month. This plan includes the latest smart phone.
Neither plan has any additional payments at the start or end.
The only difference between the plans is the phone, so what is the implied cost of the phone as a present value?
Assume that the discount rate is 2% per month given as an effective monthly rate, the same high interest rate on credit cards.
A home loan company advertises an interest rate of 6% pa, payable monthly. Which of the following statements about the interest rate is NOT correct? All rates are given to four decimal places.
Which of the below statements about effective rates and annualised percentage rates (APR's) is NOT correct?
On his 20th birthday, a man makes a resolution. He will deposit $30 into a bank account at the end of every month starting from now, which is the start of the month. So the first payment will be in one month. He will write in his will that when he dies the money in the account should be given to charity.
The bank account pays interest at 6% pa compounding monthly, which is not expected to change.
If the man lives for another 60 years, how much money will be in the bank account if he dies just after making his last (720th) payment?
You just borrowed $400,000 in the form of a 25 year interest-only mortgage with monthly payments of $3,000 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
You actually plan to pay more than the required interest payment. You plan to pay $3,300 in mortgage payments every month, which your mortgage lender allows. These extra payments will reduce the principal and the minimum interest payment required each month.
At the maturity of the mortgage, what will be the principal? That is, after the last (300th) interest payment of $3,300 in 25 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage?
Question 239 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, interest only loan
A bank grants a borrower an interest-only residential mortgage loan with a very large 50% deposit and a nominal interest rate of 6% that is not expected to change. Assume that inflation is expected to be a constant 2% pa over the life of the loan. Ignore credit risk.
From the bank's point of view, what is the long term expected nominal capital return of the loan asset?
Question 48 IRR, NPV, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds, market efficiency
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Let the 'income return' of a bond be the coupon at the end of the period divided by the market price now at the start of the period ##(C_1/P_0)##. The expected income return of a premium fixed coupon bond is:
In these tough economic times, central banks around the world have cut interest rates so low that they are practically zero. In some countries, government bond yields are also very close to zero.
A three year government bond with a face value of $100 and a coupon rate of 2% pa paid semi-annually was just issued at a yield of 0%. What is the price of the bond?
Question 96 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds paying semi-annual coupons:
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
You're trying to save enough money to buy your first car which costs $2,500. You can save $100 at the end of each month starting from now. You currently have no money at all. You just opened a bank account with an interest rate of 6% pa payable monthly.
How many months will it take to save enough money to buy the car? Assume that the price of the car will stay the same over time.
Your main expense is fuel for your car which costs $100 per month. You just refueled, so you won't need any more fuel for another month (first payment at t=1 month).
You have $2,500 in a bank account which pays interest at a rate of 6% pa, payable monthly. Interest rates are not expected to change.
Assuming that you have no income, in how many months time will you not have enough money to fully refuel your car?
Question 49 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, APR, effective rate
In Australia, nominal yields on semi-annual coupon paying Government Bonds with 2 years until maturity are currently 2.83% pa.
The inflation rate is currently 2.2% pa, given as an APR compounding per quarter. The inflation rate is not expected to change over the next 2 years.
What is the real yield on these bonds, given as an APR compounding every 6 months?
You just signed up for a 30 year interest-only mortgage with monthly payments of $3,000 per month. The interest rate is 6% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 15 years, just after the 180th payment at that time, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 6% and is not expected to change. Remember that the mortgage is interest-only and that mortgage payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
Question 56 income and capital returns, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds
Which of the following statements about risk free government bonds is NOT correct?
Hint: Total return can be broken into income and capital returns as follows:
###\begin{aligned} r_\text{total} &= \frac{c_1}{p_0} + \frac{p_1-p_0}{p_0} \\ &= r_\text{income} + r_\text{capital} \end{aligned} ###
The capital return is the growth rate of the price.
The income return is the periodic cash flow. For a bond this is the coupon payment.
Bonds A and B are issued by the same Australian company. Both bonds yield 7% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond A pays coupons of 10% pa and bond B pays coupons of 5% pa. Which of the following statements is true about the bonds' prices?
Bonds X and Y are issued by different companies, but they both pay a semi-annual coupon of 10% pa and they have the same face value ($100) and maturity (3 years).
The only difference is that bond X and Y's yields are 8 and 12% pa respectively. Which of the following statements is true?
A firm wishes to raise $20 million now. They will issue 8% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 5 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 6% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
Question 207 income and capital returns, bond pricing, coupon rate, no explanation
For a bond that pays fixed semi-annual coupons, how is the annual coupon rate defined, and how is the bond's annual income yield from time 0 to 1 defined mathematically?
Let: ##P_0## be the bond price now,
##F_T## be the bond's face value,
##T## be the bond's maturity in years,
##r_\text{total}## be the bond's total yield,
##r_\text{income}## be the bond's income yield,
##r_\text{capital}## be the bond's capital yield, and
##C_t## be the bond's coupon at time t in years. So ##C_{0.5}## is the coupon in 6 months, ##C_1## is the coupon in 1 year, and so on.
Question 213 income and capital returns, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds
The coupon rate of a fixed annual-coupon bond is constant (always the same).
What can you say about the income return (##r_\text{income}##) of a fixed annual coupon bond? Remember that:
###r_\text{total} = r_\text{income} + r_\text{capital}###
###r_\text{total, 0 to 1} = \frac{c_1}{p_0} + \frac{p_1-p_0}{p_0}###
Assume that there is no change in the bond's total annual yield to maturity from when it is issued to when it matures.
Select the most correct statement.
From its date of issue until maturity, the income return of a fixed annual coupon:
A firm wishes to raise $10 million now. They will issue 6% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 8 years and have a face value of $1,000 each. Bond yields are 10% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue? All numbers are rounded up.
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same company. Both bonds yield 10% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X pays coupons of 6% pa and bond Y pays coupons of 8% pa. Which of the following statements is true?
A 30 year Japanese government bond was just issued at par with a yield of 1.7% pa. The fixed coupon payments are semi-annual. The bond has a face value of $100.
Six months later, just after the first coupon is paid, the yield of the bond increases to 2% pa. What is the bond's new price?
There are many different ways to value a firm's assets. Which of the following will NOT give the correct market value of a levered firm's assets ##(V_L)##? Assume that:
- The firm is financed by listed common stock and vanilla annual fixed coupon bonds, which are both traded in a liquid market.
- The bonds' yield is equal to the coupon rate, so the bonds are issued at par. The yield curve is flat and yields are not expected to change. When bonds mature they will be rolled over by issuing the same number of new bonds with the same expected yield and coupon rate, and so on forever.
- Tax rates on the dividends and capital gains received by investors are equal, and capital gains tax is paid every year, even on unrealised gains regardless of when the asset is sold.
- There is no re-investment of the firm's cash back into the business. All of the firm's excess cash flow is paid out as dividends so real growth is zero.
- The firm operates in a mature industry with zero real growth.
- All cash flows and rates in the below equations are real (not nominal) and are expected to be stable forever. Therefore the perpetuity equation with no growth is suitable for valuation.
Where:
###r_\text{WACC before tax} = r_D.\frac{D}{V_L} + r_{EL}.\frac{E_L}{V_L} = \text{Weighted average cost of capital before tax}### ###r_\text{WACC after tax} = r_D.(1-t_c).\frac{D}{V_L} + r_{EL}.\frac{E_L}{V_L} = \text{Weighted average cost of capital after tax}### ###NI_L=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-\mathbf{IntExp}).(1-t_c) = \text{Net Income Levered}### ###CFFA_L=NI_L+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+\mathbf{IntExp} = \text{Cash Flow From Assets Levered}### ###NI_U=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr).(1-t_c) = \text{Net Income Unlevered}### ###CFFA_U=NI_U+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC= \text{Cash Flow From Assets Unlevered}###Why is Capital Expenditure (CapEx) subtracted in the Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) formula?
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###
A firm has forecast its Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) for this year and management is worried that it is too low. Which one of the following actions will lead to a higher CFFA for this year (t=0 to 1)? Only consider cash flows this year. Do not consider cash flows after one year, or the change in the NPV of the firm. Consider each action in isolation.
Over the next year, the management of an unlevered company plans to:
- Achieve firm free cash flow (FFCF or CFFA) of $1m.
- Pay dividends of $1.8m
- Complete a $1.3m share buy-back.
- Spend $0.8m on new buildings without buying or selling any other fixed assets. This capital expenditure is included in the CFFA figure quoted above.
Assume that:
- All amounts are received and paid at the end of the year so you can ignore the time value of money.
- The firm has sufficient retained profits to pay the dividend and complete the buy back.
- The firm plans to run a very tight ship, with no excess cash above operating requirements currently or over the next year.
How much new equity financing will the company need? In other words, what is the value of new shares that will need to be issued?
Over the next year, the management of an unlevered company plans to:
- Make $5m in sales, $1.9m in net income and $2m in equity free cash flow (EFCF).
- Pay dividends of $1m.
- Complete a $1.3m share buy-back.
Assume that:
- All amounts are received and paid at the end of the year so you can ignore the time value of money.
- The firm has sufficient retained profits to legally pay the dividend and complete the buy back.
- The firm plans to run a very tight ship, with no excess cash above operating requirements currently or over the next year.
How much new equity financing will the company need? In other words, what is the value of new shares that will need to be issued?
Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 2 years | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $6m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year for tax purposes | $1m | |
| Unit sales per year | 4m | |
| Sale price per unit | $8 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $3 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $1.5m | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
Note 1: The equipment will have a book value of $4m at the end of the project for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $0.9 million when it is sold at t=2.
Note 2: Due to the project, the firm will have to purchase $0.8m of inventory initially, which it will sell at t=1. The firm will buy another $0.8m at t=1 and sell it all again at t=2 with zero inventory left. The project will have no effect on the firm's current liabilities.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero, one and two. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Value the following business project to manufacture a new product.
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 2 yrs | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $6m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $3m | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | $0.6m | |
| Unit sales per year | 4m | |
| Sale price per unit | $8 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $5 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $1m | |
| Interest expense per year | 0 | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Weighted average cost of capital after tax per annum | 10% | |
Notes
- The firm's current assets and current liabilities are $3m and $2m respectively right now. This net working capital will not be used in this project, it will be used in other unrelated projects.
Due to the project, current assets (mostly inventory) will grow by $2m initially (at t = 0), and then by $0.2m at the end of the first year (t=1).
Current liabilities (mostly trade creditors) will increase by $0.1m at the end of the first year (t=1).
At the end of the project, the net working capital accumulated due to the project can be sold for the same price that it was bought. - The project cost $0.5m to research which was incurred one year ago.
Assumptions
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The business considering the project is run as a 'sole tradership' (run by an individual without a company) and is therefore eligible for a 50% capital gains tax discount when the equipment is sold, as permitted by the Australian Tax Office.
What is the expected net present value (NPV) of the project?
Question 572 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements about yield curves is NOT correct?
A student won $1m in a lottery. Currently the money is in a bank account which pays interest at 6% pa, given as an APR compounding per month.
She plans to spend $20,000 at the beginning of every month from now on (so the first withdrawal will be at t=0). After each withdrawal, she will check how much money is left in the account. When there is less than $500,000 left, she will donate that remaining amount to charity.
In how many months will she make her last withdrawal and donate the remainder to charity?
On 22-Mar-2013 the Australian Government issued series TB139 treasury bonds with a combined face value $23.4m, listed on the ASX with ticker code GSBG25.
The bonds mature on 21-Apr-2025, the fixed coupon rate is 3.25% pa and coupons are paid semi-annually on the 21st of April and October of each year. Each bond's face value is $1,000.
At market close on Friday 11-Sep-2015 the bonds' yield was 2.736% pa.
At market close on Monday 14-Sep-2015 the bonds' yield was 2.701% pa. Both yields are given as annualised percentage rates (APR's) compounding every 6 months. For convenience, assume 183 days in 6 months and 366 days in a year.
What was the historical total return over those 3 calendar days between Friday 11-Sep-2015 and Monday 14-Sep-2015?
There are 183 calendar days from market close on the last coupon 21-Apr-2015 to the market close of the next coupon date on 21-Oct-2015.
Between the market close times from 21-Apr-2015 to 11-Sep-2015 there are 143 calendar days. From 21-Apr-2015 to 14-Sep-2015 there are 146 calendar days.
From 14-Sep-2015 there were 20 coupons remaining to be paid including the next one on 21-Oct-2015.
All of the below answers are given as effective 3 day rates.
One year ago you bought $100,000 of shares partly funded using a margin loan. The margin loan size was $70,000 and the other $30,000 was your own wealth or 'equity' in the share assets.
The interest rate on the margin loan was 7.84% pa.
Over the year, the shares produced a dividend yield of 4% pa and a capital gain of 5% pa.
What was the total return on your wealth? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and dividends) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates above are effective annual rates.
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
Interest expense (IntExp) is an important part of a company's income statement (or 'profit and loss' or 'statement of financial performance').
How does an accountant calculate the annual interest expense of a fixed-coupon bond that has a liquid secondary market? Select the most correct answer:
Annual interest expense is equal to:
A firm has a debt-to-equity ratio of 25%. What is its debt-to-assets ratio?
A manufacturing company is considering a new project in the more risky services industry. The cash flows from assets (CFFA) are estimated for the new project, with interest expense excluded from the calculations. To get the levered value of the project, what should these unlevered cash flows be discounted by?
Assume that the manufacturing firm has a target debt-to-assets ratio that it sticks to.
The US firm Google operates in the online advertising business. In 2011 Google bought Motorola Mobility which manufactures mobile phones.
Assume the following:
- Google had a 10% after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC) before it bought Motorola.
- Motorola had a 20% after-tax WACC before it merged with Google.
- Google and Motorola have the same level of gearing.
- Both companies operate in a classical tax system.
You are a manager at Motorola. You must value a project for making mobile phones. Which method(s) will give the correct valuation of the mobile phone manufacturing project? Select the most correct answer.
The mobile phone manufacturing project's:
There are many ways to calculate a firm's free cash flow (FFCF), also called cash flow from assets (CFFA). Some include the annual interest tax shield in the cash flow and some do not.
Which of the below FFCF formulas include the interest tax shield in the cash flow?
###(1) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp### ###(2) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp.(1-t_c)### ###(3) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c )+ Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(4) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c) + Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(5) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(6) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(7) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(8) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c### ###(9) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(10) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c###The formulas for net income (NI also called earnings), EBIT and EBITDA are given below. Assume that depreciation and amortisation are both represented by 'Depr' and that 'FC' represents fixed costs such as rent.
###NI=(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###EBIT=Rev - COGS - FC-Depr### ###EBITDA=Rev - COGS - FC### ###Tax =(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).t_c= \dfrac{NI.t_c}{1-t_c}###Question 337 capital structure, interest tax shield, leverage, real and nominal returns and cash flows, multi stage growth model
A fast-growing firm is suitable for valuation using a multi-stage growth model.
It's nominal unlevered cash flow from assets (##CFFA_U##) at the end of this year (t=1) is expected to be $1 million. After that it is expected to grow at a rate of:
- 12% pa for the next two years (from t=1 to 3),
- 5% over the fourth year (from t=3 to 4), and
- -1% forever after that (from t=4 onwards). Note that this is a negative one percent growth rate.
Assume that:
- The nominal WACC after tax is 9.5% pa and is not expected to change.
- The nominal WACC before tax is 10% pa and is not expected to change.
- The firm has a target debt-to-equity ratio that it plans to maintain.
- The inflation rate is 3% pa.
- All rates are given as nominal effective annual rates.
What is the levered value of this fast growing firm's assets?
A retail furniture company buys furniture wholesale and distributes it through its retail stores. The owner believes that she has some good ideas for making stylish new furniture. She is considering a project to buy a factory and employ workers to manufacture the new furniture she's designed. Furniture manufacturing has more systematic risk than furniture retailing.
Her furniture retailing firm's after-tax WACC is 20%. Furniture manufacturing firms have an after-tax WACC of 30%. Both firms are optimally geared. Assume a classical tax system.
Which method(s) will give the correct valuation of the new furniture-making project? Select the most correct answer.
A method commonly seen in textbooks for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is the following:
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp)(1-t_c) + \\ &\space\space\space+ Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp(1-t_c) \\ \end{aligned}###
All things remaining equal, the higher the correlation of returns between two stocks:
What is the correlation of a variable X with itself?
The corr(X, X) or ##\rho_{X,X}## equals:
What is the correlation of a variable X with a constant C?
The corr(X, C) or ##\rho_{X,C}## equals:
The covariance and correlation of two stocks X and Y's annual returns are calculated over a number of years. The units of the returns are in percent per annum ##(\% pa)##.
What are the units of the covariance ##(\sigma_{X,Y})## and correlation ##(\rho_{X,Y})## of returns respectively?
Hint: Visit Wikipedia to understand the difference between percentage points ##(\text{pp})## and percent ##(\%)##.
Let the standard deviation of returns for a share per month be ##\sigma_\text{monthly}##.
What is the formula for the standard deviation of the share's returns per year ##(\sigma_\text{yearly})##?
Assume that returns are independently and identically distributed (iid) so they have zero auto correlation, meaning that if the return was higher than average today, it does not indicate that the return tomorrow will be higher or lower than average.
Stock A has a beta of 0.5 and stock B has a beta of 1. Which statement is NOT correct?
Question 513 stock split, reverse stock split, stock dividend, bonus issue, rights issue
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 566 capital structure, capital raising, rights issue, on market repurchase, dividend, stock split, bonus issue
A company's share price fell by 20% and its number of shares rose by 25%. Assume that there are no taxes, no signalling effects and no transaction costs.
Which one of the following corporate events may have happened?
Question 99 capital structure, interest tax shield, Miller and Modigliani, trade off theory of capital structure
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of debt and using the funds to repurchase shares. Its assets are unchanged.
Assume that:
- The firm and individual investors can borrow at the same rate and have the same tax rates.
- The firm's debt and shares are fairly priced and the shares are repurchased at the market price, not at a premium.
- There are no market frictions relating to debt such as asymmetric information or transaction costs.
- Shareholders wealth is measured in terms of utiliity. Shareholders are wealth-maximising and risk-averse. They have a preferred level of overall leverage. Before the firm's capital restructure all shareholders were optimally levered.
According to Miller and Modigliani's theory, which statement is correct?
A firm plans to issue equity and use the cash raised to pay off its debt. No assets will be bought or sold. Ignore the costs of financial distress.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct, all things remaining equal?
For a price of $100, Andrea will sell you a 2 year bond paying annual coupons of 10% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with the same risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 6% pa.
A company has:
- 100 million ordinary shares outstanding which are trading at a price of $5 each. Market analysts estimated that the company's ordinary stock has a beta of 1.5. The risk-free rate is 5% and the market return is 10%.
- 1 million preferred shares which have a face (or par) value of $100 and pay a constant annual dividend of 9% of par. The next dividend will be paid in one year. Assume that all preference dividends will be paid when promised. They currently trade at a price of $90 each.
- Debentures that have a total face value of $200 million and a yield to maturity of 6% per annum. They are publicly traded and their market price is equal to 110% of their face value.
The corporate tax rate is 30%. All returns and yields are given as effective annual rates.
What is the company's after-tax Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)? Assume a classical tax system.
Question 246 foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate, cross currency interest rate parity
Suppose the Australian cash rate is expected to be 8.15% pa and the US federal funds rate is expected to be 3.00% pa over the next 2 years, both given as nominal effective annual rates. The current exchange rate is at parity, so 1 USD = 1 AUD.
What is the implied 2 year forward foreign exchange rate?
Question 383 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
In the Merton model of corporate debt, buying a levered company's debt is equivalent to buying the company's assets and:
The below three graphs show probability density functions (PDF) of three different random variables Red, Green and Blue.
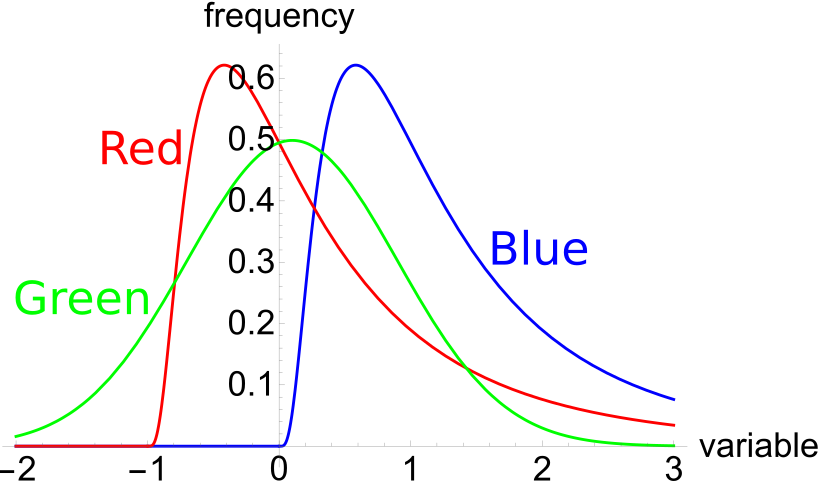
Which of the below statements is NOT correct?
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of equity and using the funds to repay debt. Its assets are unchanged. Ignore interest tax shields.
According to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which statement is correct?
Suppose that the US government recently announced that subsidies for fresh milk producers will be gradually phased out over the next year. Newspapers say that there are expectations of a 40% increase in the spot price of fresh milk over the next year.
Option prices on fresh milk trading on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) reflect expectations of this 40% increase in spot prices over the next year. Similarly to the rest of the market, you believe that prices will rise by 40% over the next year.
What option trades are likely to be profitable, or to be more specific, result in a positive Net Present Value (NPV)?
Assume that:
- Only the spot price is expected to increase and there is no change in expected volatility or other variables that affect option prices.
- No taxes, transaction costs, information asymmetry, bid-ask spreads or other market frictions.
A firm has 1 million shares which trade at a price of $30 each. The firm is expected to announce earnings of $3 million at the end of the year and pay an annual dividend of $1.50 per share.
What is the firm's (forward looking) price/earnings (PE) ratio?
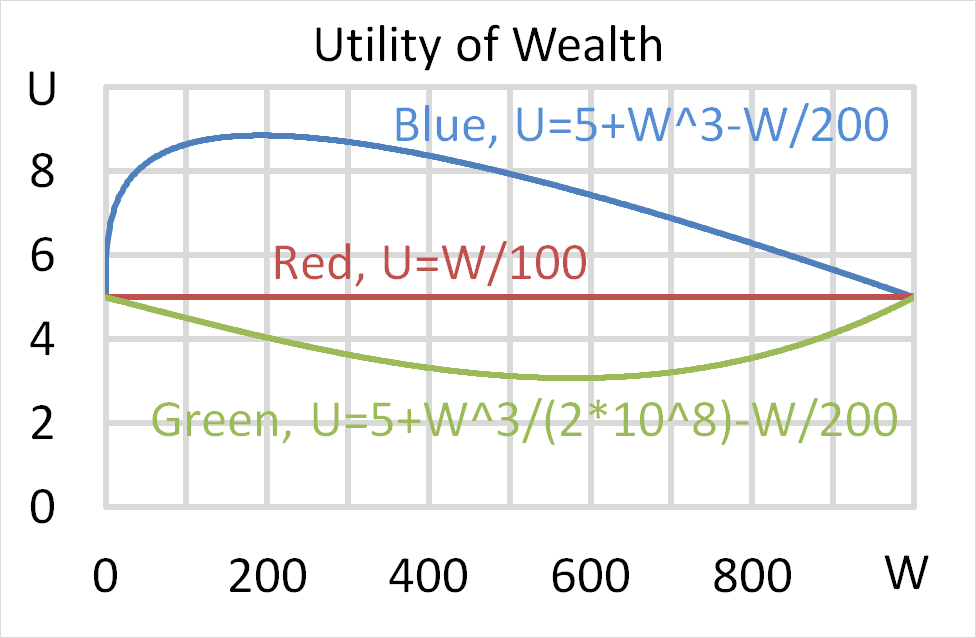
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
In Australia, domestic university students are allowed to buy concession tickets for the bus, train and ferry which sell at a discount of 50% to full-price tickets.
The Australian Government do not allow international university students to buy concession tickets, they have to pay the full price.
Some international students see this as unfair and they are willing to pay for fake university identification cards which have the concession sticker.
What is the most that an international student would be willing to pay for a fake identification card?
Assume that international students:
- consider buying their fake card on the morning of the first day of university from their neighbour, just before they leave to take the train into university.
- buy their weekly train tickets on the morning of the first day of each week.
- ride the train to university and back home again every day seven days per week until summer holidays 40 weeks from now. The concession card only lasts for those 40 weeks. Assume that there are 52 weeks in the year for the purpose of interest rate conversion.
- a single full-priced one-way train ride costs $5.
- have a discount rate of 11% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Approach this question from a purely financial view point, ignoring the illegality, embarrassment and the morality of committing fraud.
A project's NPV is positive. Select the most correct statement:
Question 319 foreign exchange rate, monetary policy, American and European terms
Investors expect the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to keep the policy rate steady at their next meeting.
Then unexpectedly, the RBA announce that they will increase the policy rate by 25 basis points due to fears that the economy is growing too fast and that inflation will be above their target rate of 2 to 3 per cent.
What do you expect to happen to Australia's exchange rate in the short term? The Australian dollar is likely to:
Question 415 income and capital returns, real estate, no explanation
You just bought a residential apartment as an investment property for $500,000.
You intend to rent it out to tenants. They are ready to move in, they would just like to know how much the monthly rental payments will be, then they will sign a twelve-month lease.
You require a total return of 8% pa and a rental yield of 5% pa.
What would the monthly paid-in-advance rental payments have to be this year to receive that 5% annual rental yield?
Also, if monthly rental payments can be increased each year when a new lease agreement is signed, by how much must you increase rents per year to realise the 8% pa total return on the property?
Ignore all taxes and the costs of renting such as maintenance costs, real estate agent fees, utilities and so on. Assume that there will be no periods of vacancy and that tenants will promptly pay the rental prices you charge.
Note that the first rental payment will be received at t=0. The first lease agreement specifies the first 12 equal payments from t=0 to 11. The next lease agreement can have a rental increase, so the next twelve equal payments from t=12 to 23 can be higher than previously, and so on forever.
A managed fund charges fees based on the amount of money that you keep with them. The fee is 2% of the end-of-year amount, paid at the end of every year.
This fee is charged regardless of whether the fund makes gains or losses on your money.
The fund offers to invest your money in shares which have an expected return of 10% pa before fees.
You are thinking of investing $100,000 in the fund and keeping it there for 40 years when you plan to retire.
How much money do you expect to have in the fund in 40 years? Also, what is the future value of the fees that the fund expects to earn from you? Give both amounts as future values in 40 years. Assume that:
- The fund has no private information.
- Markets are weak and semi-strong form efficient.
- The fund's transaction costs are negligible.
- The cost and trouble of investing your money in shares by yourself, without the managed fund, is negligible.
- The fund invests its fees in the same companies as it invests your funds in, but with no fees.
The below answer choices list your expected wealth in 40 years, and then the fund's expected wealth in 40 years.
Question 548 equivalent annual cash flow, time calculation, no explanation
An Apple iPhone 6 smart phone can be bought now for $999. An Android Kogan Agora 4G+ smart phone can be bought now for $240.
If the Kogan phone lasts for one year, approximately how long must the Apple phone last for to have the same equivalent annual cost?
Assume that both phones have equivalent features besides their lifetimes, that both are worthless once they've outlasted their life, the discount rate is 10% pa given as an effective annual rate, and there are no extra costs or benefits from either phone.
A stock is expected to pay a dividend of $5 per share in 1 month and $5 again in 7 months.
The stock price is $100, and the risk-free rate of interest is 10% per annum with continuous compounding. The yield curve is flat. Assume that investors are risk-neutral.
An investor has just taken a short position in a one year forward contract on the stock.
Find the forward price ##(F_1)## and value of the contract ##(V_0)## initially. Also find the value of the short futures contract in 6 months ##(V_\text{0.5, SF})## if the stock price fell to $90.
A wholesale store offers credit to its customers. Customers are given 60 days to pay for their goods, but if they pay immediately they will get a 1.5% discount.
What is the effective interest rate implicit in the discount being offered? Assume 365 days in a year and that all customers pay either immediately or the 60th day. All of the below answer choices are given as effective annual interest rates.
Which one of the following is NOT usually considered an 'investable' asset for long-term wealth creation?
Acquirer firm plans to launch a takeover of Target firm. The deal is expected to create a present value of synergies totaling $105 million. A scrip offer will be made that pays the fair price for the target's shares plus 75% of the total synergy value.
| Firms Involved in the Takeover | ||
| Acquirer | Target | |
| Assets ($m) | 6,000 | 700 |
| Debt ($m) | 4,800 | 400 |
| Share price ($) | 40 | 20 |
| Number of shares (m) | 30 | 15 |
Ignore transaction costs and fees. Assume that the firms' debt and equity are fairly priced, and that each firms' debts' risk, yield and values remain constant. The acquisition is planned to occur immediately, so ignore the time value of money.
Calculate the merged firm's share price and total number of shares after the takeover has been completed.
You are promised 20 payments of $100, where the first payment is immediate (t=0) and the last is at the end of the 19th year (t=19). The effective annual discount rate is ##r##.
Which of the following equations does NOT give the correct present value of these 20 payments?