Question 448 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system
A small private company has a single shareholder. This year the firm earned a $100 profit before tax. All of the firm's after tax profits will be paid out as dividends to the owner.
The corporate tax rate is 30% and the sole shareholder's personal marginal tax rate is 45%.
The Australian imputation tax system applies because the company generates all of its income in Australia and pays corporate tax to the Australian Tax Office. Therefore all of the company's dividends are fully franked. The sole shareholder is an Australian for tax purposes and can therefore use the franking credits to offset his personal income tax liability.
What will be the personal tax payable by the shareholder and the corporate tax payable by the company?
Question 469 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system, no explanation
A firm pays a fully franked cash dividend of $70 to one of its Australian shareholders who has a personal marginal tax rate of 45%. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What will be the shareholder's personal tax payable due to the dividend payment?
Question 494 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system
A firm pays a fully franked cash dividend of $100 to one of its Australian shareholders who has a personal marginal tax rate of 15%. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What will be the shareholder's personal tax payable due to the dividend payment?
Which of the following decisions relates to the current assets and current liabilities of the firm?
Question 738 financial statement, balance sheet, income statement
Where can a private firm's market value of equity be found? It can be sourced from the company's:
Question 767 idiom, corporate financial decision theory, no explanation
The sayings "Don't cry over spilt milk", "Don't regret the things that you can't change" and "What's done is done" are most closely related to which financial concept?
Question 624 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system, no explanation
Which of the following statements about Australian franking credits is NOT correct? Franking credits:
Question 443 corporate financial decision theory, investment decision, financing decision, working capital decision, payout policy
Business people make lots of important decisions. Which of the following is the most important long term decision?
By convention, money market securities' yields are always quoted as:
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? Money market securities are:
You want to buy an apartment priced at $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $30,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $270,000 as an interest only loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 12% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments? Remember that mortgage payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
You just borrowed $400,000 in the form of a 25 year interest-only mortgage with monthly payments of $3,000 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
You actually plan to pay more than the required interest payment. You plan to pay $3,300 in mortgage payments every month, which your mortgage lender allows. These extra payments will reduce the principal and the minimum interest payment required each month.
At the maturity of the mortgage, what will be the principal? That is, after the last (300th) interest payment of $3,300 in 25 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage?
In Australia in the 1980's, inflation was around 8% pa, and residential mortgage loan interest rates were around 14%.
In 2013, inflation was around 2.5% pa, and residential mortgage loan interest rates were around 4.5%.
If a person can afford constant mortgage loan payments of $2,000 per month, how much more can they borrow when interest rates are 4.5% pa compared with 14.0% pa?
Give your answer as a proportional increase over the amount you could borrow when interest rates were high ##(V_\text{high rates})##, so:
###\text{Proportional increase} = \dfrac{V_\text{low rates}-V_\text{high rates}}{V_\text{high rates}} ###
Assume that:
- Interest rates are expected to be constant over the life of the loan.
- Loans are interest-only and have a life of 30 years.
- Mortgage loan payments are made every month in arrears and all interest rates are given as annualised percentage rates (APR's) compounding per month.
The following cash flows are expected:
- 10 yearly payments of $80, with the first payment in 3 years from now (first payment at t=3).
- 1 payment of $600 in 5 years and 6 months (t=5.5) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
On his 20th birthday, a man makes a resolution. He will deposit $30 into a bank account at the end of every month starting from now, which is the start of the month. So the first payment will be in one month. He will write in his will that when he dies the money in the account should be given to charity.
The bank account pays interest at 6% pa compounding monthly, which is not expected to change.
If the man lives for another 60 years, how much money will be in the bank account if he dies just after making his last (720th) payment?
You are promised 20 payments of $100, where the first payment is immediate (t=0) and the last is at the end of the 19th year (t=19). The effective annual discount rate is ##r##.
Which of the following equations does NOT give the correct present value of these 20 payments?
Your friend overheard that you need some cash and asks if you would like to borrow some money. She can lend you $5,000 now (t=0), and in return she wants you to pay her back $1,000 in two years (t=2) and every year after that for the next 5 years, so there will be 6 payments of $1,000 from t=2 to t=7 inclusive.
What is the net present value (NPV) of borrowing from your friend?
Assume that banks loan funds at interest rates of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same US company. Both bonds yield 10% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X and Y's coupon rates are 8 and 12% pa respectively. Which of the following statements is true?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at a discount?
In these tough economic times, central banks around the world have cut interest rates so low that they are practically zero. In some countries, government bond yields are also very close to zero.
A three year government bond with a face value of $100 and a coupon rate of 2% pa paid semi-annually was just issued at a yield of 0%. What is the price of the bond?
For a price of $95, Nicole will sell you a 10 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 8% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with the same risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 8% pa.
An investor bought a 20 year 5% pa fixed coupon government bond priced at par. The face value is $100. Coupons are paid semi-annually and the next one is in 6 months.
Six months later, just after the coupon at that time was paid, yields suddenly and unexpectedly rose to 5.5% pa. Note that all yields above are given as APR's compounding semi-annually.
What was the bond investors' historical total return over that first 6 month period, given as an effective semi-annual rate?
Question 905 market capitalisation of equity, PE ratio, payout ratio
The below graph shows the computer software company Microsoft's stock price (MSFT) at the market close on the NASDAQ on Friday 1 June 2018.
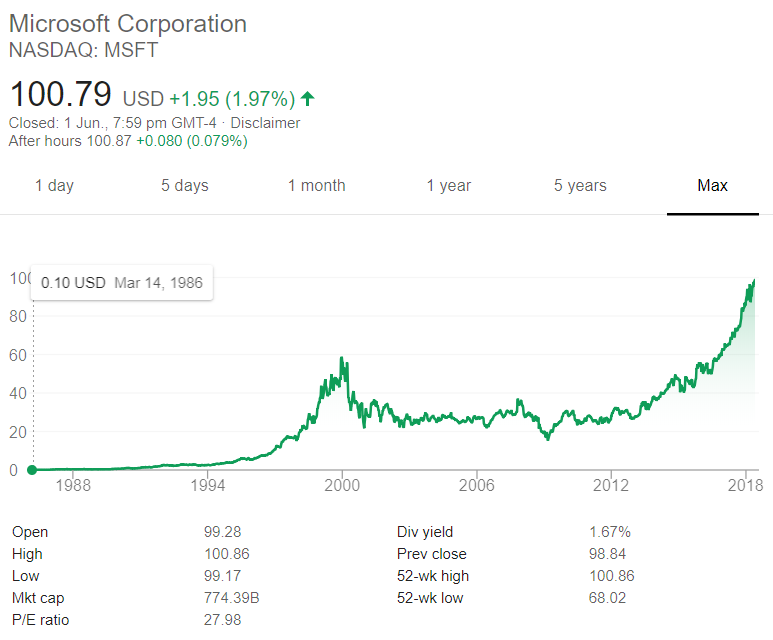
Based on the screenshot above, which of the following statements about MSFT is NOT correct? MSFT's:
A stock is expected to pay its next dividend of $1 in one year. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. So the first dividend of $1 will be in one year, the year after that $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1), and a year later $1.0404 (=1*(1+0.02)^2) and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
The perpetuity with growth formula, also known as the dividend discount model (DDM) or Gordon growth model, is appropriate for valuing a company's shares. ##P_0## is the current share price, ##C_1## is next year's expected dividend, ##r## is the total required return and ##g## is the expected growth rate of the dividend.
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
The below graph shows the expected future price path of the company's shares. Which of the following statements about the graph is NOT correct?
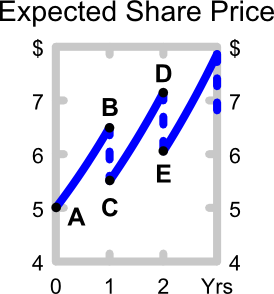
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### P_{0} = \frac{C_1}{r_{\text{eff}} - g_{\text{eff}}} ###
What would you call the expression ## C_1/P_0 ##?
The following is the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) used to price stocks:
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
If the assumptions of the DDM hold and the stock is fairly priced, which one of the following statements is NOT correct? The long term expected:
A stock is expected to pay its first dividend of $20 in 3 years (t=3), which it will continue to pay for the next nine years, so there will be ten $20 payments altogether with the last payment in year 12 (t=12).
From the thirteenth year onward, the dividend is expected to be 4% more than the previous year, forever. So the dividend in the thirteenth year (t=13) will be $20.80, then $21.632 in year 14, and so on forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa. All rates are effective annual rates. Calculate the current (t=0) stock price.
Question 50 DDM, stock pricing, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Most listed Australian companies pay dividends twice per year, the 'interim' and 'final' dividends, which are roughly 6 months apart.
You are an equities analyst trying to value the company BHP. You decide to use the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) as a starting point, so you study BHP's dividend history and you find that BHP tends to pay the same interim and final dividend each year, and that both grow by the same rate.
You expect BHP will pay a $0.55 interim dividend in six months and a $0.55 final dividend in one year. You expect each to grow by 4% next year and forever, so the interim and final dividends next year will be $0.572 each, and so on in perpetuity.
Assume BHP's cost of equity is 8% pa. All rates are quoted as nominal effective rates. The dividends are nominal cash flows and the inflation rate is 2.5% pa.
What is the current price of a BHP share?
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume an equal amount now (t=0) and in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end (t=1).
How much can you consume at each time?
You're considering a business project which costs $11m now and is expected to pay a single cash flow of $11m in one year. So you pay $11m now, then one year later you receive $11m.
Assume that the initial $11m cost is funded using the your firm's existing cash so no new equity or debt will be raised. The cost of capital is 10% pa.
Which of the following statements about the net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR) and payback period is NOT correct?
Your neighbour asks you for a loan of $100 and offers to pay you back $120 in one year.
You don't actually have any money right now, but you can borrow and lend from the bank at a rate of 10% pa. Rates are given as effective annual rates.
Assume that your neighbour will definitely pay you back. Ignore interest tax shields and transaction costs.
The Net Present Value (NPV) of lending to your neighbour is $9.09. Describe what you would do to actually receive a $9.09 cash flow right now with zero net cash flows in the future.
A pharmaceutical firm has just discovered a valuable new drug. So far the news has been kept a secret.
The net present value of making and commercialising the drug is $200 million, but $600 million of bonds will need to be issued to fund the project and buy the necessary plant and equipment.
The firm will release the news of the discovery and bond raising to shareholders simultaneously in the same announcement. The bonds will be issued shortly after.
Once the announcement is made and the bonds are issued, what is the expected increase in the value of the firm's assets (ΔV), market capitalisation of debt (ΔD) and market cap of equity (ΔE)?
The triangle symbol is the Greek letter capital delta which means change or increase in mathematics.
Ignore the benefit of interest tax shields from having more debt.
Remember: ##ΔV = ΔD+ΔE##
An investor owns an empty block of land that has local government approval to be developed into a petrol station, car wash or car park. The council will only allow a single development so the projects are mutually exclusive.
All of the development projects have the same risk and the required return of each is 10% pa. Each project has an immediate cost and once construction is finished in one year the land and development will be sold. The table below shows the estimated costs payable now, expected sale prices in one year and the internal rates of returns (IRR's).
| Mutually Exclusive Projects | |||
| Project | Cost now ($) |
Sale price in one year ($) |
IRR (% pa) |
| Petrol station | 9,000,000 | 11,000,000 | 22.22 |
| Car wash | 800,000 | 1,100,000 | 37.50 |
| Car park | 70,000 | 110,000 | 57.14 |
Which project should the investor accept?
Question 96 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds paying semi-annual coupons:
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 572 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 573 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, liquidity premium theory, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 693 boot strapping zero coupon yield, forward interest rate, term structure of interest rates
Information about three risk free Government bonds is given in the table below.
| Federal Treasury Bond Data | ||||
| Maturity | Yield to maturity | Coupon rate | Face value | Price |
| (years) | (pa, compounding semi-annually) | (pa, paid semi-annually) | ($) | ($) |
| 0.5 | 3% | 4% | 100 | 100.4926 |
| 1 | 4% | 4% | 100 | 100.0000 |
| 1.5 | 5% | 4% | 100 | 98.5720 |
Based on the above government bonds' yields to maturity, which of the below statements about the spot zero rates and forward zero rates is NOT correct?
Question 784 boot strapping zero coupon yield, forward interest rate, term structure of interest rates
Information about three risk free Government bonds is given in the table below.
| Federal Treasury Bond Data | ||||
| Maturity | Yield to maturity | Coupon rate | Face value | Price |
| (years) | (pa, compounding annually) | (pa, paid annually) | ($) | ($) |
| 1 | 0% | 2% | 100 | 102 |
| 2 | 1% | 2% | 100 | 101.9703951 |
| 3 | 2% | 2% | 100 | 100 |
Based on the above government bonds' yields to maturity, which of the below statements about the spot zero rates and forward zero rates is NOT correct?
Treasury bonds currently have a return of 5% pa. A stock has a beta of 0.5 and the market return is 10% pa. What is the expected return of the stock?
According to the theory of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), total variance can be broken into two components, systematic variance and idiosyncratic variance. Which of the following events would be considered the most diversifiable according to the theory of the CAPM?
A stock's required total return will increase when its:
A stock has a beta of 1.5. The market's expected total return is 10% pa and the risk free rate is 5% pa, both given as effective annual rates.
Over the last year, bad economic news was released showing a higher chance of recession. Over this time the share market fell by 1%. So ##r_{m} = (P_{0} - P_{-1})/P_{-1} = -0.01##, where the current time is zero and one year ago is time -1. The risk free rate was unchanged.
What do you think was the stock's historical return over the last year, given as an effective annual rate?
A fairly priced stock has an expected return equal to the market's. Treasury bonds yield 5% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa. What is the stock's beta?
Stock A has a beta of 0.5 and stock B has a beta of 1. Which statement is NOT correct?
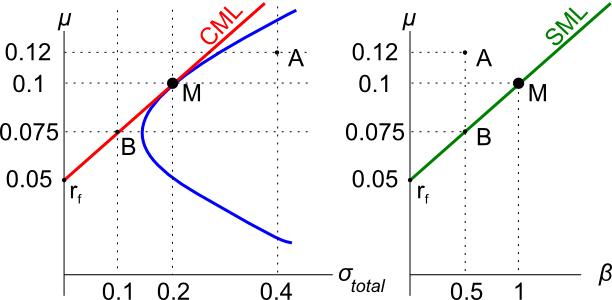
Assets A, B, M and ##r_f## are shown on the graphs above. Asset M is the market portfolio and ##r_f## is the risk free yield on government bonds. Assume that investors can borrow and lend at the risk free rate. Which of the below statements is NOT correct?