The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of the project?
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 121 |
The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of the project?
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 11 |
| 2 | 121 |
What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of the project detailed in the table below?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time. All answers are given as effective annual rates.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 121 |
If a project's net present value (NPV) is zero, then its internal rate of return (IRR) will be:
A project's NPV is positive. Select the most correct statement:
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume twice as much now (t=0) as in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end.
How much can you consume at time zero and one? The answer choices are given in the same order.
The below graph shows a project's net present value (NPV) against its annual discount rate.
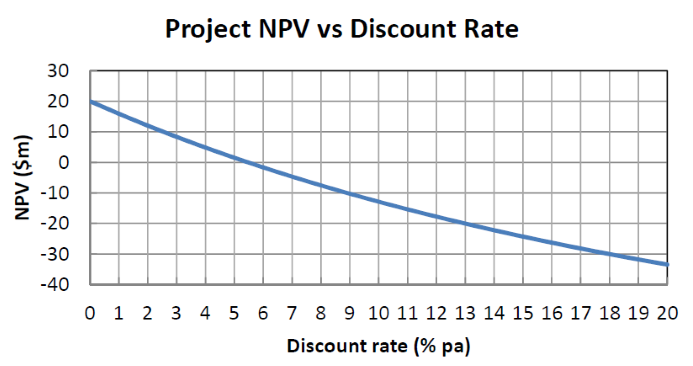
For what discount rate or range of discount rates would you accept and commence the project?
All answer choices are given as approximations from reading off the graph.
The below graph shows a project's net present value (NPV) against its annual discount rate.

Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A firm is considering a business project which costs $11m now and is expected to pay a constant $1m at the end of every year forever.
Assume that the initial $11m cost is funded using the firm's existing cash so no new equity or debt will be raised. The cost of capital is 10% pa.
Which of the following statements about net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR) and payback period is NOT correct?
A firm is considering a business project which costs $10m now and is expected to pay a single cash flow of $12.1m in two years.
Assume that the initial $10m cost is funded using the firm's existing cash so no new equity or debt will be raised. The cost of capital is 10% pa.
Which of the following statements about net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR) and payback period is NOT correct?
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume an equal amount now (t=0) and in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end (t=1).
How much can you consume at each time?
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume an equal amount now (t=0), in one year (t=1) and in two years (t=2), and still have $50,000 in the bank after that (t=2).
How much can you consume at each time?
Your neighbour asks you for a loan of $100 and offers to pay you back $120 in one year.
You don't actually have any money right now, but you can borrow and lend from the bank at a rate of 10% pa. Rates are given as effective annual rates.
Assume that your neighbour will definitely pay you back. Ignore interest tax shields and transaction costs.
The Net Present Value (NPV) of lending to your neighbour is $9.09. Describe what you would do to actually receive a $9.09 cash flow right now with zero net cash flows in the future.
An investor owns an empty block of land that has local government approval to be developed into a petrol station, car wash or car park. The council will only allow a single development so the projects are mutually exclusive.
All of the development projects have the same risk and the required return of each is 10% pa. Each project has an immediate cost and once construction is finished in one year the land and development will be sold. The table below shows the estimated costs payable now, expected sale prices in one year and the internal rates of returns (IRR's).
| Mutually Exclusive Projects | |||
| Project | Cost now ($) |
Sale price in one year ($) |
IRR (% pa) |
| Petrol station | 9,000,000 | 11,000,000 | 22.22 |
| Car wash | 800,000 | 1,100,000 | 37.50 |
| Car park | 70,000 | 110,000 | 57.14 |
Which project should the investor accept?
Question 542 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to double every 10 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
Question 543 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to triple every 5 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
An investor owns a whole level of an old office building which is currently worth $1 million. There are three mutually exclusive projects that can be started by the investor. The office building level can be:
- Rented out to a tenant for one year at $0.1m paid immediately, and then sold for $0.99m in one year.
- Refurbished into more modern commercial office rooms at a cost of $1m now, and then sold for $2.4m when the refurbishment is finished in one year.
- Converted into residential apartments at a cost of $2m now, and then sold for $3.4m when the conversion is finished in one year.
All of the development projects have the same risk so the required return of each is 10% pa. The table below shows the estimated cash flows and internal rates of returns (IRR's).
| Mutually Exclusive Projects | |||
| Project | Cash flow now ($) |
Cash flow in one year ($) |
IRR (% pa) |
| Rent then sell as is | -900,000 | 990,000 | 10 |
| Refurbishment into modern offices | -2,000,000 | 2,400,000 | 20 |
| Conversion into residential apartments | -3,000,000 | 3,400,000 | 13.33 |
Which project should the investor accept?
The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the payback period of the project in years?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are received smoothly over the year. So the $121 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 11 |
| 2 | 121 |
A project has the following cash flows:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 500 |
What is the payback period of the project in years?
Normally cash flows are assumed to happen at the given time. But here, assume that the cash flows are received smoothly over the year. So the $500 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2.
A project to build a toll road will take 3 years to complete, costing three payments of $50 million, paid at the start of each year (at times 0, 1, and 2).
After completion, the toll road will yield a constant $10 million at the end of each year forever with no costs. So the first payment will be at t=4.
The required return of the project is 10% pa given as an effective nominal rate. All cash flows are nominal.
What is the payback period?
Question 579 price gains and returns over time, time calculation, effective rate
How many years will it take for an asset's price to double if the price grows by 10% pa?
Question 580 price gains and returns over time, time calculation, effective rate
How many years will it take for an asset's price to quadruple (be four times as big, say from $1 to $4) if the price grows by 15% pa?
Katya offers to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years (t=1,2,3,4,5) if you pay her $50 now (t=0). You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. Ignore credit risk.
There are many ways to write the ordinary annuity formula.
Which of the following is NOT equal to the ordinary annuity formula?
This annuity formula ##\dfrac{C_1}{r}\left(1-\dfrac{1}{(1+r)^3} \right)## is equivalent to which of the following formulas? Note the 3.
In the below formulas, ##C_t## is a cash flow at time t. All of the cash flows are equal, but paid at different times.
The following cash flows are expected:
- 10 yearly payments of $80, with the first payment in 6.5 years from now (first payment at t=6.5).
- A single payment of $500 in 4 years and 3 months (t=4.25) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
Your friend overheard that you need some cash and asks if you would like to borrow some money. She can lend you $5,000 now (t=0), and in return she wants you to pay her back $1,000 in two years (t=2) and every year after that for the next 5 years, so there will be 6 payments of $1,000 from t=2 to t=7 inclusive.
What is the net present value (NPV) of borrowing from your friend?
Assume that banks loan funds at interest rates of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Some countries' interest rates are so low that they're zero.
If interest rates are 0% pa and are expected to stay at that level for the foreseeable future, what is the most that you would be prepared to pay a bank now if it offered to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years?
In other words, what is the present value of five $10 payments at time 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 if interest rates are 0% pa?
You are promised 20 payments of $100, where the first payment is immediate (t=0) and the last is at the end of the 19th year (t=19). The effective annual discount rate is ##r##.
Which of the following equations does NOT give the correct present value of these 20 payments?
A stock is expected to pay its next dividend of $1 in one year. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. So the first dividend of $1 will be in one year, the year after that $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1), and a year later $1.0404 (=1*(1+0.02)^2) and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
A stock just paid a dividend of $1. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. The next dividend of $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1) will be in one year, and the year after that the dividend will be $1.0404 (=1*(1+0.02)^2), and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
A stock is just about to pay a dividend of $1 tonight. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. The next dividend of $1 will be paid tonight, and the year after that the dividend will be $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1), and a year later 1.0404 (=1*(1+0.04)^2) and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
Discounted cash flow (DCF) valuation prices assets by finding the present value of the asset's future cash flows. The single cash flow, annuity, and perpetuity equations are very useful for this.
Which of the following equations is the 'perpetuity with growth' equation?
The following equation is called the Dividend Discount Model (DDM), Gordon Growth Model or the perpetuity with growth formula: ### P_0 = \frac{ C_1 }{ r - g } ###
What is ##g##? The value ##g## is the long term expected:
For a price of $13, Carla will sell you a share paying a dividend of $1 in one year and every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
The first payment of a constant perpetual annual cash flow is received at time 5. Let this cash flow be ##C_5## and the required return be ##r##.
So there will be equal annual cash flows at time 5, 6, 7 and so on forever, and all of the cash flows will be equal so ##C_5 = C_6 = C_7 = ...##
When the perpetuity formula is used to value this stream of cash flows, it will give a value (V) at time:
For a price of $1040, Camille will sell you a share which just paid a dividend of $100, and is expected to pay dividends every year forever, growing at a rate of 5% pa.
So the next dividend will be ##100(1+0.05)^1=$105.00##, and the year after it will be ##100(1+0.05)^2=110.25## and so on.
The required return of the stock is 15% pa.
The perpetuity with growth formula, also known as the dividend discount model (DDM) or Gordon growth model, is appropriate for valuing a company's shares. ##P_0## is the current share price, ##C_1## is next year's expected dividend, ##r## is the total required return and ##g## is the expected growth rate of the dividend.
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
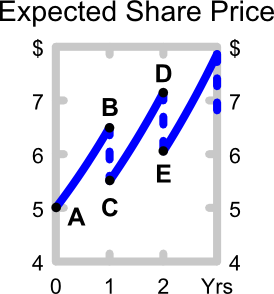
The below graph shows the expected future price path of the company's shares. Which of the following statements about the graph is NOT correct?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
###P_0=\frac{d_1}{r-g}###
A stock pays dividends annually. It just paid a dividend, but the next dividend (##d_1##) will be paid in one year.
According to the DDM, what is the correct formula for the expected price of the stock in 2.5 years?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### P_{0} = \frac{C_1}{r_{\text{eff}} - g_{\text{eff}}} ###
What would you call the expression ## C_1/P_0 ##?
A stock just paid its annual dividend of $9. The share price is $60. The required return of the stock is 10% pa as an effective annual rate.
What is the implied growth rate of the dividend per year?
Question 497 income and capital returns, DDM, ex dividend date
A stock will pay you a dividend of $10 tonight if you buy it today. Thereafter the annual dividend is expected to grow by 5% pa, so the next dividend after the $10 one tonight will be $10.50 in one year, then in two years it will be $11.025 and so on. The stock's required return is 10% pa.
What is the stock price today and what do you expect the stock price to be tomorrow, approximately?
In the dividend discount model:
###P_0 = \dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
The return ##r## is supposed to be the:
Two years ago Fred bought a house for $300,000.
Now it's worth $500,000, based on recent similar sales in the area.
Fred's residential property has an expected total return of 8% pa.
He rents his house out for $2,000 per month, paid in advance. Every 12 months he plans to increase the rental payments.
The present value of 12 months of rental payments is $23,173.86.
The future value of 12 months of rental payments one year ahead is $25,027.77.
What is the expected annual growth rate of the rental payments? In other words, by what percentage increase will Fred have to raise the monthly rent by each year to sustain the expected annual total return of 8%?
A stock pays annual dividends which are expected to continue forever. It just paid a dividend of $10. The growth rate in the dividend is 2% pa. You estimate that the stock's required return is 10% pa. Both the discount rate and growth rate are given as effective annual rates. Using the dividend discount model, what will be the share price?
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 1.15 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at 5% pa, so;
- the dividend at t=5 will be $1.15(1+0.05),
- the dividend at t=6 will be $1.15(1+0.05)^2, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates. What is the current price of the stock?
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 1.15 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at 5% pa, so;
- the dividend at t=5 will be $1.15(1+0.05),
- the dividend at t=6 will be $1.15(1+0.05)^2, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates.
What will be the price of the stock in three and a half years (t = 3.5)?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### p_0 = \frac{d_1}{r - g} ###
Which expression is NOT equal to the expected dividend yield?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
###p_0=\frac{d_1}{r_\text{eff}-g_\text{eff}}###
Which expression is NOT equal to the expected capital return?
A stock is expected to pay a dividend of $15 in one year (t=1), then $25 for 9 years after that (payments at t=2 ,3,...10), and on the 11th year (t=11) the dividend will be 2% less than at t=10, and will continue to shrink at the same rate every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10%. All rates are effective annual rates.
What is the price of the stock now?
Estimate the US bank JP Morgan's share price using a price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only:
- The major US banks JP Morgan Chase (JPM), Citi Group (C) and Wells Fargo (WFC) are comparable companies;
- JP Morgan Chase's historical earnings per share (EPS) is $4.37;
- Citi Group's share price is $50.05 and historical EPS is $4.26;
- Wells Fargo's share price is $48.98 and historical EPS is $3.89.
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 24 March 2014.
Estimate the Chinese bank ICBC's share price using a backward-looking price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only. Note that the renminbi (RMB) is the Chinese currency, also known as the yuan (CNY).
- The 4 major Chinese banks ICBC, China Construction Bank (CCB), Bank of China (BOC) and Agricultural Bank of China (ABC) are comparable companies;
- ICBC 's historical earnings per share (EPS) is RMB 0.74;
- CCB's backward-looking PE ratio is 4.59;
- BOC 's backward-looking PE ratio is 4.78;
- ABC's backward-looking PE ratio is also 4.78;
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 25 March 2014. Share prices are from the Shanghai stock exchange.
Estimate Microsoft's (MSFT) share price using a price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only:
- Apple, Google and Microsoft are comparable companies,
- Apple's (AAPL) share price is $526.24 and historical EPS is $40.32.
- Google's (GOOG) share price is $1,215.65 and historical EPS is $36.23.
- Micrsoft's (MSFT) historical earnings per share (EPS) is $2.71.
Source: Google Finance 28 Feb 2014.
Estimate the French bank Societe Generale's share price using a backward-looking price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only. Note that EUR is the euro, the European monetary union's currency.
- The 4 major European banks Credit Agricole (ACA), Deutsche Bank AG (DBK), UniCredit (UCG) and Banco Santander (SAN) are comparable companies to Societe Generale (GLE);
- Societe Generale's (GLE's) historical earnings per share (EPS) is EUR 2.92;
- ACA's backward-looking PE ratio is 16.29 and historical EPS is EUR 0.84;
- DBK's backward-looking PE ratio is 25.01 and historical EPS is EUR 1.26;
- SAN's backward-looking PE ratio is 14.71 and historical EPS is EUR 0.47;
- UCG's backward-looking PE ratio is 15.78 and historical EPS is EUR 0.40;
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 27 March 2015.
Which of the following investable assets are NOT suitable for valuation using PE multiples techniques?
Which firms tend to have low forward-looking price-earnings (PE) ratios?
Only consider firms with positive earnings, disregard firms with negative earnings and therefore negative PE ratios.
Which firms tend to have high forward-looking price-earnings (PE) ratios?
Private equity firms are known to buy medium sized private companies operating in the same industry, merge them together into a larger company, and then sell it off in a public float (initial public offering, IPO).
If medium-sized private companies trade at PE ratios of 5 and larger listed companies trade at PE ratios of 15, what return can be achieved from this strategy?
Assume that:
- The medium-sized companies can be bought, merged and sold in an IPO instantaneously.
- There are no costs of finding, valuing, merging and restructuring the medium sized companies. Also, there is no competition to buy the medium-sized companies from other private equity firms.
- The large merged firm's earnings are the sum of the medium firms' earnings.
- The only reason for the difference in medium and large firm's PE ratios is due to the illiquidity of the medium firms' shares.
- Return is defined as: ##r_{0→1} = (p_1-p_0+c_1)/p_0## , where time zero is just before the merger and time one is just after.
A low-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $1,000 and will last for 1 year before it will be scrapped for nothing.
A high-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $4,900 and it will last for 5 years before it will be scrapped for nothing.
What is the equivalent annual cost of each car? Assume a discount rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
The answer choices are given as the equivalent annual cost of the low-quality car and then the high quality car.
You're advising your superstar client 40-cent who is weighing up buying a private jet or a luxury yacht. 40-cent is just as happy with either, but he wants to go with the more cost-effective option. These are the cash flows of the two options:
- The private jet can be bought for $6m now, which will cost $12,000 per month in fuel, piloting and airport costs, payable at the end of each month. The jet will last for 12 years.
- Or the luxury yacht can be bought for $4m now, which will cost $20,000 per month in fuel, crew and berthing costs, payable at the end of each month. The yacht will last for 20 years.
What's unusual about 40-cent is that he is so famous that he will actually be able to sell his jet or yacht for the same price as it was bought since the next generation of superstar musicians will buy it from him as a status symbol.
Bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. You can assume that 40-cent will live for another 60 years and that when the jet or yacht's life is at an end, he will buy a new one with the same details as above.
Would you advise 40-cent to buy the or the ?
Note that the effective monthly rate is ##r_\text{eff monthly}=(1+0.1)^{1/12}-1=0.00797414##
Question 548 equivalent annual cash flow, time calculation, no explanation
An Apple iPhone 6 smart phone can be bought now for $999. An Android Kogan Agora 4G+ smart phone can be bought now for $240.
If the Kogan phone lasts for one year, approximately how long must the Apple phone last for to have the same equivalent annual cost?
Assume that both phones have equivalent features besides their lifetimes, that both are worthless once they've outlasted their life, the discount rate is 10% pa given as an effective annual rate, and there are no extra costs or benefits from either phone.
A home loan company advertises an interest rate of 6% pa, payable monthly. Which of the following statements about the interest rate is NOT correct? All rates are given to four decimal places.
A semi-annual coupon bond has a yield of 3% pa. Which of the following statements about the yield is NOT correct? All rates are given to four decimal places.
A credit card offers an interest rate of 18% pa, compounding monthly.
Find the effective monthly rate, effective annual rate and the effective daily rate. Assume that there are 365 days in a year.
All answers are given in the same order:
### r_\text{eff monthly} , r_\text{eff yearly} , r_\text{eff daily} ###
Calculate the effective annual rates of the following three APR's:
- A credit card offering an interest rate of 18% pa, compounding monthly.
- A bond offering a yield of 6% pa, compounding semi-annually.
- An annual dividend-paying stock offering a return of 10% pa compounding annually.
All answers are given in the same order:
##r_\text{credit card, eff yrly}##, ##r_\text{bond, eff yrly}##, ##r_\text{stock, eff yrly}##
You want to buy an apartment priced at $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $30,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $270,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 12% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments? Remember that mortgage loan payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
You want to buy an apartment worth $400,000. You have saved a deposit of $80,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $320,000 as a fully amortising mortgage loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $2,000 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 5 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change.
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $1,500 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 10 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change.
You just agreed to a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $2,500. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 10 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change. The below choices are given in the same order.
You want to buy an apartment priced at $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $30,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $270,000 as an interest only loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 12% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments? Remember that mortgage payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
You just borrowed $400,000 in the form of a 25 year interest-only mortgage with monthly payments of $3,000 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
You actually plan to pay more than the required interest payment. You plan to pay $3,300 in mortgage payments every month, which your mortgage lender allows. These extra payments will reduce the principal and the minimum interest payment required each month.
At the maturity of the mortgage, what will be the principal? That is, after the last (300th) interest payment of $3,300 in 25 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage?
You want to buy an apartment worth $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $60,000.
The bank has agreed to lend you $240,000 as an interest only mortgage loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid annually. So there's only one coupon per year, paid in arrears every year.
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid semi-annually. So there are two coupons per year, paid in arrears every six months.
"Buy low, sell high" is a phrase commonly heard in financial markets. It states that traders should try to buy assets at low prices and sell at high prices.
Traders in the fixed-coupon bond markets often quote promised bond yields rather than prices. Fixed-coupon bond traders should try to:
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same US company. Both bonds yield 10% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X and Y's coupon rates are 8 and 12% pa respectively. Which of the following statements is true?
Question 48 IRR, NPV, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds, market efficiency
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A bond maturing in 10 years has a coupon rate of 4% pa, paid semi-annually. The bond's yield is currently 6% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. What is its price?
A three year bond has a fixed coupon rate of 12% pa, paid semi-annually. The bond's yield is currently 6% pa. The face value is $100. What is its price?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at a discount?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at a premium?
A 10 year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 6% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 8% pa, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
Question 143 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds:
- A 6-month zero coupon bond at a yield of 6% pa, and
- A 12 month zero coupon bond at a yield of 7% pa.
What is the company's forward rate from 6 to 12 months? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 96 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
An Australian company just issued two bonds paying semi-annual coupons:
- 1 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the forward rate on the company's debt from years 1 to 2? Give your answer as an APR compounding every 6 months, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Your main expense is fuel for your car which costs $100 per month. You just refueled, so you won't need any more fuel for another month (first payment at t=1 month).
You have $2,500 in a bank account which pays interest at a rate of 6% pa, payable monthly. Interest rates are not expected to change.
Assuming that you have no income, in how many months time will you not have enough money to fully refuel your car?
You really want to go on a back packing trip to Europe when you finish university. Currently you have $1,500 in the bank. Bank interest rates are 8% pa, given as an APR compounding per month. If the holiday will cost $2,000, how long will it take for your bank account to reach that amount?
A credit card company advertises an interest rate of 18% pa, payable monthly. Which of the following statements about the interest rate is NOT correct? All rates are given to four decimal places.
Which of the following statements is NOT equivalent to the yield on debt?
Assume that the debt being referred to is fairly priced, but do not assume that it's priced at par.
A European company just issued two bonds, a
- 3 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 6% pa, and a
- 4 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 6.5% pa.
What is the company's forward rate over the fourth year (from t=3 to t=4)? Give your answer as an effective annual rate, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Question 573 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, expectations hypothesis, liquidity premium theory, forward interest rate, yield curve
In the below term structure of interest rates equation, all rates are effective annual yields and the numbers in subscript represent the years that the yields are measured over:
###(1+r_{0-3})^3 = (1+r_{0-1})(1+r_{1-2})(1+r_{2-3}) ###
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
For a price of $100, Vera will sell you a 2 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 10% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with similar risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 8% pa.
For a price of $95, Nicole will sell you a 10 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 8% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with the same risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 8% pa.
Bonds A and B are issued by the same company. They have the same face value, maturity, seniority and coupon payment frequency. The only difference is that bond A has a 5% coupon rate, while bond B has a 10% coupon rate. The yield curve is flat, which means that yields are expected to stay the same.
Which bond would have the higher current price?
A two year Government bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 0.5% and a fixed coupon rate of 0.5%, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
A young lady is trying to decide if she should attend university or not.
The young lady's parents say that she must attend university because otherwise all of her hard work studying and attending school during her childhood was a waste.
What's the correct way to classify this item from a capital budgeting perspective when trying to decide whether to attend university?
The hard work studying at school in her childhood should be classified as:
A young lady is trying to decide if she should attend university. Her friends say that she should go to university because she is more likely to meet a clever young man than if she begins full time work straight away.
What's the correct way to classify this item from a capital budgeting perspective when trying to find the Net Present Value of going to university rather than working?
The opportunity to meet a desirable future spouse should be classified as:
A man has taken a day off from his casual painting job to relax.
It's the end of the day and he's thinking about the hours that he could have spent working (in the past) which are now:
Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| One Year Mining Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in building mine and equipment | $9m | |
| Depreciation of mine and equipment over the year | $8m | |
| Kilograms of gold mined at end of year | 1,000 | |
| Sale price per kilogram | $0.05m | |
| Variable cost per kilogram | $0.03m | |
| Before-tax cost of closing mine at end of year | $4m | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
Note 1: Due to the project, the firm also anticipates finding some rare diamonds which will give before-tax revenues of $1m at the end of the year.
Note 2: The land that will be mined actually has thermal springs and a family of koalas that could be sold to an eco-tourist resort for an after-tax amount of $3m right now. However, if the mine goes ahead then this natural beauty will be destroyed.
Note 3: The mining equipment will have a book value of $1m at the end of the year for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $2.5m when it is sold.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero and one. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m), with the first cash flow at time zero, and the second at time one.
A stock's required total return will increase when its: