Your friend just bought a house for $1,000,000. He financed it using a $900,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $100,000.
In the context of residential housing and mortgages, the 'equity' or 'net wealth' tied up in a house is the value of the house less the value of the mortgage loan. Assuming that your friend's only asset is his house, his net wealth is $100,000.
If house prices suddenly fall by 15%, what would be your friend's percentage change in net wealth?
Assume that:
- No income (rent) was received from the house during the short time over which house prices fell.
- Your friend will not declare bankruptcy, he will always pay off his debts.
One year ago you bought $100,000 of shares partly funded using a margin loan. The margin loan size was $70,000 and the other $30,000 was your own wealth or 'equity' in the share assets.
The interest rate on the margin loan was 7.84% pa.
Over the year, the shares produced a dividend yield of 4% pa and a capital gain of 5% pa.
What was the total return on your wealth? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and dividends) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates above are effective annual rates.
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
Question 408 leverage, portfolio beta, portfolio risk, real estate, CAPM
You just bought a house worth $1,000,000. You financed it with an $800,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $200,000.
You estimate that:
- The house has a beta of 1;
- The mortgage loan has a beta of 0.2.
What is the beta of the equity (the $200,000 deposit) that you have in your house?
Also, if the risk free rate is 5% pa and the market portfolio's return is 10% pa, what is the expected return on equity in your house? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and rent) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates are effective annual rates.
Question 800 leverage, portfolio return, risk, portfolio risk, capital structure, no explanation
Which of the following assets would you expect to have the highest required rate of return? All values are current market values.
Jan asks you for a loan. He wants $100 now and offers to pay you back $120 in 1 year. You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Ignore credit risk. Remember:
### V_0 = \frac{V_t}{(1+r_\text{eff})^t} ###
What proportion of managers are evaluating projects correctly, based on table 8 from Meier and Tarhan's (2006) survey of corporate managers?
| Table 8: Consistency of nominal or real hurdle rates and cash flows | |||
| Hurdle rate | Cash flows | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal | Real | ||
| Nominal | 29.8% | 11.6% | 41.3% |
| Real | 19.8% | 38.4% | 58.7% |
| Total | 49.6% | 50.4% | 100.0% |
Table 8 footnote: The rows in this cross-tabulation show whether the firm uses a nominal or real hurdle rate, the columns indicate whether cash flows are calculated in nominal or real terms. The fractions denote the number of firms for each combination relative to the total of 123 respondents that responded to both separate survey questions.
What proportion of managers are evaluating projects correctly?
Question 1013 book build, initial public offering, capital raising, demand schedule
A firm is floating its stock in an IPO and its underwriter has received the following bids, listed in order from highest to lowest share price:
| IPO Book Build Bids | ||
| Bidders | Share price | Number of shares |
| $/share | millions | |
| BidderA | 2.5 | 2 |
| BidderB | 2 | 1.5 |
| BidderC | 1.5 | 4 |
| BidderD | 1 | 3 |
| BidderE | 0.5 | 2 |
Suppose that the firm's owner wishes to sell all of their 8 million shares, so no new money will be raised and no money will re-invested back into the firm. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 1014 book build, initial public offering, capital raising, demand schedule
A firm is floating its stock in an IPO and its underwriter has received the following bids, listed in order from highest to lowest share price:
| IPO Book Build Bids | ||
| Bidders | Share price | Number of shares |
| $/share | millions | |
| BidderA | 2.5 | 2 |
| BidderB | 2 | 1.5 |
| BidderC | 1.5 | 4 |
| BidderD | 1 | 3 |
| BidderE | 0.5 | 2 |
Suppose that the firm's owner wishes to raise $6 million to expand the business by selling new stock in the initial public offering (IPO). The owner currently holds 8 million stock which are not for sale. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 278 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Imagine that the interest rate on your savings account was 1% per year and inflation was 2% per year.
Question 992 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
You currently have $100 in the bank which pays a 10% pa interest rate.
Oranges currently cost $1 each at the shop and inflation is 5% pa which is the expected growth rate in the orange price.
This information is summarised in the table below, with some parts missing that correspond to the answer options. All rates are given as effective annual rates. Note that when payments are not specified as real, as in this question, they're conventionally assumed to be nominal.
| Wealth in Dollars and Oranges | ||||
| Time (year) | Bank account wealth ($) | Orange price ($) | Wealth in oranges | |
| 0 | 100 | 1 | 100 | |
| 1 | 110 | 1.05 | (a) | |
| 2 | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? Your:
Question 295 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, NPV
When valuing assets using discounted cash flow (net present value) methods, it is important to consider inflation. To properly deal with inflation:
(I) Discount nominal cash flows by nominal discount rates.
(II) Discount nominal cash flows by real discount rates.
(III) Discount real cash flows by nominal discount rates.
(IV) Discount real cash flows by real discount rates.
Which of the above statements is or are correct?
Question 353 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 6% pa and nominal capital return of 3% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns? The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Question 526 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, no explanation
How can a nominal cash flow be precisely converted into a real cash flow?
Question 1022 inflation linked bond, breakeven inflation rate, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Below is a graph of 10-year US treasury fixed coupon bond yields (red), inflation-indexed bond yields (green) and the 'breakeven' inflation rate (blue). Note that inflation-indexed bonds are also called treasury inflation protected securities (TIPS) in the US. In other countries they're called inflation-linked bonds (ILB's). For more information, see PIMCO's great article about inflation linked bonds here.
The 10 year breakeven inflation rate (blue) equals the:
PIMCO gives the following example of an Inflation Linked Bond (ILB), called Treasury Inflation Protected Securities (TIPS) in the US.
How do ILBs work?
An ILB’s explicit link to a nationally-recognized inflation measure means that any increase in price levels directly translates into higher principal values. As a hypothetical example, consider a $1,000 20-year U.S. TIPS with a 2.5% coupon (1.25% on semiannual basis), and an inflation rate of 4%. The principal on the TIPS note will adjust upward on a daily basis to account for the 4% inflation rate. At maturity, the principal value will be $2,208 (4% per year, compounded semiannually). Additionally, while the coupon rate remains fixed at 2.5%, the dollar value of each interest payment will rise, as the coupon will be paid on the inflation-adjusted principal value. The first semiannual coupon of 1.25% paid on the inflation-adjusted principal of $1,020 is $12.75, while the final semiannual interest payment will be 1.25% of $2,208, which is $27.60.
Forecast the semi-annual coupon paid in 10 years based on the bond details given above. The 20th semi-annual coupon, paid in 10 years, is expected to be:
Estimate the US bank JP Morgan's share price using a price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only:
- The major US banks JP Morgan Chase (JPM), Citi Group (C) and Wells Fargo (WFC) are comparable companies;
- JP Morgan Chase's historical earnings per share (EPS) is $4.37;
- Citi Group's share price is $50.05 and historical EPS is $4.26;
- Wells Fargo's share price is $48.98 and historical EPS is $3.89.
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 24 March 2014.
Private equity firms are known to buy medium sized private companies operating in the same industry, merge them together into a larger company, and then sell it off in a public float (initial public offering, IPO).
If medium-sized private companies trade at PE ratios of 5 and larger listed companies trade at PE ratios of 15, what return can be achieved from this strategy?
Assume that:
- The medium-sized companies can be bought, merged and sold in an IPO instantaneously.
- There are no costs of finding, valuing, merging and restructuring the medium sized companies. Also, there is no competition to buy the medium-sized companies from other private equity firms.
- The large merged firm's earnings are the sum of the medium firms' earnings.
- The only reason for the difference in medium and large firm's PE ratios is due to the illiquidity of the medium firms' shares.
- Return is defined as: ##r_{0→1} = (p_1-p_0+c_1)/p_0## , where time zero is just before the merger and time one is just after.
A new company's Firm Free Cash Flow (FFCF, same as CFFA) is forecast in the graph below.
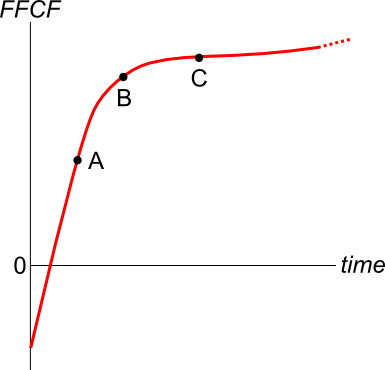
To value the firm's assets, the terminal value needs to be calculated using the perpetuity with growth formula:
###V_{\text{terminal, }t-1} = \dfrac{FFCF_{\text{terminal, }t}}{r-g}###
Which point corresponds to the best time to calculate the terminal value?
A new company's Firm Free Cash Flow (FFCF, same as CFFA) is forecast in the graph below.
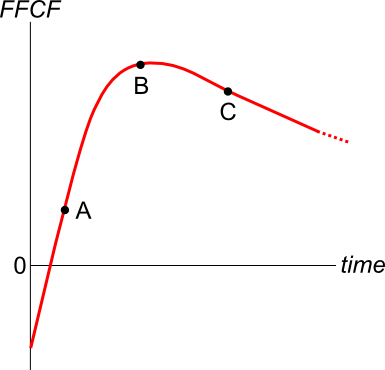
To value the firm's assets, the terminal value needs to be calculated using the perpetuity with growth formula:
###V_{\text{terminal, }t-1} = \dfrac{FFCF_{\text{terminal, }t}}{r-g}###
Which point corresponds to the best time to calculate the terminal value?
Use the below information to value a levered company with constant annual perpetual cash flows from assets. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now, so a perpetuity can be used to value this firm. Both the operating and firm free cash flows are constant (but not equal to each other).
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}## | $100m | Operating free cash flow |
| ##\text{FFCF or CFFA}## | $112m | Firm free cash flow or cash flow from assets (includes interest tax shields) |
| ##g## | 0% pa | Growth rate of OFCF and FFCF |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{BeforeTax}## | 7% pa | Weighted average cost of capital before tax |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{AfterTax}## | 6.25% pa | Weighted average cost of capital after tax |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 5% pa | Cost of debt |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 9% pa | Cost of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 50% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
What is the value of the levered firm including interest tax shields?
Investment bank Canaccord's Think Childcare (TNK) initiation of coverage states: "What's the Differentiator? TNK are operators, not consolidators - Other listed childcare companies have led highly successful consolidation strategies involving multiple arbitrage combined with scale benefits and operating efficiencies. TNK’s focus is on operating the centres to the best of their individual potentials..." (Canaccord, 2016). Multiples arbitrage involves:
Read these quotes from Adir Shiffman's 26 July 2021 article in the AFR 'Roll up, roll up and make a mint off Amazon sellers'.
"Amazon sellers outsource their warehousing and logistics to the tech giant in a model known as “fulfilled by Amazon”, or FBA. Joining FBA provides access to one of the world’s largest global warehousing operations and even a fleet of Boeing 747 cargo jets. Just as significantly, FBA sellers can much more easily qualify for Amazon’s Prime program, which guarantees free and fast shipping to members."
"Companies want to acquire and integrate a selection, or in business parlance, do a 'roll-up'."
"More than 100 companies are now racing to roll-up FBA sellers, and almost all have launched since 2017. At least a dozen of these boast war chests of more than $US100 million. The largest, Thrasio, was founded in 2018 and has raised more than $US1.7 billion. Thrasio targets businesses with high quality and differentiated products that generate $US1 to $US100 million in revenue annually" (Shiffman, 2021).
If Thrasio's total funds available to spend on the roll up is $1.7 billion, and it's buying targets at price-to-revenue multiples of 2, what's the largest number of firms with $50 million of annual revenue that it could buy?
Below is a table showing GMO's 2016 estimates of different assets' durations, appearing in Slater (2017).
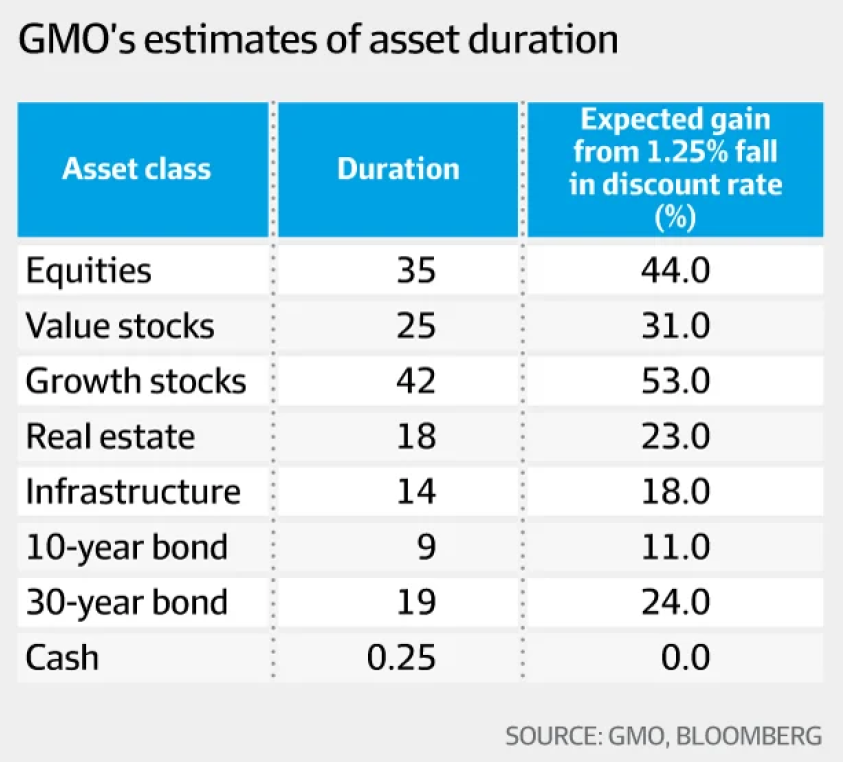
If you were certain that interest rates would fall more than the market expects, into what asset might you allocate more funds?
A stock has a beta of 0.5. Its next dividend is expected to be $3, paid one year from now. Dividends are expected to be paid annually and grow by 2% pa forever. Treasury bonds yield 3% pa and the market risk premium (MRP) is 6% pa. All returns are effective annual rates.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 852 gross domestic product, inflation, employment, no explanation
When the economy is booming (in an upswing), you tend to see:
Question 1039 gross domestic product, inflation, business cycle
In this business cycle graph shown in the RBA's article explaining recessions, how might 'output' on the y-axis be measured?
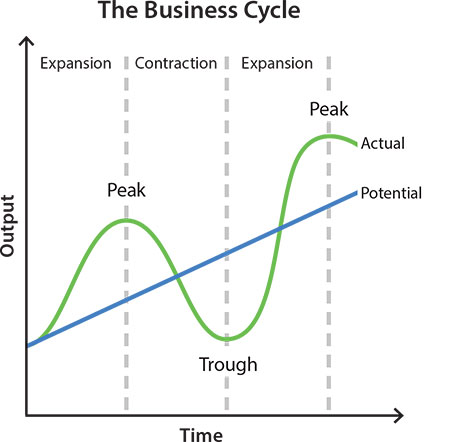
The ‘output’ y-axis amount in the business cycle chart can be measured by:
Question 566 capital structure, capital raising, rights issue, on market repurchase, dividend, stock split, bonus issue
A company's share price fell by 20% and its number of shares rose by 25%. Assume that there are no taxes, no signalling effects and no transaction costs.
Which one of the following corporate events may have happened?
A firm wishes to raise $50 million now. They will issue 7% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 6 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 5% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
A levered firm has only 2 assets on its balance sheet with the below market values and CAPM betas. The risk free rate is 3% pa and the market risk premium is 5% pa. Assume that the CAPM is correct and all assets are fairly priced.
| Balance Sheet Market Values and Betas | ||
| Balance sheet item | Market value ($m) | Beta |
| Cash asset | 0.5 | 0 |
| Truck assets | 0.5 | 2 |
| Loan liabilities | 0.25 | 0.1 |
| Equity funding | ? | ? |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 993 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
In February 2020, the RBA cash rate was 0.75% pa and the Australian CPI inflation rate was 1.8% pa.
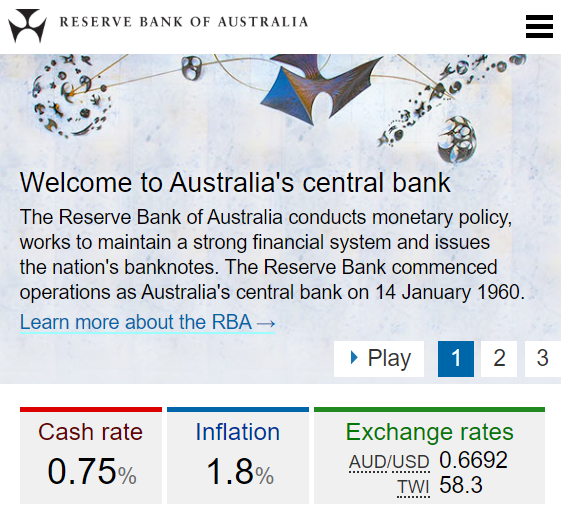
You currently have $100 in the bank which pays a 0.75% pa interest rate.
Apples currently cost $1 each at the shop and inflation is 1.8% pa which is the expected growth rate in the apple price.
This information is summarised in the table below, with some parts missing that correspond to the answer options. All rates are given as effective annual rates. Note that when payments are not specified as real, as in this question, they're conventionally assumed to be nominal.
| Wealth in Dollars and Apples | ||||
| Time (year) | Bank account wealth ($) | Apple price ($) | Wealth in apples | |
| 0 | 100 | 1 | 100 | |
| 1 | 100.75 | 1.018 | (a) | |
| 2 | (b) | (c) | (d) | |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? Your:
Question 575 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
You expect a nominal payment of $100 in 5 years. The real discount rate is 10% pa and the inflation rate is 3% pa. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 1023 monetary policy, inflation, breakeven inflation rate
If the breakeven inflation rate was far above the US Fed's long term 2% average inflation target, the Fed would be expected to:
An analyst is valuing a levered company whose owners insist on keeping the dollar amount of debt funding fixed. So the company cannot issue or repay its debt, its dollar value must remain constant. Any funding gaps will be met with equity.
The analyst is wondering, as he changes inputs into his valuation, such as the forecast growth rate of sales, then asset values and other things will change. This makes it hard to figure out which values can be held constant and would therefore make good model inputs, rather than outputs which vary depending on the inputs. Assume that the cost of debt (yield) remains constant and the company’s asset beta will also remain constant since any expansion (or downsize) will involve buying (or selling) more of the same assets.
Which of the following values can be assumed to stay constant when projected sales growth increases?
Question 905 market capitalisation of equity, PE ratio, payout ratio
The below graph shows the computer software company Microsoft's stock price (MSFT) at the market close on the NASDAQ on Friday 1 June 2018.
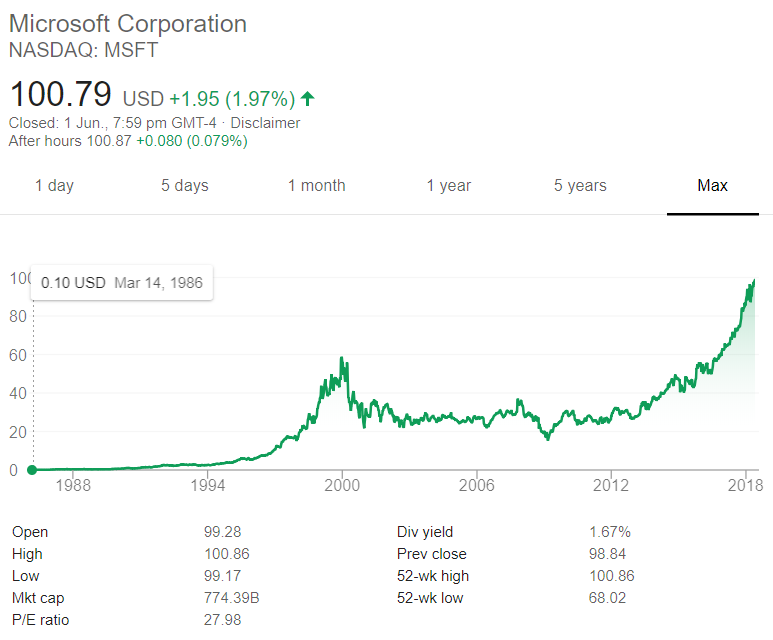
Based on the screenshot above, which of the following statements about MSFT is NOT correct? MSFT's:
Question 1045 payout policy, leverage, capital structure, beta
A levered firm has only 2 assets on its balance sheet with the below market values and CAPM betas. The risk free rate is 3% pa and the market risk premium is 5% pa. Assume that the CAPM is correct and all assets are fairly priced.
| Balance Sheet Market Values and Betas | ||
| Balance sheet item | Market value ($m) | Beta |
| Cash asset | 0.5 | 0 |
| Truck assets | 0.5 | 2 |
| Loan liabilities | 0.25 | 0.1 |
| Equity funding | ? | ? |
The firm then pays out all of its cash as a dividend. Assume that the beta and yield on the loan liability remain unchanged. Ignore taxes, transaction costs, signalling, information asymmetries and other frictions.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? This event led to a:
A levered firm has only 2 assets on its balance sheet with the below market values and CAPM betas. The risk free rate is 3% pa and the market risk premium is 5% pa. Assume that the CAPM is correct and all assets are fairly priced.
| Balance Sheet Market Values and Betas | ||
| Balance sheet item | Market value ($m) | Beta |
| Cash asset | 0.5 | 0 |
| Truck assets | 0.5 | 2 |
| Loan liabilities | 0.25 | 0.1 |
| Equity funding | ? | ? |
The firm then pays off (retires) all of its loan liabilities using its cash. Ignore interest tax shields.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? All answers are given to 6 decimal places. This event led to a:
Question 25 bond pricing, zero coupon bond, term structure of interest rates, forward interest rate
A European company just issued two bonds, a
- 2 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 8% pa, and a
- 3 year zero coupon bond at a yield of 10% pa.
What is the company's forward rate over the third year (from t=2 to t=3)? Give your answer as an effective annual rate, which is how the above bond yields are quoted.
Fundamentalists who analyse company financial reports and news announcements (but who don't have inside information) will make positive abnormal returns if:
Katya offers to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years (t=1,2,3,4,5) if you pay her $50 now (t=0). You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. Ignore credit risk.
Question 237 WACC, Miller and Modigliani, interest tax shield
Which of the following discount rates should be the highest for a levered company? Ignore the costs of financial distress.
Former RBA Governor Phil Lowe says that when the RBA raise interest rates, homeowners' mortgage loan interest expense will be:
Question 1020 Federal funds rate, monetary policy, dot plot
US Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell showed the 'dot plot' of Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) members' estimated future Fed fund rates following their quarterly summary of economic projections on 15 Dec 2021. The dot plot shows that committee members intended to make monetary policy more:
In the dividend discount model:
### P_0= \frac{d_1}{r-g} ###
The pronumeral ##g## is supposed to be the:
You believe that the price of a share will fall significantly very soon, but the rest of the market does not. The market thinks that the share price will remain the same. Assuming that your prediction will soon be true, which of the following trades is a bad idea? In other words, which trade will NOT make money or prevent losses?
A man just sold a call option to his counterparty, a lady. The man has just now:
A European call option will mature in ##T## years with a strike price of ##K## dollars. The underlying asset has a price of ##S## dollars.
What is an expression for the payoff at maturity ##(f_T)## in dollars from owning (being long) the call option?
A company runs a number of slaughterhouses which supply hamburger meat to McDonalds. The company is afraid that live cattle prices will increase over the next year, even though there is widespread belief in the market that they will be stable. What can the company do to hedge against the risk of increasing live cattle prices? Which statement(s) are correct?
(i) buy call options on live cattle.
(ii) buy put options on live cattle.
(iii) sell call options on live cattle.
Select the most correct response:
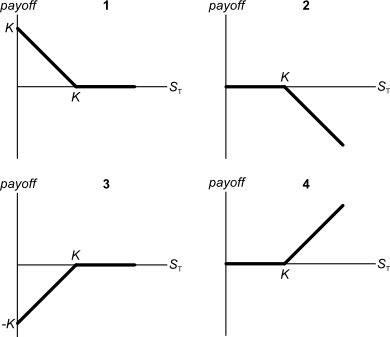
Below are 4 option graphs. Note that the y-axis is payoff at maturity (T). What options do they depict? List them in the order that they are numbered.
Question 363 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 8% pa and nominal capital return of 3% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns? The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Former RBA Governor Phil Lowe says that if the economy is growing very strongly, then prices might be growing too:
A stock has a beta of 1.2. Its next dividend is expected to be $20, paid one year from now.
Dividends are expected to be paid annually and grow by 1.5% pa forever.
Treasury bonds yield 3% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 7% pa. All returns are effective annual rates.
What is the price of the stock now?
A company increases the proportion of debt funding it uses to finance its assets by issuing bonds and using the cash to repurchase stock, leaving assets unchanged.
Ignoring the costs of financial distress, which of the following statements is NOT correct:
A firm has a debt-to-equity ratio of 60%. What is its debt-to-assets ratio?
Question 536 idiom, bond pricing, capital structure, leverage
The expression 'my word is my bond' is often used in everyday language to make a serious promise.
Why do you think this expression uses the metaphor of a bond rather than a share?
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 20%. What is its debt-to-equity ratio?
Find the Macaulay duration of a 2 year 5% pa semi-annual fixed coupon bond which has a $100 face value and currently has a yield to maturity of 8% pa. The Macaulay duration is:
A method commonly seen in textbooks for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is the following:
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp)(1-t_c) + \\ &\space\space\space+ Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp(1-t_c) \\ \end{aligned}###
One formula for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to use earnings before interest and tax (EBIT).
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (EBIT)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ \end{aligned} \\###
Question 987 interest tax shield, capital structure, debt terminology
What creates interest tax shields for a company?
Question 121 capital structure, leverage, financial distress, interest tax shield
Fill in the missing words in the following sentence:
All things remaining equal, as a firm's amount of debt funding falls, benefits of interest tax shields __________ and the costs of financial distress __________.
Which form of production is included in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) reported by the government statistics agency?
Question 850 gross domestic product, gross domestic product per capita
Below is a table showing some countries’ GDP, population and GDP per capita.
| Countries' GDP and Population | |||
| GDP | Population | GDP per capita | |
| USD million | millions of people | USD | |
| United States | 18,036,648 | 325 | 55,492 |
| China | 11,158,457 | 1,383 | 8,066 |
| Japan | 4,383,076 | 127 | 34,586 |
| Germany | 3,363,600 | 83 | 40,623 |
| Norway | 500,519 | 5 | 95,027 |
Source: "GDP and its breakdown at current prices in US Dollars" United Nations Statistics Division. December 2016.
Using this data only, which one of these countries’ citizens have the highest living standards?
A European call option will mature in ##T## years with a strike price of ##K## dollars. The underlying asset has a price of ##S## dollars.
What is an expression for the payoff at maturity ##(f_T)## in dollars from having written (being short) the call option?
A European put option will mature in ##T## years with a strike price of ##K## dollars. The underlying asset has a price of ##S## dollars.
What is an expression for the payoff at maturity ##(f_T)## in dollars from having written (being short) the put option?
Question 432 option, option intrinsic value, no explanation
An American style call option with a strike price of ##K## dollars will mature in ##T## years. The underlying asset has a price of ##S## dollars.
What is an expression for the current intrinsic value in dollars from owning (being long) the American style call option? Note that the intrinsic value of an option does not subtract the premium paid to buy the option.
Which of the following statements about option contracts is NOT correct? For every:
If trader A has sold the right that allows counterparty B to buy the underlying asset from him at maturity if counterparty B wants then trader A is:
After doing extensive fundamental analysis of a company, you believe that their shares are overpriced and will soon fall significantly. The market believes that there will be no such fall.
Which of the following strategies is NOT a good idea, assuming that your prediction is true?
Question 636 option, option payoff at maturity, no explanation
Which of the below formulas gives the payoff ##(f)## at maturity ##(T)## from being long a call option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T## and the exercise price be ##X_T##.
Question 639 option, option payoff at maturity, no explanation
Which of the below formulas gives the payoff ##(f)## at maturity ##(T)## from being short a put option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T## and the exercise price be ##X_T##.
Which one of the below option and futures contracts gives the possibility of potentially unlimited gains?
A trader buys one crude oil European style call option contract on the CME expiring in one year with an exercise price of $44 per barrel for a price of $6.64. The crude oil spot price is $40.33. If the trader doesn’t close out her contract before maturity, then at maturity she will have the:
Which of the below formulas gives the profit ##(\pi)## from being long a call option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T##, the exercise price be ##X_T## and the option price be ##f_{LC,0}##. Note that ##S_T##, ##X_T## and ##f_{LC,0}## are all positive numbers.
Which of the below formulas gives the profit ##(\pi)## from being short a call option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T##, the exercise price be ##X_T## and the option price be ##f_{LC,0}##. Note that ##S_T##, ##X_T## and ##f_{LC,0}## are all positive numbers.
Which of the below formulas gives the profit ##(\pi)## from being long a put option? Let the underlying asset price at maturity be ##S_T##, the exercise price be ##X_T## and the option price be ##f_{LP,0}##. Note that ##S_T##, ##X_T## and ##f_{LP,0}## are all positive numbers.
A trader buys one crude oil European style put option contract on the CME expiring in one year with an exercise price of $44 per barrel for a price of $6.64. The crude oil spot price is $40.33. If the trader doesn’t close out her contract before maturity, then at maturity she will have the:
Which of the following statements about call options is NOT correct?
A trader just bought a European style put option on CBA stock. The current option premium is $2, the exercise price is $75, the option matures in one year and the spot CBA stock price is $74.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 271 CAPM, option, risk, systematic risk, systematic and idiosyncratic risk
All things remaining equal, according to the capital asset pricing model, if the systematic variance of an asset increases, its required return will increase and its price will decrease.
If the idiosyncratic variance of an asset increases, its price will be unchanged.
What is the relationship between the price of a call or put option and the total, systematic and idiosyncratic variance of the underlying asset that the option is based on? Select the most correct answer.
Call and put option prices increase when the:
Acquirer firm plans to launch a takeover of Target firm. The deal is expected to create a present value of synergies totaling $105 million. A 40% scrip and 60% cash offer will be made that pays the fair price for the target's shares plus 75% of the total synergy value. The cash will be paid out of the firm's cash holdings, no new debt or equity will be raised.
| Firms Involved in the Takeover | ||
| Acquirer | Target | |
| Assets ($m) | 6,000 | 700 |
| Debt ($m) | 4,800 | 400 |
| Share price ($) | 40 | 20 |
| Number of shares (m) | 30 | 15 |
Ignore transaction costs and fees. Assume that the firms' debt and equity are fairly priced, and that each firms' debts' risk, yield and values remain constant. The acquisition is planned to occur immediately, so ignore the time value of money.
Calculate the merged firm's share price and total number of shares after the takeover has been completed.
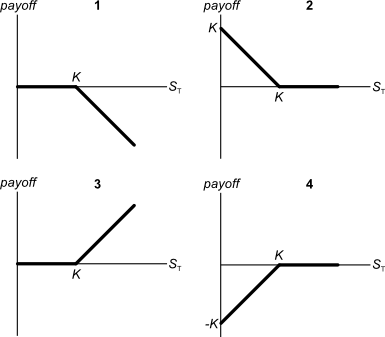
Below are 4 option graphs. Note that the y-axis is payoff at maturity (T). What options do they depict? List them in the order that they are numbered
Suppose you had $100 in a savings account and the interest rate was 2% per year.
After 5 years, how much do you think you would have in the account if you left the money to grow?
A one year European-style call option has a strike price of $4. The option's underlying stock pays no dividends and currently trades at $5. The risk-free interest rate is 10% pa continuously compounded. Use a single step binomial tree to calculate the option price, assuming that the price could rise to $8 ##(u = 1.6)## or fall to $3.125 ##(d = 1/1.6)## in one year. The call option price now is:
Question 794 option, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing, option delta, no explanation
Which of the following quantities from the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing formula gives the Delta of a European call option?
Where:
###d_1=\dfrac{\ln[S_0/K]+(r+\sigma^2/2).T)}{\sigma.\sqrt{T}}### ###d_2=d_1-\sigma.\sqrt{T}=\dfrac{\ln[S_0/K]+(r-\sigma^2/2).T)}{\sigma.\sqrt{T}}###Question 795 option, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing, option delta, no explanation
Which of the following quantities from the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing formula gives the Delta of a European put option?
Question 796 option, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing, option delta, no explanation
Which of the following quantities from the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing formula gives the risk-neutral probability that a European call option will be exercised?
Question 797 option, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing, option delta, no explanation
Which of the following quantities from the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing formula gives the risk-neutral probability that a European put option will be exercised?
Question 382 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
In the Merton model of corporate debt, buying a levered company's shares is equivalent to:
Question 385 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
A risky firm will last for one period only (t=0 to 1), then it will be liquidated. So it's assets will be sold and the debt holders and equity holders will be paid out in that order. The firm has the following quantities:
##V## = Market value of assets.
##E## = Market value of (levered) equity.
##D## = Market value of zero coupon bonds.
##F_1## = Total face value of zero coupon bonds which is promised to be paid in one year.

The levered equity graph above contains bold labels a to e. Which of the following statements about those labels is NOT correct?
Question 397 financial distress, leverage, capital structure, NPV
A levered firm has a market value of assets of $10m. Its debt is all comprised of zero-coupon bonds which mature in one year and have a combined face value of $9.9m.
Investors are risk-neutral and therefore all debt and equity holders demand the same required return of 10% pa.
Therefore the current market capitalisation of debt ##(D_0)## is $9m and equity ##(E_0)## is $1m.
A new project presents itself which requires an investment of $2m and will provide a:
- $6.6m cash flow with probability 0.5 in the good state of the world, and a
- -$4.4m (notice the negative sign) cash flow with probability 0.5 in the bad state of the world.
The project can be funded using the company's excess cash, no debt or equity raisings are required.
What would be the new market capitalisation of equity ##(E_\text{0, with project})## if shareholders vote to proceed with the project, and therefore should shareholders proceed with the project?
Question 398 financial distress, capital raising, leverage, capital structure, NPV
A levered firm has zero-coupon bonds which mature in one year and have a combined face value of $9.9m.
Investors are risk-neutral and therefore all debt and equity holders demand the same required return of 10% pa.
In one year the firm's assets will be worth:
- $13.2m with probability 0.5 in the good state of the world, or
- $6.6m with probability 0.5 in the bad state of the world.
A new project presents itself which requires an investment of $2m and will provide a certain cash flow of $3.3m in one year.
The firm doesn't have any excess cash to make the initial $2m investment, but the funds can be raised from shareholders through a fairly priced rights issue. Ignore all transaction costs.
Should shareholders vote to proceed with the project and equity raising? What will be the gain in shareholder wealth if they decide to proceed?
Question 383 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
In the Merton model of corporate debt, buying a levered company's debt is equivalent to buying the company's assets and:
You're thinking of starting a new cafe business, but you're not sure if it will be profitable.
You have to decide what type of cups, mugs and glasses you wish to buy. You can pay to have your cafe's name printed on them, or just buy the plain un-marked ones. For marketing reasons it's better to have the cafe name printed. But the plain un-marked cups, mugs and glasses maximise your:
Acquirer firm plans to launch a takeover of Target firm. The deal is expected to create a present value of synergies totaling $105 million. A cash offer will be made that pays the fair price for the target's shares plus 75% of the total synergy value. The cash will be paid out of the firm's cash holdings, no new debt or equity will be raised.
| Firms Involved in the Takeover | ||
| Acquirer | Target | |
| Assets ($m) | 6,000 | 700 |
| Debt ($m) | 4,800 | 400 |
| Share price ($) | 40 | 20 |
| Number of shares (m) | 30 | 15 |
Ignore transaction costs and fees. Assume that the firms' debt and equity are fairly priced, and that each firms' debts' risk, yield and values remain constant. The acquisition is planned to occur immediately, so ignore the time value of money.
Calculate the merged firm's share price and total number of shares after the takeover has been completed.