An Apple (NASDAQ:AAPL) stock was purchased by an investor for $120 and one year later was sold for $150. A dividend of $4 was also collected at the end of the year just before the stock was sold.
Which of the following statements about the stock investment is NOT correct? Ignore taxes.
Over the year, the investor made a:
.
Question 525 income and capital returns, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation
Which of the following statements about cash in the form of notes and coins is NOT correct? Assume that inflation is positive.
Notes and coins:
The perpetuity with growth formula, also known as the dividend discount model (DDM) or Gordon growth model, is appropriate for valuing a company's shares. ##P_0## is the current share price, ##C_1## is next year's expected dividend, ##r## is the total required return and ##g## is the expected growth rate of the dividend.
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
The below graph shows the expected future price path of the company's shares. Which of the following statements about the graph is NOT correct?
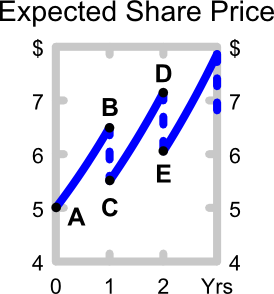
The following equation is called the Dividend Discount Model (DDM), Gordon Growth Model or the perpetuity with growth formula: ### P_0 = \frac{ C_1 }{ r - g } ###
What is ##g##? The value ##g## is the long term expected:
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### P_{0} = \frac{C_1}{r_{\text{eff}} - g_{\text{eff}}} ###
What would you call the expression ## C_1/P_0 ##?
The following is the Dividend Discount Model (DDM) used to price stocks:
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
If the assumptions of the DDM hold and the stock is fairly priced, which one of the following statements is NOT correct? The long term expected:
In these tough economic times, central banks around the world have cut interest rates so low that they are practically zero. In some countries, government bond yields are also very close to zero.
A three year government bond with a face value of $100 and a coupon rate of 2% pa paid semi-annually was just issued at a yield of 0%. What is the price of the bond?
Question 56 income and capital returns, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds
Which of the following statements about risk free government bonds is NOT correct?
Hint: Total return can be broken into income and capital returns as follows:
###\begin{aligned} r_\text{total} &= \frac{c_1}{p_0} + \frac{p_1-p_0}{p_0} \\ &= r_\text{income} + r_\text{capital} \end{aligned} ###
The capital return is the growth rate of the price.
The income return is the periodic cash flow. For a bond this is the coupon payment.
Which of the following is NOT the Australian central bank’s responsibility?
Question 1021 Federal funds rate, monetary policy, quantitative easing, tapering
US Fed Chair Jerome Powell held a news conference following the 25-26 January 2022 FOMC meeting.
Nick Timiraos reporting for The Wall Street Journal asked: "Raising rates and reducing the balance sheet both restrain the economy, both tighten monetary policy. How should we think about the relationship between the two? For example, how much passive runoff is equal to every quarter percentage point increase in your benchmark rate?"
Jerome Powell replied: "So, again, we think of the balance sheet as moving in a predictable manner, sort of in the background, and that the active tool meeting to meeting is not -- both of them, it's the federal funds rate. There are rules of thumbs. I'm reluctant to land on one of them that equate this. And there's also an element of uncertainty around the balance sheet. I think we have a much better sense, frankly, of how rate increases affect financial conditions and, hence, economic conditions. Balance sheet is still a relatively new thing for the markets and for us, so we're less certain about that." (US Fed, 2022)
When Nick Timiraos mentioned 'reducing the balance sheet', he's referring to:
Question 295 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, NPV
When valuing assets using discounted cash flow (net present value) methods, it is important to consider inflation. To properly deal with inflation:
(I) Discount nominal cash flows by nominal discount rates.
(II) Discount nominal cash flows by real discount rates.
(III) Discount real cash flows by nominal discount rates.
(IV) Discount real cash flows by real discount rates.
Which of the above statements is or are correct?
Question 353 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 6% pa and nominal capital return of 3% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns? The answer choices below are given in the same order.
In the 'Austin Powers' series of movies, the character Dr. Evil threatens to destroy the world unless the United Nations pays him a ransom (video 1, video 2). Dr. Evil makes the threat on two separate occasions:
- In 1969 he demands a ransom of $1 million (=10^6), and again;
- In 1997 he demands a ransom of $100 billion (=10^11).
If Dr. Evil's demands are equivalent in real terms, in other words $1 million will buy the same basket of goods in 1969 as $100 billion would in 1997, what was the implied inflation rate over the 28 years from 1969 to 1997?
The answer choices below are given as effective annual rates:
Question 575 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
You expect a nominal payment of $100 in 5 years. The real discount rate is 10% pa and the inflation rate is 3% pa. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 578 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Which of the following statements about inflation is NOT correct?
Question 664 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, no explanation
What is the present value of real payments of $100 every year forever, with the first payment in one year? The nominal discount rate is 7% pa and the inflation rate is 4% pa.
Question 728 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, income and capital returns, no explanation
Which of the following statements about gold is NOT correct? Assume that the gold price increases by inflation. Gold has a:
Question 740 real and nominal returns and cash flows, DDM, inflation
Taking inflation into account when using the DDM can be hard. Which of the following formulas will NOT give a company's current stock price ##(P_0)##? Assume that the annual dividend was just paid ##(C_0)##, and the next dividend will be paid in one year ##(C_1)##.
When someone says that they're "buying American dollars" (USD), what type of asset are they probably buying? They're probably buying:
Question 626 cross currency interest rate parity, foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate
The Australian cash rate is expected to be 2% pa over the next one year, while the Japanese cash rate is expected to be 0% pa, both given as nominal effective annual rates. The current exchange rate is 100 JPY per AUD.
What is the implied 1 year forward foreign exchange rate?
Question 246 foreign exchange rate, forward foreign exchange rate, cross currency interest rate parity
Suppose the Australian cash rate is expected to be 8.15% pa and the US federal funds rate is expected to be 3.00% pa over the next 2 years, both given as nominal effective annual rates. The current exchange rate is at parity, so 1 USD = 1 AUD.
What is the implied 2 year forward foreign exchange rate?
The Chinese government attempts to fix its exchange rate against the US dollar and at the same time use monetary policy to fix its interest rate at a set level.
To be able to fix its exchange rate and interest rate in this way, what does the Chinese government actually do?
- Adopts capital controls to prevent financial arbitrage by private firms and individuals.
- Adopts the same interest rate (monetary policy) as the United States.
- Fixes inflation so that the domestic real interest rate is equal to the United States' real interest rate.
Which of the above statements is or are true?
Question 606 foreign exchange rate, American and European terms
Which of the following FX quotes (current in October 2015) is given in American terms?
You're considering making an investment in a particular company. They have preference shares, ordinary shares, senior debt and junior debt.
Which is the safest investment? Which has the highest expected returns?
A newly floated farming company is financed with senior bonds, junior bonds, cumulative non-voting preferred stock and common stock. The new company has no retained profits and due to floods it was unable to record any revenues this year, leading to a loss. The firm is not bankrupt yet since it still has substantial contributed equity (same as paid-up capital).
On which securities must it pay interest or dividend payments in this terrible financial year?
Question 531 bankruptcy or insolvency, capital structure, risk, limited liability
Who is most in danger of being personally bankrupt? Assume that all of their businesses' assets are highly liquid and can therefore be sold immediately.
Which one of the following businesses is likely to be a public company in Australia, judging by its name?
Question 771 debt terminology, interest expense, interest tax shield, credit risk, no explanation
You deposit money into a bank account. Which of the following statements about this deposit is NOT correct?
The following steps outline the process of ‘negative gearing’ an investment property in Australia. Which of these steps or statements is NOT correct? To successfully achieve negative gearing on an investment property:
Question 802 negative gearing, leverage, capital structure, no explanation
Which of the following statements about ‘negative gearing’ is NOT correct?
Question 990 Multiples valuation, EV to EBITDA ratio, enterprise value
A firm has:
2 million shares;
$200 million EBITDA expected over the next year;
$100 million in cash (not included in EV);
1/3 market debt-to-assets ratio is (market assets = EV + cash);
4% pa expected dividend yield over the next year, paid annually with the next dividend expected in one year;
2% pa expected dividend growth rate;
40% expected payout ratio over the next year;10 times EV/EBITDA ratio.
30% corporate tax rate.
The stock can be valued using the EV/EBITDA multiple, dividend discount model, Gordon growth model or PE multiple. Which of the below statements is NOT correct based on an EV/EBITDA multiple valuation?
Use the below information to value a mature levered company with growing annual perpetual cash flows and a constant debt-to-assets ratio. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now, so a perpetuity can be used to value this firm. The firm's debt funding comprises annual fixed coupon bonds that all have the same seniority and coupon rate. When these bonds mature, new bonds will be re-issued, and so on in perpetuity. The yield curve is flat.
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}_1## | $12.5m | Operating free cash flow at time 1 |
| ##\text{FFCF}_1 \text{ or }\text{CFFA}_1## | $14m | Firm free cash flow or cash flow from assets at time 1 |
| ##\text{EFCF}_1## | $11m | Equity free cash flow at time 1 |
| ##\text{BondCoupons}_1## | $1.2m | Bond coupons paid to debt holders at time 1 |
| ##g## | 2% pa | Growth rate of OFCF, FFCF, EFCF and Debt cash flow |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{BeforeTax}## | 9% pa | Weighted average cost of capital before tax |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{AfterTax}## | 8.25% pa | Weighted average cost of capital after tax |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 5% pa | Bond yield |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 13% pa | Cost or required return of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 50% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##n_\text{shares}## | 1m | Number of shares |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
There are many ways to calculate a firm's free cash flow (FFCF), also called cash flow from assets (CFFA). Some include the annual interest tax shield in the cash flow and some do not.
Which of the below FFCF formulas include the interest tax shield in the cash flow?
###(1) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp### ###(2) \quad FFCF=NI + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC + IntExp.(1-t_c)### ###(3) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c )+ Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(4) \quad FFCF=EBIT.(1-t_c) + Depr- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(5) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC+IntExp.t_c### ###(6) \quad FFCF=EBITDA.(1-t_c )+Depr.t_c- CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(7) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(8) \quad FFCF=EBIT-Tax + Depr - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c### ###(9) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC### ###(10) \quad FFCF=EBITDA-Tax - CapEx -ΔNWC-IntExp.t_c###The formulas for net income (NI also called earnings), EBIT and EBITDA are given below. Assume that depreciation and amortisation are both represented by 'Depr' and that 'FC' represents fixed costs such as rent.
###NI=(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###EBIT=Rev - COGS - FC-Depr### ###EBITDA=Rev - COGS - FC### ###Tax =(Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp).t_c= \dfrac{NI.t_c}{1-t_c}###Question 657 systematic and idiosyncratic risk, CAPM, no explanation
A stock's required total return will decrease when its:
Question 809 Markowitz portfolio theory, CAPM, Jensens alpha, CML, systematic and idiosyncratic risk
A graph of assets’ expected returns ##(\mu)## versus standard deviations ##(\sigma)## is given in the graph below. The CML is the capital market line.
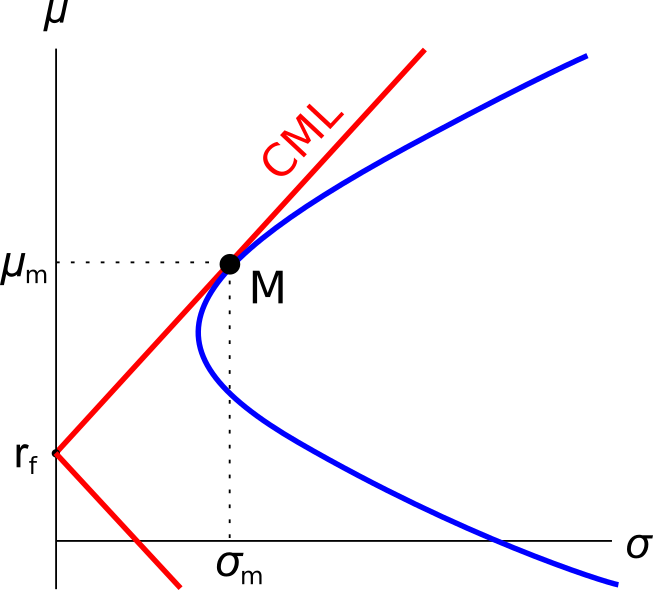
Which of the following statements about this graph, Markowitz portfolio theory and the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) theory is NOT correct?
Four retail business people compete in the same city. They are all exactly the same except that they have different ways of funding or leasing the shop real estate needed to run their retail business.
The two main assets that retail stores need are:
- Inventory typically worth $1 million which has a beta of 2, and;
- Shopfront real estate worth $1 million which has a beta of 1. Shops can be bought or leased.
Lease contract prices are fixed for the term of the lease and based on expectations of the future state of the economy. When leases end, a new lease contract is negotiated and the lease cost may be higher or lower depending on the state of the economy and demand and supply if the economy is:
- Booming, shop real estate is worth more and lease costs are higher.
- In recession, shop real estate is worth less and lease costs are low.
Which retail business person will have the LOWEST beta of equity (or net wealth)?
A levered firm has only 2 assets on its balance sheet with the below market values and CAPM betas. The risk free rate is 3% pa and the market risk premium is 5% pa. Assume that the CAPM is correct and all assets are fairly priced.
| Balance Sheet Market Values and Betas | ||
| Balance sheet item | Market value ($m) | Beta |
| Cash asset | 0.5 | 0 |
| Truck assets | 0.5 | 2 |
| Loan liabilities | 0.25 | 0.1 |
| Equity funding | ? | ? |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 1045 payout policy, leverage, capital structure, beta
A levered firm has only 2 assets on its balance sheet with the below market values and CAPM betas. The risk free rate is 3% pa and the market risk premium is 5% pa. Assume that the CAPM is correct and all assets are fairly priced.
| Balance Sheet Market Values and Betas | ||
| Balance sheet item | Market value ($m) | Beta |
| Cash asset | 0.5 | 0 |
| Truck assets | 0.5 | 2 |
| Loan liabilities | 0.25 | 0.1 |
| Equity funding | ? | ? |
The firm then pays out all of its cash as a dividend. Assume that the beta and yield on the loan liability remain unchanged. Ignore taxes, transaction costs, signalling, information asymmetries and other frictions.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? This event led to a:
The famous investor Warren Buffett is one of few portfolio managers who appears to have consistently beaten the market. His company Berkshire Hathaway (BRK) appears to have outperformed the US S&P500 market index, shown in the graph below.
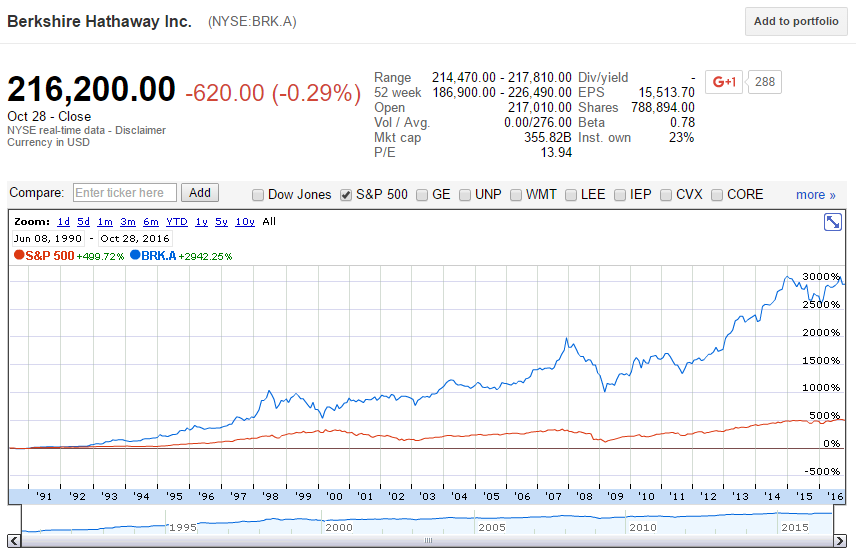
Read the below statements about Warren Buffett and the implications for the Efficient Markets Hypothesis (EMH) theory of Eugene Fama. Assume that the first sentence is true. Analyse the second sentence and select the answer option which is NOT correct. In other words, find the false statement in the second sentence.
Select the most correct statement from the following.
'Chartists', also known as 'technical traders', believe that:
A managed fund charges fees based on the amount of money that you keep with them. The fee is 2% of the end-of-year amount, paid at the end of every year.
This fee is charged regardless of whether the fund makes gains or losses on your money.
The fund offers to invest your money in shares which have an expected return of 10% pa before fees.
You are thinking of investing $100,000 in the fund and keeping it there for 40 years when you plan to retire.
How much money do you expect to have in the fund in 40 years? Also, what is the future value of the fees that the fund expects to earn from you? Give both amounts as future values in 40 years. Assume that:
- The fund has no private information.
- Markets are weak and semi-strong form efficient.
- The fund's transaction costs are negligible.
- The cost and trouble of investing your money in shares by yourself, without the managed fund, is negligible.
- The fund invests its fees in the same companies as it invests your funds in, but with no fees.
The below answer choices list your expected wealth in 40 years, and then the fund's expected wealth in 40 years.
A company advertises an investment costing $1,000 which they say is underpriced. They say that it has an expected total return of 15% pa, but a required return of only 10% pa. Assume that there are no dividend payments so the entire 15% total return is all capital return.
Assuming that the company's statements are correct, what is the NPV of buying the investment if the 15% return lasts for the next 100 years (t=0 to 100), then reverts to 10% pa after that time? Also, what is the NPV of the investment if the 15% return lasts forever?
In both cases, assume that the required return of 10% remains constant. All returns are given as effective annual rates.
The answer choices below are given in the same order (15% for 100 years, and 15% forever):
A company advertises an investment costing $1,000 which they say is underpriced. They say that it has an expected total return of 15% pa, but a required return of only 10% pa. Of the 15% pa total expected return, the dividend yield is expected to always be 7% pa and rest is the capital yield.
Assuming that the company's statements are correct, what is the NPV of buying the investment if the 15% total return lasts for the next 100 years (t=0 to 100), then reverts to 10% after that time? Also, what is the NPV of the investment if the 15% return lasts forever?
In both cases, assume that the required return of 10% remains constant, the dividends can only be re-invested at 10% pa and all returns are given as effective annual rates.
The answer choices below are given in the same order (15% for 100 years, and 15% forever):
Question 780 mispriced asset, NPV, DDM, market efficiency, no explanation
A company advertises an investment costing $1,000 which they say is under priced. They say that it has an expected total return of 15% pa, but a required return of only 10% pa. Of the 15% pa total expected return, the dividend yield is expected to be 4% pa and the capital yield 11% pa. Assume that the company's statements are correct.
What is the NPV of buying the investment if the 15% total return lasts for the next 100 years (t=0 to 100), then reverts to 10% after that time? Also, what is the NPV of the investment if the 15% return lasts forever?
In both cases, assume that the required return of 10% remains constant, the dividends can only be re-invested at 10% pa and all returns are given as effective annual rates. The answer choices below are given in the same order (15% for 100 years, and 15% forever):
Question 338 market efficiency, CAPM, opportunity cost, technical analysis
A man inherits $500,000 worth of shares.
He believes that by learning the secrets of trading, keeping up with the financial news and doing complex trend analysis with charts that he can quit his job and become a self-employed day trader in the equities markets.
What is the expected gain from doing this over the first year? Measure the net gain in wealth received at the end of this first year due to the decision to become a day trader. Assume the following:
- He earns $60,000 pa in his current job, paid in a lump sum at the end of each year.
- He enjoys examining share price graphs and day trading just as much as he enjoys his current job.
- Stock markets are weak form and semi-strong form efficient.
- He has no inside information.
- He makes 1 trade every day and there are 250 trading days in the year. Trading costs are $20 per trade. His broker invoices him for the trading costs at the end of the year.
- The shares that he currently owns and the shares that he intends to trade have the same level of systematic risk as the market portfolio.
- The market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa.
Measure the net gain over the first year as an expected wealth increase at the end of the year.
A managed fund charges fees based on the amount of money that you keep with them. The fee is 2% of the start-of-year amount, but it is paid at the end of every year.
This fee is charged regardless of whether the fund makes gains or losses on your money.
The fund offers to invest your money in shares which have an expected return of 10% pa before fees.
You are thinking of investing $100,000 in the fund and keeping it there for 40 years when you plan to retire.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of investing your money in the fund? Note that the question is not asking how much money you will have in 40 years, it is asking: what is the NPV of investing in the fund? Assume that:
- The fund has no private information.
- Markets are weak and semi-strong form efficient.
- The fund's transaction costs are negligible.
- The cost and trouble of investing your money in shares by yourself, without the managed fund, is negligible.
Question 1029 Buffett ratio
Tesla CEO Elon Musk asked a question to ARK Invest CEO Cathie Wood on 6 April 2021: "What do you think of the unusually high ratio of the S&P market cap to GDP?", to which Cathie Wood replied.
What are the units of this S&P500 market cap to GDP ratio, commonly known as the Buffett ratio?
Question 1035 Minsky financial instability hypothesis, leverage
Which of the following statements about 'The Financial Instability Hypothesis' (Minsky, 1992) is NOT correct? Borrowers with sufficient income to pay:
Question 918 duration, Macaulay duration, modified duration, bond convexity
A fixed coupon bond’s modified duration is 10 years, and yields are currently 5% pa compounded annually. Which of the following statements about the bond is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements about vanilla floating coupon bonds paying quarterly coupons is NOT correct? A vanilla floating coupon bond's:
Question 1009 lemons problem, asymmetric information, adverse selection
Akerlof’s 1970 paper ‘The Market for "Lemons": Quality Uncertainty and the Market Mechanism’ provides a famous example of asymmetric information leading to market failure. This example is commonly known as the ‘Lemons Problem’. Imagine that half of all second hand cars are:
- Lemons worth $5,000 each. Lemons are bad second-hand cars with hidden faults that only the seller knows about; and the other half are
- Plums worth $10,000 each. Plums are good second-hand cars without faults.
Car buyers can’t tell the difference between lemon and plum cars.
Car sellers know whether their car is a lemon or a plum since they’ve driven the car for a long time. However, plum car owners cannot prove their cars’ higher quality to buyers. Also, lemon car owners are known to dis-honestly claim that their cars are plums.
What will be the market price of second hand cars?
In general, stock prices tend to rise. What does this mean for futures on equity?
Which of the following statements about futures contracts on shares is NOT correct, assuming that markets are efficient?
When an equity future is first negotiated (at t=0):
The current gold price is $700, gold storage costs are 2% pa and the risk free rate is 10% pa, both with continuous compounding.
What should be the 3 year gold futures price?
A European call option will mature in ##T## years with a strike price of ##K## dollars. The underlying asset has a price of ##S## dollars.
What is an expression for the payoff at maturity ##(f_T)## in dollars from having written (being short) the call option?
Which one of the below option and futures contracts gives the possibility of potentially unlimited gains?
A trader just bought a European style put option on CBA stock. The current option premium is $2, the exercise price is $75, the option matures in one year and the spot CBA stock price is $74.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
You operate a cattle farm that supplies hamburger meat to the big fast food chains. You buy a lot of grain to feed your cattle, and you sell the fully grown cattle on the livestock market.
You're afraid of adverse movements in grain and livestock prices. What options should you buy to hedge your exposures in the grain and cattle livestock markets?
Select the most correct response:
Question 903 option, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing, option on stock index
A six month European-style call option on the S&P500 stock index has a strike price of 2800 points.
The underlying S&P500 stock index currently trades at 2700 points, has a continuously compounded dividend yield of 2% pa and a standard deviation of continuously compounded returns of 25% pa.
The risk-free interest rate is 5% pa continuously compounded.
Use the Black-Scholes-Merton formula to calculate the option price. The call option price now is:
Question 795 option, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing, option delta, no explanation
Which of the following quantities from the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing formula gives the Delta of a European put option?
Question 797 option, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing, option delta, no explanation
Which of the following quantities from the Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing formula gives the risk-neutral probability that a European put option will be exercised?
Question 793 option, hedging, delta hedging, gamma hedging, gamma, Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing
A bank buys 1000 European put options on a $10 non-dividend paying stock at a strike of $12. The bank wishes to hedge this exposure. The bank can trade the underlying stocks and European call options with a strike price of 7 on the same stock with the same maturity. Details of the call and put options are given in the table below. Each call and put option is on a single stock.
| European Options on a Non-dividend Paying Stock | |||
| Description | Symbol | Put Values | Call Values |
| Spot price ($) | ##S_0## | 10 | 10 |
| Strike price ($) | ##K_T## | 12 | 7 |
| Risk free cont. comp. rate (pa) | ##r## | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Standard deviation of the stock's cont. comp. returns (pa) | ##\sigma## | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Option maturity (years) | ##T## | 1 | 1 |
| Option price ($) | ##p_0## or ##c_0## | 2.495350486 | 3.601466138 |
| ##N[d_1]## | ##\partial c/\partial S## | 0.888138405 | |
| ##N[d_2]## | ##N[d_2]## | 0.792946442 | |
| ##-N[-d_1]## | ##\partial p/\partial S## | -0.552034778 | |
| ##N[-d_2]## | ##N[-d_2]## | 0.207053558 | |
| Gamma | ##\Gamma = \partial^2 c/\partial S^2## or ##\partial^2 p/\partial S^2## | 0.098885989 | 0.047577422 |
| Theta | ##\Theta = \partial c/\partial T## or ##\partial p/\partial T## | 0.348152078 | 0.672379961 |
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 386 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
A risky firm will last for one period only (t=0 to 1), then it will be liquidated. So it's assets will be sold and the debt holders and equity holders will be paid out in that order. The firm has the following quantities:
##V## = Market value of assets.
##E## = Market value of (levered) equity.
##D## = Market value of zero coupon bonds.
##F_1## = Total face value of zero coupon bonds which is promised to be paid in one year.

The risky corporate debt graph above contains bold labels a to e. Which of the following statements about those labels is NOT correct?
Question 433 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option, no explanation
A risky firm will last for one period only (t=0 to 1), then it will be liquidated. So it's assets will be sold and the debt holders and equity holders will be paid out in that order. The firm has the following quantities:
##V## = Market value of assets.
##E## = Market value of (levered) equity.
##D## = Market value of zero coupon bonds.
##F_1## = Total face value of zero coupon bonds which is promised to be paid in one year.
What is the payoff to equity holders at maturity, assuming that they keep their shares until maturity?
Question 434 Merton model of corporate debt, real option, option
A risky firm will last for one period only (t=0 to 1), then it will be liquidated. So it's assets will be sold and the debt holders and equity holders will be paid out in that order. The firm has the following quantities:
##V## = Market value of assets.
##E## = Market value of (levered) equity.
##D## = Market value of zero coupon bonds.
##F_1## = Total face value of zero coupon bonds which is promised to be paid in one year.
What is the payoff to debt holders at maturity, assuming that they keep their debt until maturity?
Question 381 Merton model of corporate debt, option, real option
In the Merton model of corporate debt, buying a levered company's debt is equivalent to buying risk free government bonds and:
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions. Which of the statements about the 3 utility functions is NOT correct?
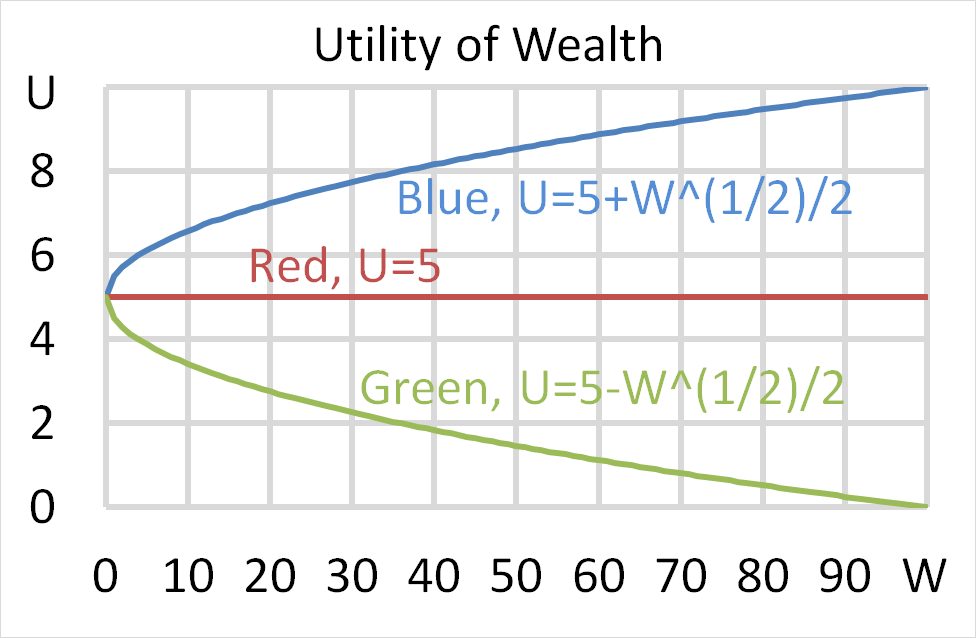
Question 699 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
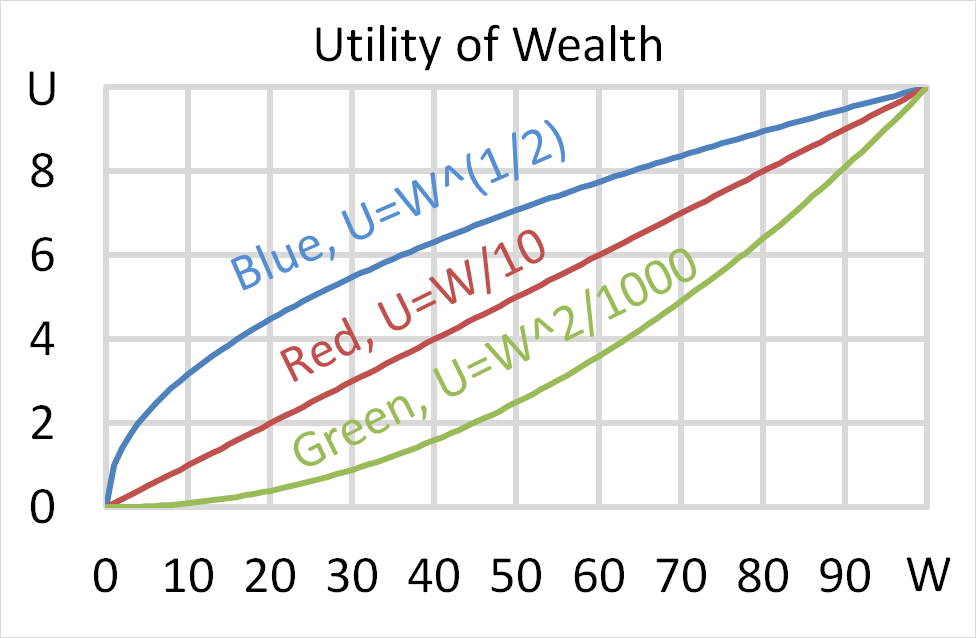
Question 704 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $256 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $256. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $256. If they flip tails then they will lose $256. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
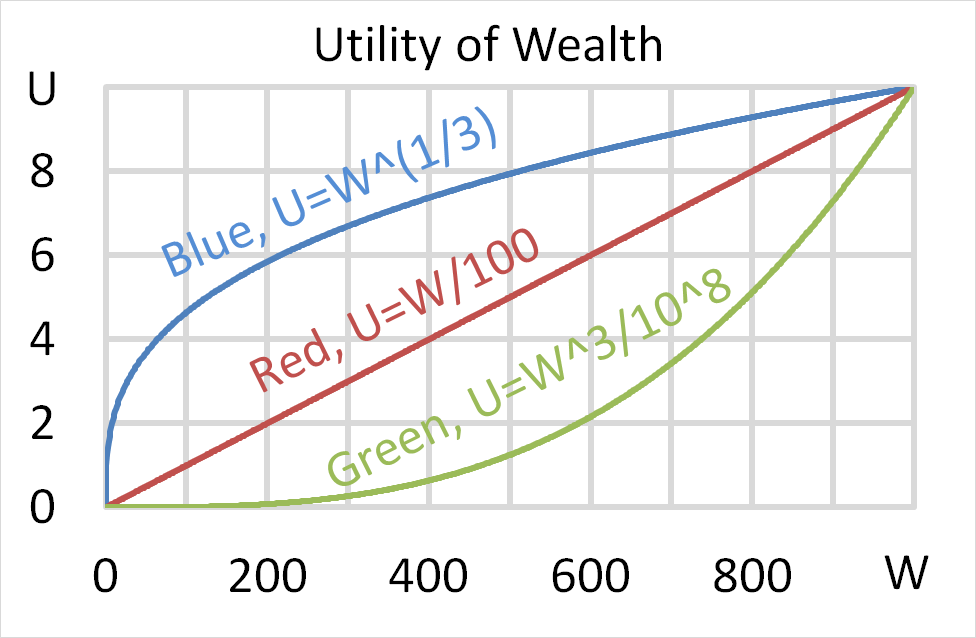
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
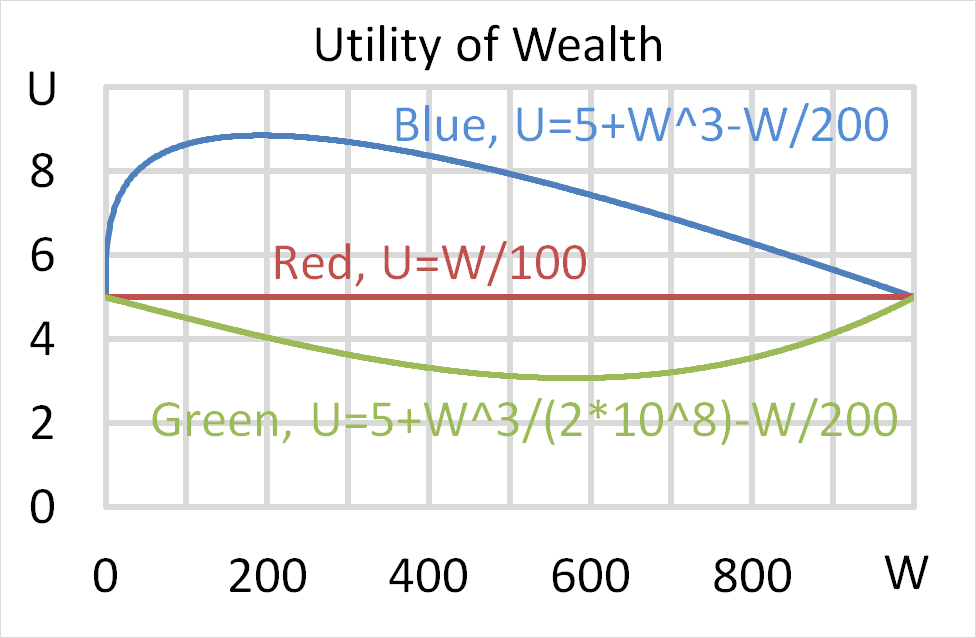
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Note that a fair gamble is a bet that has an expected value of zero, such as paying $0.50 to win $1 in a coin flip with heads or nothing if it lands tails. Fairly priced insurance is when the expected present value of the insurance premiums is equal to the expected loss from the disaster that the insurance protects against, such as the cost of rebuilding a home after a catastrophic fire.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?

Below is a graph of 3 peoples’ utility functions, Mr Blue (U=W^(1/2) ), Miss Red (U=W/10) and Mrs Green (U=W^2/1000). Assume that each of them currently have $50 of wealth.

Which of the following statements about them is NOT correct?
(a) Mr Blue would prefer to invest his wealth in a well diversified portfolio of stocks rather than a single stock, assuming that all stocks had the same total risk and return.
Question 707 continuously compounding rate, continuously compounding rate conversion
Convert a 10% effective annual rate ##(r_\text{eff annual})## into a continuously compounded annual rate ##(r_\text{cc annual})##. The equivalent continuously compounded annual rate is:
Question 710 continuously compounding rate, continuously compounding rate conversion
A continuously compounded monthly return of 1% ##(r_\text{cc monthly})## is equivalent to a continuously compounded annual return ##(r_\text{cc annual})## of:
The below three graphs show probability density functions (PDF) of three different random variables Red, Green and Blue. Let ##P_1## be the unknown price of a stock in one year. ##P_1## is a random variable. Let ##P_0 = 1##, so the share price now is $1. This one dollar is a constant, it is not a variable.
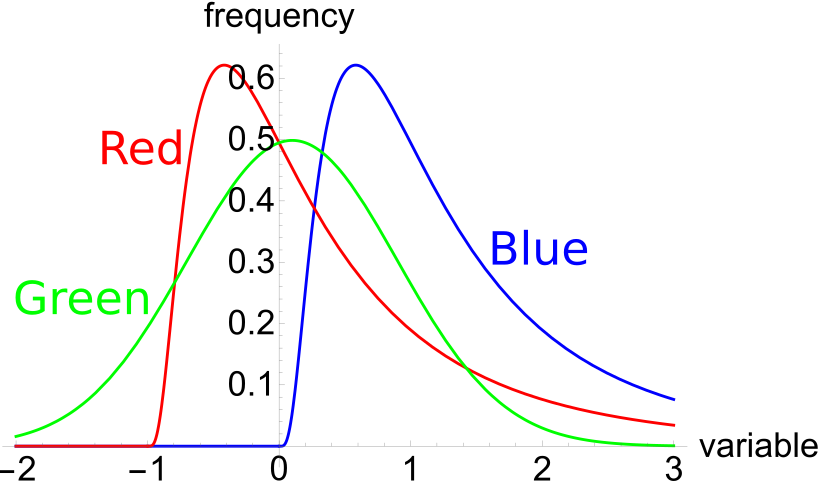
Which of the below statements is NOT correct? Financial practitioners commonly assume that the shape of the PDF represented in the colour:
Question 811 log-normal distribution, mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages
Which of the following statements about probability distributions is NOT correct?
Question 722 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
Here is a table of stock prices and returns. Which of the statements below the table is NOT correct?
| Price and Return Population Statistics | ||||
| Time | Prices | LGDR | GDR | NDR |
| 0 | 100 | |||
| 1 | 50 | -0.6931 | 0.5 | -0.5 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.6931 | 2 | 1 |
| Arithmetic average | 0 | 1.25 | 0.25 | |
| Arithmetic standard deviation | 0.9802 | 1.0607 | 1.0607 | |
Question 720 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
A stock has an arithmetic average continuously compounded return (AALGDR) of 10% pa, a standard deviation of continuously compounded returns (SDLGDR) of 80% pa and current stock price of $1. Assume that stock prices are log-normally distributed.
In 5 years, what do you expect the median and mean prices to be? The answer options are given in the same order.
Question 723 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
Here is a table of stock prices and returns. Which of the statements below the table is NOT correct?
| Price and Return Population Statistics | ||||
| Time | Prices | LGDR | GDR | NDR |
| 0 | 100 | |||
| 1 | 99 | -0.010050 | 0.990000 | -0.010000 |
| 2 | 180.40 | 0.600057 | 1.822222 | 0.822222 |
| 3 | 112.73 | 0.470181 | 0.624889 | 0.375111 |
| Arithmetic average | 0.0399 | 1.1457 | 0.1457 | |
| Arithmetic standard deviation | 0.4384 | 0.5011 | 0.5011 | |
Question 792 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate, log-normal distribution, confidence interval
A risk manager has identified that their investment fund’s continuously compounded portfolio returns are normally distributed with a mean of 10% pa and a standard deviation of 40% pa. The fund’s portfolio is currently valued at $1 million. Assume that there is no estimation error in the above figures. To simplify your calculations, all answers below use 2.33 as an approximation for the normal inverse cumulative density function at 99%. All answers are rounded to the nearest dollar. Assume one month is 1/12 of a year. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 877 arithmetic and geometric averages, utility, utility function
Gross discrete returns in different states of the world are presented in the table below. A gross discrete return is defined as ##P_1/P_0##, where ##P_0## is the price now and ##P_1## is the expected price in the future. An investor can purchase only a single asset, A, B, C or D. Assume that a portfolio of assets is not possible.
| Gross Discrete Returns | ||
| In Different States of the World | ||
| Investment | World states (probability) | |
| asset | Good (50%) | Bad (50%) |
| A | 2 | 0.5 |
| B | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| C | 1.1 | 0.95 |
| D | 1.01 | 1.01 |
Which of the following statements about the different assets is NOT correct? Asset:
Question 925 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate, no explanation
The arithmetic average and standard deviation of returns on the ASX200 accumulation index over the 24 years from 31 Dec 1992 to 31 Dec 2016 were calculated as follows:
###\bar{r}_\text{yearly} = \dfrac{ \displaystyle\sum\limits_{t=1992}^{24}{\left( \ln \left( \dfrac{P_{t+1}}{P_t} \right) \right)} }{T} = \text{AALGDR} =0.0949=9.49\% \text{ pa}###
###\sigma_\text{yearly} = \dfrac{ \displaystyle\sum\limits_{t=1992}^{24}{\left( \left( \ln \left( \dfrac{P_{t+1}}{P_t} \right) - \bar{r}_\text{yearly} \right)^2 \right)} }{T} = \text{SDLGDR} = 0.1692=16.92\text{ pp pa}###
Assume that the log gross discrete returns are normally distributed and that the above estimates are true population statistics, not sample statistics, so there is no standard error in the sample mean or standard deviation estimates. Also assume that the standardised normal Z-statistic corresponding to a one-tail probability of 2.5% is exactly -1.96.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? If you invested $1m today in the ASX200, then over the next 4 years:
Question 926 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
The arithmetic average continuously compounded or log gross discrete return (AALGDR) on the ASX200 accumulation index over the 24 years from 31 Dec 1992 to 31 Dec 2016 is 9.49% pa.
The arithmetic standard deviation (SDLGDR) is 16.92 percentage points pa.
Assume that the log gross discrete returns are normally distributed and that the above estimates are true population statistics, not sample statistics, so there is no standard error in the sample mean or standard deviation estimates. Also assume that the standardised normal Z-statistic corresponding to a one-tail probability of 2.5% is exactly -1.96.
If you had a $1 million fund that replicated the ASX200 accumulation index, in how many years would the median dollar value of your fund first be expected to lie outside the 95% confidence interval forecast?
Question 927 mean and median returns, mode return, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
The arithmetic average continuously compounded or log gross discrete return (AALGDR) on the ASX200 accumulation index over the 24 years from 31 Dec 1992 to 31 Dec 2016 is 9.49% pa.
The arithmetic standard deviation (SDLGDR) is 16.92 percentage points pa.
Assume that the log gross discrete returns are normally distributed and that the above estimates are true population statistics, not sample statistics, so there is no standard error in the sample mean or standard deviation estimates. Also assume that the standardised normal Z-statistic corresponding to a one-tail probability of 2.5% is exactly -1.96.
If you had a $1 million fund that replicated the ASX200 accumulation index, in how many years would the mean dollar value of your fund first be expected to lie outside the 95% confidence interval forecast?
Question 928 mean and median returns, mode return, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate, no explanation
The arithmetic average continuously compounded or log gross discrete return (AALGDR) on the ASX200 accumulation index over the 24 years from 31 Dec 1992 to 31 Dec 2016 is 9.49% pa.
The arithmetic standard deviation (SDLGDR) is 16.92 percentage points pa.
Assume that the log gross discrete returns are normally distributed and that the above estimates are true population statistics, not sample statistics, so there is no standard error in the sample mean or standard deviation estimates. Also assume that the standardised normal Z-statistic corresponding to a one-tail probability of 2.5% is exactly -1.96.
If you had a $1 million fund that replicated the ASX200 accumulation index, in how many years would the mode dollar value of your fund first be expected to lie outside the 95% confidence interval forecast?
Note that the mode of a log-normally distributed future price is: ##P_{T \text{ mode}} = P_0.e^{(\text{AALGDR} - \text{SDLGDR}^2 ).T} ##