What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of the project detailed in the table below?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time. All answers are given as effective annual rates.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 121 |
If a project's net present value (NPV) is zero, then its internal rate of return (IRR) will be:
The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the payback period of the project in years?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are received smoothly over the year. So the $121 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 11 |
| 2 | 121 |
A project has the following cash flows:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 500 |
What is the payback period of the project in years?
Normally cash flows are assumed to happen at the given time. But here, assume that the cash flows are received smoothly over the year. So the $500 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2.
The below graph shows a project's net present value (NPV) against its annual discount rate.
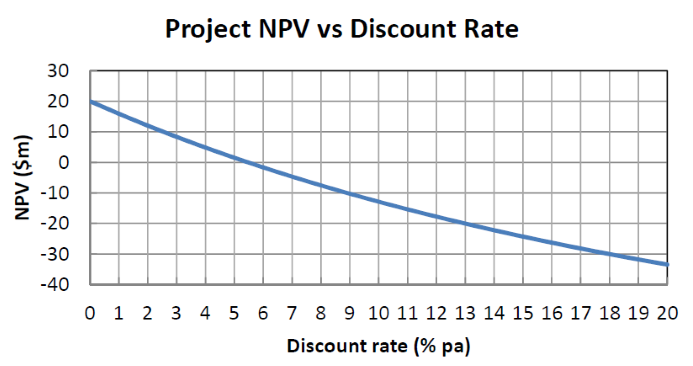
For what discount rate or range of discount rates would you accept and commence the project?
All answer choices are given as approximations from reading off the graph.
The below graph shows a project's net present value (NPV) against its annual discount rate.

Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume an equal amount now (t=0) and in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end (t=1).
How much can you consume at each time?
An investor owns a whole level of an old office building which is currently worth $1 million. There are three mutually exclusive projects that can be started by the investor. The office building level can be:
- Rented out to a tenant for one year at $0.1m paid immediately, and then sold for $0.99m in one year.
- Refurbished into more modern commercial office rooms at a cost of $1m now, and then sold for $2.4m when the refurbishment is finished in one year.
- Converted into residential apartments at a cost of $2m now, and then sold for $3.4m when the conversion is finished in one year.
All of the development projects have the same risk so the required return of each is 10% pa. The table below shows the estimated cash flows and internal rates of returns (IRR's).
| Mutually Exclusive Projects | |||
| Project | Cash flow now ($) |
Cash flow in one year ($) |
IRR (% pa) |
| Rent then sell as is | -900,000 | 990,000 | 10 |
| Refurbishment into modern offices | -2,000,000 | 2,400,000 | 20 |
| Conversion into residential apartments | -3,000,000 | 3,400,000 | 13.33 |
Which project should the investor accept?
Question 579 price gains and returns over time, time calculation, effective rate
How many years will it take for an asset's price to double if the price grows by 10% pa?
Question 580 price gains and returns over time, time calculation, effective rate
How many years will it take for an asset's price to quadruple (be four times as big, say from $1 to $4) if the price grows by 15% pa?
Total cash flows can be broken into income and capital cash flows. What is the name given to the income cash flow from owning shares?
An asset's total expected return over the next year is given by:
###r_\text{total} = \dfrac{c_1+p_1-p_0}{p_0} ###
Where ##p_0## is the current price, ##c_1## is the expected income in one year and ##p_1## is the expected price in one year. The total return can be split into the income return and the capital return.
Which of the following is the expected capital return?
A share was bought for $30 (at t=0) and paid its annual dividend of $6 one year later (at t=1).
Just after the dividend was paid, the share price fell to $27 (at t=1). What were the total, capital and income returns given as effective annual rates?
The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}## , ##r_\text{capital}## , ##r_\text{dividend}##.
Question 542 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to double every 10 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
Question 278 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Imagine that the interest rate on your savings account was 1% per year and inflation was 2% per year.
Question 353 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 6% pa and nominal capital return of 3% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns? The answer choices below are given in the same order.
The expression 'you have to spend money to make money' relates to which business decision?
Question 443 corporate financial decision theory, investment decision, financing decision, working capital decision, payout policy
Business people make lots of important decisions. Which of the following is the most important long term decision?
Question 445 financing decision, corporate financial decision theory
The financing decision primarily affects which part of a business?
Question 444 investment decision, corporate financial decision theory
The investment decision primarily affects which part of a business?
The below screenshot of Commonwealth Bank of Australia's (CBA) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 7 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.
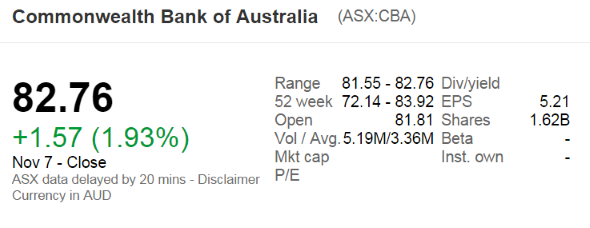
What was CBA's market capitalisation of equity?
Which of the following statements about book and market equity is NOT correct?
Question 531 bankruptcy or insolvency, capital structure, risk, limited liability
Who is most in danger of being personally bankrupt? Assume that all of their businesses' assets are highly liquid and can therefore be sold immediately.
Which business structure or structures have the advantage of limited liability for equity investors?
Question 577 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
What is the present value of a real payment of $500 in 2 years? The nominal discount rate is 7% pa and the inflation rate is 4% pa.
Question 407 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
A stock has a real expected total return of 7% pa and a real expected capital return of 2% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What is the nominal expected total return, capital return and dividend yield? The answers below are given in the same order.
Question 526 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, no explanation
How can a nominal cash flow be precisely converted into a real cash flow?
Katya offers to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years (t=1,2,3,4,5) if you pay her $50 now (t=0). You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. Ignore credit risk.
This annuity formula ##\dfrac{C_1}{r}\left(1-\dfrac{1}{(1+r)^3} \right)## is equivalent to which of the following formulas? Note the 3.
In the below formulas, ##C_t## is a cash flow at time t. All of the cash flows are equal, but paid at different times.
Your friend overheard that you need some cash and asks if you would like to borrow some money. She can lend you $5,000 now (t=0), and in return she wants you to pay her back $1,000 in two years (t=2) and every year after that for the next 5 years, so there will be 6 payments of $1,000 from t=2 to t=7 inclusive.
What is the net present value (NPV) of borrowing from your friend?
Assume that banks loan funds at interest rates of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Some countries' interest rates are so low that they're zero.
If interest rates are 0% pa and are expected to stay at that level for the foreseeable future, what is the most that you would be prepared to pay a bank now if it offered to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years?
In other words, what is the present value of five $10 payments at time 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 if interest rates are 0% pa?
Discounted cash flow (DCF) valuation prices assets by finding the present value of the asset's future cash flows. The single cash flow, annuity, and perpetuity equations are very useful for this.
Which of the following equations is the 'perpetuity with growth' equation?
A stock is expected to pay its next dividend of $1 in one year. Future annual dividends are expected to grow by 2% pa. So the first dividend of $1 will be in one year, the year after that $1.02 (=1*(1+0.02)^1), and a year later $1.0404 (=1*(1+0.02)^2) and so on forever.
Its required total return is 10% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates.
Calculate the current stock price.
For a price of $13, Carla will sell you a share paying a dividend of $1 in one year and every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
The perpetuity with growth formula, also known as the dividend discount model (DDM) or Gordon growth model, is appropriate for valuing a company's shares. ##P_0## is the current share price, ##C_1## is next year's expected dividend, ##r## is the total required return and ##g## is the expected growth rate of the dividend.
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
The below graph shows the expected future price path of the company's shares. Which of the following statements about the graph is NOT correct?
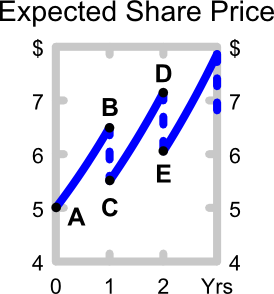
In the dividend discount model:
###P_0 = \dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
The return ##r## is supposed to be the:
A stock pays annual dividends which are expected to continue forever. It just paid a dividend of $10. The growth rate in the dividend is 2% pa. You estimate that the stock's required return is 10% pa. Both the discount rate and growth rate are given as effective annual rates. Using the dividend discount model, what will be the share price?
A fairly valued share's current price is $4 and it has a total required return of 30%. Dividends are paid annually and next year's dividend is expected to be $1. After that, dividends are expected to grow by 5% pa in perpetuity. All rates are effective annual returns.
What is the expected dividend income paid at the end of the second year (t=2) and what is the expected capital gain from just after the first dividend (t=1) to just after the second dividend (t=2)? The answers are given in the same order, the dividend and then the capital gain.
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### p_0 = \frac{d_1}{r - g} ###
Which expression is NOT equal to the expected dividend yield?
Question 535 DDM, real and nominal returns and cash flows, stock pricing
You are an equities analyst trying to value the equity of the Australian telecoms company Telstra, with ticker TLS. In Australia, listed companies like Telstra tend to pay dividends every 6 months. The payment around August is called the final dividend and the payment around February is called the interim dividend. Both occur annually.
- Today is mid-March 2015.
- TLS's last interim dividend of $0.15 was one month ago in mid-February 2015.
- TLS's last final dividend of $0.15 was seven months ago in mid-August 2014.
Judging by TLS's dividend history and prospects, you estimate that the nominal dividend growth rate will be 1% pa. Assume that TLS's total nominal cost of equity is 6% pa. The dividends are nominal cash flows and the inflation rate is 2.5% pa. All rates are quoted as nominal effective annual rates. Assume that each month is exactly one twelfth (1/12) of a year, so you can ignore the number of days in each month.
Calculate the current TLS share price.
Estimate Microsoft's (MSFT) share price using a price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only:
- Apple, Google and Microsoft are comparable companies,
- Apple's (AAPL) share price is $526.24 and historical EPS is $40.32.
- Google's (GOOG) share price is $1,215.65 and historical EPS is $36.23.
- Micrsoft's (MSFT) historical earnings per share (EPS) is $2.71.
Source: Google Finance 28 Feb 2014.
You own some nice shoes which you use once per week on date nights. You bought them 2 years ago for $500. In your experience, shoes used once per week last for 6 years. So you expect yours to last for another 4 years.
Your younger sister said that she wants to borrow your shoes once per week. With the increased use, your shoes will only last for another 2 years rather than 4.
What is the present value of the cost of letting your sister use your current shoes for the next 2 years?
Assume: that bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate; you will buy a new pair of shoes when your current pair wears out and your sister will not use the new ones; your sister will only use your current shoes so she will only use it for the next 2 years; and the price of new shoes never changes.
The following cash flows are expected:
- 10 yearly payments of $80, with the first payment in 3 years from now (first payment at t=3).
- 1 payment of $600 in 5 years and 6 months (t=5.5) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
Question 727 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
The Australian Federal Government lends money to domestic students to pay for their university education. This is known as the Higher Education Contribution Scheme (HECS). The nominal interest rate on the HECS loan is set equal to the consumer price index (CPI) inflation rate. The interest is capitalised every year, which means that the interest is added to the principal. The interest and principal does not need to be repaid by students until they finish study and begin working.
Which of the following statements about HECS loans is NOT correct?
Question 729 book and market values, balance sheet, no explanation
If a firm makes a profit and pays no dividends, which of the firm’s accounts will increase?
In the dividend discount model (DDM), share prices fall when dividends are paid. Let the high price before the fall be called the peak, and the low price after the fall be called the trough.
###P_0=\dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
Which of the following statements about the DDM is NOT correct?
Question 732 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, income and capital returns
An investor bought a bond for $100 (at t=0) and one year later it paid its annual coupon of $1 (at t=1). Just after the coupon was paid, the bond price was $100.50 (at t=1). Inflation over the past year (from t=0 to t=1) was 3% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? The bond investment produced a:
Question 734 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, DDM, no explanation
An equities analyst is using the dividend discount model to price a company's shares. The company operates domestically and has no plans to expand overseas. It is part of a mature industry with stable positive growth prospects.
The analyst has estimated the real required return (r) of the stock and the value of the dividend that the stock just paid a moment before ##(C_\text{0 before})##.
What is the highest perpetual real growth rate of dividends (g) that can be justified? Select the most correct statement from the following choices. The highest perpetual real expected growth rate of dividends that can be justified is the country's expected:
A share currently worth $100 is expected to pay a constant dividend of $4 for the next 5 years with the first dividend in one year (t=1) and the last in 5 years (t=5).
The total required return is 10% pa.
What do you expected the share price to be in 5 years, just after the dividend at that time has been paid?
You're trying to save enough money to buy your first car which costs $2,500. You can save $100 at the end of each month starting from now. You currently have no money at all. You just opened a bank account with an interest rate of 6% pa payable monthly.
How many months will it take to save enough money to buy the car? Assume that the price of the car will stay the same over time.
You really want to go on a back packing trip to Europe when you finish university. Currently you have $1,500 in the bank. Bank interest rates are 8% pa, given as an APR compounding per month. If the holiday will cost $2,000, how long will it take for your bank account to reach that amount?
When using the dividend discount model, care must be taken to avoid using a nominal dividend growth rate that exceeds the country's nominal GDP growth rate. Otherwise the firm is forecast to take over the country since it grows faster than the average business forever.
Suppose a firm's nominal dividend grows at 10% pa forever, and nominal GDP growth is 5% pa forever. The firm's total dividends are currently $1 billion (t=0). The country's GDP is currently $1,000 billion (t=0).
In approximately how many years will the company's total dividends be as large as the country's GDP?
Which of the following equations is NOT equal to the total return of an asset?
Let ##p_0## be the current price, ##p_1## the expected price in one year and ##c_1## the expected income in one year.
A stock was bought for $8 and paid a dividend of $0.50 one year later (at t=1 year). Just after the dividend was paid, the stock price was $7 (at t=1 year).
What were the total, capital and dividend returns given as effective annual rates? The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}##, ##r_\text{capital}##, ##r_\text{dividend}##.
A fixed coupon bond was bought for $90 and paid its annual coupon of $3 one year later (at t=1 year). Just after the coupon was paid, the bond price was $92 (at t=1 year). What was the total return, capital return and income return? Calculate your answers as effective annual rates.
The choices are given in the same order: ## r_\text{total},r_\text{capital},r_\text{income} ##.
In the 'Austin Powers' series of movies, the character Dr. Evil threatens to destroy the world unless the United Nations pays him a ransom (video 1, video 2). Dr. Evil makes the threat on two separate occasions:
- In 1969 he demands a ransom of $1 million (=10^6), and again;
- In 1997 he demands a ransom of $100 billion (=10^11).
If Dr. Evil's demands are equivalent in real terms, in other words $1 million will buy the same basket of goods in 1969 as $100 billion would in 1997, what was the implied inflation rate over the 28 years from 1969 to 1997?
The answer choices below are given as effective annual rates:
Question 363 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 8% pa and nominal capital return of 3% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns? The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Question 155 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, Loan, effective rate conversion
You are a banker about to grant a 2 year loan to a customer. The loan's principal and interest will be repaid in a single payment at maturity, sometimes called a zero-coupon loan, discount loan or bullet loan.
You require a real return of 6% pa over the two years, given as an effective annual rate. Inflation is expected to be 2% this year and 4% next year, both given as effective annual rates.
You judge that the customer can afford to pay back $1,000,000 in 2 years, given as a nominal cash flow. How much should you lend to her right now?
The below screenshot of Microsoft's (MSFT) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 28 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.
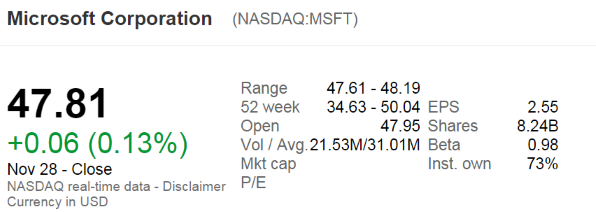
What was MSFT's market capitalisation of equity?
Question 461 book and market values, ROE, ROA, market efficiency
One year ago a pharmaceutical firm floated by selling its 1 million shares for $100 each. Its book and market values of equity were both $100m. Its debt totalled $50m. The required return on the firm's assets was 15%, equity 20% and debt 5% pa.
In the year since then, the firm:
- Earned net income of $29m.
- Paid dividends totaling $10m.
- Discovered a valuable new drug that will lead to a massive 1,000 times increase in the firm's net income in 10 years after the research is commercialised. News of the discovery was publicly announced. The firm's systematic risk remains unchanged.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? All statements are about current figures, not figures one year ago.
Hint: Book return on assets (ROA) and book return on equity (ROE) are ratios that accountants like to use to measure a business's past performance.
###\text{ROA}= \dfrac{\text{Net income}}{\text{Book value of assets}}###
###\text{ROE}= \dfrac{\text{Net income}}{\text{Book value of equity}}###
The required return on assets ##r_V## is a return that financiers like to use to estimate a business's future required performance which compensates them for the firm's assets' risks. If the business were to achieve realised historical returns equal to its required returns, then investment into the business's assets would have been a zero-NPV decision, which is neither good nor bad but fair.
###r_\text{V, 0 to 1}= \dfrac{\text{Cash flow from assets}_\text{1}}{\text{Market value of assets}_\text{0}} = \dfrac{CFFA_\text{1}}{V_\text{0}}###
Similarly for equity and debt.
Question 446 working capital decision, corporate financial decision theory
The working capital decision primarily affects which part of a business?
Question 447 payout policy, corporate financial decision theory
Payout policy is most closely related to which part of a business?
A newly floated farming company is financed with senior bonds, junior bonds, cumulative non-voting preferred stock and common stock. The new company has no retained profits and due to floods it was unable to record any revenues this year, leading to a loss. The firm is not bankrupt yet since it still has substantial contributed equity (same as paid-up capital).
On which securities must it pay interest or dividend payments in this terrible financial year?
There are many ways to write the ordinary annuity formula.
Which of the following is NOT equal to the ordinary annuity formula?
Question 58 NPV, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, Annuity
A project to build a toll bridge will take two years to complete, costing three payments of $100 million at the start of each year for the next three years, that is at t=0, 1 and 2.
After completion, the toll bridge will yield a constant $50 million at the end of each year for the next 10 years. So the first payment will be at t=3 and the last at t=12. After the last payment at t=12, the bridge will be given to the government.
The required return of the project is 21% pa given as an effective annual nominal rate.
All cash flows are real and the expected inflation rate is 10% pa given as an effective annual rate. Ignore taxes.
The Net Present Value is:
The following equation is called the Dividend Discount Model (DDM), Gordon Growth Model or the perpetuity with growth formula: ### P_0 = \frac{ C_1 }{ r - g } ###
What is ##g##? The value ##g## is the long term expected:
The first payment of a constant perpetual annual cash flow is received at time 5. Let this cash flow be ##C_5## and the required return be ##r##.
So there will be equal annual cash flows at time 5, 6, 7 and so on forever, and all of the cash flows will be equal so ##C_5 = C_6 = C_7 = ...##
When the perpetuity formula is used to value this stream of cash flows, it will give a value (V) at time:
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### P_{0} = \frac{C_1}{r_{\text{eff}} - g_{\text{eff}}} ###
What would you call the expression ## C_1/P_0 ##?
A stock just paid its annual dividend of $9. The share price is $60. The required return of the stock is 10% pa as an effective annual rate.
What is the implied growth rate of the dividend per year?
A share just paid its semi-annual dividend of $10. The dividend is expected to grow at 2% every 6 months forever. This 2% growth rate is an effective 6 month rate. Therefore the next dividend will be $10.20 in six months. The required return of the stock 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the price of the share now?
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 1.15 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at 5% pa, so;
- the dividend at t=5 will be $1.15(1+0.05),
- the dividend at t=6 will be $1.15(1+0.05)^2, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates. What is the current price of the stock?
A stock pays semi-annual dividends. It just paid a dividend of $10. The growth rate in the dividend is 1% every 6 months, given as an effective 6 month rate. You estimate that the stock's required return is 21% pa, as an effective annual rate.
Using the dividend discount model, what will be the share price?
Question 498 NPV, Annuity, perpetuity with growth, multi stage growth model
A business project is expected to cost $100 now (t=0), then pay $10 at the end of the third (t=3), fourth, fifth and sixth years, and then grow by 5% pa every year forever. So the cash flow will be $10.5 at the end of the seventh year (t=7), then $11.025 at the end of the eighth year (t=8) and so on perpetually. The total required return is 10℅ pa.
Which of the following formulas will NOT give the correct net present value of the project?
A low-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $1,000 and will last for 1 year before it will be scrapped for nothing.
A high-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $4,900 and it will last for 5 years before it will be scrapped for nothing.
What is the equivalent annual cost of each car? Assume a discount rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
The answer choices are given as the equivalent annual cost of the low-quality car and then the high quality car.
You're advising your superstar client 40-cent who is weighing up buying a private jet or a luxury yacht. 40-cent is just as happy with either, but he wants to go with the more cost-effective option. These are the cash flows of the two options:
- The private jet can be bought for $6m now, which will cost $12,000 per month in fuel, piloting and airport costs, payable at the end of each month. The jet will last for 12 years.
- Or the luxury yacht can be bought for $4m now, which will cost $20,000 per month in fuel, crew and berthing costs, payable at the end of each month. The yacht will last for 20 years.
What's unusual about 40-cent is that he is so famous that he will actually be able to sell his jet or yacht for the same price as it was bought since the next generation of superstar musicians will buy it from him as a status symbol.
Bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. You can assume that 40-cent will live for another 60 years and that when the jet or yacht's life is at an end, he will buy a new one with the same details as above.
Would you advise 40-cent to buy the or the ?
Note that the effective monthly rate is ##r_\text{eff monthly}=(1+0.1)^{1/12}-1=0.00797414##
Question 215 equivalent annual cash flow, effective rate conversion
You're about to buy a car. These are the cash flows of the two different cars that you can buy:
- You can buy an old car for $5,000 now, for which you will have to buy $90 of fuel at the end of each week from the date of purchase. The old car will last for 3 years, at which point you will sell the old car for $500.
- Or you can buy a new car for $14,000 now for which you will have to buy $50 of fuel at the end of each week from the date of purchase. The new car will last for 4 years, at which point you will sell the new car for $1,000.
Bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that there are exactly 52 weeks in a year. Ignore taxes and environmental and pollution factors.
Should you buy the or the ?
Question 249 equivalent annual cash flow, effective rate conversion
Details of two different types of desserts or edible treats are given below:
- High-sugar treats like candy, chocolate and ice cream make a person very happy. High sugar treats are cheap at only $2 per day.
- Low-sugar treats like nuts, cheese and fruit make a person equally happy if these foods are of high quality. Low sugar treats are more expensive at $4 per day.
The advantage of low-sugar treats is that a person only needs to pay the dentist $2,000 for fillings and root canal therapy once every 15 years. Whereas with high-sugar treats, that treatment needs to be done every 5 years.
The real discount rate is 10%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that there are 365 days in every year and that all cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% given as an effective annual rate.
Find the equivalent annual cash flow (EAC) of the high-sugar treats and low-sugar treats, including dental costs. The below choices are listed in that order.
Ignore the pain of dental therapy, personal preferences and other factors.
You just bought a nice dress which you plan to wear once per month on nights out. You bought it a moment ago for $600 (at t=0). In your experience, dresses used once per month last for 6 years.
Your younger sister is a student with no money and wants to borrow your dress once a month when she hits the town. With the increased use, your dress will only last for another 3 years rather than 6.
What is the present value of the cost of letting your sister use your current dress for the next 3 years?
Assume: that bank interest rates are 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate; you will buy a new dress when your current one wears out; your sister will only use the current dress, not the next one that you will buy; and the price of a new dress never changes.
Estimate the Chinese bank ICBC's share price using a backward-looking price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only. Note that the renminbi (RMB) is the Chinese currency, also known as the yuan (CNY).
- The 4 major Chinese banks ICBC, China Construction Bank (CCB), Bank of China (BOC) and Agricultural Bank of China (ABC) are comparable companies;
- ICBC 's historical earnings per share (EPS) is RMB 0.74;
- CCB's backward-looking PE ratio is 4.59;
- BOC 's backward-looking PE ratio is 4.78;
- ABC's backward-looking PE ratio is also 4.78;
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 25 March 2014. Share prices are from the Shanghai stock exchange.
Which of the following investable assets are NOT suitable for valuation using PE multiples techniques?
Which firms tend to have low forward-looking price-earnings (PE) ratios?
Only consider firms with positive earnings, disregard firms with negative earnings and therefore negative PE ratios.
Which of the following investable assets are NOT suitable for valuation using PE multiples techniques?
Which firms tend to have high forward-looking price-earnings (PE) ratios?
Which firms tend to have low forward-looking price-earnings (PE) ratios? Only consider firms with positive PE ratios.
Private equity firms are known to buy medium sized private companies operating in the same industry, merge them together into a larger company, and then sell it off in a public float (initial public offering, IPO).
If medium-sized private companies trade at PE ratios of 5 and larger listed companies trade at PE ratios of 15, what return can be achieved from this strategy?
Assume that:
- The medium-sized companies can be bought, merged and sold in an IPO instantaneously.
- There are no costs of finding, valuing, merging and restructuring the medium sized companies. Also, there is no competition to buy the medium-sized companies from other private equity firms.
- The large merged firm's earnings are the sum of the medium firms' earnings.
- The only reason for the difference in medium and large firm's PE ratios is due to the illiquidity of the medium firms' shares.
- Return is defined as: ##r_{0→1} = (p_1-p_0+c_1)/p_0## , where time zero is just before the merger and time one is just after.
Which of the below statements about effective rates and annualised percentage rates (APR's) is NOT correct?
A European bond paying annual coupons of 6% offers a yield of 10% pa.
Convert the yield into an effective monthly rate, an effective annual rate and an effective daily rate. Assume that there are 365 days in a year.
All answers are given in the same order:
### r_\text{eff, monthly} , r_\text{eff, yearly} , r_\text{eff, daily} ###
A semi-annual coupon bond has a yield of 3% pa. Which of the following statements about the yield is NOT correct? All rates are given to four decimal places.
You want to buy an apartment worth $400,000. You have saved a deposit of $80,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $320,000 as a fully amortising mortgage loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $2,000 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 5 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change.
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $1,500 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 10 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change.
You just agreed to a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $2,500. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 10 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change. The below choices are given in the same order.
You want to buy an apartment priced at $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $30,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $270,000 as an interest only loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 12% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments? Remember that mortgage payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
You want to buy an apartment worth $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $60,000.
The bank has agreed to lend you $240,000 as an interest only mortgage loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid annually. So there's only one coupon per year, paid in arrears every year.
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same US company. Both bonds yield 10% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X and Y's coupon rates are 8 and 12% pa respectively. Which of the following statements is true?
Question 48 IRR, NPV, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds, market efficiency
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A bond maturing in 10 years has a coupon rate of 4% pa, paid semi-annually. The bond's yield is currently 6% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. What is its price?
A three year bond has a fixed coupon rate of 12% pa, paid semi-annually. The bond's yield is currently 6% pa. The face value is $100. What is its price?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at a premium?
Below are some statements about loans and bonds. The first descriptive sentence is correct. But one of the second sentences about the loans' or bonds' prices is not correct. Which statement is NOT correct? Assume that interest rates are positive.
Note that coupons or interest payments are the periodic payments made throughout a bond or loan's life. The face or par value of a bond or loan is the amount paid at the end when the debt matures.
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume twice as much now (t=0) as in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end.
How much can you consume at time zero and one? The answer choices are given in the same order.
You have $100,000 in the bank. The bank pays interest at 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
You wish to consume half as much now (t=0) as in one year (t=1) and have nothing left in the bank at the end.
How much can you consume at time zero and one? The answer choices are given in the same order.
Total cash flows can be broken into income and capital cash flows.
What is the name given to the cash flow generated from selling shares at a higher price than they were bought?
Question 543 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to triple every 5 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
Question 524 risk, expected and historical returns, bankruptcy or insolvency, capital structure, corporate financial decision theory, limited liability
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 604 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Apples and oranges currently cost $1 each. Inflation is 5% pa, and apples and oranges are equally affected by this inflation rate. Note that when payments are not specified as real, as in this question, they're conventionally assumed to be nominal.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 578 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Which of the following statements about inflation is NOT correct?
Question 576 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
What is the present value of a nominal payment of $1,000 in 4 years? The nominal discount rate is 8% pa and the inflation rate is 2% pa.
Question 522 income and capital returns, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 6% pa and nominal capital return of 2.5% pa. Inflation is expected to be 2.5% pa.
All of the above are effective nominal rates and investors believe that they will stay the same in perpetuity.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns?
The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Question 523 income and capital returns, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation
A low-growth mature stock has an expected nominal total return of 6% pa and nominal capital return of 2% pa. Inflation is expected to be 3% pa.
All of the above are effective nominal rates and investors believe that they will stay the same in perpetuity.
What are the stock's expected real total, capital and income returns?
The answer choices below are given in the same order.
You want to buy an apartment priced at $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as an interest only loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
You want to buy an apartment priced at $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
A prospective home buyer can afford to pay $2,000 per month in mortgage loan repayments. The central bank recently lowered its policy rate by 0.25%, and residential home lenders cut their mortgage loan rates from 4.74% to 4.49%.
How much more can the prospective home buyer borrow now that interest rates are 4.49% rather than 4.74%? Give your answer as a proportional increase over the original amount he could borrow (##V_\text{before}##), so:
###\text{Proportional increase} = \frac{V_\text{after}-V_\text{before}}{V_\text{before}} ###Assume that:
- Interest rates are expected to be constant over the life of the loan.
- Loans are interest-only and have a life of 30 years.
- Mortgage loan payments are made every month in arrears and all interest rates are given as annualised percentage rates compounding per month.
Question 56 income and capital returns, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds
Which of the following statements about risk free government bonds is NOT correct?
Hint: Total return can be broken into income and capital returns as follows:
###\begin{aligned} r_\text{total} &= \frac{c_1}{p_0} + \frac{p_1-p_0}{p_0} \\ &= r_\text{income} + r_\text{capital} \end{aligned} ###
The capital return is the growth rate of the price.
The income return is the periodic cash flow. For a bond this is the coupon payment.
A two year Government bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 0.5% and a fixed coupon rate of 0.5%, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
A young lady is trying to decide if she should attend university or not.
The young lady's parents say that she must attend university because otherwise all of her hard work studying and attending school during her childhood was a waste.
What's the correct way to classify this item from a capital budgeting perspective when trying to decide whether to attend university?
The hard work studying at school in her childhood should be classified as:
Why is Capital Expenditure (CapEx) subtracted in the Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) formula?
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###
A firm has forecast its Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) for this year and management is worried that it is too low. Which one of the following actions will lead to a higher CFFA for this year (t=0 to 1)? Only consider cash flows this year. Do not consider cash flows after one year, or the change in the NPV of the firm. Consider each action in isolation.
Your friend just bought a house for $400,000. He financed it using a $320,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $80,000.
In the context of residential housing and mortgages, the 'equity' tied up in the value of a person's house is the value of the house less the value of the mortgage. So the initial equity your friend has in his house is $80,000. Let this amount be E, let the value of the mortgage be D and the value of the house be V. So ##V=D+E##.
If house prices suddenly fall by 10%, what would be your friend's percentage change in equity (E)? Assume that the value of the mortgage is unchanged and that no income (rent) was received from the house during the short time over which house prices fell.
Remember:
### r_{0\rightarrow1}=\frac{p_1-p_0+c_1}{p_0} ###
where ##r_{0-1}## is the return (percentage change) of an asset with price ##p_0## initially, ##p_1## one period later, and paying a cash flow of ##c_1## at time ##t=1##.
One year ago you bought $100,000 of shares partly funded using a margin loan. The margin loan size was $70,000 and the other $30,000 was your own wealth or 'equity' in the share assets.
The interest rate on the margin loan was 7.84% pa.
Over the year, the shares produced a dividend yield of 4% pa and a capital gain of 5% pa.
What was the total return on your wealth? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and dividends) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates above are effective annual rates.
Hint: Remember that wealth in this context is your equity (E) in the house asset (V = D+E) which is funded by the loan (D) and your deposit or equity (E).
A firm has a debt-to-equity ratio of 25%. What is its debt-to-assets ratio?
A manufacturing company is considering a new project in the more risky services industry. The cash flows from assets (CFFA) are estimated for the new project, with interest expense excluded from the calculations. To get the levered value of the project, what should these unlevered cash flows be discounted by?
Assume that the manufacturing firm has a target debt-to-assets ratio that it sticks to.
The US firm Google operates in the online advertising business. In 2011 Google bought Motorola Mobility which manufactures mobile phones.
Assume the following:
- Google had a 10% after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC) before it bought Motorola.
- Motorola had a 20% after-tax WACC before it merged with Google.
- Google and Motorola have the same level of gearing.
- Both companies operate in a classical tax system.
You are a manager at Motorola. You must value a project for making mobile phones. Which method(s) will give the correct valuation of the mobile phone manufacturing project? Select the most correct answer.
The mobile phone manufacturing project's:
One formula for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to use earnings before interest and tax (EBIT).
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (EBIT)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ \end{aligned} \\###
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 50%. The firm then issues a large amount of debt to raise money for new projects of similar market risk to the company's existing projects. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is correct?
A man is thinking about taking a day off from his casual painting job to relax.
He just woke up early in the morning and he's about to call his boss to say that he won't be coming in to work.
But he's thinking about the hours that he could work today (in the future) which are:
A man has taken a day off from his casual painting job to relax.
It's the end of the day and he's thinking about the hours that he could have spent working (in the past) which are now:
Find Candys Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Candys Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 200 | |
| COGS | 50 | |
| Operating expense | 10 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Interest expense | 10 | |
| Income before tax | 110 | |
| Tax at 30% | 33 | |
| Net income | 77 | |
| Candys Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets | 220 | 180 |
| PPE | ||
| Cost | 300 | 340 |
| Accumul. depr. | 60 | 40 |
| Carrying amount | 240 | 300 |
| Total assets | 460 | 480 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | 175 | 190 |
| Non-current liabilities | 135 | 130 |
| Owners' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | 50 | 60 |
| Contributed equity | 100 | 100 |
| Total L and OE | 460 | 480 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
To value a business's assets, the free cash flow of the firm (FCFF, also called CFFA) needs to be calculated. This requires figures from the firm's income statement and balance sheet. For what figures is the balance sheet needed? Note that the balance sheet is sometimes also called the statement of financial position.
Which one of the following will decrease net income (NI) but increase cash flow from assets (CFFA) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI = (Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###Which one of the following will have no effect on net income (NI) but decrease cash flow from assets (CFFA or FFCF) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - ΔNWC+IntExp###Your friend just bought a house for $1,000,000. He financed it using a $900,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $100,000.
In the context of residential housing and mortgages, the 'equity' or 'net wealth' tied up in a house is the value of the house less the value of the mortgage loan. Assuming that your friend's only asset is his house, his net wealth is $100,000.
If house prices suddenly fall by 15%, what would be your friend's percentage change in net wealth?
Assume that:
- No income (rent) was received from the house during the short time over which house prices fell.
- Your friend will not declare bankruptcy, he will always pay off his debts.
Here are the Net Income (NI) and Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) equations:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c)###
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+IntExp###
What is the formula for calculating annual interest expense (IntExp) which is used in the equations above?
Select one of the following answers. Note that D is the value of debt which is constant through time, and ##r_D## is the cost of debt.
Which one of the following will decrease net income (NI) but increase cash flow from assets (CFFA) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - ΔNWC+IntExp###A firm has a debt-to-equity ratio of 60%. What is its debt-to-assets ratio?
A firm is considering a new project of similar risk to the current risk of the firm. This project will expand its existing business. The cash flows of the project have been calculated assuming that there is no interest expense. In other words, the cash flows assume that the project is all-equity financed.
In fact the firm has a target debt-to-equity ratio of 1, so the project will be financed with 50% debt and 50% equity. To find the levered value of the firm's assets, what discount rate should be applied to the project's unlevered cash flows? Assume a classical tax system.
You bought a house, primarily funded using a home loan from a bank. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 737 financial statement, balance sheet, income statement
Where can a publicly listed firm's book value of equity be found? It can be sourced from the company's:
Question 738 financial statement, balance sheet, income statement
Where can a private firm's market value of equity be found? It can be sourced from the company's:
Question 739 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation
There are a number of different formulas involving real and nominal returns and cash flows. Which one of the following formulas is NOT correct? All returns are effective annual rates. Note that the symbol ##\approx## means 'approximately equal to'.
A home loan company advertises an interest rate of 4.5% pa, payable monthly. Which of the following statements about the interest rate is NOT correct?
Question 742 price gains and returns over time, no explanation
For an asset's price to quintuple (be five times as big, say from $1 to $5) every 5 years, what must be its effective annual capital return?
Question 743 price gains and returns over time, no explanation
How many years will it take for an asset's price to triple (increase from say $1 to $3) if it grows by 5% pa?
Question 744 income and capital returns, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation
If someone says "my shares rose by 10% last year", what do you assume that they mean? The effective annual:
A stock is expected to pay a dividend of $1 in one year. Its future annual dividends are expected to grow by 10% pa. So the first dividend of $1 is in one year, and the year after that the dividend will be $1.1 (=1*(1+0.1)^1), and a year later $1.21 (=1*(1+0.1)^2) and so on forever.
Its required total return is 30% pa. The total required return and growth rate of dividends are given as effective annual rates. The stock is fairly priced.
Calculate the pay back period of buying the stock and holding onto it forever, assuming that the dividends are received as at each time, not smoothly over each year.
Question 748 income and capital returns, DDM, ex dividend date
A stock will pay you a dividend of $2 tonight if you buy it today.
Thereafter the annual dividend is expected to grow by 3% pa, so the next dividend after the $2 one tonight will be $2.06 in one year, then in two years it will be $2.1218 and so on. The stock's required return is 8% pa.
What is the stock price today and what do you expect the stock price to be tomorrow, approximately?
Question 749 Multiples valuation, PE ratio, price to revenue ratio, price to book ratio, NPV
A real estate agent says that the price of a house in Sydney Australia is approximately equal to the gross weekly rent times 1000.
What type of valuation method is the real estate agent using?
Itau Unibanco is a major listed bank in Brazil with a market capitalisation of equity equal to BRL 85.744 billion, EPS of BRL 3.96 and 2.97 billion shares on issue.
Banco Bradesco is another major bank with total earnings of BRL 8.77 billion and 2.52 billion shares on issue.
Estimate Banco Bradesco's current share price using a price-earnings multiples approach assuming that Itau Unibanco is a comparable firm.
Note that BRL is the Brazilian Real, their currency. Figures sourced from Google Finance on the market close of the BVMF on 24 July 2015.
Telsa Motors advertises that its Model S electric car saves $570 per month in fuel costs. Assume that Tesla cars last for 10 years, fuel and electricity costs remain the same, and savings are made at the end of each month with the first saving of $570 in one month from now.
The effective annual interest rate is 15.8%, and the effective monthly interest rate is 1.23%. What is the present value of the savings?
How much more can you borrow using an interest-only loan compared to a 25-year fully amortising loan if interest rates are 4% pa compounding per month and are not expected to change? If it makes it easier, assume that you can afford to pay $2,000 per month on either loan. Express your answer as a proportional increase using the following formula:
###\text{Proportional Increase} = \dfrac{V_\text{0,interest only}}{V_\text{0,fully amortising}} - 1###A firm wishes to raise $50 million now. They will issue 7% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 6 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 5% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
A firm wishes to raise $50 million now. They will issue 5% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 3 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 6% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
Question 758 time calculation, fully amortising loan, no explanation
Two years ago you entered into a fully amortising home loan with a principal of $1,000,000, an interest rate of 6% pa compounding monthly with a term of 25 years.
Then interest rates suddenly fall to 4.5% pa (t=0), but you continue to pay the same monthly home loan payments as you did before. How long will it now take to pay off your home loan? Measure the time taken to pay off the home loan from the current time which is 2 years after the home loan was first entered into.
Assume that the lower interest rate was given to you immediately after the loan repayment at the end of year 2, which was the 24th payment since the loan was granted. Also assume that rates were and are expected to remain constant.
Question 759 time calculation, fully amortising loan, no explanation
Five years ago you entered into a fully amortising home loan with a principal of $500,000, an interest rate of 4.5% pa compounding monthly with a term of 25 years.
Then interest rates suddenly fall to 3% pa (t=0), but you continue to pay the same monthly home loan payments as you did before. How long will it now take to pay off your home loan? Measure the time taken to pay off the home loan from the current time which is 5 years after the home loan was first entered into.
Assume that the lower interest rate was given to you immediately after the loan repayment at the end of year 5, which was the 60th payment since the loan was granted. Also assume that rates were and are expected to remain constant.
Use the below information to value a levered company with constant annual perpetual cash flows from assets. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now, so a perpetuity can be used to value this firm. Both the operating and firm free cash flows are constant (but not equal to each other).
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}## | $100m | Operating free cash flow |
| ##\text{FFCF or CFFA}## | $112m | Firm free cash flow or cash flow from assets (includes interest tax shields) |
| ##g## | 0% pa | Growth rate of OFCF and FFCF |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{BeforeTax}## | 7% pa | Weighted average cost of capital before tax |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{AfterTax}## | 6.25% pa | Weighted average cost of capital after tax |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 5% pa | Cost of debt |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 9% pa | Cost of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 50% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
What is the value of the levered firm including interest tax shields?
Which one of the following will increase the Cash Flow From Assets in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Question 559 variance, standard deviation, covariance, correlation
Which of the following statements about standard statistical mathematics notation is NOT correct?
Diversification in a portfolio of two assets works best when the correlation between their returns is:
All things remaining equal, the variance of a portfolio of two positively-weighted stocks rises as:
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Correlation ##(\rho_{A,B})## | Dollars invested |
||
| A | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 60 | ||
| B | 0.2 | 0.6 | 140 | |||
What is the standard deviation (not variance) of returns of the above portfolio?
Two risky stocks A and B comprise an equal-weighted portfolio. The correlation between the stocks' returns is 70%.
If the variance of stock A's returns increases but the:
- Prices and expected returns of each stock stays the same,
- Variance of stock B's returns stays the same,
- Correlation of returns between the stocks stays the same.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
All things remaining equal, the higher the correlation of returns between two stocks:
An investor wants to make a portfolio of two stocks A and B with a target expected portfolio return of 6% pa.
- Stock A has an expected return of 5% pa.
- Stock B has an expected return of 10% pa.
What portfolio weights should the investor have in stocks A and B respectively?
What is the correlation of a variable X with itself?
The corr(X, X) or ##\rho_{X,X}## equals:
The covariance and correlation of two stocks X and Y's annual returns are calculated over a number of years. The units of the returns are in percent per annum ##(\% pa)##.
What are the units of the covariance ##(\sigma_{X,Y})## and correlation ##(\rho_{X,Y})## of returns respectively?
Hint: Visit Wikipedia to understand the difference between percentage points ##(\text{pp})## and percent ##(\%)##.