What is the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) of the project detailed in the table below?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time. All answers are given as effective annual rates.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 121 |
If a project's net present value (NPV) is zero, then its internal rate of return (IRR) will be:
The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate.
What is the payback period of the project in years?
Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are received smoothly over the year. So the $121 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2.
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 11 |
| 2 | 121 |
A project has the following cash flows:
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -400 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 500 |
What is the payback period of the project in years?
Normally cash flows are assumed to happen at the given time. But here, assume that the cash flows are received smoothly over the year. So the $500 at time 2 is actually earned smoothly from t=1 to t=2.
Total cash flows can be broken into income and capital cash flows. What is the name given to the income cash flow from owning shares?
Which of the following equations is NOT equal to the total return of an asset?
Let ##p_0## be the current price, ##p_1## the expected price in one year and ##c_1## the expected income in one year.
An asset's total expected return over the next year is given by:
###r_\text{total} = \dfrac{c_1+p_1-p_0}{p_0} ###
Where ##p_0## is the current price, ##c_1## is the expected income in one year and ##p_1## is the expected price in one year. The total return can be split into the income return and the capital return.
Which of the following is the expected capital return?
A stock was bought for $8 and paid a dividend of $0.50 one year later (at t=1 year). Just after the dividend was paid, the stock price was $7 (at t=1 year).
What were the total, capital and dividend returns given as effective annual rates? The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}##, ##r_\text{capital}##, ##r_\text{dividend}##.
A fixed coupon bond was bought for $90 and paid its annual coupon of $3 one year later (at t=1 year). Just after the coupon was paid, the bond price was $92 (at t=1 year). What was the total return, capital return and income return? Calculate your answers as effective annual rates.
The choices are given in the same order: ## r_\text{total},r_\text{capital},r_\text{income} ##.
Question 278 inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
Imagine that the interest rate on your savings account was 1% per year and inflation was 2% per year.
In the 'Austin Powers' series of movies, the character Dr. Evil threatens to destroy the world unless the United Nations pays him a ransom (video 1, video 2). Dr. Evil makes the threat on two separate occasions:
- In 1969 he demands a ransom of $1 million (=10^6), and again;
- In 1997 he demands a ransom of $100 billion (=10^11).
If Dr. Evil's demands are equivalent in real terms, in other words $1 million will buy the same basket of goods in 1969 as $100 billion would in 1997, what was the implied inflation rate over the 28 years from 1969 to 1997?
The answer choices below are given as effective annual rates:
Question 353 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 6% pa and nominal capital return of 3% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns? The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Question 363 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, real estate
A residential investment property has an expected nominal total return of 8% pa and nominal capital return of 3% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What are the property's expected real total, capital and income returns? The answer choices below are given in the same order.
Question 407 income and capital returns, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows
A stock has a real expected total return of 7% pa and a real expected capital return of 2% pa.
Inflation is expected to be 2% pa. All rates are given as effective annual rates.
What is the nominal expected total return, capital return and dividend yield? The answers below are given in the same order.
The below screenshot of Commonwealth Bank of Australia's (CBA) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 7 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.
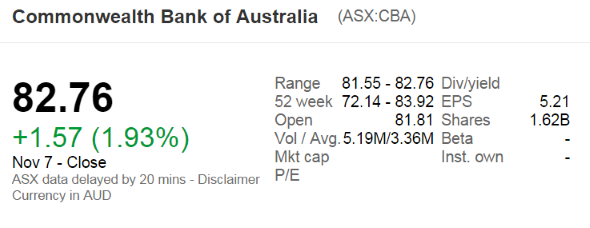
What was CBA's market capitalisation of equity?
The below screenshot of Microsoft's (MSFT) details were taken from the Google Finance website on 28 Nov 2014. Some information has been deliberately blanked out.
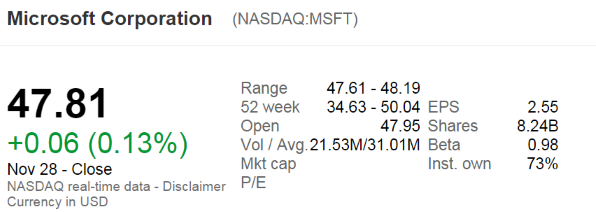
What was MSFT's market capitalisation of equity?
Question 461 book and market values, ROE, ROA, market efficiency
One year ago a pharmaceutical firm floated by selling its 1 million shares for $100 each. Its book and market values of equity were both $100m. Its debt totalled $50m. The required return on the firm's assets was 15%, equity 20% and debt 5% pa.
In the year since then, the firm:
- Earned net income of $29m.
- Paid dividends totaling $10m.
- Discovered a valuable new drug that will lead to a massive 1,000 times increase in the firm's net income in 10 years after the research is commercialised. News of the discovery was publicly announced. The firm's systematic risk remains unchanged.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? All statements are about current figures, not figures one year ago.
Hint: Book return on assets (ROA) and book return on equity (ROE) are ratios that accountants like to use to measure a business's past performance.
###\text{ROA}= \dfrac{\text{Net income}}{\text{Book value of assets}}###
###\text{ROE}= \dfrac{\text{Net income}}{\text{Book value of equity}}###
The required return on assets ##r_V## is a return that financiers like to use to estimate a business's future required performance which compensates them for the firm's assets' risks. If the business were to achieve realised historical returns equal to its required returns, then investment into the business's assets would have been a zero-NPV decision, which is neither good nor bad but fair.
###r_\text{V, 0 to 1}= \dfrac{\text{Cash flow from assets}_\text{1}}{\text{Market value of assets}_\text{0}} = \dfrac{CFFA_\text{1}}{V_\text{0}}###
Similarly for equity and debt.
Question 444 investment decision, corporate financial decision theory
The investment decision primarily affects which part of a business?
Question 446 working capital decision, corporate financial decision theory
The working capital decision primarily affects which part of a business?
Question 445 financing decision, corporate financial decision theory
The financing decision primarily affects which part of a business?
Question 447 payout policy, corporate financial decision theory
Payout policy is most closely related to which part of a business?
Question 443 corporate financial decision theory, investment decision, financing decision, working capital decision, payout policy
Business people make lots of important decisions. Which of the following is the most important long term decision?
You're considering making an investment in a particular company. They have preference shares, ordinary shares, senior debt and junior debt.
Which is the safest investment? Which has the highest expected returns?
Which business structure or structures have the advantage of limited liability for equity investors?
A share was bought for $30 (at t=0) and paid its annual dividend of $6 one year later (at t=1).
Just after the dividend was paid, the share price fell to $27 (at t=1). What were the total, capital and income returns given as effective annual rates?
The choices are given in the same order:
##r_\text{total}## , ##r_\text{capital}## , ##r_\text{dividend}##.
Katya offers to pay you $10 at the end of every year for the next 5 years (t=1,2,3,4,5) if you pay her $50 now (t=0). You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate. Ignore credit risk.
There are many ways to write the ordinary annuity formula.
Which of the following is NOT equal to the ordinary annuity formula?
The following cash flows are expected:
- 10 yearly payments of $60, with the first payment in 3 years from now (first payment at t=3 and last at t=12).
- 1 payment of $400 in 5 years and 6 months (t=5.5) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
Question 58 NPV, inflation, real and nominal returns and cash flows, Annuity
A project to build a toll bridge will take two years to complete, costing three payments of $100 million at the start of each year for the next three years, that is at t=0, 1 and 2.
After completion, the toll bridge will yield a constant $50 million at the end of each year for the next 10 years. So the first payment will be at t=3 and the last at t=12. After the last payment at t=12, the bridge will be given to the government.
The required return of the project is 21% pa given as an effective annual nominal rate.
All cash flows are real and the expected inflation rate is 10% pa given as an effective annual rate. Ignore taxes.
The Net Present Value is:
Discounted cash flow (DCF) valuation prices assets by finding the present value of the asset's future cash flows. The single cash flow, annuity, and perpetuity equations are very useful for this.
Which of the following equations is the 'perpetuity with growth' equation?
The following equation is called the Dividend Discount Model (DDM), Gordon Growth Model or the perpetuity with growth formula: ### P_0 = \frac{ C_1 }{ r - g } ###
What is ##g##? The value ##g## is the long term expected:
For a price of $13, Carla will sell you a share paying a dividend of $1 in one year and every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
The first payment of a constant perpetual annual cash flow is received at time 5. Let this cash flow be ##C_5## and the required return be ##r##.
So there will be equal annual cash flows at time 5, 6, 7 and so on forever, and all of the cash flows will be equal so ##C_5 = C_6 = C_7 = ...##
When the perpetuity formula is used to value this stream of cash flows, it will give a value (V) at time:
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
### P_{0} = \frac{C_1}{r_{\text{eff}} - g_{\text{eff}}} ###
What would you call the expression ## C_1/P_0 ##?
The following equation is the Dividend Discount Model, also known as the 'Gordon Growth Model' or the 'Perpetuity with growth' equation.
###P_0=\frac{d_1}{r-g}###
A stock pays dividends annually. It just paid a dividend, but the next dividend (##d_1##) will be paid in one year.
According to the DDM, what is the correct formula for the expected price of the stock in 2.5 years?
In the dividend discount model:
###P_0 = \dfrac{C_1}{r-g}###
The return ##r## is supposed to be the:
Question 498 NPV, Annuity, perpetuity with growth, multi stage growth model
A business project is expected to cost $100 now (t=0), then pay $10 at the end of the third (t=3), fourth, fifth and sixth years, and then grow by 5% pa every year forever. So the cash flow will be $10.5 at the end of the seventh year (t=7), then $11.025 at the end of the eighth year (t=8) and so on perpetually. The total required return is 10℅ pa.
Which of the following formulas will NOT give the correct net present value of the project?
A low-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $1,000 and will last for 1 year before it will be scrapped for nothing.
A high-quality second-hand car can be bought now for $4,900 and it will last for 5 years before it will be scrapped for nothing.
What is the equivalent annual cost of each car? Assume a discount rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
The answer choices are given as the equivalent annual cost of the low-quality car and then the high quality car.
Estimate the US bank JP Morgan's share price using a price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only:
- The major US banks JP Morgan Chase (JPM), Citi Group (C) and Wells Fargo (WFC) are comparable companies;
- JP Morgan Chase's historical earnings per share (EPS) is $4.37;
- Citi Group's share price is $50.05 and historical EPS is $4.26;
- Wells Fargo's share price is $48.98 and historical EPS is $3.89.
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 24 March 2014.
Estimate the Chinese bank ICBC's share price using a backward-looking price earnings (PE) multiples approach with the following assumptions and figures only. Note that the renminbi (RMB) is the Chinese currency, also known as the yuan (CNY).
- The 4 major Chinese banks ICBC, China Construction Bank (CCB), Bank of China (BOC) and Agricultural Bank of China (ABC) are comparable companies;
- ICBC 's historical earnings per share (EPS) is RMB 0.74;
- CCB's backward-looking PE ratio is 4.59;
- BOC 's backward-looking PE ratio is 4.78;
- ABC's backward-looking PE ratio is also 4.78;
Note: Figures sourced from Google Finance on 25 March 2014. Share prices are from the Shanghai stock exchange.
A project to build a toll road will take 3 years to complete, costing three payments of $50 million, paid at the start of each year (at times 0, 1, and 2).
After completion, the toll road will yield a constant $10 million at the end of each year forever with no costs. So the first payment will be at t=4.
The required return of the project is 10% pa given as an effective nominal rate. All cash flows are nominal.
What is the payback period?
You really want to go on a back packing trip to Europe when you finish university. Currently you have $1,500 in the bank. Bank interest rates are 8% pa, given as an APR compounding per month. If the holiday will cost $2,000, how long will it take for your bank account to reach that amount?
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $1,500 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
To your surprise, you can actually afford to pay $2,000 per month and your mortgage allows early repayments without fees. If you maintain these higher monthly payments, how long will it take to pay off your mortgage?
Question 452 limited liability, expected and historical returns
What is the lowest and highest expected share price and expected return from owning shares in a company over a finite period of time?
Let the current share price be ##p_0##, the expected future share price be ##p_1##, the expected future dividend be ##d_1## and the expected return be ##r##. Define the expected return as:
##r=\dfrac{p_1-p_0+d_1}{p_0} ##
The answer choices are stated using inequalities. As an example, the first answer choice "(a) ##0≤p<∞## and ##0≤r< 1##", states that the share price must be larger than or equal to zero and less than positive infinity, and that the return must be larger than or equal to zero and less than one.
A stock pays annual dividends which are expected to continue forever. It just paid a dividend of $10. The growth rate in the dividend is 2% pa. You estimate that the stock's required return is 10% pa. Both the discount rate and growth rate are given as effective annual rates. Using the dividend discount model, what will be the share price?
A stock is expected to pay the following dividends:
| Cash Flows of a Stock | ||||||
| Time (yrs) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ... |
| Dividend ($) | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 1.10 | 1.15 | ... |
After year 4, the annual dividend will grow in perpetuity at 5% pa, so;
- the dividend at t=5 will be $1.15(1+0.05),
- the dividend at t=6 will be $1.15(1+0.05)^2, and so on.
The required return on the stock is 10% pa. Both the growth rate and required return are given as effective annual rates. What is the current price of the stock?
The following cash flows are expected:
- 10 yearly payments of $80, with the first payment in 3 years from now (first payment at t=3).
- 1 payment of $600 in 5 years and 6 months (t=5.5) from now.
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
Question 729 book and market values, balance sheet, no explanation
If a firm makes a profit and pays no dividends, which of the firm’s accounts will increase?
Question 732 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, income and capital returns
An investor bought a bond for $100 (at t=0) and one year later it paid its annual coupon of $1 (at t=1). Just after the coupon was paid, the bond price was $100.50 (at t=1). Inflation over the past year (from t=0 to t=1) was 3% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? The bond investment produced a:
Question 734 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, DDM, no explanation
An equities analyst is using the dividend discount model to price a company's shares. The company operates domestically and has no plans to expand overseas. It is part of a mature industry with stable positive growth prospects.
The analyst has estimated the real required return (r) of the stock and the value of the dividend that the stock just paid a moment before ##(C_\text{0 before})##.
What is the highest perpetual real growth rate of dividends (g) that can be justified? Select the most correct statement from the following choices. The highest perpetual real expected growth rate of dividends that can be justified is the country's expected:
Question 548 equivalent annual cash flow, time calculation, no explanation
An Apple iPhone 6 smart phone can be bought now for $999. An Android Kogan Agora 4G+ smart phone can be bought now for $240.
If the Kogan phone lasts for one year, approximately how long must the Apple phone last for to have the same equivalent annual cost?
Assume that both phones have equivalent features besides their lifetimes, that both are worthless once they've outlasted their life, the discount rate is 10% pa given as an effective annual rate, and there are no extra costs or benefits from either phone.
Which of the following statements is NOT equivalent to the yield on debt?
Assume that the debt being referred to is fairly priced, but do not assume that it's priced at par.
A credit card offers an interest rate of 18% pa, compounding monthly.
Find the effective monthly rate, effective annual rate and the effective daily rate. Assume that there are 365 days in a year.
All answers are given in the same order:
### r_\text{eff monthly} , r_\text{eff yearly} , r_\text{eff daily} ###
Calculate the effective annual rates of the following three APR's:
- A credit card offering an interest rate of 18% pa, compounding monthly.
- A bond offering a yield of 6% pa, compounding semi-annually.
- An annual dividend-paying stock offering a return of 10% pa compounding annually.
All answers are given in the same order:
##r_\text{credit card, eff yrly}##, ##r_\text{bond, eff yrly}##, ##r_\text{stock, eff yrly}##
You want to buy an apartment priced at $300,000. You have saved a deposit of $30,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $270,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 12% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments? Remember that mortgage loan payments are paid in arrears (at the end of the month).
You want to buy an apartment worth $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as a fully amortising mortgage loan with a term of 25 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments?
You want to buy an apartment worth $400,000. You have saved a deposit of $80,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $320,000 as a fully amortising mortgage loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid annually. So there's only one coupon per year, paid in arrears every year.
Calculate the price of a newly issued ten year bond with a face value of $100, a yield of 8% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 6% pa, paid semi-annually. So there are two coupons per year, paid in arrears every six months.
For a price of $100, Vera will sell you a 2 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 10% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with similar risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 8% pa.
For a price of $95, Nicole will sell you a 10 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 8% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with the same risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 8% pa.
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same US company. Both bonds yield 10% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X and Y's coupon rates are 8 and 12% pa respectively. Which of the following statements is true?
Bonds A and B are issued by the same company. They have the same face value, maturity, seniority and coupon payment frequency. The only difference is that bond A has a 5% coupon rate, while bond B has a 10% coupon rate. The yield curve is flat, which means that yields are expected to stay the same.
Which bond would have the higher current price?
A two year Government bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 0.5% and a fixed coupon rate of 0.5%, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
Question 48 IRR, NPV, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds, market efficiency
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
The theory of fixed interest bond pricing is an application of the theory of Net Present Value (NPV). Also, a 'fairly priced' asset is not over- or under-priced. Buying or selling a fairly priced asset has an NPV of zero.
Considering this, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
A bond maturing in 10 years has a coupon rate of 4% pa, paid semi-annually. The bond's yield is currently 6% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. What is its price?
Bonds A and B are issued by the same Australian company. Both bonds yield 7% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond A pays coupons of 10% pa and bond B pays coupons of 5% pa. Which of the following statements is true about the bonds' prices?
You want to buy an apartment priced at $500,000. You have saved a deposit of $50,000. The bank has agreed to lend you the $450,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 6% pa and is not expected to change. What will be your monthly payments?
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage with monthly payments of $1,000 per month. The interest rate is 6% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 20 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 6% and is not expected to change.
You just signed up for a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $1,500 per month. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 10 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change.
You just agreed to a 30 year fully amortising mortgage loan with monthly payments of $2,500. The interest rate is 9% pa which is not expected to change.
How much did you borrow? After 10 years, how much will be owing on the mortgage? The interest rate is still 9% and is not expected to change. The below choices are given in the same order.
You want to buy a house priced at $400,000. You have saved a deposit of $40,000. The bank has agreed to lend you $360,000 as a fully amortising loan with a term of 30 years. The interest rate is 8% pa payable monthly and is not expected to change.
What will be your monthly payments?
A three year bond has a fixed coupon rate of 12% pa, paid semi-annually. The bond's yield is currently 6% pa. The face value is $100. What is its price?
Bonds X and Y are issued by different companies, but they both pay a semi-annual coupon of 10% pa and they have the same face value ($100), maturity (3 years) and yield (10%) as each other.
Which of the following statements is true?
A four year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 6% and a fixed coupon rate of 12%, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at a discount?
A firm wishes to raise $20 million now. They will issue 8% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 5 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 6% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
A five year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 12% and a fixed coupon rate of 6%, paid semi-annually.
What is the bond's price?
Which one of the following bonds is trading at par?
A firm wishes to raise $8 million now. They will issue 7% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 10 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 10% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
Question 207 income and capital returns, bond pricing, coupon rate, no explanation
For a bond that pays fixed semi-annual coupons, how is the annual coupon rate defined, and how is the bond's annual income yield from time 0 to 1 defined mathematically?
Let: ##P_0## be the bond price now,
##F_T## be the bond's face value,
##T## be the bond's maturity in years,
##r_\text{total}## be the bond's total yield,
##r_\text{income}## be the bond's income yield,
##r_\text{capital}## be the bond's capital yield, and
##C_t## be the bond's coupon at time t in years. So ##C_{0.5}## is the coupon in 6 months, ##C_1## is the coupon in 1 year, and so on.
Which one of the following bonds is trading at a premium?
An investor bought two fixed-coupon bonds issued by the same company, a zero-coupon bond and a 7% pa semi-annual coupon bond. Both bonds have a face value of $1,000, mature in 10 years, and had a yield at the time of purchase of 8% pa.
A few years later, yields fell to 6% pa. Which of the following statements is correct? Note that a capital gain is an increase in price.
A firm wishes to raise $10 million now. They will issue 6% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 8 years and have a face value of $1,000 each. Bond yields are 10% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue? All numbers are rounded up.
A four year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 9% and a fixed coupon rate of 6%, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
A 10 year bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 6% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 8% pa, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same company. Both bonds yield 10% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X pays coupons of 6% pa and bond Y pays coupons of 8% pa. Which of the following statements is true?
A 30 year Japanese government bond was just issued at par with a yield of 1.7% pa. The fixed coupon payments are semi-annual. The bond has a face value of $100.
Six months later, just after the first coupon is paid, the yield of the bond increases to 2% pa. What is the bond's new price?
A 10 year Australian government bond was just issued at par with a yield of 3.9% pa. The fixed coupon payments are semi-annual. The bond has a face value of $1,000.
Six months later, just after the first coupon is paid, the yield of the bond decreases to 3.65% pa. What is the bond's new price?
Bonds X and Y are issued by the same US company. Both bonds yield 6% pa, and they have the same face value ($100), maturity, seniority, and payment frequency.
The only difference is that bond X pays coupons of 8% pa and bond Y pays coupons of 12% pa. Which of the following statements is true?
Why is Capital Expenditure (CapEx) subtracted in the Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) formula?
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \Delta NWC+IntExp###
Suppose you had $100 in a savings account and the interest rate was 2% per year.
After 5 years, how much do you think you would have in the account if you left the money to grow?
Jan asks you for a loan. He wants $100 now and offers to pay you back $120 in 1 year. You can borrow and lend from the bank at an interest rate of 10% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
Ignore credit risk. Remember:
### V_0 = \frac{V_t}{(1+r_\text{eff})^t} ###
For a price of $6, Carlos will sell you a share which will pay a dividend of $1 in one year and every year after that forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa.
For a price of $102, Andrea will sell you a share which just paid a dividend of $10 yesterday, and is expected to pay dividends every year forever, growing at a rate of 5% pa.
So the next dividend will be ##10(1+0.05)^1=$10.50## in one year from now, and the year after it will be ##10(1+0.05)^2=11.025## and so on.
The required return of the stock is 15% pa.
Your friend just bought a house for $1,000,000. He financed it using a $900,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $100,000.
In the context of residential housing and mortgages, the 'equity' or 'net wealth' tied up in a house is the value of the house less the value of the mortgage loan. Assuming that your friend's only asset is his house, his net wealth is $100,000.
If house prices suddenly fall by 15%, what would be your friend's percentage change in net wealth?
Assume that:
- No income (rent) was received from the house during the short time over which house prices fell.
- Your friend will not declare bankruptcy, he will always pay off his debts.
Here are the Net Income (NI) and Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA) equations:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c)###
###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+IntExp###
What is the formula for calculating annual interest expense (IntExp) which is used in the equations above?
Select one of the following answers. Note that D is the value of debt which is constant through time, and ##r_D## is the cost of debt.
Which one of the following will increase the Cash Flow From Assets in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Which one of the following will decrease net income (NI) but increase cash flow from assets (CFFA) in this year for a tax-paying firm, all else remaining constant?
Remember:
###NI=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-IntExp).(1-t_c )### ###CFFA=NI+Depr-CapEx - ΔNWC+IntExp###Value the following business project to manufacture a new product.
| Project Data | ||
| Project life | 2 yrs | |
| Initial investment in equipment | $6m | |
| Depreciation of equipment per year | $3m | |
| Expected sale price of equipment at end of project | $0.6m | |
| Unit sales per year | 4m | |
| Sale price per unit | $8 | |
| Variable cost per unit | $5 | |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $1m | |
| Interest expense per year | 0 | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
| Weighted average cost of capital after tax per annum | 10% | |
Notes
- The firm's current assets and current liabilities are $3m and $2m respectively right now. This net working capital will not be used in this project, it will be used in other unrelated projects.
Due to the project, current assets (mostly inventory) will grow by $2m initially (at t = 0), and then by $0.2m at the end of the first year (t=1).
Current liabilities (mostly trade creditors) will increase by $0.1m at the end of the first year (t=1).
At the end of the project, the net working capital accumulated due to the project can be sold for the same price that it was bought. - The project cost $0.5m to research which was incurred one year ago.
Assumptions
- All cash flows occur at the start or end of the year as appropriate, not in the middle or throughout the year.
- All rates and cash flows are real. The inflation rate is 3% pa.
- All rates are given as effective annual rates.
- The business considering the project is run as a 'sole tradership' (run by an individual without a company) and is therefore eligible for a 50% capital gains tax discount when the equipment is sold, as permitted by the Australian Tax Office.
What is the expected net present value (NPV) of the project?
One formula for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to use earnings before interest and tax (EBIT).
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (EBIT)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp.t_c \\ \end{aligned} \\###
One method for calculating a firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to ignore interest expense. That is, pretend that interest expense ##(IntExp)## is zero:
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - IntExp)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC + IntExp \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC - 0)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC - 0\\ \end{aligned}###
One formula for calculating a levered firm's free cash flow (FFCF, or CFFA) is to use net operating profit after tax (NOPAT).
###\begin{aligned} FFCF &= NOPAT + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC \\ &= (Rev - COGS - Depr - FC)(1-t_c) + Depr - CapEx -\Delta NWC \\ \end{aligned} \\###
Question 69 interest tax shield, capital structure, leverage, WACC
Which statement about risk, required return and capital structure is the most correct?
A firm is considering a new project of similar risk to the current risk of the firm. This project will expand its existing business. The cash flows of the project have been calculated assuming that there is no interest expense. In other words, the cash flows assume that the project is all-equity financed.
In fact the firm has a target debt-to-equity ratio of 1, so the project will be financed with 50% debt and 50% equity. To find the levered value of the firm's assets, what discount rate should be applied to the project's unlevered cash flows? Assume a classical tax system.
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 50%. The firm then issues a large amount of equity to raise money for new projects of similar systematic risk to the company's existing projects. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is correct?
Question 99 capital structure, interest tax shield, Miller and Modigliani, trade off theory of capital structure
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of debt and using the funds to repurchase shares. Its assets are unchanged.
Assume that:
- The firm and individual investors can borrow at the same rate and have the same tax rates.
- The firm's debt and shares are fairly priced and the shares are repurchased at the market price, not at a premium.
- There are no market frictions relating to debt such as asymmetric information or transaction costs.
- Shareholders wealth is measured in terms of utiliity. Shareholders are wealth-maximising and risk-averse. They have a preferred level of overall leverage. Before the firm's capital restructure all shareholders were optimally levered.
According to Miller and Modigliani's theory, which statement is correct?
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 50%. The firm then issues a large amount of debt to raise money for new projects of similar market risk to the company's existing projects. Assume a classical tax system. Which statement is correct?
Question 121 capital structure, leverage, financial distress, interest tax shield
Fill in the missing words in the following sentence:
All things remaining equal, as a firm's amount of debt funding falls, benefits of interest tax shields __________ and the costs of financial distress __________.
A firm plans to issue equity and use the cash raised to pay off its debt. No assets will be bought or sold. Ignore the costs of financial distress.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct, all things remaining equal?
For a price of $100, Carol will sell you a 5 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 16% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with similar risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 12% pa.
For a price of $100, Rad will sell you a 5 year bond paying semi-annual coupons of 16% pa. The face value of the bond is $100. Other bonds with the same risk, maturity and coupon characteristics trade at a yield of 6% pa.
You own an apartment which you rent out as an investment property.
What is the price of the apartment using discounted cash flow (DCF, same as NPV) valuation?
Assume that:
- You just signed a contract to rent the apartment out to a tenant for the next 12 months at $2,000 per month, payable in advance (at the start of the month, t=0). The tenant is just about to pay you the first $2,000 payment.
- The contract states that monthly rental payments are fixed for 12 months. After the contract ends, you plan to sign another contract but with rental payment increases of 3%. You intend to do this every year.
So rental payments will increase at the start of the 13th month (t=12) to be $2,060 (=2,000(1+0.03)), and then they will be constant for the next 12 months.
Rental payments will increase again at the start of the 25th month (t=24) to be $2,121.80 (=2,000(1+0.03)2), and then they will be constant for the next 12 months until the next year, and so on. - The required return of the apartment is 8.732% pa, given as an effective annual rate.
- Ignore all taxes, maintenance, real estate agent, council and strata fees, periods of vacancy and other costs. Assume that the apartment will last forever and so will the rental payments.
The required return of a project is 10%, given as an effective annual rate. Assume that the cash flows shown in the table are paid all at once at the given point in time.
What is the Net Present Value (NPV) of the project?
| Project Cash Flows | |
| Time (yrs) | Cash flow ($) |
| 0 | -100 |
| 1 | 11 |
| 2 | 121 |
A project's NPV is positive. Select the most correct statement:
Question 543 price gains and returns over time, IRR, NPV, income and capital returns, effective return
For an asset price to triple every 5 years, what must be the expected future capital return, given as an effective annual rate?
You deposit money into a bank. Which of the following statements is NOT correct? You:
You bought a house, primarily funded using a home loan from a bank. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 737 financial statement, balance sheet, income statement
Where can a publicly listed firm's book value of equity be found? It can be sourced from the company's:
Question 738 financial statement, balance sheet, income statement
Where can a private firm's market value of equity be found? It can be sourced from the company's:
A home loan company advertises an interest rate of 4.5% pa, payable monthly. Which of the following statements about the interest rate is NOT correct?
Question 742 price gains and returns over time, no explanation
For an asset's price to quintuple (be five times as big, say from $1 to $5) every 5 years, what must be its effective annual capital return?
Question 743 price gains and returns over time, no explanation
How many years will it take for an asset's price to triple (increase from say $1 to $3) if it grows by 5% pa?
Question 744 income and capital returns, real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation
If someone says "my shares rose by 10% last year", what do you assume that they mean? The effective annual:
Question 745 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, income and capital returns
If the nominal gold price is expected to increase at the same rate as inflation which is 3% pa, which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Question 748 income and capital returns, DDM, ex dividend date
A stock will pay you a dividend of $2 tonight if you buy it today.
Thereafter the annual dividend is expected to grow by 3% pa, so the next dividend after the $2 one tonight will be $2.06 in one year, then in two years it will be $2.1218 and so on. The stock's required return is 8% pa.
What is the stock price today and what do you expect the stock price to be tomorrow, approximately?
Telsa Motors advertises that its Model S electric car saves $570 per month in fuel costs. Assume that Tesla cars last for 10 years, fuel and electricity costs remain the same, and savings are made at the end of each month with the first saving of $570 in one month from now.
The effective annual interest rate is 15.8%, and the effective monthly interest rate is 1.23%. What is the present value of the savings?
The following cash flows are expected:
- A perpetuity of yearly payments of $30, with the first payment in 5 years (first payment at t=5, which continues every year after that forever).
- One payment of $100 in 6 years and 3 months (t=6.25).
What is the NPV of the cash flows if the discount rate is 10% given as an effective annual rate?
A firm wishes to raise $50 million now. They will issue 7% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 6 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 5% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
A two year Government bond has a face value of $100, a yield of 2.5% pa and a fixed coupon rate of 0.5% pa, paid semi-annually. What is its price?
Question 213 income and capital returns, bond pricing, premium par and discount bonds
The coupon rate of a fixed annual-coupon bond is constant (always the same).
What can you say about the income return (##r_\text{income}##) of a fixed annual coupon bond? Remember that:
###r_\text{total} = r_\text{income} + r_\text{capital}###
###r_\text{total, 0 to 1} = \frac{c_1}{p_0} + \frac{p_1-p_0}{p_0}###
Assume that there is no change in the bond's total annual yield to maturity from when it is issued to when it matures.
Select the most correct statement.
From its date of issue until maturity, the income return of a fixed annual coupon:
A firm wishes to raise $50 million now. They will issue 5% pa semi-annual coupon bonds that will mature in 10 years and have a face value of $100 each. Bond yields are 5% pa, given as an APR compounding every 6 months, and the yield curve is flat.
How many bonds should the firm issue?
A stock is expected to pay its first dividend of $20 in 3 years (t=3), which it will continue to pay for the next nine years, so there will be ten $20 payments altogether with the last payment in year 12 (t=12).
From the thirteenth year onward, the dividend is expected to be 4% more than the previous year, forever. So the dividend in the thirteenth year (t=13) will be $20.80, then $21.632 in year 14, and so on forever. The required return of the stock is 10% pa. All rates are effective annual rates. Calculate the current (t=0) stock price.
Use the below information to value a levered company with constant annual perpetual cash flows from assets. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now, so a perpetuity can be used to value this firm. Both the operating and firm free cash flows are constant (but not equal to each other).
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}## | $100m | Operating free cash flow |
| ##\text{FFCF or CFFA}## | $112m | Firm free cash flow or cash flow from assets (includes interest tax shields) |
| ##g## | 0% pa | Growth rate of OFCF and FFCF |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{BeforeTax}## | 7% pa | Weighted average cost of capital before tax |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{AfterTax}## | 6.25% pa | Weighted average cost of capital after tax |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 5% pa | Cost of debt |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 9% pa | Cost of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 50% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
What is the value of the levered firm including interest tax shields?
Use the below information to value a levered company with constant annual perpetual cash flows from assets. The next cash flow will be generated in one year from now, so a perpetuity can be used to value this firm. Both the operating and firm free cash flows are constant (but not equal to each other).
| Data on a Levered Firm with Perpetual Cash Flows | ||
| Item abbreviation | Value | Item full name |
| ##\text{OFCF}## | $48.5m | Operating free cash flow |
| ##\text{FFCF or CFFA}## | $50m | Firm free cash flow or cash flow from assets |
| ##g## | 0% pa | Growth rate of OFCF and FFCF |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{BeforeTax}## | 10% pa | Weighted average cost of capital before tax |
| ##\text{WACC}_\text{AfterTax}## | 9.7% pa | Weighted average cost of capital after tax |
| ##r_\text{D}## | 5% pa | Cost of debt |
| ##r_\text{EL}## | 11.25% pa | Cost of levered equity |
| ##D/V_L## | 20% pa | Debt to assets ratio, where the asset value includes tax shields |
| ##t_c## | 30% | Corporate tax rate |
What is the value of the levered firm including interest tax shields?
A credit card company advertises an interest rate of 18% pa, payable monthly. Which of the following statements about the interest rate is NOT correct? All rates are given to four decimal places.
Question 758 time calculation, fully amortising loan, no explanation
Two years ago you entered into a fully amortising home loan with a principal of $1,000,000, an interest rate of 6% pa compounding monthly with a term of 25 years.
Then interest rates suddenly fall to 4.5% pa (t=0), but you continue to pay the same monthly home loan payments as you did before. How long will it now take to pay off your home loan? Measure the time taken to pay off the home loan from the current time which is 2 years after the home loan was first entered into.
Assume that the lower interest rate was given to you immediately after the loan repayment at the end of year 2, which was the 24th payment since the loan was granted. Also assume that rates were and are expected to remain constant.
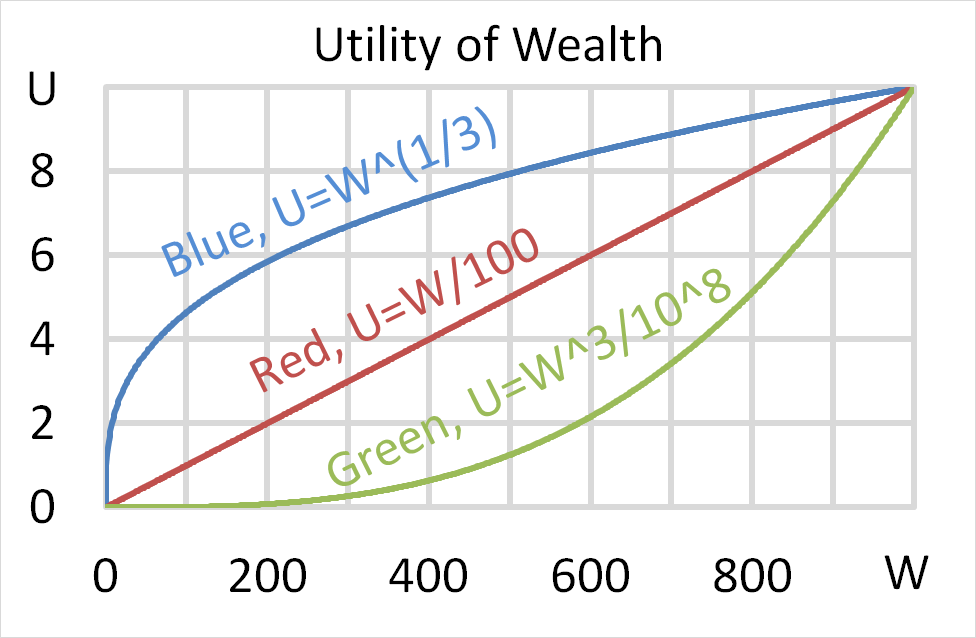
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Note that a fair gamble is a bet that has an expected value of zero, such as paying $0.50 to win $1 in a coin flip with heads or nothing if it lands tails. Fairly priced insurance is when the expected present value of the insurance premiums is equal to the expected loss from the disaster that the insurance protects against, such as the cost of rebuilding a home after a catastrophic fire.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
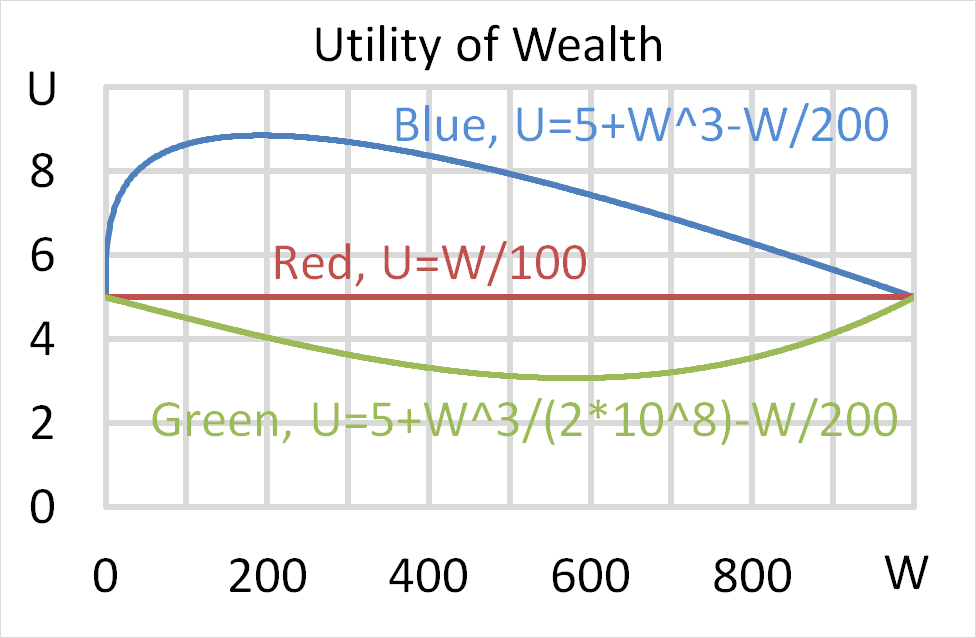
Question 704 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $256 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $256. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $256. If they flip tails then they will lose $256. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?

Question 711 continuously compounding rate, continuously compounding rate conversion
A continuously compounded semi-annual return of 5% ##(r_\text{cc 6mth})## is equivalent to a continuously compounded annual return ##(r_\text{cc annual})## of:
An effective semi-annual return of 5% ##(r_\text{eff 6mth})## is equivalent to an effective annual return ##(r_\text{eff annual})## of:
Question 691 continuously compounding rate, effective rate, continuously compounding rate conversion, no explanation
A bank quotes an interest rate of 6% pa with quarterly compounding. Note that another way of stating this rate is that it is an annual percentage rate (APR) compounding discretely every 3 months.
Which of the following statements about this rate is NOT correct? All percentages are given to 6 decimal places. The equivalent:
If a variable, say X, is normally distributed with mean ##\mu## and variance ##\sigma^2## then mathematicians write ##X \sim \mathcal{N}(\mu, \sigma^2)##.
If a variable, say Y, is log-normally distributed and the underlying normal distribution has mean ##\mu## and variance ##\sigma^2## then mathematicians write ## Y \sim \mathbf{ln} \mathcal{N}(\mu, \sigma^2)##.
The below three graphs show probability density functions (PDF) of three different random variables Red, Green and Blue.
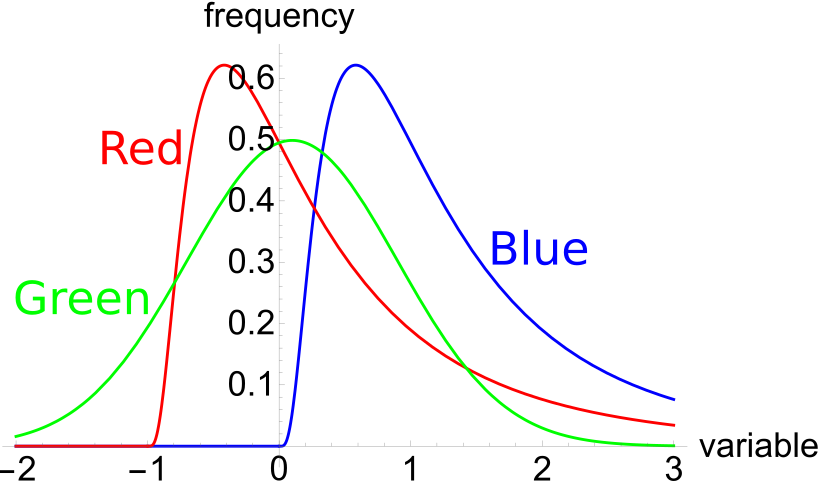
Select the most correct statement:
Question 720 mean and median returns, return distribution, arithmetic and geometric averages, continuously compounding rate
A stock has an arithmetic average continuously compounded return (AALGDR) of 10% pa, a standard deviation of continuously compounded returns (SDLGDR) of 80% pa and current stock price of $1. Assume that stock prices are log-normally distributed.
In 5 years, what do you expect the median and mean prices to be? The answer options are given in the same order.
In 2014 the median starting salaries of male and female Australian bachelor degree accounting graduates aged less than 25 years in their first full-time industry job was $50,000 before tax, according to Graduate Careers Australia. See page 9 of this report. Personal income tax rates published by the Australian Tax Office are reproduced for the 2014-2015 financial year in the table below.
| Taxable income | Tax on this income |
|---|---|
| 0 – $18,200 | Nil |
| $18,201 – $37,000 | 19c for each $1 over $18,200 |
| $37,001 – $80,000 | $3,572 plus 32.5c for each $1 over $37,000 |
| $80,001 – $180,000 | $17,547 plus 37c for each $1 over $80,000 |
| $180,001 and over | $54,547 plus 45c for each $1 over $180,000 |
The above rates do not include the Medicare levy of 2%. Exclude the Medicare levy from your calculations
How much personal income tax would you have to pay per year if you earned $50,000 per annum before-tax?
Question 494 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system
A firm pays a fully franked cash dividend of $100 to one of its Australian shareholders who has a personal marginal tax rate of 15%. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What will be the shareholder's personal tax payable due to the dividend payment?
A company conducts a 4 for 3 stock split. What is the percentage change in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order.
Question 566 capital structure, capital raising, rights issue, on market repurchase, dividend, stock split, bonus issue
A company's share price fell by 20% and its number of shares rose by 25%. Assume that there are no taxes, no signalling effects and no transaction costs.
Which one of the following corporate events may have happened?
Which of the below statements about utility is NOT generally accepted by economists? Most people are thought to:
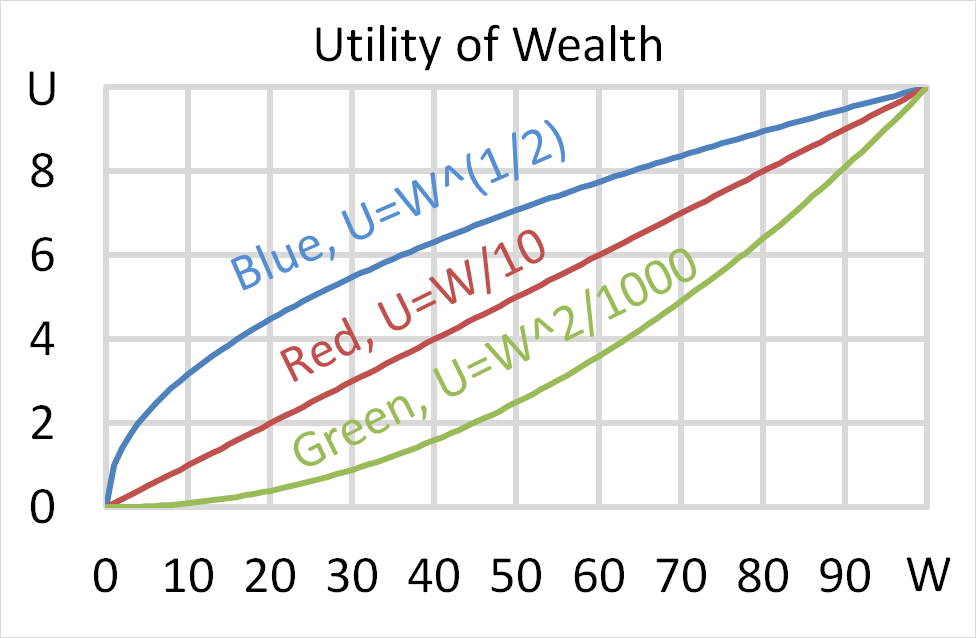
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions. Which of the statements about the 3 utility functions is NOT correct?
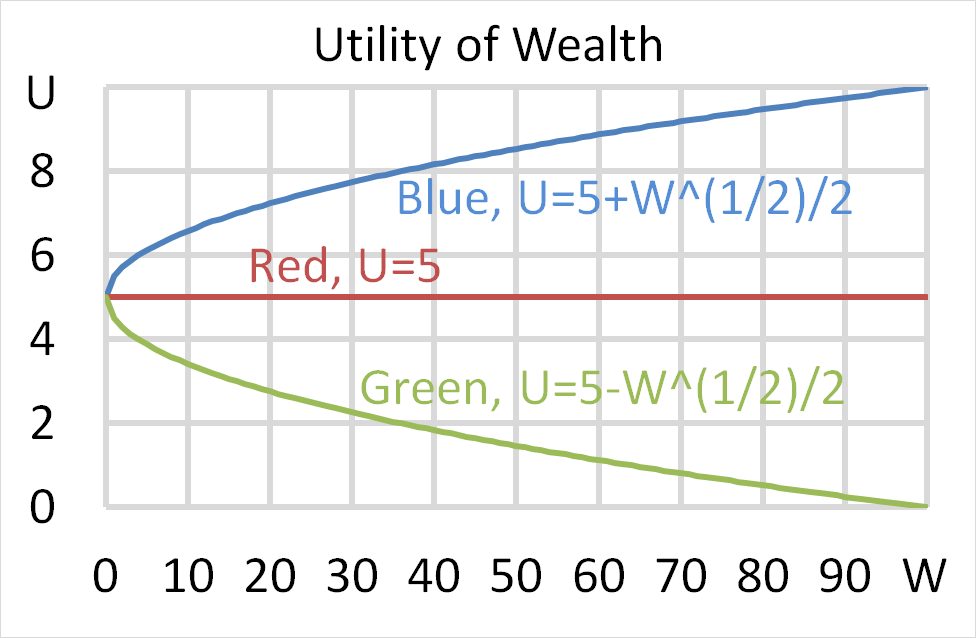
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions. Which of the statements about the 3 utility functions is NOT correct?
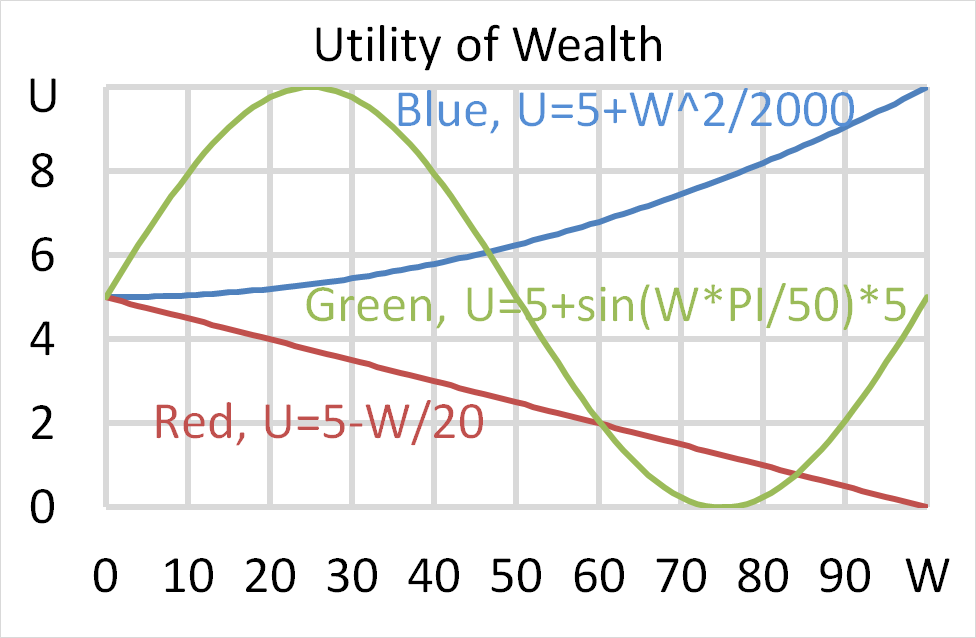
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions. Which of the statements about the 3 utility functions is NOT correct?
Question 700 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?

Question 701 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?
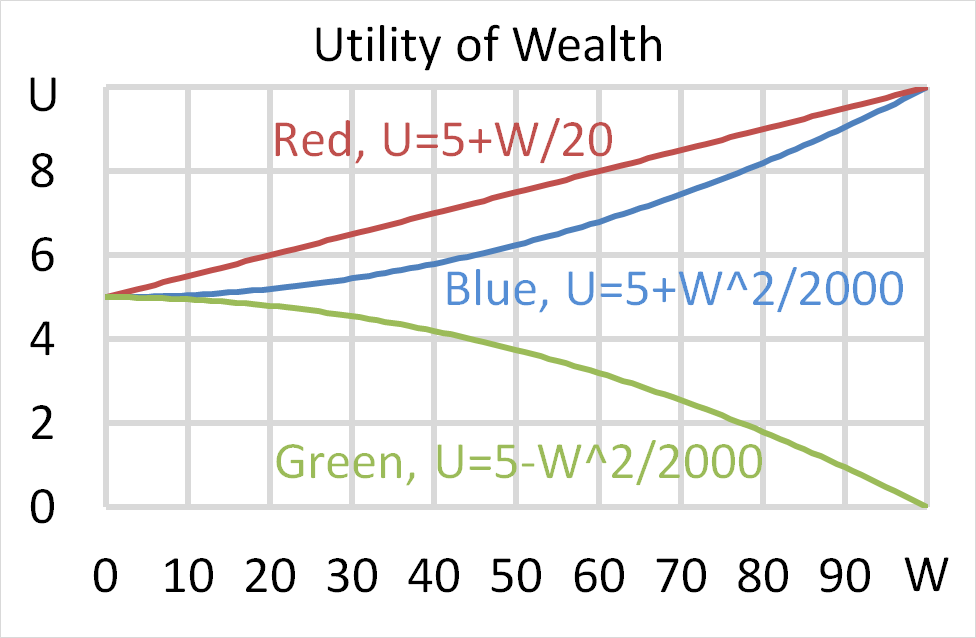
Question 702 utility, risk aversion, utility function, gamble
Mr Blue, Miss Red and Mrs Green are people with different utility functions.
Each person has $50 of initial wealth. A coin toss game is offered to each person at a casino where the player can win or lose $50. Each player can flip a coin and if they flip heads, they receive $50. If they flip tails then they will lose $50. Which of the following statements is NOT correct?

The following table shows a sample of historical total returns of shares in two different companies A and B.
| Stock Returns | ||
| Total effective annual returns | ||
| Year | ##r_A## | ##r_B## |
| 2007 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| 2008 | 0.04 | -0.2 |
| 2009 | -0.1 | -0.3 |
| 2010 | 0.18 | 0.5 |
What is the historical sample covariance (##\hat{\sigma}_{A,B}##) and correlation (##\rho_{A,B}##) of stock A and B's total effective annual returns?
Stock A and B's returns have a correlation of 0.3. Which statement is NOT correct?
Question 282 expected and historical returns, income and capital returns
You're the boss of an investment bank's equities research team. Your five analysts are each trying to find the expected total return over the next year of shares in a mining company. The mining firm:
- Is regarded as a mature company since it's quite stable in size and was floated around 30 years ago. It is not a high-growth company;
- Share price is very sensitive to changes in the price of the market portfolio, economic growth, the exchange rate and commodities prices. Due to this, its standard deviation of total returns is much higher than that of the market index;
- Experienced tough times in the last 10 years due to unexpected falls in commodity prices.
- Shares are traded in an active liquid market.
- The analysts' source data is correct and true, but their inferences might be wrong;
- All returns and yields are given as effective annual nominal rates.
Which of the following statements about short-selling is NOT true?
The standard deviation and variance of a stock's annual returns are calculated over a number of years. The units of the returns are percent per annum ##(\% pa)##.
What are the units of the standard deviation ##(\sigma)## and variance ##(\sigma^2)## of returns respectively?
Hint: Visit Wikipedia to understand the difference between percentage points ##(\text{pp})## and percent ##(\%)##.
Let the variance of returns for a share per month be ##\sigma_\text{monthly}^2##.
What is the formula for the variance of the share's returns per year ##(\sigma_\text{yearly}^2)##?
Assume that returns are independently and identically distributed (iid) so they have zero auto correlation, meaning that if the return was higher than average today, it does not indicate that the return tomorrow will be higher or lower than average.
An investor owns a portfolio with:
- 80% invested in stock A; and
- 20% invested in stock B.
Today there was a:
- 10% rise in stock A's price; and
- No change in stock B's price.
No dividends were paid on either stock. What was the total historical portfolio return on this day? All returns above and answer options below are given as effective daily rates.
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Correlation ##(\rho_{A,B})## | Dollars invested |
||
| A | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 60 | ||
| B | 0.2 | 0.6 | 140 | |||
What is the standard deviation (not variance) of returns of the above portfolio?
Find the sample standard deviation of returns using the data in the table:
| Stock Returns | |
| Year | Return pa |
| 2008 | 0.3 |
| 2009 | 0.02 |
| 2010 | -0.2 |
| 2011 | 0.4 |
The returns above and standard deviations below are given in decimal form.
Question 559 variance, standard deviation, covariance, correlation
Which of the following statements about standard statistical mathematics notation is NOT correct?
| Portfolio Details | ||||||
| Stock | Expected return |
Standard deviation |
Correlation | Beta | Dollars invested |
|
| A | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.12 | 0.5 | 40 | |
| B | 0.3 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 80 | ||
What is the beta of the above portfolio?
Three important classes of investable risky assets are:
- Corporate debt which has low total risk,
- Real estate which has medium total risk,
- Equity which has high total risk.
Assume that the correlation between total returns on:
- Corporate debt and real estate is 0.1,
- Corporate debt and equity is 0.1,
- Real estate and equity is 0.5.
You are considering investing all of your wealth in one or more of these asset classes. Which portfolio will give the lowest total risk? You are restricted from shorting any of these assets. Disregard returns and the risk-return trade-off, pretend that you are only concerned with minimising risk.
All things remaining equal, the higher the correlation of returns between two stocks:
Question 408 leverage, portfolio beta, portfolio risk, real estate, CAPM
You just bought a house worth $1,000,000. You financed it with an $800,000 mortgage loan and a deposit of $200,000.
You estimate that:
- The house has a beta of 1;
- The mortgage loan has a beta of 0.2.
What is the beta of the equity (the $200,000 deposit) that you have in your house?
Also, if the risk free rate is 5% pa and the market portfolio's return is 10% pa, what is the expected return on equity in your house? Ignore taxes, assume that all cash flows (interest payments and rent) were paid and received at the end of the year, and all rates are effective annual rates.
The accounting identity states that the book value of a company's assets (A) equals its liabilities (L) plus owners equity (OE), so A = L + OE.
The finance version states that the market value of a company's assets (V) equals the market value of its debt (D) plus equity (E), so V = D + E.
Therefore a business's assets can be seen as a portfolio of the debt and equity that fund the assets.
Let ##\sigma_\text{V total}^2## be the total variance of returns on assets, ##\sigma_\text{V syst}^2## be the systematic variance of returns on assets, and ##\sigma_\text{V idio}^2## be the idiosyncratic variance of returns on assets, and ##\rho_\text{D idio, E idio}## be the correlation between the idiosyncratic returns on debt and equity.
Which of the following equations is NOT correct?
Government bonds currently have a return of 5% pa. A stock has an expected return of 6% pa and the market return is 7% pa. What is the beta of the stock?
Government bonds currently have a return of 5%. A stock has a beta of 2 and the market return is 7%. What is the expected return of the stock?
Diversification is achieved by investing in a large amount of stocks. What type of risk is reduced by diversification?
A company has:
- 140 million shares outstanding.
- The market price of one share is currently $2.
- The company's debentures are publicly traded and their market price is equal to 93% of the face value.
- The debentures have a total face value of $50,000,000 and the current yield to maturity of corporate debentures is 12% per annum.
- The risk-free rate is 8.50% and the market return is 13.7%.
- Market analysts estimated that the company's stock has a beta of 0.90.
- The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What is the company's after-tax weighted average cost of capital (WACC) in a classical tax system?
Treasury bonds currently have a return of 5% pa. A stock has a beta of 0.5 and the market return is 10% pa. What is the expected return of the stock?
A firm can issue 3 year annual coupon bonds at a yield of 10% pa and a coupon rate of 8% pa.
The beta of its levered equity is 2. The market's expected return is 10% pa and 3 year government bonds yield 6% pa with a coupon rate of 4% pa.
The market value of equity is $1 million and the market value of debt is $1 million. The corporate tax rate is 30%.
What is the firm's after-tax WACC? Assume a classical tax system.
According to the theory of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), total variance can be broken into two components, systematic variance and idiosyncratic variance. Which of the following events would be considered the most diversifiable according to the theory of the CAPM?
Question 104 CAPM, payout policy, capital structure, Miller and Modigliani, risk
Assume that there exists a perfect world with no transaction costs, no asymmetric information, no taxes, no agency costs, equal borrowing rates for corporations and individual investors, the ability to short the risk free asset, semi-strong form efficient markets, the CAPM holds, investors are rational and risk-averse and there are no other market frictions.
For a firm operating in this perfect world, which statement(s) are correct?
(i) When a firm changes its capital structure and/or payout policy, share holders' wealth is unaffected.
(ii) When the idiosyncratic risk of a firm's assets increases, share holders do not expect higher returns.
(iii) When the systematic risk of a firm's assets increases, share holders do not expect higher returns.
Select the most correct response:
A fairly priced stock has an expected return of 15% pa. Treasury bonds yield 5% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa. What is the beta of the stock?
The security market line (SML) shows the relationship between beta and expected return.
Buying investment projects that plot above the SML would lead to:
According to the theory of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), total risk can be broken into two components, systematic risk and idiosyncratic risk. Which of the following events would be considered a systematic, undiversifiable event according to the theory of the CAPM?
A firm changes its capital structure by issuing a large amount of equity and using the funds to repay debt. Its assets are unchanged. Ignore interest tax shields.
According to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which statement is correct?
A fairly priced stock has a beta that is the same as the market portfolio's beta. Treasury bonds yield 5% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa. What is the expected return of the stock?
Question 235 SML, NPV, CAPM, risk
The security market line (SML) shows the relationship between beta and expected return.
Investment projects that plot on the SML would have:
A stock has a beta of 0.5. Its next dividend is expected to be $3, paid one year from now. Dividends are expected to be paid annually and grow by 2% pa forever. Treasury bonds yield 5% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa. All returns are effective annual rates.
What is the price of the stock now?
Question 244 CAPM, SML, NPV, risk
Examine the following graph which shows stocks' betas ##(\beta)## and expected returns ##(\mu)##:
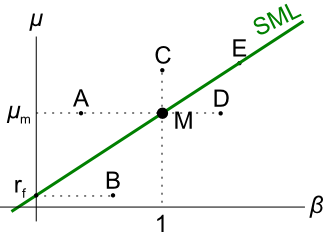
Assume that the CAPM holds and that future expectations of stocks' returns and betas are correctly measured. Which statement is NOT correct?
Which of the following statements about the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is NOT correct?
There are many different ways to value a firm's assets. Which of the following will NOT give the correct market value of a levered firm's assets ##(V_L)##? Assume that:
- The firm is financed by listed common stock and vanilla annual fixed coupon bonds, which are both traded in a liquid market.
- The bonds' yield is equal to the coupon rate, so the bonds are issued at par. The yield curve is flat and yields are not expected to change. When bonds mature they will be rolled over by issuing the same number of new bonds with the same expected yield and coupon rate, and so on forever.
- Tax rates on the dividends and capital gains received by investors are equal, and capital gains tax is paid every year, even on unrealised gains regardless of when the asset is sold.
- There is no re-investment of the firm's cash back into the business. All of the firm's excess cash flow is paid out as dividends so real growth is zero.
- The firm operates in a mature industry with zero real growth.
- All cash flows and rates in the below equations are real (not nominal) and are expected to be stable forever. Therefore the perpetuity equation with no growth is suitable for valuation.
Where:
###r_\text{WACC before tax} = r_D.\frac{D}{V_L} + r_{EL}.\frac{E_L}{V_L} = \text{Weighted average cost of capital before tax}### ###r_\text{WACC after tax} = r_D.(1-t_c).\frac{D}{V_L} + r_{EL}.\frac{E_L}{V_L} = \text{Weighted average cost of capital after tax}### ###NI_L=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr-\mathbf{IntExp}).(1-t_c) = \text{Net Income Levered}### ###CFFA_L=NI_L+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC+\mathbf{IntExp} = \text{Cash Flow From Assets Levered}### ###NI_U=(Rev-COGS-FC-Depr).(1-t_c) = \text{Net Income Unlevered}### ###CFFA_U=NI_U+Depr-CapEx - \varDelta NWC= \text{Cash Flow From Assets Unlevered}###A fairly priced stock has an expected return equal to the market's. Treasury bonds yield 5% pa and the market portfolio's expected return is 10% pa. What is the stock's beta?
The CAPM can be used to find a business's expected opportunity cost of capital:
###r_i=r_f+β_i (r_m-r_f)###
What should be used as the risk free rate ##r_f##?
"Buy low, sell high" is a phrase commonly heard in financial markets. It states that traders should try to buy assets at low prices and sell at high prices.
Traders in the fixed-coupon bond markets often quote promised bond yields rather than prices. Fixed-coupon bond traders should try to:
To value a business's assets, the free cash flow of the firm (FCFF, also called CFFA) needs to be calculated. This requires figures from the firm's income statement and balance sheet. For what figures is the balance sheet needed? Note that the balance sheet is sometimes also called the statement of financial position.
Let the 'income return' of a bond be the coupon at the end of the period divided by the market price now at the start of the period ##(C_1/P_0)##. The expected income return of a premium fixed coupon bond is:
Question 624 franking credit, personal tax on dividends, imputation tax system, no explanation
Which of the following statements about Australian franking credits is NOT correct? Franking credits:
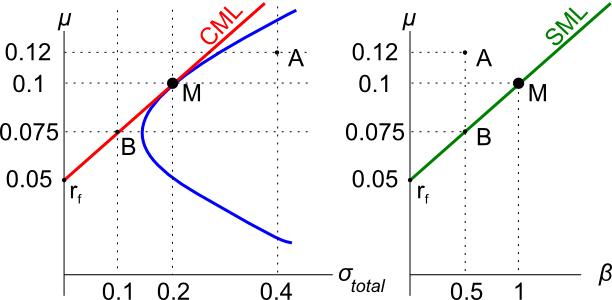
Assets A, B, M and ##r_f## are shown on the graphs above. Asset M is the market portfolio and ##r_f## is the risk free yield on government bonds. Which of the below statements is NOT correct?
Find Trademark Corporation's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Trademark Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 100 | |
| COGS | 25 | |
| Operating expense | 5 | |
| Depreciation | 20 | |
| Interest expense | 20 | |
| Income before tax | 30 | |
| Tax at 30% | 9 | |
| Net income | 21 | |
| Trademark Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets | 120 | 80 |
| PPE | ||
| Cost | 150 | 140 |
| Accumul. depr. | 60 | 40 |
| Carrying amount | 90 | 100 |
| Total assets | 210 | 180 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | 75 | 65 |
| Non-current liabilities | 75 | 55 |
| Owners' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | 10 | 10 |
| Contributed equity | 50 | 50 |
| Total L and OE | 210 | 180 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Find UniBar Corp's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| UniBar Corp | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 80 | |
| COGS | 40 | |
| Operating expense | 15 | |
| Depreciation | 10 | |
| Interest expense | 5 | |
| Income before tax | 10 | |
| Tax at 30% | 3 | |
| Net income | 7 | |
| UniBar Corp | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets | 120 | 90 |
| PPE | ||
| Cost | 360 | 320 |
| Accumul. depr. | 40 | 30 |
| Carrying amount | 320 | 290 |
| Total assets | 440 | 380 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | 110 | 60 |
| Non-current liabilities | 190 | 180 |
| Owners' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | 95 | 95 |
| Contributed equity | 45 | 45 |
| Total L and OE | 440 | 380 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Find Piano Bar's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| Piano Bar | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 310 | |
| COGS | 185 | |
| Operating expense | 20 | |
| Depreciation | 15 | |
| Interest expense | 10 | |
| Income before tax | 80 | |
| Tax at 30% | 24 | |
| Net income | 56 | |
| Piano Bar | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets | 240 | 230 |
| PPE | ||
| Cost | 420 | 400 |
| Accumul. depr. | 50 | 35 |
| Carrying amount | 370 | 365 |
| Total assets | 610 | 595 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | 180 | 190 |
| Non-current liabilities | 290 | 265 |
| Owners' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | 90 | 90 |
| Contributed equity | 50 | 50 |
| Total L and OE | 610 | 595 |
Note: all figures are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Find World Bar's Cash Flow From Assets (CFFA), also known as Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF), over the year ending 30th June 2013.
| World Bar | ||
| Income Statement for | ||
| year ending 30th June 2013 | ||
| $m | ||
| Sales | 300 | |
| COGS | 150 | |
| Operating expense | 50 | |
| Depreciation | 40 | |
| Interest expense | 10 | |
| Taxable income | 50 | |
| Tax at 30% | 15 | |
| Net income | 35 | |
| World Bar | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| as at 30th June | 2013 | 2012 |
| $m | $m | |
| Assets | ||
| Current assets | 200 | 230 |
| PPE | ||
| Cost | 400 | 400 |
| Accumul. depr. | 75 | 35 |
| Carrying amount | 325 | 365 |
| Total assets | 525 | 595 |
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | 150 | 205 |
| Non-current liabilities | 235 | 250 |
| Owners' equity | ||
| Retained earnings | 100 | 100 |
| Contributed equity | 40 | 40 |
| Total L and OE | 525 | 595 |
Note: all figures above and below are given in millions of dollars ($m).
A new company's Firm Free Cash Flow (FFCF, same as CFFA) is forecast in the graph below.
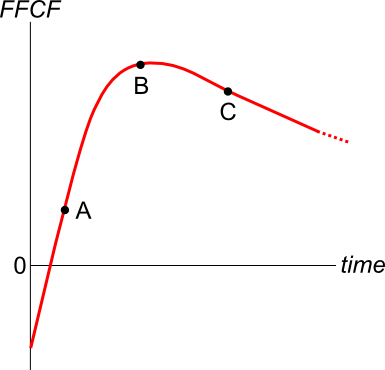
To value the firm's assets, the terminal value needs to be calculated using the perpetuity with growth formula:
###V_{\text{terminal, }t-1} = \dfrac{FFCF_{\text{terminal, }t}}{r-g}###
Which point corresponds to the best time to calculate the terminal value?
The hardest and most important aspect of business project valuation is the estimation of the:
The 'time value of money' is most closely related to which of the following concepts?
Question 771 debt terminology, interest expense, interest tax shield, credit risk, no explanation
You deposit money into a bank account. Which of the following statements about this deposit is NOT correct?
Question 658 CFFA, income statement, balance sheet, no explanation
To value a business's assets, the free cash flow of the firm (FCFF, also called CFFA) needs to be calculated. This requires figures from the firm's income statement and balance sheet. For what figures is the income statement needed? Note that the income statement is sometimes also called the profit and loss, P&L, or statement of financial performance.
A firm has a debt-to-assets ratio of 20%. What is its debt-to-equity ratio?
Question 664 real and nominal returns and cash flows, inflation, no explanation
What is the present value of real payments of $100 every year forever, with the first payment in one year? The nominal discount rate is 7% pa and the inflation rate is 4% pa.
A company conducts a 10 for 3 stock split. What is the percentage increase in the stock price and the number of shares outstanding? The answers are given in the same order.
Question 668 buy and hold, market efficiency, idiom
A quote from the famous investor Warren Buffet: "Much success can be attributed to inactivity. Most investors cannot resist the temptation to constantly buy and sell."
Buffet is referring to the buy-and-hold strategy which is to buy and never sell shares. Which of the following is a disadvantage of a buy-and-hold strategy? Assume that share markets are semi-strong form efficient. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of the strict buy-and-hold strategy? A disadvantage of the buy-and-hold strategy is that it reduces:
Which of the following is NOT a valid method for estimating the beta of a company's stock? Assume that markets are efficient, a long history of past data is available, the stock possesses idiosyncratic and market risk. The variances and standard deviations below denote total risks.
Question 767 idiom, corporate financial decision theory, no explanation
The sayings "Don't cry over spilt milk", "Don't regret the things that you can't change" and "What's done is done" are most closely related to which financial concept?
Question 768 accounting terminology, book and market values, no explanation
Accountants and finance professionals have lots of names for the same things which can be quite confusing.
Which of the following groups of items are NOT synonyms?
"Buy low, sell high" is a well-known saying. It suggests that investors should buy low then sell high, in that order.
How would you re-phrase that saying to describe short selling?
Question 770 expected and historical returns, income and capital returns, coupon rate, bond pricing
Which of the following statements is NOT correct? Assume that all events are a surprise and that all other things remain equal. So for example, don't assume that just because a company's dividends and profit rise that its required return will also rise, assume the required return stays the same.
Question 772 interest tax shield, capital structure, leverage
A firm issues debt and uses the funds to buy back equity. Assume that there are no costs of financial distress or transactions costs. Which of the following statements about interest tax shields is NOT correct?
Below is a graph of 3 peoples’ utility functions, Mr Blue (U=W^(1/2) ), Miss Red (U=W/10) and Mrs Green (U=W^2/1000). Assume that each of them currently have $50 of wealth.

Which of the following statements about them is NOT correct?
(a) Mr Blue would prefer to invest his wealth in a well diversified portfolio of stocks rather than a single stock, assuming that all stocks had the same total risk and return.
Question 776 market efficiency, systematic and idiosyncratic risk, beta, income and capital returns
Which of the following statements about returns is NOT correct? A stock's:
The market's expected total return is 10% pa and the risk free rate is 5% pa, both given as effective annual rates.
A stock has a beta of 0.5.
In the last 5 minutes, the federal government unexpectedly raised taxes. Over this time the share market fell by 3%. The risk free rate was unchanged.
What do you think was the stock's historical return over the last 5 minutes, given as an effective 5 minute rate?
Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| Project Data | |
| Project life | 2 years |
| Initial investment in equipment | $8m |
| Depreciation of equipment per year for tax purposes | $3m |
| Unit sales per year | 10m |
| Sale price per unit | $9 |
| Variable cost per unit | $4 |
| Fixed costs per year, paid at the end of each year | $2m |
| Tax rate | 30% |
Note 1: Due to the project, the firm will have to purchase $40m of inventory initially (at t=0). Half of this inventory will be sold at t=1 and the other half at t=2.
Note 2: The equipment will have a book value of $2m at the end of the project for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $1m when it is sold. Assume that the full capital loss is tax-deductible and taxed at the full corporate tax rate.
Note 3: The project will be fully funded by equity which investors will expect to pay dividends totaling $10m at the end of each year.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero, one and two. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m).
Find the cash flow from assets (CFFA) of the following project.
| One Year Mining Project Data | ||
| Project life | 1 year | |
| Initial investment in building mine and equipment | $9m | |
| Depreciation of mine and equipment over the year | $8m | |
| Kilograms of gold mined at end of year | 1,000 | |
| Sale price per kilogram | $0.05m | |
| Variable cost per kilogram | $0.03m | |
| Before-tax cost of closing mine at end of year | $4m | |
| Tax rate | 30% | |
Note 1: Due to the project, the firm also anticipates finding some rare diamonds which will give before-tax revenues of $1m at the end of the year.
Note 2: The land that will be mined actually has thermal springs and a family of koalas that could be sold to an eco-tourist resort for an after-tax amount of $3m right now. However, if the mine goes ahead then this natural beauty will be destroyed.
Note 3: The mining equipment will have a book value of $1m at the end of the year for tax purposes. However, the equipment is expected to fetch $2.5m when it is sold.
Find the project's CFFA at time zero and one. Answers are given in millions of dollars ($m), with the first cash flow at time zero, and the second at time one.
In the home loan market, the acronym LVR stands for Loan to Valuation Ratio. If you bought a house worth one million dollars, partly funded by an $800,000 home loan, then your LVR was 80%. The LVR is equivalent to which of the following ratios?
The following steps outline the process of ‘negative gearing’ an investment property in Australia. Which of these steps or statements is NOT correct? To successfully achieve negative gearing on an investment property:
Question 803 capital raising, rights issue, initial public offering, on market repurchase, no explanation
Which one of the following capital raisings or payouts involve the sale of shares to existing shareholders only?
A firm conducts a two-for-one stock split. Which of the following consequences would NOT be expected?
Question 807 market efficiency, expected and historical returns, CAPM, beta, systematic risk, no explanation
You work in Asia and just woke up. It looked like a nice day but then you read the news and found out that last night the American share market fell by 10% while you were asleep due to surprisingly poor macro-economic world news. You own a portfolio of liquid stocks listed in Asia with a beta of 1.6. When the Asian equity markets open, what do you expect to happen to your share portfolio? Assume that the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is correct and that the market portfolio contains all shares in the world, of which American shares are a big part. Your portfolio beta is measured against this world market portfolio.
When the Asian equity market opens for trade, you would expect your portfolio value to:
A graph of assets’ expected returns ##(\mu)## versus standard deviations ##(\sigma)## is given in the below diagram.
Each letter corresponds to a separate coloured area. The portfolios at the boundary of the areas, on the black lines, are excluded from each area. Assume that all assets represented in this graph are fairly priced, and that all risky assets can be short-sold.
Which of the following statements about this graph and Markowitz portfolio theory is NOT correct?
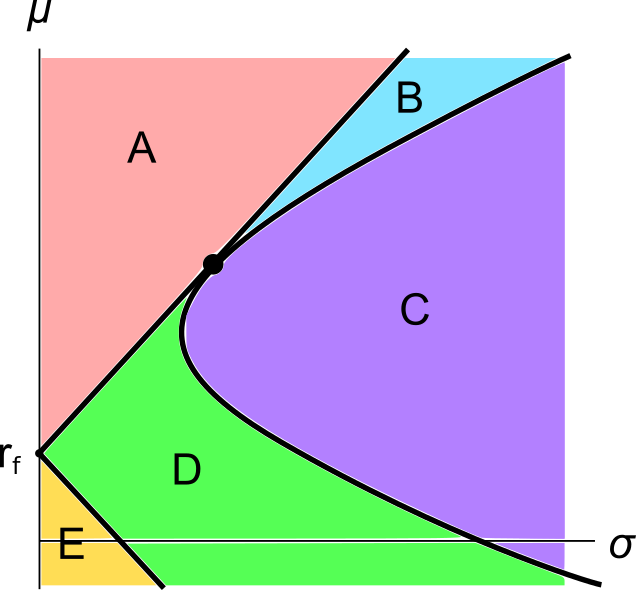
Question 809 Markowitz portfolio theory, CAPM, Jensens alpha, CML, systematic and idiosyncratic risk
A graph of assets’ expected returns ##(\mu)## versus standard deviations ##(\sigma)## is given in the graph below. The CML is the capital market line.
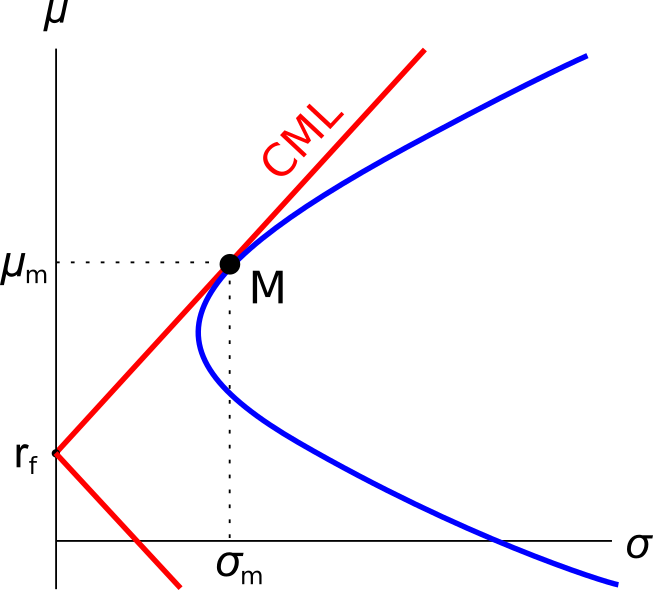
Which of the following statements about this graph, Markowitz portfolio theory and the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) theory is NOT correct?
The famous investor Warren Buffett is one of few portfolio managers who appears to have consistently beaten the market. His company Berkshire Hathaway (BRK) appears to have outperformed the US S&P500 market index, shown in the graph below.
Read the below statements about Warren Buffett and the implications for the Efficient Markets Hypothesis (EMH) theory of Eugene Fama. Assume that the first sentence is true. Analyse the second sentence and select the answer option which is NOT correct. In other words, find the false statement in the second sentence.
The expression 'cash is king' emphasizes the importance of having enough cash to pay your short term debts to avoid bankruptcy. Which business decision is this expression most closely related to?
The expression 'you have to spend money to make money' relates to which business decision?
Question 536 idiom, bond pricing, capital structure, leverage
The expression 'my word is my bond' is often used in everyday language to make a serious promise.
Why do you think this expression uses the metaphor of a bond rather than a share?
Which of the following statements about futures contracts on shares is NOT correct, assuming that markets are efficient?
When an equity future is first negotiated (at t=0):